The Characteristic of Muscle Function for Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Real-World Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Demographic and Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Body Composition
2.4. Muscle Function
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with RA
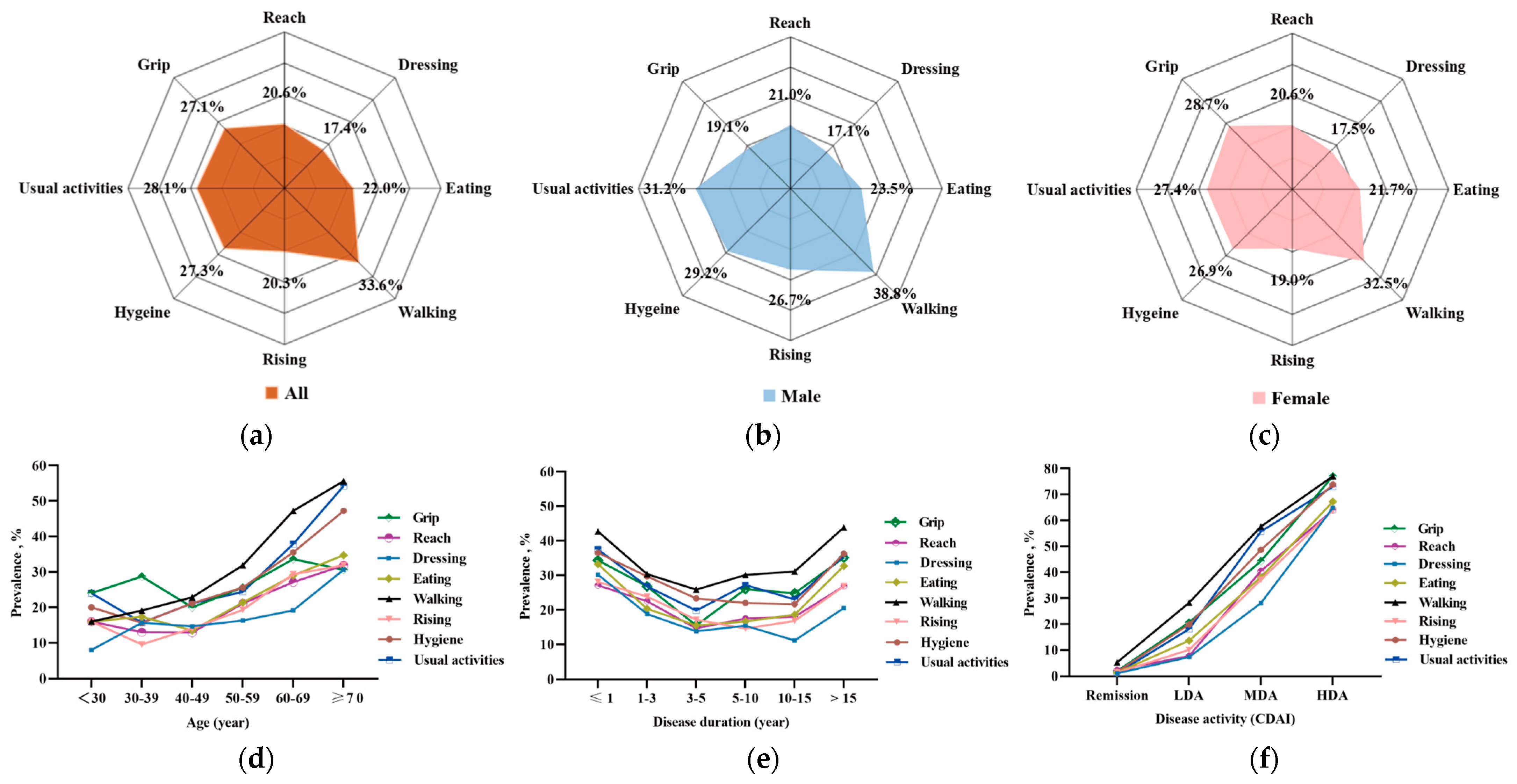
3.2. Activity Function in Eight Subdimensions in Patients with RA
3.3. Muscle Mass and Function in Patients with RA
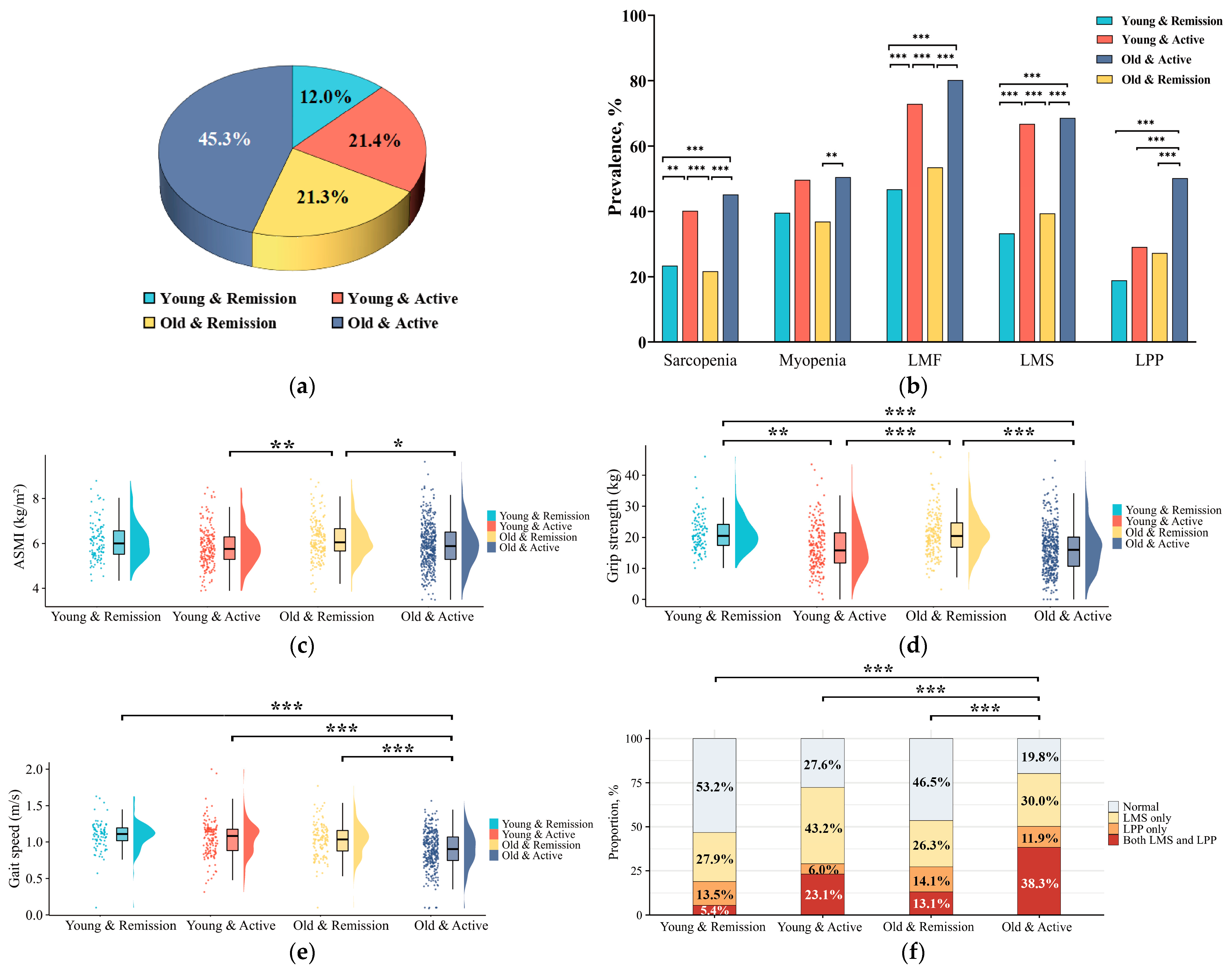
3.4. Comparisons of Characteristics Among Patients with RA in Muscle Function Categorizations
3.5. Characteristics of Patients with RA in Subgroups According to Age and Disease Activity
| Disease Characteristics | Before Propensity Score Matching | After Propensity Score Matching | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (n = 289) | LMS Only (n = 295) | LPP Only (n = 105) | Both LMS and LPP (n = 239) | p | Normal (n = 103) | LMS Only (n = 105) | LPP Only (n = 105) | Both LMS and LPP (n = 103) | p | |
| Female, n (%) | 251 (86.9) | 239 (81.0) | 92 (87.6) | 189 (79.1) | 0.044 | 91 (88.3) | 95 (90.5) | 92 (87.6) | 91 (88.3) | 0.924 |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 51.0 ± 10.6 | 51.5 ± 12.9 | 53.8 ± 10.7 | 57.7 ± 12.0 a,b,c | <0.001 | 53.2 ± 10.2 | 53.0 ± 12.0 | 53.8 ± 10.7 | 54.4 ± 11.6 | 0.703 |
| Disease duration, month, median (IQR) | 72 (35, 128) | 88 (35, 141) | 90 (44, 160) | 96 (34, 186) | 0.067 | 66 (30, 115) | 82 (27, 131) | 90 (44, 160) a | 95 (35, 199) | 0.031 |
| Active smoking, n (%) | 17 (5.9) | 31 (10.5) | 8 (7.6) | 33 (13.8) a | 0.017 | 8 (7.8) | 8 (7.6) | 8 (7.6) | 12 (11.7) | 0.669 |
| Positive RF, n (%) | 214 (74.0) | 226 (76.6) | 81 (77.1) | 181 (75.7) | 0.878 | 79 (76.7) | 82 (78.1) | 81 (77.1) | 80 (77.7) | 0.996 |
| Positive ACPA, n (%) | 271 (93.8) | 275 (93.2) | 101 (96.2) | 224 (93.7) | 0.751 | 97 (94.2) | 96 (91.4) | 101 (96.2) | 97 (94.2) | 0.545 |
| Core disease activity indicators | ||||||||||
| 28TJC, median (IQR) | 0 (0, 2) | 2 (0, 6) a | 1 (0,3) | 4 (1, 9) a,b,c | <0.001 | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (0, 6) a | 1 (0, 3) b | 4 (1, 9) a,b,c | <0.001 |
| 28SJC, median (IQR) | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 3) a | 0 (0, 1) b | 2 (0, 5) a,b,c | <0.001 | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 3) a | 0 (0, 1) b | 2 (0, 7) a,b,c | <0.001 |
| PtGA, median (IQR) | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (1, 4) a | 2 (0, 4) | 4 (2, 6) a,b,c | <0.001 | 1 (0, 3) | 2 (1, 3) | 2 (0, 4) | 5 (2, 6) a,b,c | <0.001 |
| PrGA, median (IQR) | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (0, 3) a | 1 (0, 3) a | 4 (2, 6) a,b,c | <0.001 | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (1, 3) a | 1 (0, 3) | 4 (2, 5) a,b,c | <0.001 |
| PainVAS, median (IQR) | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (0, 3) a | 1 (0, 3) a | 3 (1, 5) a,b,c | <0.001 | 1 (0, 2) | 2 (0, 3) | 1 (0, 3) | 3 (1, 5) a,c | <0.001 |
| ESR, mm/h, median (IQR) | 18 (10, 31) | 26 (16, 47) a | 27 (15, 40) | 35 (18, 62) a,b | <0.001 | 23 (11, 35) | 28 (18, 53) | 27 (15, 40) | 33 (18, 60) a | 0.015 |
| CRP, mg/L, median (IQR) | 3.3 (3.2, 4.2) | 3.6 (3.3, 10.3) a | 3.6 (3.3, 6.6) a | 5.1 (3.4, 13.2) a,c | <0.001 | 3.3 (3.2, 4.2) | 5.0 (3.4, 19.7) | 3.6 (3.3, 6.6) | 4.4 (3.4, 10.6) a | 0.017 |
| CDAI, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 7) | 8 (2, 18) a | 4 (0, 12) | 14 (7, 25) a,b,c | <0.001 | 3 (0, 8) | 8 (2, 17) a | 4 (0, 12) b | 15 (7, 26) a,b,c | <0.001 |
| Radiographic assessments | ||||||||||
| mTSS, median (IQR) | 4 (0, 11) | 10 (2, 31) a | 7 (2, 23) | 16 (4, 56) a | <0.001 | 3 (0, 8) | 10 (2, 29) a | 7 (2, 23) | 12 (3, 53) a | 0.001 |
| JSN subscore, median (IQR) | 0 (0, 4) | 3 (0, 17) a | 1 (0, 9) | 6 (1, 23) a | <0.001 | 0 (0, 2) | 3 (0, 12) | 1 (0, 9) | 5 (0, 32) a | 0.007 |
| JE subscore, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 8) | 6 (1, 15) a | 5 (0, 16) | 9 (3, 30) a | <0.001 | 2 (0, 6) | 7 (5, 16) | 5 (1, 16) | 9 (3, 30) a | 0.002 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 46 (15.9) | 51 (17.3) | 25 (23.8) | 51 (21.3) | 0.190 | 20 (19.4) | 17 (16.2) | 25 (23.8) | 18 (17.5) | 0.522 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 16 (5.5) | 14 (4.7) | 8 (7.6) | 24 (10.0) | 0.077 | 8 (7.8) | 4 (3.8) | 8 (7.6) | 11 (10.7) | 0.309 |
| Cardiovascular diseases, n (%) | 2 (0.7) | 9 (3.1) | 4 (3.8) | 11 (4.6) a | 0.045 | 1 (1.0) | 2 (1.9) | 4 (3.8) | 6 (5.8) | 0.192 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 71 (24.6) | 63 (21.4) | 28 (26.7) | 62 (25.9) | 0.559 | 27 (26.2) | 23 (21.9) | 28 (26.7) | 26 (25.2) | 0.855 |
| Previous medications | ||||||||||
| Treatment naïve, n (%) | 62 (21.5) | 75 (25.4) | 22 (21.0) | 52 (21.8) | 0.614 | 26 (25.2) | 27 (25.7) | 22 (21.0) | 25 (24.3) | 0.851 |
| Glucocorticoids, n (%) | 129 (44.6) | 171 (58.0) a | 50 (47.6) | 137 (57.3) a | 0.003 | 46 (44.7) | 56 (53.3) | 50 (47.6) | 56 (54.4) | 0.446 |
| csDMARDs, n (%) | 256 (88.6) | 236 (80.0) a | 95 (90.5) | 192 (80.3) | 0.003 | 91 (88.3) | 83 (79.0) | 95 (90.5) | 80 (77.7) | 0.022 |
| bDMADRs/tsDMARDs, n (%) | 45 (15.6) | 63 (21.4) | 21 (20.0) | 37 (15.5) | 0.192 | 20 (19.4) | 22 (21.0) | 21 (20.0) | 18 (17.5) | 0.935 |
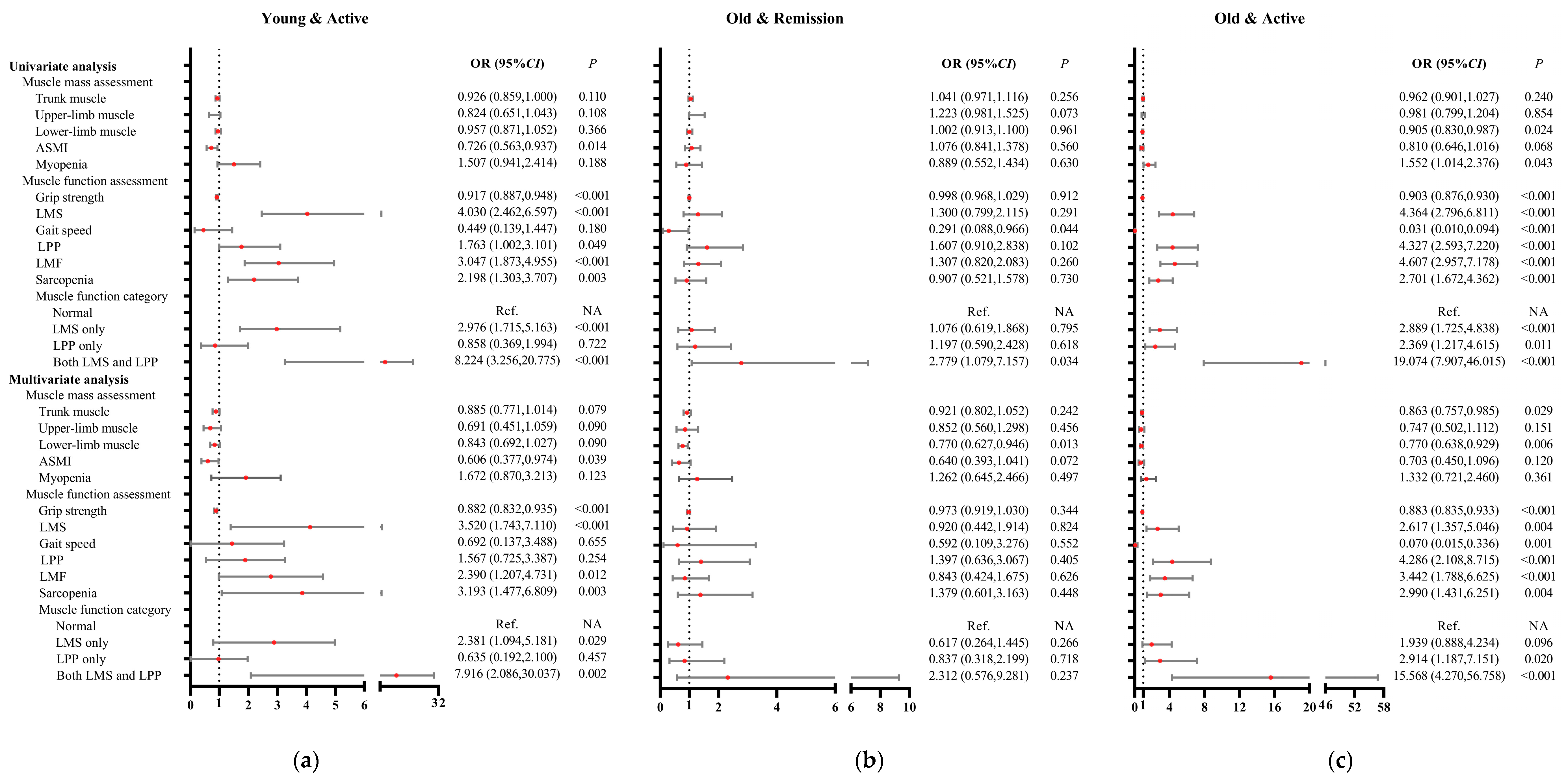
3.6. Associations of Muscle Mass and Function with Patients with Young and Active Disease
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 28TJC | 28-joint tender joint count |
| 28SJC | 28-joint swollen joint count |
| ACPA | Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| ASMI | Appendicular skeletal muscle mass index |
| AWGS | Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia |
| BC | Body composition |
| bDMADRs | Biological DMADRs |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CDAI | Clinical disease activity index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| csDMARDs | Conventional synthetic DMARDs |
| DAS28-CRP | Disease Activity Score in 28 joints including C-reactive protein |
| DAS28-ESR | Disease Activity Score in 28 joints including erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| DMARDs | Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| EULAR | European League Against Rheumatism |
| EWGSOP | European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People |
| HAD | High disease activity |
| HAQ-DI | Health assessment questionnaire disability index |
| IFNγ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JE | Joint erosion |
| JSN | Joint space narrowing |
| LDA | Low disease activity |
| LMF | Low muscle function |
| LMS | Low muscle strength |
| LPP | low physical performance |
| MDA | Moderate disease activity |
| mTSS | Modified total Sharp score |
| MuSCs | Muscle stem cells |
| NA | Not applicable |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| Pain VAS | Pain visual analogue scale |
| PrGA | Provider global assessment of disease activity |
| PtGA | Patient global assessment of disease activity |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Ref | Reference |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| SDAI | Simplified disease activity index |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| tsDMARDs | Targeted-synthetic DMADRs |
| UPS | Ubiquitin–proteasome system |
References
- Sayer, A.A.; Cooper, R.; Arai, H.; Cawthon, P.M.; Ntsama Essomba, M.J.; Fielding, R.A.; Grounds, M.D.; Witham, M.D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Sarcopenia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, M.; Itaya, T.; Minamino, H.; Katsushima, M.; Fujita, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Oshima, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Ito, H.; Arai, H.; et al. Management of sarcopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2023, 33, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.L.; Pratt, A.G.; Dodds, R.; Sayer, A.A.; Isaacs, J.D. Rheumatoid sarcopenia: Loss of skeletal muscle strength and mass in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letarouilly, J.G.; Flipo, R.M.; Cortet, B.; Tournadre, A.; Paccou, J. Body composition in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A narrative literature review. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschou, D.; Krikelis, M.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Mole, E.; Chronopoulos, E.; Tournis, S.; Mavragani, C.; Makris, K.; Dontas, I.; Gazi, S. Sarcopenia in Rheumatoid arthritis. A narrative review. J. Frailty Sarcopenia Falls 2023, 8, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Che, X.; Wu, G. Frontiers in sarcopenia: Advancements in diagnostics, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Aspects Med. 2024, 97, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Z.; Liang, J.J.; Ma, J.D.; Li, Q.H.; Mo, Y.Q.; Cheng, W.M.; He, X.L.; Li, N.; Cao, M.H.; Xu, D.; et al. Myopenia is associated with joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zou, Y.W.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Lin, J.Z.; Wu, T.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, H.W.; He, X.L.; et al. Muscle mass loss is associated with physical dysfunction in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1007184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.D.; Chen, C.T.; Lin, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Chen, L.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Zheng, D.H.; Dai, L. Muscle wasting, a neglected complication associated with physical dysfunction in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional observational study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 50, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Z.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.D.; Mo, Y.Q.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, L.F.; Li, Q.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Zheng, D.H.; Ling, L.; et al. Reduced skeletal muscle independently predicts 1-year aggravated joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X20946220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.; Wong-Pack, M.; Liu, T.; Adachi, J.; Lau, A.; Ma, J.; Papaioannou, A.; Rodrigues, I.B. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes Associated With Sarcopenia in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 30, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Liu, C.W.; Su, C.F.; Tsai, H.C.; Tsao, Y.P.; Liao, H.T.; Chen, M.H.; Chuang, C.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; et al. The prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, B.R.; Tiong, B.K.; Bergman, M.J.; Curtis, J.R.; Kazi, S.; Mikuls, T.R.; O’Dell, J.R.; Ranganath, V.K.; Limanni, A.; Suter, L.G.; et al. 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology Recommended Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Measures. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 1540–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijde, D. How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 261–263. [Google Scholar]
- Maska, L.; Anderson, J.; Michaud, K. Measures of functional status and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ), Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ), Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), Health Assessment Questionnaire II (HAQ-II), Improved Health Assessment Questionnaire (Improved HAQ), and Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life (RAQoL). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. S11), S4–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radner, H.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Nikiphorou, E.; Gossec, L.; Hyrich, K.L.; Zabalan, C.; van Eijk-Hustings, Y.; Williamson, P.R.; Balanescu, A.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. 2017 EULAR recommendations for a core data set to support observational research and clinical care in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Tizaoui, K.; Terrazzino, S.; Cargnin, S.; Lee, K.H.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Smith, L.; et al. Sarcopenia in Autoimmune and Rheumatic Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Kirk, B.; Phu, S.; Vogrin, S.; Duque, G. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and its Association with Antirheumatic Drugs in Middle-Aged and Older Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 109, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraoui, A.; Ebo’o, F.B.; Sadni, S.; Majjad, A.; Hamza, T.; Mounach, A. Is there a relation between pre-sarcopenia, sarcopenia, cachexia and osteoporosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. Changes in body composition and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with psoriatic arthritis. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, T.; Yano, K.; Ikari, K.; Okazaki, K. Sarcopenia-associated factors in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, L.P.; do Espírito Santo, R.C.; Pena, É.; Dória, L.D.; Hax, V.; Brenol, C.V.; Monticielo, O.A.; Chakr, R.M.D.S.; Xavier, R.M. Morphological Parameters in Quadriceps Muscle Were Associated with Clinical Features and Muscle Strength of Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmey, A.B.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Clayton, R.J.; Sheikh, F.; Whale, J.; Jones, H.S.; Ahmad, Y.A.; Chitale, S.; Jones, J.G.; Maddison, P.J.; et al. Tight control of disease activity fails to improve body composition or physical function in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, K.M.; Jessee, R.; Andonian, B.; Davis, B.N.; Narowski, R.; Huebner, J.L.; Kraus, V.B.; McCracken, J.; Gilmore, B.F.; Tune, K.N.; et al. Molecular alterations in skeletal muscle in rheumatoid arthritis are related to disease activity, physical inactivity, and disability. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima-Terrén, M.; Campanario, S.; Ramírez-Pardo, I.; Cisneros, A.; Hong, X.; Perdiguero, E.; Serrano, A.L.; Isern, J.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Muscle aging and sarcopenia: The pathology, etiology, and most promising therapeutic targets. Mol. Aspects Med. 2024, 100, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olie, C.S.; O’Brien, D.P.; Jones, H.B.L.; Liang, Z.; Damianou, A.; Sur-Erdem, I.; Pinto-Fernández, A.; Raz, V.; Kessler, B.M. Deubiquitinases in muscle physiology and disorders. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, P.; Wu, H.; Yang, P.; Guo, H.; Tian, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q. Sarcopenia: Molecular regulatory network for loss of muscle mass and function. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1037200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolny, G.; Barbiera, A.; Sica, G.; Scicchitano, B.M. Age-Related Alterations at Neuromuscular Junction: Role of Oxidative Stress and Epigenetic Modifications. Cells 2021, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanti, F.; Lo Buglio, A.; Vendemiale, G. Mitochondrial Impairment in Sarcopenia. Biology 2021, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Sinha, I.; Sweeney, H.L. Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Molecular Circuitry of Stem Cell Fate in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamar, D.; Er, G.; Terlemez, R.; Ustun, I.; Can, G.; Saridogan, M. Disease activity, handgrip strengths, and hand dexterity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Compán, V.; Landewé, R.; Provan, S.A.; Ødegård, S.; Uhlig, T.; Kvien, T.K.; Keszei, A.P.; Ramiro, S.; van der Heijde, D. Relationship between types of radiographic damage and disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the EURIDISS cohort: A longitudinal study. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Chang, M.; Liu, R.; Qiu, J.; Wang, K.; Deng, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Inflammation: Roles in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabarse, P.V.G.; Lora, P.S.; Silva, J.M.S.; Santo, R.C.E.; Freitas, E.C.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Almeida, A.S.; Immig, M.; Teixeira, V.O.N.; Filippin, L.I.; et al. Collagen-induced arthritis as an animal model of rheumatoid cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozada-Mellado, M.; Llorente, L.; Hinojosa-Azaola, A.; Ogata-Medel, M.; Valdez-Echeverría, R.D.; Lira-Reyes, A.R.; Castillo-Martínez, L. Inflammatory profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and sarcopenia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careccia, G.; Mangiavini, L.; Cirillo, F. Regulation of Satellite Cells Functions during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: A Critical Step in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Grabovac, I.; Berner, C.; Lamprecht, T.; Fenzl, K.H.; Erlacher, L.; Quittan, M.; Dorner, T.E. Frailty in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients of working age: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Pratt, A.G.; Hyrich, K.L. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ 2024, 384, e070856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, B.R.; Smith, B.J.; Baker, N.A.; Barton, J.L.; Oatis, C.A.; Guyatt, G.; Anandarajah, A.; Carandang, K.; Chan, K.K.; Constien, D.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for Exercise, Rehabilitation, Diet, and Additional Integrative Interventions for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.D.; Chen, H.C.; Huang, S.W.; Liou, T.H. Exercise therapy for sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Rehabil. 2022, 36, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Syed, B.; Leapart, J.; Shehabat, M.; Ansari, U.; Akhtar, M.; Razick, D.; Pai, D. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) Effects on Physical Performance: A Systematic Review of Randomized Control Trials. Clin. Endocrinol. 2025, 102, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, B.D.; Ward, C.W. Myostatin/Activin Receptor Ligands in Muscle and the Development Status of Attenuating Drugs. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 329–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Z.; Ma, J.D.; Yang, L.J.; Zou, Y.W.; Zhang, X.P.; Pan, J.; Li, Q.H.; Li, H.G.; Yang, Z.H.; Wu, T.; et al. Myokine myostatin is a novel predictor of one-year radiographic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective cohort study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1005161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Hu, S.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dai, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, G.; Tang, C.H. Myostatin induces tumor necrosis factor-α expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 9793–9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ponce, F.; Ramirez-Villafaña, M.; Gomez-Ramirez, E.E.; Saldaña-Cruz, A.M.; Gallardo-Moya, S.G.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, N.A.; Jacobo-Cuevas, H.; Nava-Valdivia, C.A.; Avalos-Salgado, F.A.; Totsuka-Sutto, S.; et al. Role of Myostatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review of the Clinical Impact. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Zhan, R.Z.; Rao, L.; Bursac, N. Exercise mimetics and JAK inhibition attenuate IFN-γ-induced wasting in engineered human skeletal muscle. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Álvarez, I.; Pérez-Baos, S.; Gratal, P.; Medina, J.P.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Mediero, A. Effects of Tofacitinib on Muscle Remodeling in Experimental Rheumatoid Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Disease Characteristics | All RA (n = 928) |
|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 771 (83.1) |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 53.2 ± 12.0 |
| Disease duration, month, median (IQR) | 84 (36, 145) |
| Active smoking, n (%) | 89 (11.2) |
| Positive RF, n (%) | 702 (75.6) |
| Positive ACPA, n (%) | 871 (93.9) |
| Core disease activity indicators | |
| 28TJC, median (IQR) | 1 (0, 5) |
| 28SJC, median (IQR) | 0 (0, 2) |
| PtGA, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 4) |
| PrGA, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 4) |
| PainVAS, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 3) |
| ESR, mm/h, median (IQR) | 25 (14, 44) |
| CRP, mg/L, median (IQR) | 3.6 (3.3, 8.7) |
| CDAI, median (IQR) | 7 (1, 15) |
| Radiographic assessments | |
| mTSS, median (IQR) | 7 (2, 25) |
| JSN, median (IQR) | 2 (0, 11) |
| JE, median (IQR) | 5 (1, 14) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 173 (18.6) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 62 (6.7) |
| Cardiovascular diseases, n (%) | 26 (2.8) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 224 (24.1) |
| Previous medications | |
| Treatment naïve, n (%) | 211 (22.7) |
| Glucocorticoids, n (%) | 487 (52.5) |
| csDMARDs, n (%) | 779 (83.9) |
| bDMADRs/tsDMARDs, n (%) | 166 (17.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, P.-W.; Lin, J.-Z.; Zou, Y.-W.; Ouyang, Z.-M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, K.-M.; Liang, L.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Ma, J.-D.; et al. The Characteristic of Muscle Function for Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Real-World Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040551
Jia P-W, Lin J-Z, Zou Y-W, Ouyang Z-M, Yang Y, Yang K-M, Liang L-H, Han J-Y, Yang Z-H, Ma J-D, et al. The Characteristic of Muscle Function for Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Real-World Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040551
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Pei-Wen, Jian-Zi Lin, Yao-Wei Zou, Zhi-Ming Ouyang, Ying Yang, Kui-Min Yang, Liu-Hong Liang, Jin-Yuan Han, Ze-Hong Yang, Jian-Da Ma, and et al. 2025. "The Characteristic of Muscle Function for Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Real-World Cross-Sectional Study" Medicina 61, no. 4: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040551
APA StyleJia, P.-W., Lin, J.-Z., Zou, Y.-W., Ouyang, Z.-M., Yang, Y., Yang, K.-M., Liang, L.-H., Han, J.-Y., Yang, Z.-H., Ma, J.-D., & Dai, L. (2025). The Characteristic of Muscle Function for Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Real-World Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina, 61(4), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040551







