Anti-Virulence Properties of Curcumin/CuO-NPs and Their Role in Accelerating Wound Healing In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. MIC and MBC Determination
2.2. Estimation of Quorum Sensing (Q.S)-Controlled Virulence Factors
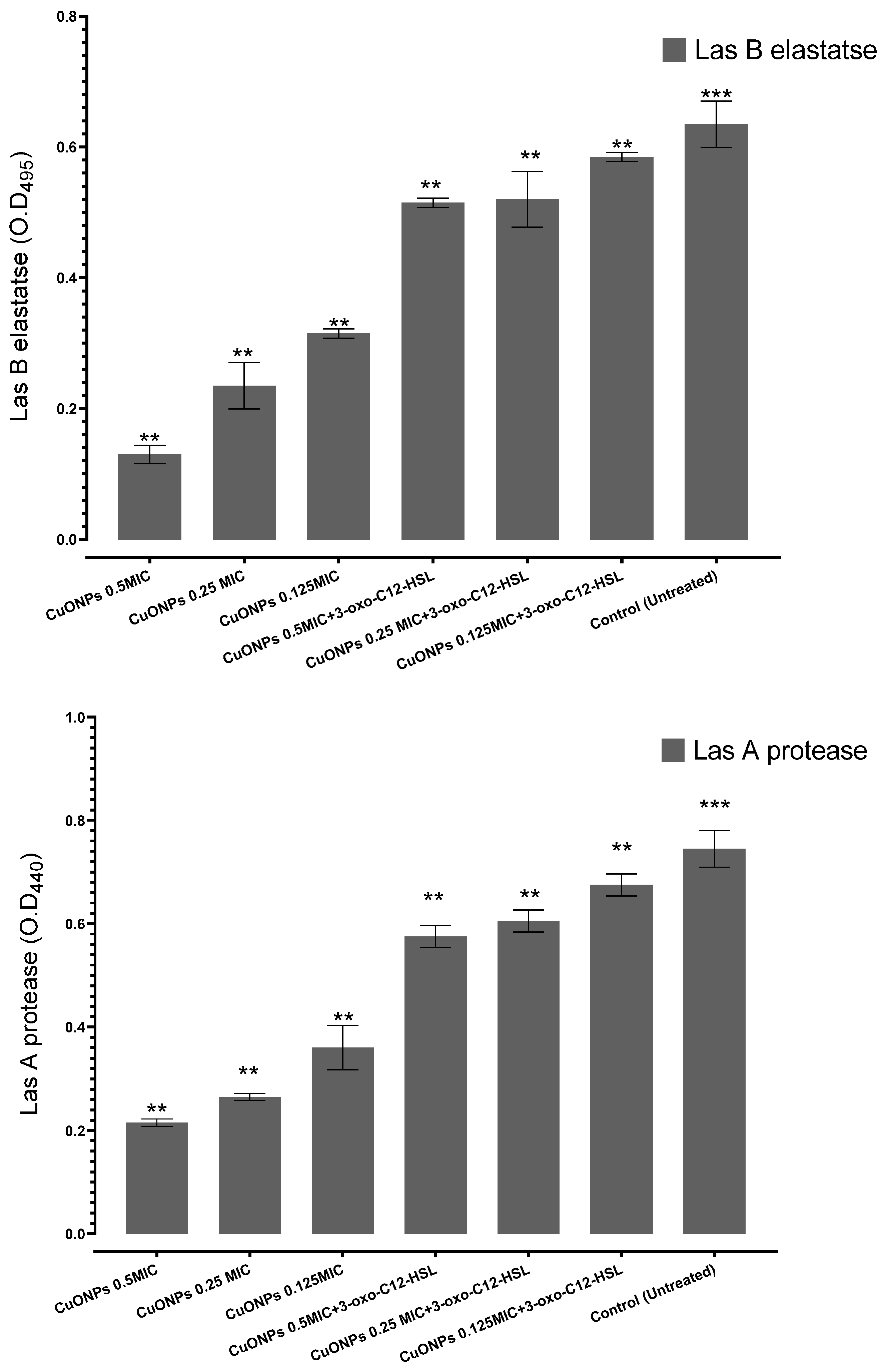
2.3. LasA Protease Assay
2.4. LasB Elastase Assay
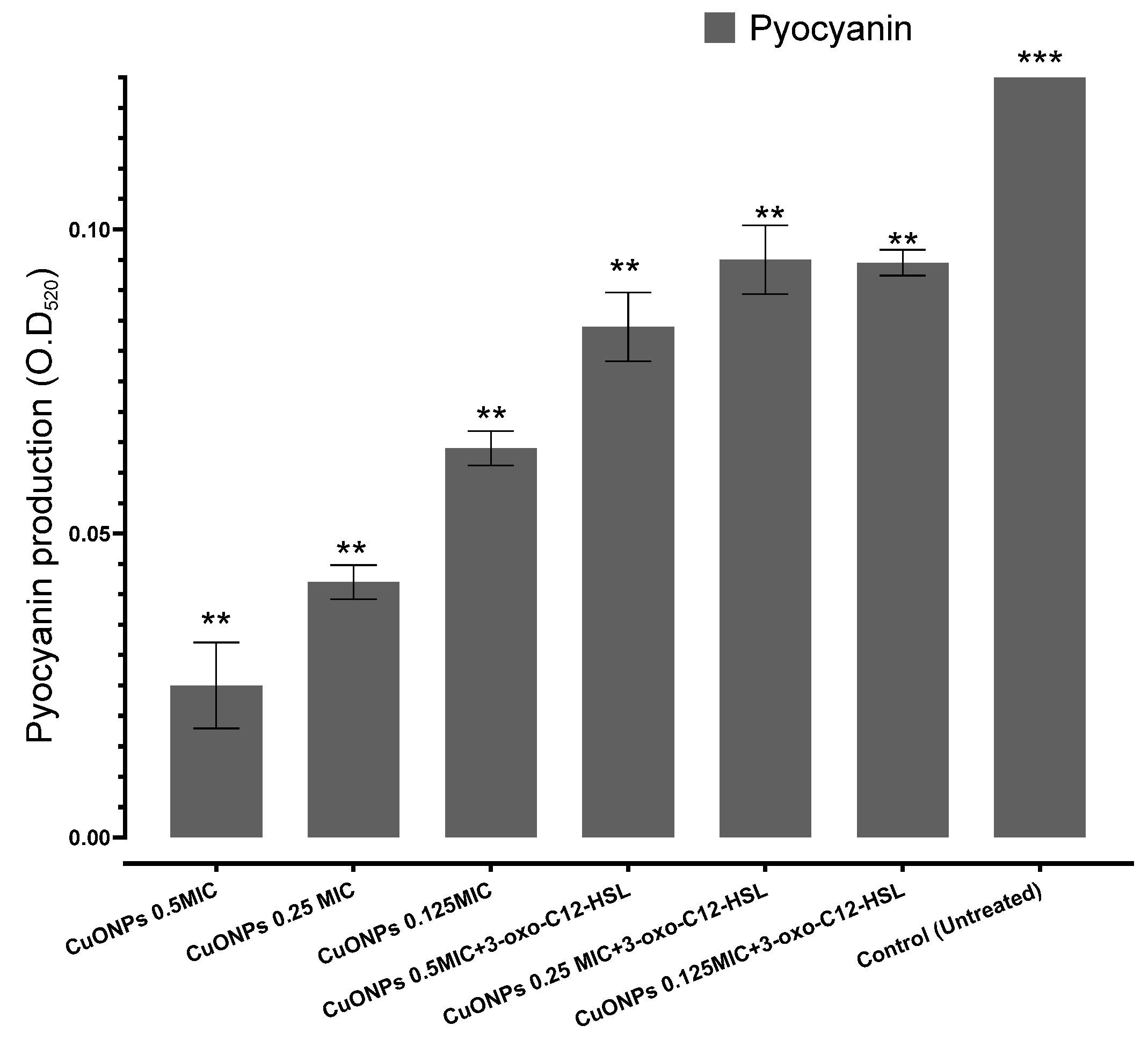
2.5. Pyocyanin Assay
2.6. Antioxidant Property of CuO-NPs
2.7. Cytotoxicity and Wound Healing Assay
2.8. In Vivo Wound Healing Evaluation
2.9. Histopathological Analysis
2.10. Result Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
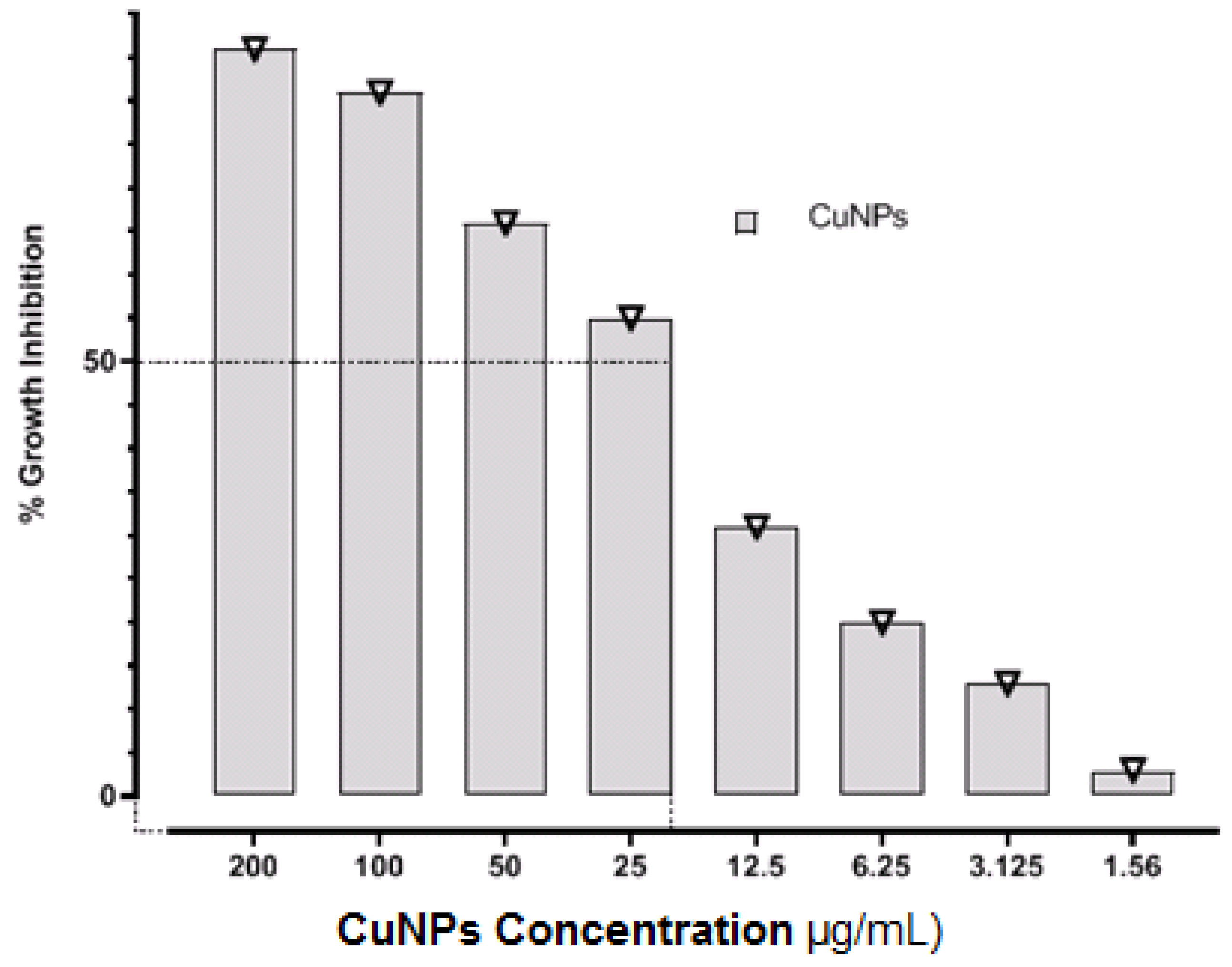
3.1. Determination of MIC and MBC
3.2. Effects of CuO-NPs on Q.S-Controlled Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of CuO-NPs
3.4. Cell Migration Assay
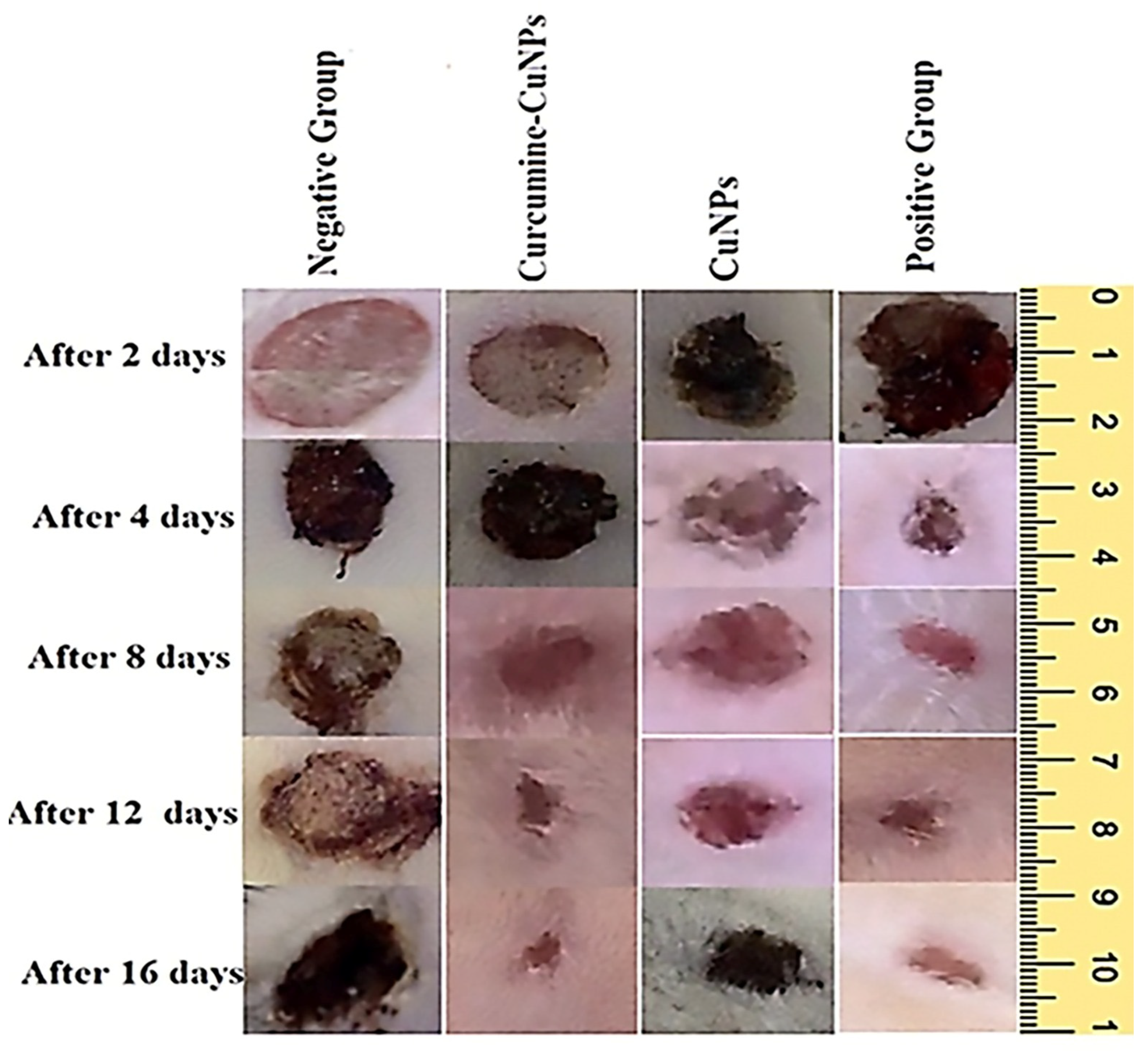
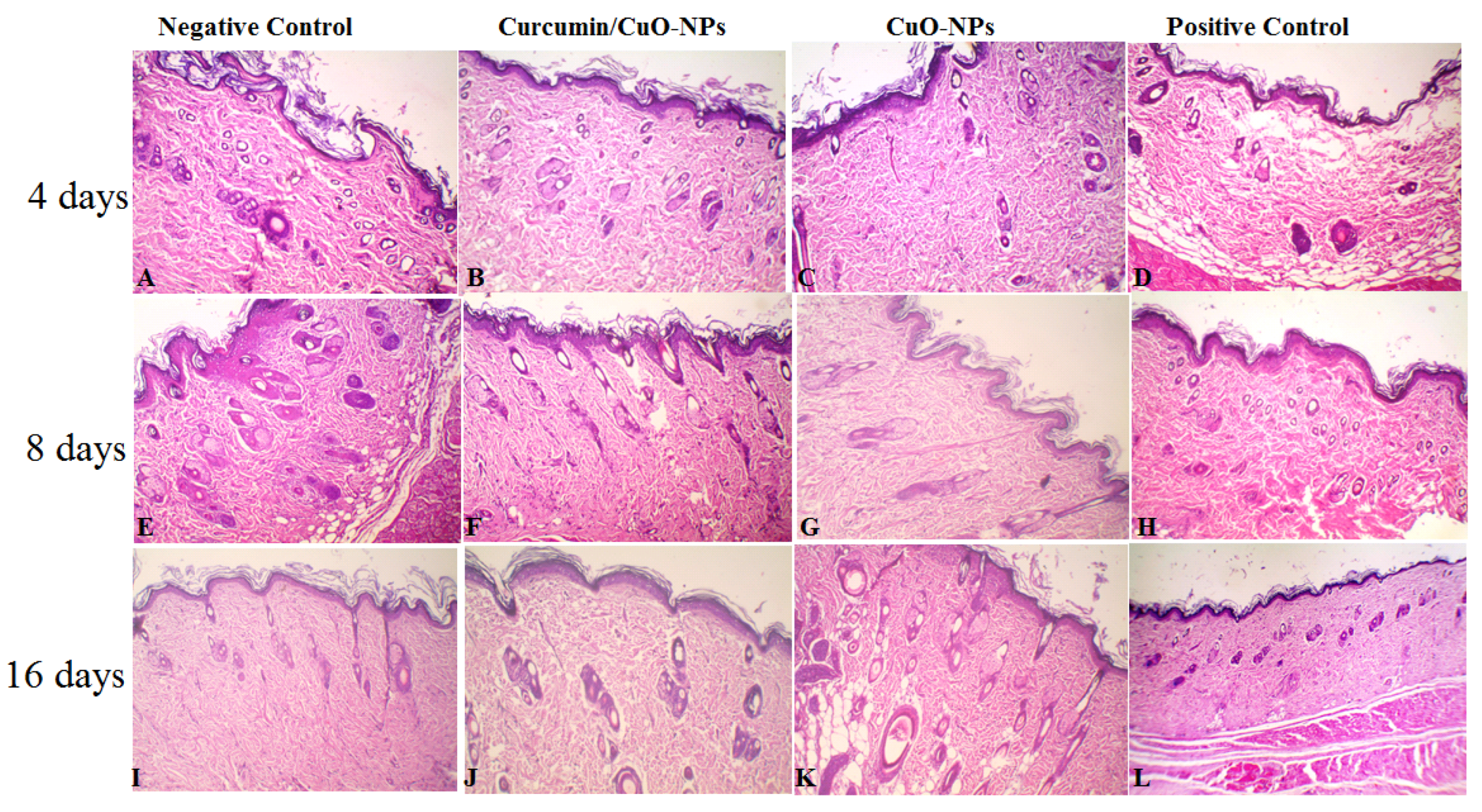
3.5. Effect of Topical Application of CuO-NPs-CUR on Wound Maturity
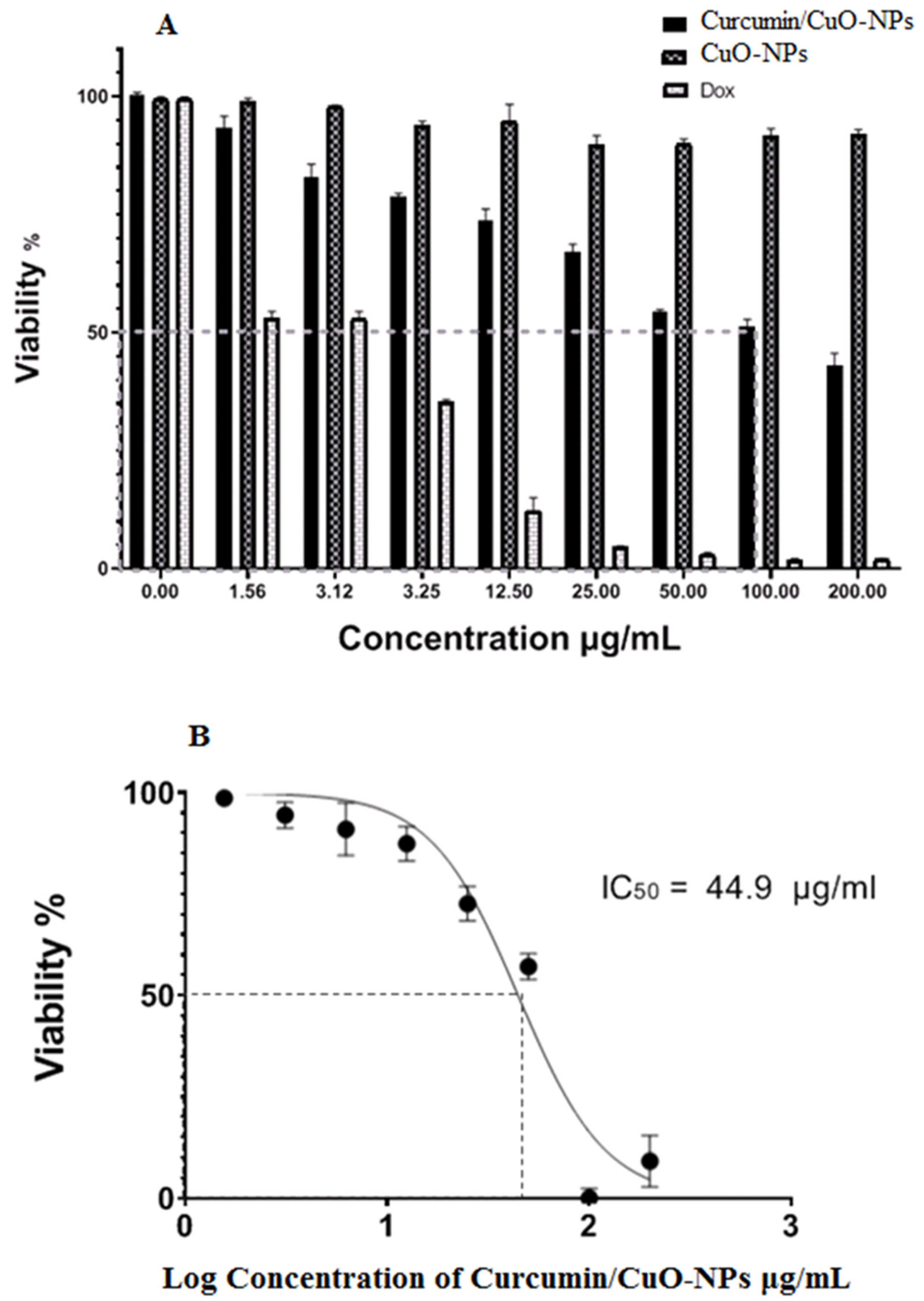
3.6. Cytotoxic Activity
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masoud, A.G.; Gahlan, A.A.; Ameen, M.G.; Shatat, A.R. Evaluating The Possible Effective Protective Role Of Curcumin And Copper (I)-Nicotinate Complex After Inducing Hepatotoxicity In Rat Liver. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2024, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.E.; Nisa, M.U.; Koohi, M.; Raza, A.; Shahmabadi, H.E. Revolutionizing Wound Healing: Exploring Scarless Solutions through Drug Delivery Innovations. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 1056–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, J.; Karthikeyan, E.; Rajeshkumar, S. Nanomaterials for wound healing: Current status and futuristic frontier. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 6, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Lin, J.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Velkov, T.; Shen, J. The natural product curcumin as an antibacterial agent: Current achievements and problems. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Bravo, D.; Soto, C.; Maturana, G.; Cordero-Machuca, J.; Zúñiga-López, M.C.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.; Quest, A.F. The Anti-Oxidant Curcumin Solubilized as Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions or Chitosan Nanocapsules Effectively Reduces Helicobacter pylori Growth, Bacterial Biofilm Formation, Gastric Cell Adhesion and Internalization. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbeny, F.E.M.; Abu-Elnaga, N.A.; El-Azez, A.; Asmaa, M.; Ahmed Osman, N.H. The possible role of curcumin-chitosan nanocomposite in reducing the impairment effect of carbon tetrachloride on the testis tissue in liver fibrosis model. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2022, 33, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elebiary, D.M.; Mahdy, H.M.; Mansour, A.M.; Amer, W.H.; Abu-Elghait, M. Evaluation of Arabic gum antibacterial and wound healing activities against Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained from skin infections. Microb. Biosyst. 2024, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, M.; Gouda, G.A.; Nagiub, A.M. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Characterization, Organic Dye Degradation and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2023, 34, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Mohanty, D.L.; Divya, N.; Bakshi, V.; Mohanty, A.; Rath, D.; Das, S.; Mondal, A.; Roy, S.; Sabui, R. A critical review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. Intell. Pharm. 2024, 3, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamani, M.M.; Hughes, A.C.; Zhang, H.-L.; Wang, Y. Revolutionizing agriculture with nanotechnology: Innovative approaches in fungal disease management and plant health monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Banerjee, J.; Chakraborty, P.; Banerjee, A.; Chanda, S.; Ray, K.; Acharya, K.; Sarkar, J. Green synthesis of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles and their applications: A review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmad, J.; Salami, M.; Zarei, M.H. Comparative toxic effect of bulk copper oxide (CuO) and CuO nanoparticles on human red blood cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, H.; Sajjad, A.; Haya, R.T.; Khan, M.M.; Zia, M. Copper oxide nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo toxicity, mechanisms of action and factors influencing their toxicology. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 271, 109682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Qin, P.; Wei, G.; Chen, C. Comparing the inhibitory effects of CuO-rGO, CuO NPs, and CuCl 2 on the oomycete Phytophthora sojae: Insights from phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.; Yusefi-Tanha, E.; Peralta-Videa, J.R. Interaction of nanoparticles and reactive oxygen species and their impact on macromolecules and plant production. Plant Nano Biol. 2024, 10, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Kiani, S.; Toushmalani, R.; Zangeneh, A.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Goorani, S.; Morovvati, H. Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) using sodium lignosulfonate and evaluation of its cutaneous wound healing properties. Mater. Express 2023, 13, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, C.; Ríos, G.; Sepúlveda, N.; Salvo, J.; Souza-Mello, V.; Farías, J. Effectiveness of copper nanoparticles in wound healing process using in vivo and in vitro studies: A systematic review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hagras, F.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Kamel, M.R.; Ahmed, M.A.; Atia, K.H.; Salem, S.S. Potential antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties of copper oxide nanoparticles: Time-kill kinetic essay and ultrastructure of pathogenic bacterial cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Gazelly, A.M.; Sharaf, M.H.; Moghannemm, S.A.; Ismail, M.K.; El-Hawary, A.S. Exploitation of the antibacterial, antibiofilm and antioxidant activities of Salvadora Persica (Miswak) extract. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2023, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, E.; Safrin, M.; Olson, J.; Ohman, D. Secreted LasA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a staphylolytic protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 7503–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashin, I.; Hasanin, M.; Hassan, S.A.; Hashem, A.H. Green biosynthesis of zinc and selenium oxide nanoparticles using callus extract of Ziziphus spina-christi: Characterization, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activity. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 10133–10146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Al-Askar, A.A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Hagras, F.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Kamel, M.R.; Ahmed, M.A.; Atia, K.H.; Hashem, A.H. Wound Dressing Scaffold with High Anti-biofilm Performance Based on Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan-Hydrolyzed Starch Nanocomposite: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 6421–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaCosta, M.V.J. Morphological, Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Response of Rice Seedlings to Metallo-Nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, Goa University, Taleigao, Goa, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Khare, M.; Singh, P. Immune and oxidative stress variation in the patients of hypothyroidism on the basis of hormonal changes. In Recent Advances in Biotechnology & Nanobiotechnology; Amity Institute of biotechnology Amity University Madhya Pradesh: Gwalior India, 2016; pp. 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Decho, A.W. Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: Their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1990, 28, 73–153. [Google Scholar]
- Finlay, B.B.; Falkow, S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, M.D. A Systems Approach to Recognition Imaging: Micropatterning and Scanning Force Microscopy in the Development of Engineered Biomaterials; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, C.D.; Collison, D.; Pidcock, E. The nature of the coordination sites of transition metals in proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1996, 354, 325–357. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, D.L.; O’Halloran, T.V. Function, structure, and mechanism of intracellular copper trafficking proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweadner, K.J.; Donnet, C. Structural similarities of Na, K-ATPase and SERCA, the Ca2+-ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Shafiq, A.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carum copticum: Assessment of its quorum sensing and biofilm inhibitory potential against gram negative bacterial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 144, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.A.N.; dos Santos, G.A.; dos Santos, C.T.; Soares, D.C.F.; Saraiva, M.F.; Leal, D.H.S.; Sachs, D. Eugenol as a promising antibiofilm and anti-quorum sensing agent: A systematic review. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 196, 106937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Altaf, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Al-Rayes, B.F.; Abuhasil, M.S.A.; Almaroai, Y.A. Biofabricated silver nanoparticles exhibit broad-spectrum antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activity against Gram-negative bacteria. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13700–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, K.A.; Paczkowski, J.E. Resistance is not futile: The role of quorum sensing plasticity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections and its link to intrinsic mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capatina, D.; Feier, B.; Hosu, O.; Tertis, M.; Cristea, C. Analytical methods for the characterization and diagnosis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1204, 339696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogardt, M.; Heesemann, J. Microevolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to a chronic pathogen of the cystic fibrosis lung. In Between Pathogenicity and Commensalism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 91–118. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo, F.; Scognamiglio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Buommino, E.; D’abrosca, B. Plant derived natural products against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus: Antibiofilm activity and molecular mechanisms. Molecules 2020, 25, 5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molahloe, T.S. Phytochemical and Bioactivity Investigations on Aptosimum Elongatum Engl. Extracts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harishchandra, B.D.; Pappuswamy, M.; Antony, P.U.; Shama, G.; Pragatheesh, A.; Arumugam, V.A.; Periyaswamy, T.; Sundaram, R. Copper nanoparticles: A review on synthesis, characterization and applications. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Biol. 2020, 5, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.F.; Hanafy, S.M.; Abdelgalil, R.M.; Abo-Ouf, A.M. Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) on the testes of adult male albino rats and the possible protective role of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Arshad, F.; Hussain, Z.; Mukhtar, M. Green adeptness in the synthesis and stabilization of copper nanoparticles: Catalytic, antibacterial, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant activities. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jing, L.; Yang, T.; Cui, H.; Deng, H.; Zuo, Z.; et al. Molecular Regulatory Mechanism of Nano-Se Against Copper-Induced Spermatogenesis Disorder. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 203, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.S.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Gaber, S.E.; Khalil, A.M.A.; Saleh, A.M.; Al zoubi, O.M.; Hashem, A.H. Protective Role of Mycosynthesized Bimetallic ZnO-CuO Nanoparticles as Therapeutic Nutrients to Enhance the Resistance of Vicia faba against Fusarium Wilt Disease. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Gul, A.; Zia, M. Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles: A review study. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napagoda, M.; Madhushanthi, P.; Witharana, S. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration, in Nanotechnology in Modern Medicine; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Favara, G.; Lio, R.M.S.; Evola, G.; Agodi, A.; Basile, G. Nutrition and wound healing: An overview focusing on the beneficial effects of curcumin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfelder, U.; Abel, M.; Wiegand, C.; Klemm, D.; Elsner, P.; Hipler, U.-C. Influence of selected wound dressings on PMN elastase in chronic wound fluid and their antioxidative potential in vitro. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6664–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkowska, H.; Wojewodzka, U.; Olszewski, W.L. Chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors in keratinocytes and dermal endothelial cells in the margin of chronic diabetic foot ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006, 14, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.P.; Suresh, D.; Sneharani, A. Eco-friendly Ag-CuO nanoparticles for antidiabetic, antimicrobial, anti-cancer, platelet aggregation inducing, antioxidant and photocatalytic applications. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafagh, M.; Rahmani, F.; Delirezh, N. CuO nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human K562 cancer cell line via mitochondrial pathway, through reactive oxygen species and P53. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zughaibi, T.A.; Mirza, A.A.; Suhail, M.; Jabir, N.R.; Zaidi, S.K.; Wasi, S.; Zawawi, A.; Tabrez, S. Evaluation of anticancer potential of biogenic copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) against breast cancer. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 5326355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridasappa, A.; Rangappa, D.; Maheswarappa, G.S.; Marilingaiah, N.R.; Thammaiah, C.K.; Shareef, I.M.; Subbegowda, R.K.; Shivaramu, P.D. Phytofabrication of cupric oxide nanoparticles using Simarouba glauca and Celastrus paniculatus extracts and their enhanced apoptotic inducing and anticancer effects. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1393–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antimicrobial Agents | MIC | MBC | MBC/MIC Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| (CuO-NPs) (µg/mL) | 25 | 50 | 2 |
| Levofloxacin (µg/mL) | 3.25 | 6.5 | 2 |
| Ceftazidime (µg/mL) | 6.5 | 13 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehabeldine, A.M.; Badr, B.M.; Elkady, F.M.; Watanabe, T.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; Alamri, A.M.; Alrokayan, S.; Abdelaziz, A.M. Anti-Virulence Properties of Curcumin/CuO-NPs and Their Role in Accelerating Wound Healing In Vivo. Medicina 2025, 61, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030515
Shehabeldine AM, Badr BM, Elkady FM, Watanabe T, Abdel-Maksoud MA, Alamri AM, Alrokayan S, Abdelaziz AM. Anti-Virulence Properties of Curcumin/CuO-NPs and Their Role in Accelerating Wound Healing In Vivo. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030515
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehabeldine, Amr M., Bahaa M. Badr, Fathy M. Elkady, Toru Watanabe, Mostafa A. Abdel-Maksoud, Abdulaziz M. Alamri, Salman Alrokayan, and Amer M. Abdelaziz. 2025. "Anti-Virulence Properties of Curcumin/CuO-NPs and Their Role in Accelerating Wound Healing In Vivo" Medicina 61, no. 3: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030515
APA StyleShehabeldine, A. M., Badr, B. M., Elkady, F. M., Watanabe, T., Abdel-Maksoud, M. A., Alamri, A. M., Alrokayan, S., & Abdelaziz, A. M. (2025). Anti-Virulence Properties of Curcumin/CuO-NPs and Their Role in Accelerating Wound Healing In Vivo. Medicina, 61(3), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030515







