Evaluating Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric UTIs: Five-Year Data from a Tertiary Hospital in Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UTIs | Urinary tract infections |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| TMP-SMX | Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole |
References
- Mert, D.; Çeken, S.; Ertek, M. İdrar yolu enfeksiyonlarında kültürden izole edilen bakteriler ve antibiyotik duyarlılıkları. Türk Hij. Deney. Biyol. Derg. 2020, 77, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, R.; Murt, A. Epidemiology of urological infections: A global burden. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.C.; Lin, T.C.; Wu, R.X.; Yang, Y.S.; Hsiao, P.J.; Lee, Y.; Wu, T.C.; Kuo, S.C. Etiologies of community-onset urinary tract infections requiring hospitalization and antimicrobial susceptibilities of causative microorganisms. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emre, S. Üriner Sistem Enfeksiyonları. In Pediatri, 4th ed.; Neyzi, O., Ertuğrul, T., Eds.; Nobel Tıp Kitabevleri: İstanbul, Turkiye, 2009; pp. 1491–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Haller, M.; Brandis, M.; Berner, R. Antibiotic resistance of urinary tract pathogens and rationale for empirical intravenous therapy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2004, 19, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söylemezoğlu, O. Üriner sistem enfeksiyonları. In Temel Pediatri; Hasanoğlu, E., Düşünsel, R., Bideci, A., Eds.; Güneş Tıp Kitabevleri: Ankara, Turkey, 2010; pp. 929–935. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, N.; Morone, N.E.; Bost, J.E.; Farrell, M.H. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in childhood: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Langlois, V. Nephrology. In The Hospital for Sick Children Handbook of Pediatrics, 11th ed.; Dipchand, A., Friedman, J., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009; pp. 632–634. [Google Scholar]
- Elder, J.S. Urinary tract infections. In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th ed.; Kliegman, R.M., Stanton, B.F., St Geme, J.W., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1829–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Sucu, N.; Aktoz-Boz, G.; Bayraktar, Ö.; Kuru, F.; Gültekin, H. Üropatojen Escherichia coli suşlarının antibiyotik duyarlılıklarının yıllar içerisindeki değişimi. Klimik Derg. 2004, 17, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, Z.S.; Davis, M.A.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, W.J. A cost-effectiveness analysis of treatment strategies for acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis in women. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2003, 10, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, M.; Kazanasmaz, H. Uropathogens and antibiotic resistance in the community and hospital-induced urinary tract infected children. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çoban, B.; Ülkü, N.; Kaplan, H.; Topal, B.; Erdoğan, H.; Baskın, E. Çocuklarda idrar yolu enfeksiyonu etkenleri ve antibiyotik dirençlerinin beş yıllık değerlendirmesi. Turk. Pediatri Ars. 2014, 49, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yasar, A.; Yaşar, B.; Özkan, E.A.; Savcı, Ü. Yozgat Yöresi Çocukluk Çağı İdrar Yolu Enfeksiyonuna En Sık Sebep Olan Etkenler ve Antibiyotik Dirençleri. Bozok Tıp Derg. 2018, 8, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Konca, C.; Tekin, M.; Uckardes, F.; Yılmaz, M.; Korkmaz, A. Antibacterial resistance patterns of pediatric community-acquired urinary infection: Overview. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömürlüoğlu, A.; Aykaç, K.; Özsürekçi, Y.; Can, D.; Aktaş, N. Gram negatif idrar yolu enfeksiyonu etkenlerinin antibiyotik direnç dağılımı: Tek merkez deneyimi. J. Pediatr. Dis. 2018, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yavaşcan, Ö.; Sözen, G.; Kara, D.; Çetin, N.; Aksu, N. Çocuklarda idrar yolu infeksiyonu etkenleri ve antibiyotik direnci. İzmir Tepecik Hast Derg. 2005, 15, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.S. Urinary tract infections. In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 20th ed.; Behrman, R.E., Kliegman, R.M., Jenson, H.B., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 2556–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Vazouras, K.; Velali, K.; Tassiou, I.; Dardavessis, T.; Maroudi, M. Antibiotic treatment and antimicrobial resistance in children with urinary tract infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baines, G.; Banjoko, A.; Brair, A.; Ghosh, S.; Onwudiwe, N. Antibiotic resistance in urinary tract infections: A re-visit after five years and experience over two sites. Post. Reprod. Health 2020, 26, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Benwan, K.; Jamal, W. Etiology and antibiotic susceptibility patterns of urinary tract infections in children in a general hospital in Kuwait: A 5-year retrospective study. Med. Princ. Pract. 2022, 31, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yolbas, I.; Tekin, R.; Kelekci, S.; Tekin, A.; Okur, M.H.; Ece, A.; Kadir, A. Community-acquired urinary tract infections in children: Pathogens, antibiotic susceptibility, and seasonal changes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Çetin, H.; Öktem, F.; Örmeci, A.R.; Yorgancıgil, B.; Yaylı, G. Escherichia coli and antibiotic resistance in childhood urinary tract infections. Suleyman Demirel Univ. Med. J. 2006, 13, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, T.B. The new American Academy of Pediatrics urinary tract infection guideline. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.B. Urinary tract infection: Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of the initial UTI in febrile infants and children 2 to 24 months. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.F.; Wang, W.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, Z.D. Distribution and resistance trends of pathogens from urinary tract infections and impact on management. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2003, 9, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tseng, M.H.; Lo, W.T.; Lin, W.J.; Teng, C.S.; Chu, M.L.; Wang, C.C. Changing trend in antimicrobial resistance of pediatric uropathogens in Taiwan. Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlin, R.S.; Shapiro, D.J.; Hersh, A.L.; Copp, H.L. Antibiotic resistance patterns of outpatient pediatric urinary tract infections. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salduz, Z.; Yiğit, O. Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from children with urinary tract infections. J. Pediatr. Inf. 2010, 4, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prais, D.; Straussberg, R.; Avitzur, Y.; Nussinovitch, M.; Harel, L.; Amir, J. Bacterial susceptibility to oral antibiotics in community-acquired urinary tract infection. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosun, S.Y.; Demirel, M.M.; Ertan, P.; Aksu, S. Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from children’s urine samples. Türk. Klin. J. Pediatr. 2004, 13, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, B.; Yiğit, Ö.; Özgürhan, G.; Aksoy, M.; Cambaz, N.; Beycan, İ. Microorganisms responsible for urinary tract infections and antibiotic resistance in children. In Proceedings of the 2nd National Pediatric Diseases Congress, Adana, Turkey, 26–29 October 2001; p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- Gündüz, T.; Tosun, S.; Demirel, M.M.; Ertan, P. Antibiotic resistance in childhood urinary tract infections: Five-year results. Pamukkale Med. J. 2008, 1, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gürgöze, M.K.; Doğan, Y.; Kizirgil, A.; Aşçı Toraman, Z.; Aygün, D. Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from children with urinary tract infections. Fırat Med. J. 2002, 7, 828–832. [Google Scholar]
- Cebe, A.; Ayvaz, A.; Yıldız, N.; Çetinkaya, S. Results of urine culture in childhood urinary tract infections in Sivas: How should the initial treatment choice be made? Van Med. J. 2008, 15, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nassereddin Mostafavi, S.; Rostami, S.; Rezaee Nejad, Y.; Ataei, B.; Mobasherizadeh, S.; Cheraghi, A.; Shokri, D. Antimicrobial resistance in hospitalized patients with community-acquired urinary tract infection in Isfahan, Iran. Arch. Iran. Med. 2021, 24, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Maraki, S.; Mantadakis, E.; Michailidis, L.; Samonis, G. Changing antibiotic susceptibilities of community-acquired uropathogens in Greece 2005–2010. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantadakis, E.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Panopoulou, M.; Tsouvala, E.; Tsalkidis, A.; Chatzimichael, A.; Gousia, P. Susceptibility patterns of uropathogens identified in hospitalized children with community-acquired urinary tract infections in Thrace, Greece. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouladfar, G.; Basiratnia, M.; Anvarinejad, M.; Abbasi, P.; Amirmoezi, F.; Zare, S. The antibiotic susceptibility patterns of uropathogens among children with urinary tract infection in Shiraz. Medicine 2017, 96, e7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahissa, A.; Pigrau, C. Tratamiento de las infecciones del tracto urinario en las embarazadas. In Infecciones del Tracto Urinario en las Embarazadas; Sociedad Española de Ginecología y Obstetricia, Ed.; Ediciones Mayo: Barcelona, Spain, 2001; pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
| Microorganism | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 1685 | 61.2 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 367 | 13.3 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 251 | 9.1 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 95 | 3.5 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 49 | 1.8 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 46 | 1.7 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 43 | 1.6 |
| Enterococcus faecium | 38 | 1.4 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 25 | 0.9 |
| Morganella morganii | 24 | 0.9 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 24 | 0.9 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 21 | 0.8 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 20 | 0.7 |
| Citrobacter | 16 | 0.6 |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 16 | 0.6 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 13 | 0.5 |
| Staphylococcus simulans | 7 | 0.3 |
| Acinetobacter | 6 | 0.2 |
| Providencia rettgeri | 5 | 0.2 |
| Cedecea | 2 | 0.1 |
| <12 Months | 12–60 Months | >60 Months | |
|---|---|---|---|
| By Gram stain | n | % | n |
| Gram-positive | 82 | 10.0 | |
| Gram-negative | 741 | 90.0 | |
| By bacterial species | E. coli | 355 | 43.1 |
| Klebsiella | 258 | 31.3 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 34 | 4.1 | |
| Other | 176 | 21.4 | |
| <12 months | 12–60 months | >60 months | |
| n | % | n | |
| By Gram stain | Gram-positive | 82 | 10.0 |
| Gram-negative | 741 | 90.0 |
| Male | Female | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <12 Months | 12–60 Months | >60 Months | <12 Months | 12–60 Months | >60 Months | p | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
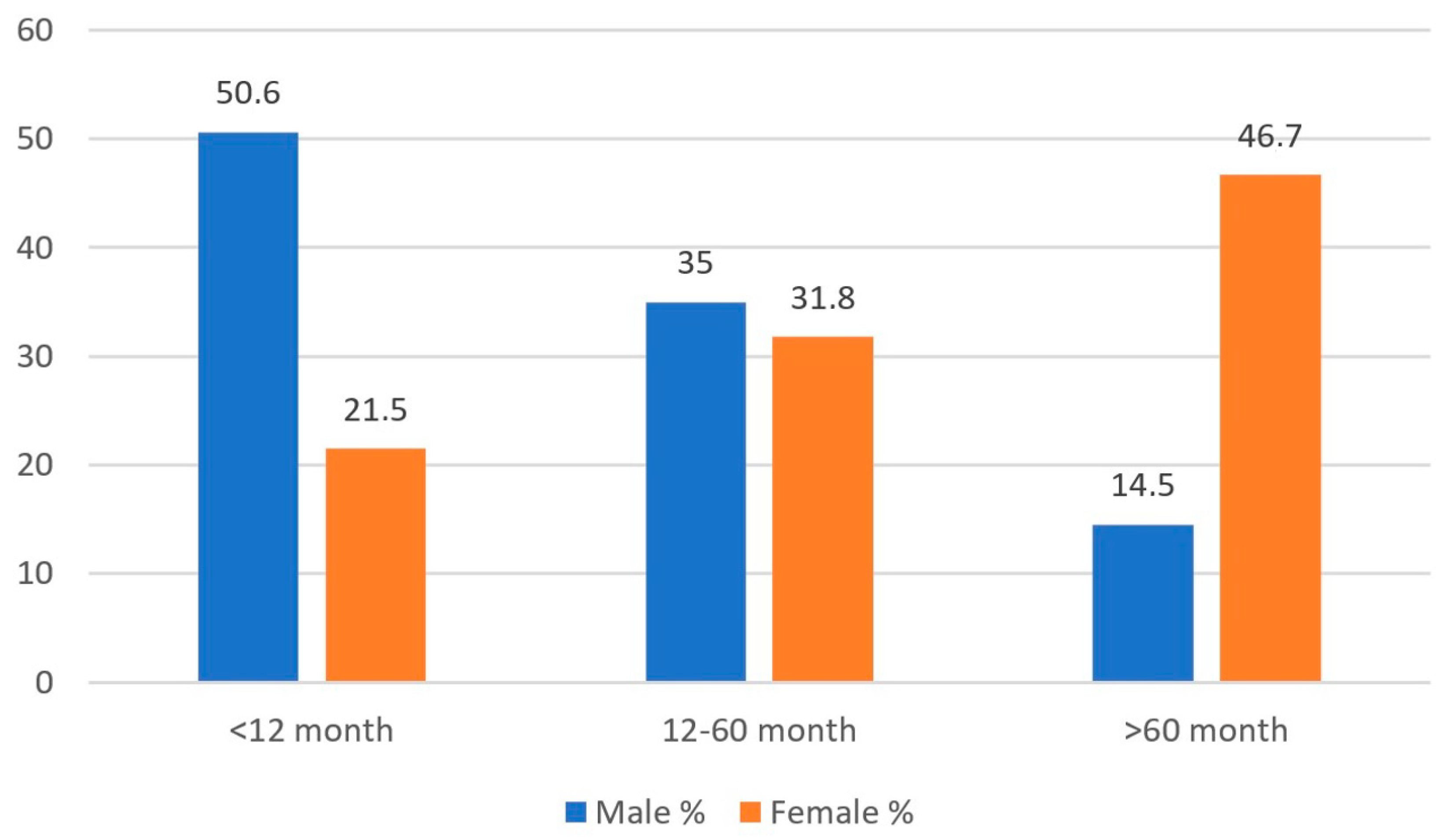
| Gram-positive | 38 | 9.5 | 25 | 9.0 | 24 | 20.9 | 44 | 10.5 | 37 | 5.9 | 75 | 8.2 | p1 = 0.633 p2 = 0.096 p3 < 0.001 |
| Gram-negative | 364 | 90.5 | 253 | 91.0 | 91 | 79.1 | 377 | 89.5 | 585 | 94.1 | 840 | 91.8 | |
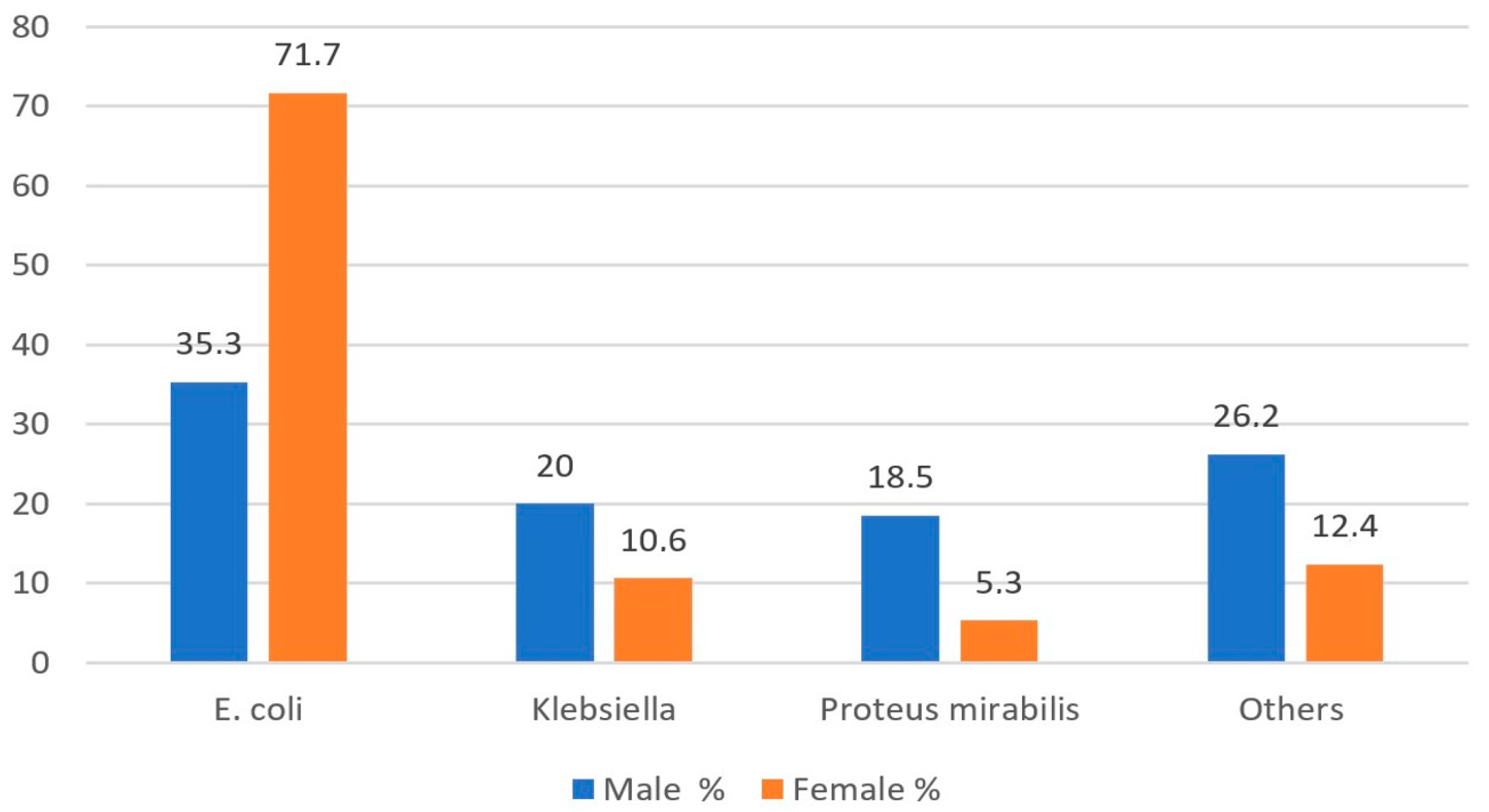
| E. coli | 156 | 38.8 | 82 | 29.5 | 43 | 37.4 | 199 | 47.3 | 482 | 77.5 | 723 | 79.0 | p1 = 0.001 p2 < 0.001 p3 < 0.001 |
| Klebsiella | 125 | 31.1 | 24 | 8.6 | 10 | 8.7 | 133 | 31.6 | 27 | 4.3 | 48 | 5.2 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 26 | 6.5 | 104 | 37.4 | 17 | 14.8 | 8 | 1.9 | 55 | 8.8 | 41 | 4.5 | |
| Other | 95 | 23.6 | 68 | 24.5 | 45 | 39.1 | 81 | 19.2 | 58 | 9.3 | 103 | 11.3 | |
| E. coli % | Klebsiella pneumoniae % | Proteus mirabilis % | All Isolated Bacteria % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicilin | 67.4 | 100.0 | 48.6 | 70.8 |
| Amikacin | 0.9 | 10.4 | 3.6 | 6.7 |
| Ceftazidime | 39.4 | 51.1 | 2.9 | 36 |
| Cefixime | 45.3 | 50.8 | 21.8 | 44.6 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 15.3 | 23.5 | 15.2 | 16.6 |
| Ceftriaxon | 38.0 | 44.3 | 13.1 | 36.4 |
| Cefazolin | 56.6 | 59.9 | 30.8 | 57.3 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 1.8 | 23.1 | 99.6 | 17.3 |
| Gentamicin | 8.7 | 22.7 | 25.2 | 16.6 |
| Imipenem | 5.6 | 16.4 | 85.7 | 16.3 |
| Levofloxacin | 13.9 | 6.6 | 14.7 | 12.5 |
| Meropenem | 3.8 | 15.5 | 4.0 | 6.3 |
| Tobramycin | 8.5 | 19.1 | 19.3 | 11.2 |
| TMP/SMX | 33.3 | 30.0 | 44.4 | 36 |
| Piperacilin/Tazobactam | 10.6 | 23.2 | 2.8 | 11.6 |
| Amoxicilin/Clavulanate | 44.9 | 44.3 | 11.8 | 43.8 |
| Ertapenem | 9.5 | 23.4 | 8.6 | 13.5 |
| Cefepime | 30.0 | 40.0 | 0.0 | 17.9 |
| Cefuroxime | 44.4 | 50.0 | 0.0 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kılıç, F.E.; Küçükkelepçe, O. Evaluating Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric UTIs: Five-Year Data from a Tertiary Hospital in Turkey. Medicina 2025, 61, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030402
Kılıç FE, Küçükkelepçe O. Evaluating Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric UTIs: Five-Year Data from a Tertiary Hospital in Turkey. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030402
Chicago/Turabian StyleKılıç, Fedli Emre, and Osman Küçükkelepçe. 2025. "Evaluating Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric UTIs: Five-Year Data from a Tertiary Hospital in Turkey" Medicina 61, no. 3: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030402
APA StyleKılıç, F. E., & Küçükkelepçe, O. (2025). Evaluating Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric UTIs: Five-Year Data from a Tertiary Hospital in Turkey. Medicina, 61(3), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030402






