Tibial Tuberosity–Tibial Intercondylar Midpoint Distance Can Be Interchangeably Measured on Axial CT and MRI: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfe, S.; Varacallo, M.A.; Thomas, J.D.; Carroll, J.J.; Kahwaji, C.I. Patellar instability. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29494034/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Fithian, D.C.; Paxton, E.W.; Stone, M.L.; Silva, P.; Davis, D.K.; Elias, D.A.; White, L.M. Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2004, 32, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, D.M.; Fithian, D.C.; Marangi, K.S.; Stone, M.L.; Dobson, B.E.; Mendelsohn, C. Characteristics of patients with primary acute lateral patellar dislocation and their recovery within the first 6 months of injury. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Ettinger, M.; Stuebig, T.; Brand, S.; Krettek, C.; Jagodzinski, M.; Omar, M. Current concepts for patellar dislocation. Arch. Trauma. Res. 2015, 4, e29301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koëter, S.; Horstmann, W.G.; Wagenaar, F.C.; Huysse, W.; Wymenga, A.B.; Anderson, P.G. A new CT scan method for measuring the tibial tubercle trochlear groove distance in patellar instability. Knee 2007, 14, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejour, H.; Walch, G.; Nove-Josserand, L.; Guier, C. Factors of patellar instability: An anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1994, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizić, D.; Šimunović, M.; Pavliša, G.; Jelić, M. Tibial tuberosity–tibial intercondylar midpoint distance measured on computed tomography scanner is not biased during knee rotation and could be clinically more relevant than current measurement systems. Int. Orthop. (SICOT) 2020, 45, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paley, D. Principles of Deformity Correction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.; Armstrong, D. Focus on alignment in total knee replacement. JBJS 2012, 4, 130. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X.; Xu, D. Relationship between the tibial mechanical axis and bony anatomical landmarks of the calf and foot as measured on radiographs obtained with a new laser-calibrated position. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Jan, M.H.; Lin, D.H.; Cheng, C.K. Different effects of femoral and tibial rotation on the different measurements of patella tilting: An axial computed tomography study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2008, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, A.; Zahediasl, S. Normality test for statistical analysis: A guide for nonstatisticians. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 10, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, M.; Altman, D. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayhan, I.A.; Kirat, A.; Alpay, Y.; Ozkul, B.; Kargin, D. Tibial tubercle-trochlear groove distance and angle are higher in children with patellar instability. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 3566–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernigou, J.; Chahidi, E.; Bouaboula, M.; Moest, E.; Callewier, A.; Kyriakydis, T.; Koulalis, D.; Bath, O. Knee size chart nomogram for evaluation of tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance in knees with or without history of patellofemoral instability. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennock, A.T.; Alam, M.; Bastrom, T. Variation in tibial tubercle-trochlear groove measurement as a function of age, sex, size, and patellar instability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camp, C.L.; Stuart, M.J.; Krych, A.J.; Levy, B.A.; Bond, J.R.; Collins, M.S.; Dahm, D.L. CT and MRI measurements of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove distances are not equivalent in patients with patellar instability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anley, C.M.; Morris, G.V.; Saithna, A.; James, S.L.; Snow, M. Defining the role of the tibial tubercle-trochlear groove and tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament distances in the work-up of patients with patellofemoral disorders. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.H.S.; Lim, B.Y.; Chng, K.S.J.; Doshi, C.; Wong, F.K.L.; Lim, A.K.S.; Hui, J.H. The difference between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging measurements of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove distance for patients with or without patellofemoral instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Knee Surg. 2020, 33, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.; Van Doninck, D.; Labey, L.; Innocenti, B.; Parizel, P.M.; Bellemans, J. How precise can bony landmarks be determined on a CT scan of the knee? Knee 2009, 16, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrish, J. The management of recurrent patellar dislocation. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 39, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D.; Bible, J.E.; Bohan, M.; Simpson, A.K.; Whang, P.G.; Grauer, J.N. Radiation exposure from musculoskeletal computerized tomographic scans. JBJS 2008, 91, 1882–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederichs, G.; Issever, A.S.; Scheffler, S. MR imaging of patellar instability: Injury patterns and assessment of risk factors. Radiographics 2010, 30, 961–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.W.; Millar, E.A.; Jones, K.C.; Elias, J.J. Variations in tibial tuberosity to trochlear groove and posterior cruciate ligament distances due to tibial external and valgus rotations. J. Knee Surg. 2017, 31, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieves, J.W.; Formica, C.; Ruffing, J.; Zion, M.; Garrett, P.; Lindsay, R.; Cosman, F. Males have larger skeletal size and bone mass than females, despite comparable body size. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 20, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, F. Common statistical mistakes in manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals. Eur. Sci. Ed. 2013, 39, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
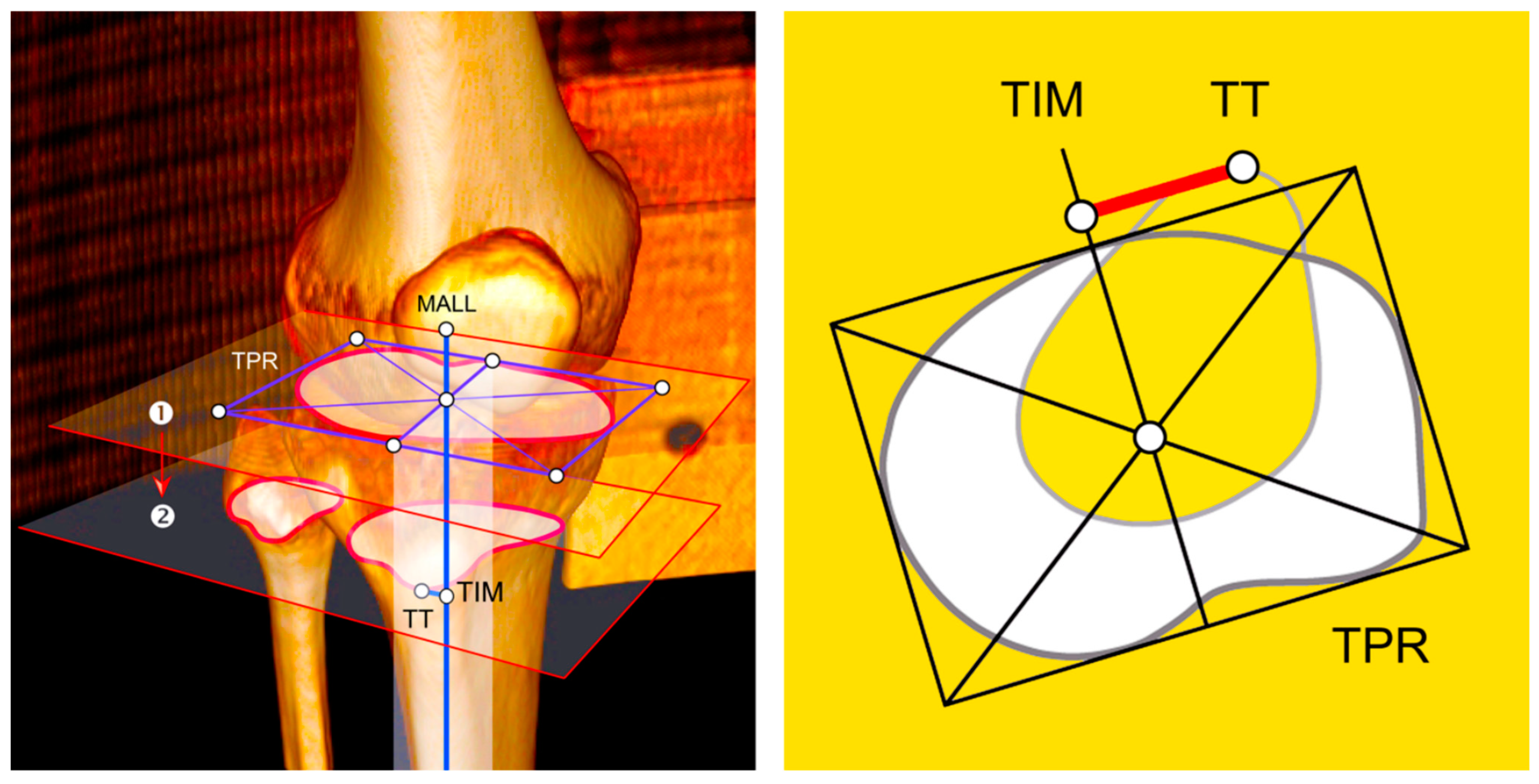
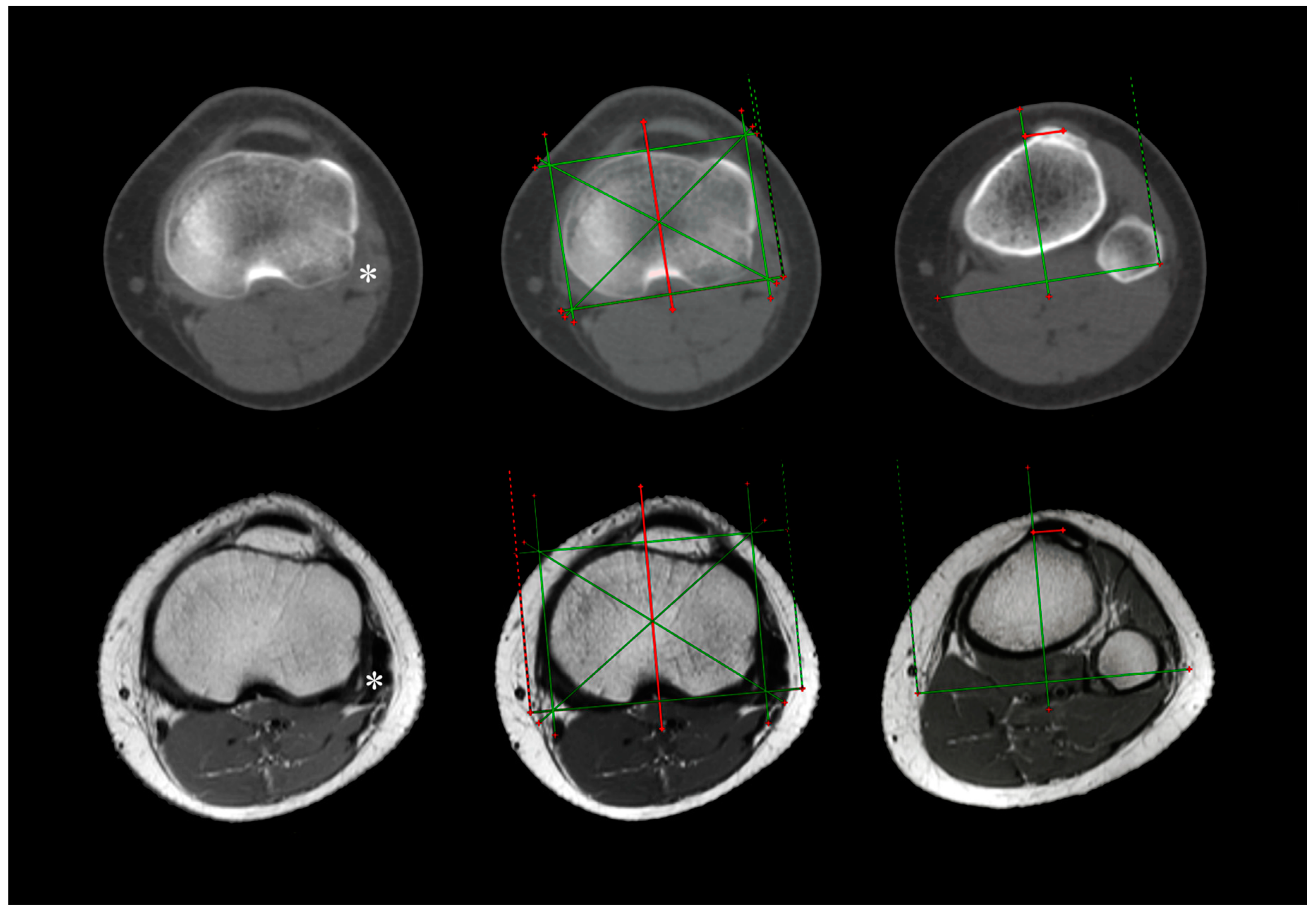
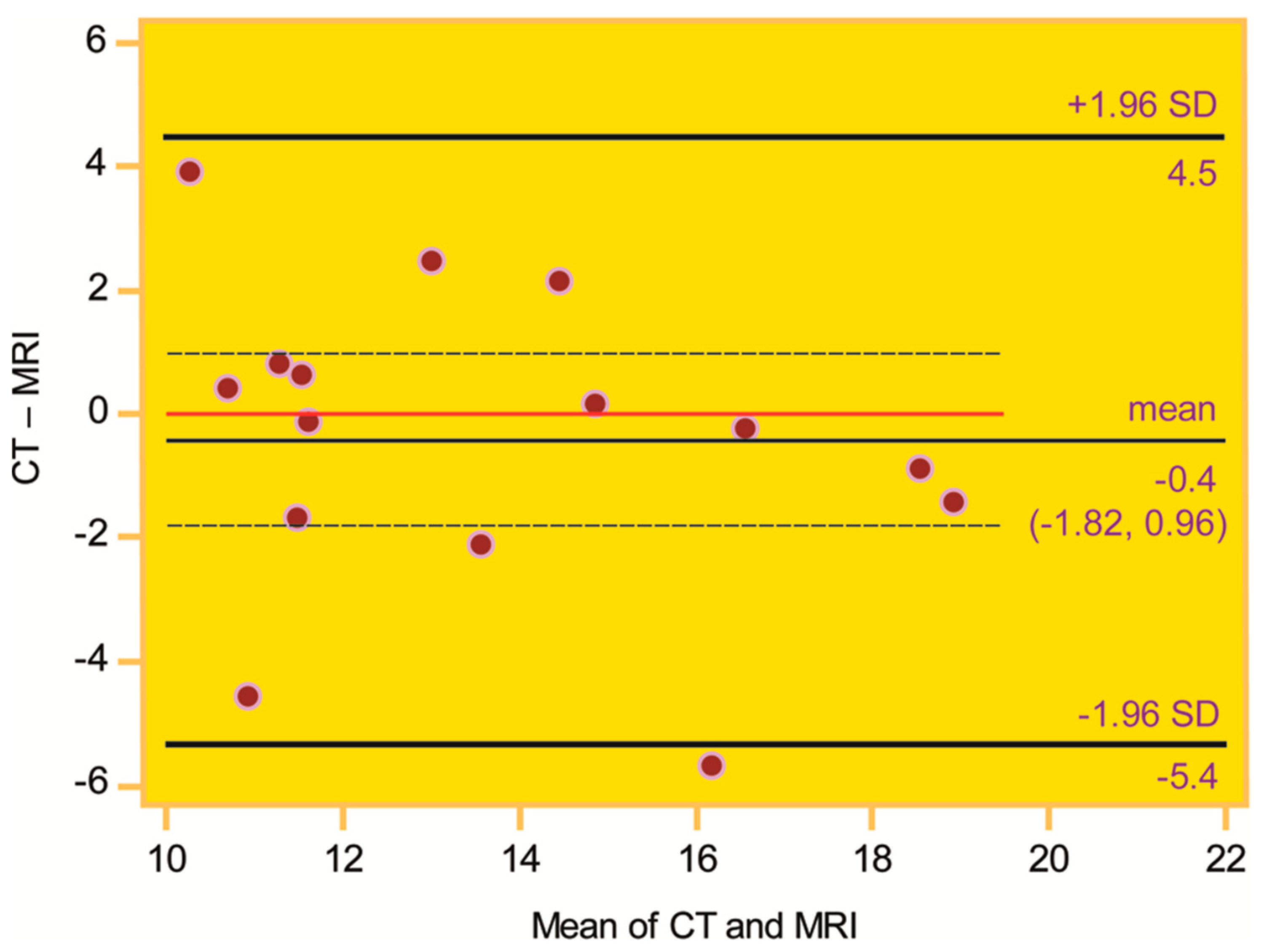
| N | Age | Sex | Side | TT–TIM Distance (mm) | TR (°) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT (1) | CT (2) | CT (m) | MRI (1) | MRI (2) | MRI (m) | CT (1) | CT (2) | CT (m) | MRI (1) | MRI (2) | MRI (m) | ||||
| 1 | 16 | F | R | 12.4 | 12.6 | 12.5 | 14.5 | 14.8 | 14.7 | −2.9 | −3.5 | −3.2 | −20.3 | −20.7 | −20.5 |
| 2 | 18 | F | R | 15.7 | 17.2 | 16.5 | 16.8 | 16.6 | 16.7 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 5.6 | −14.0 | −15.0 | −14.5 |
| 3 | L | 17.6 | 18.6 | 18.1 | 18.7 | 19.3 | 19.0 | −1.0 | −0.2 | −0.6 | −12.1 | −12.4 | −12.3 | ||
| 4 | 17 | F | R | 11.9 | 11.8 | 11.9 | 11.1 | 11.4 | 11.3 | −7.3 | −8.3 | −7.8 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 15 | F | L | 11.6 | 12.9 | 12.3 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 8.4 | −8.4 | −8.5 | −8.5 | −5.1 | −4.2 | −4.7 |
| 6 | 54 | F | R | 10.4 | 11.4 | 10.9 | 10.8 | 10.2 | 10.5 | −13.6 | −14.7 | −14.2 | −6.9 | −7.1 | −7.0 |
| 7 | L | 11.2 | 12.2 | 11.7 | 11.6 | 10.2 | 10.9 | −7.5 | −7.7 | −7.6 | −12.1 | −12.1 | −12.1 | ||
| 8 | 17 | F | R | 16.0 | 15.1 | 15.6 | 13.3 | 13.5 | 13.4 | −7.1 | −6.4 | −6.8 | 6.6 | 6.2 | 6.4 |
| 9 | 30 | F | R | 9.5 | 7.8 | 8.7 | 13.7 | 12.8 | 13.3 | −7.8 | −6.5 | −7.2 | −18.5 | −19.4 | −19.0 |
| 10 | 34 | F | R | 10.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 11.8 | 12.9 | 12.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 | −5.8 | −6.3 | −6.1 |
| 11 | L | 11.8 | 11.3 | 11.6 | 11.3 | 12.1 | 11.7 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.6 | ||
| 12 | 60 | F | R | 13.1 | 13.6 | 13.4 | 19.6 | 18.5 | 19.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.6 | −6.7 | −6.5 | −6.6 |
| 13 | 15 | F | L | 17.6 | 18.8 | 18.2 | 20.3 | 19.0 | 19.7 | −14.6 | −15.0 | −14.8 | −1.7 | −2.6 | −2.2 |
| 14 | 15 | F | L | 15.0 | 14.9 | 15.0 | 15.7 | 13.9 | 14.8 | −10.2 | −10.7 | −10.5 | −2.2 | −2.2 | −2.2 |
| 15 | 66 | M | R | 14.1 | 14.4 | 14.3 | 12.2 | 11.4 | 11.8 | −6.5 | −6.7 | −6.6 | −14.6 | −13.7 | −14.2 |
| Parameter | CT | MRI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs | 95% CI | p Value | rs | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age | −0.41 | −0.76, 0.14 | 0.14 | −0.22 | −0.66, 0.33 | 0.44 |
| Sex | 0.12 | −0.42, 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.12 | −0.60, 0.42 | 0.66 |
| Body side | 0.25 | −0.30, 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.00 | −0.51, 0.51 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nizić, D.; Šimunović, M.; Serdar, J.; Vlaić, J.; Josipović, M.; Levaj, I.; Ivić-Hofman, I.; Jelić, M. Tibial Tuberosity–Tibial Intercondylar Midpoint Distance Can Be Interchangeably Measured on Axial CT and MRI: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Comparative Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020348
Nizić D, Šimunović M, Serdar J, Vlaić J, Josipović M, Levaj I, Ivić-Hofman I, Jelić M. Tibial Tuberosity–Tibial Intercondylar Midpoint Distance Can Be Interchangeably Measured on Axial CT and MRI: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Comparative Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(2):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020348
Chicago/Turabian StyleNizić, Dinko, Marko Šimunović, Jure Serdar, Josip Vlaić, Mario Josipović, Ivan Levaj, Igor Ivić-Hofman, and Mislav Jelić. 2025. "Tibial Tuberosity–Tibial Intercondylar Midpoint Distance Can Be Interchangeably Measured on Axial CT and MRI: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Comparative Study" Medicina 61, no. 2: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020348
APA StyleNizić, D., Šimunović, M., Serdar, J., Vlaić, J., Josipović, M., Levaj, I., Ivić-Hofman, I., & Jelić, M. (2025). Tibial Tuberosity–Tibial Intercondylar Midpoint Distance Can Be Interchangeably Measured on Axial CT and MRI: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Comparative Study. Medicina, 61(2), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020348






