Dosimetric Feasibility of Tomotherapy-Based Selective Axillary Sparing Regional Nodal Irradiation for Lymphedema Risk Reduction in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
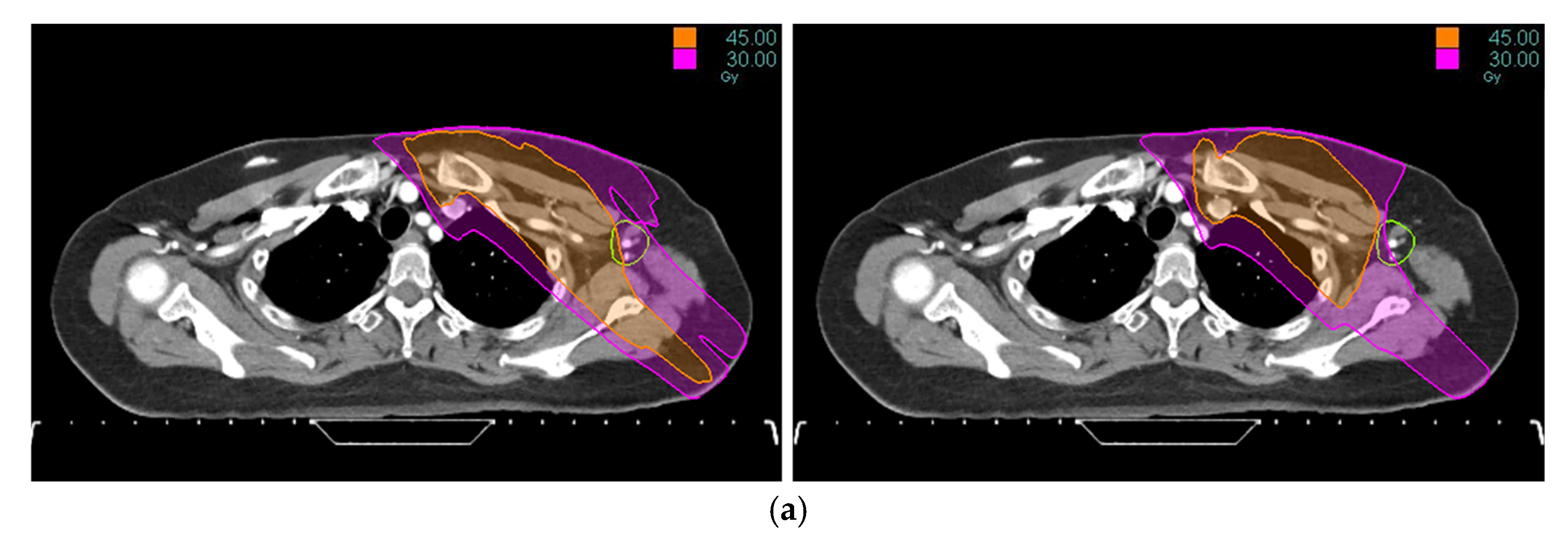
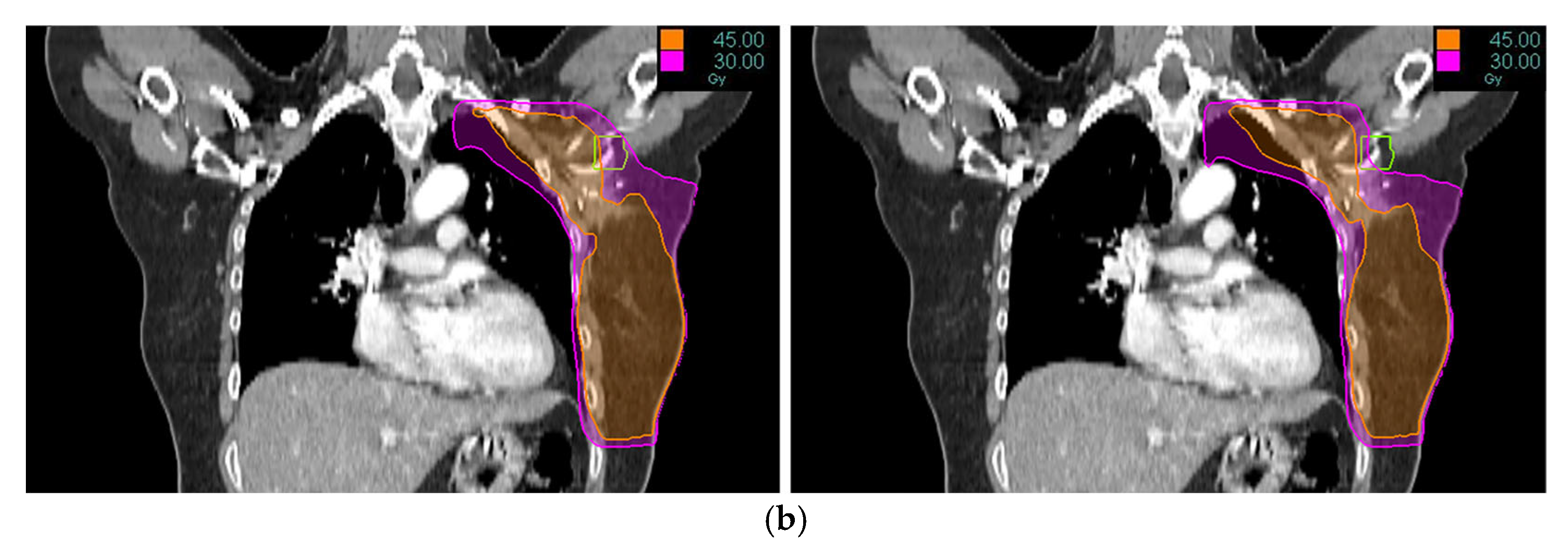
2. Materials and Methods
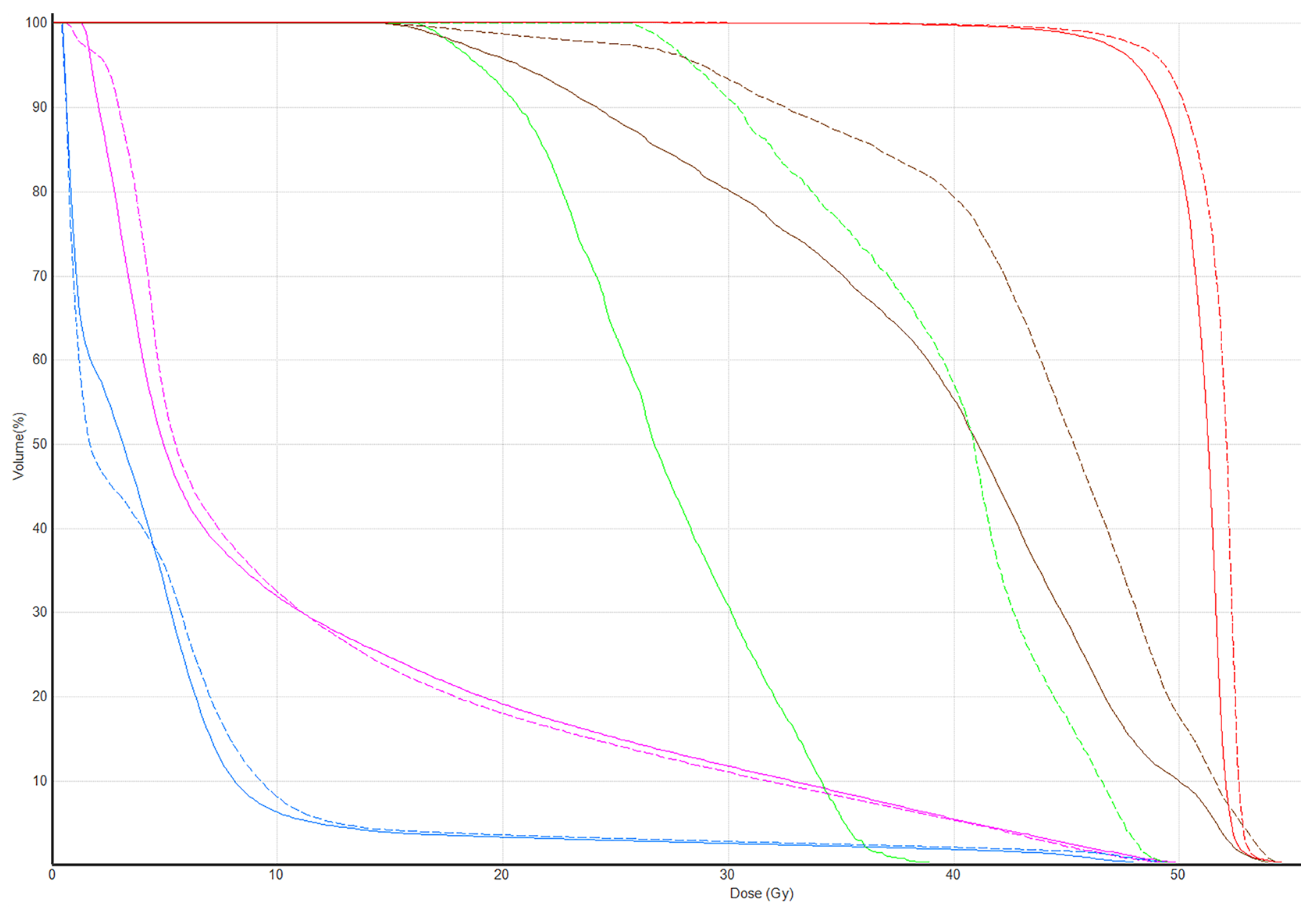
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ling, D.C.; Moppins, B.L.; Champ, C.E.; Gorantla, V.C.; Beriwal, S. Quality of Regional Nodal Irradiation Plans in Breast Cancer Patients Across a Large Network-Can We Translate Results From Randomized Trials Into the Clinic? Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, e30–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSipio, T.; Rye, S.; Newman, B.; Hayes, S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, G.E.; Roberts, S.; Brunelle, C.L.; Shui, A.M.; Salama, L.; Daniell, K.; Gillespie, T.; Bucci, L.; Smith, B.L.; Ho, A.Y.; et al. Quantifying the Impact of Axillary Surgery and Nodal Irradiation on Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema and Local Tumor Control: Long-Term Results From a Prospective Screening Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3430–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nos, C.; Clough, K.B.; Bonnier, P.; Lasry, S.; Le Bouedec, G.; Flipo, B.; Classe, J.M.; Missana, M.C.; Doridot, V.; Giard, S.; et al. Upper outer boundaries of the axillary dissection. Result of the SENTIBRAS protocol: Multicentric protocol using axillary reverse mapping in breast cancer patients requiring axillary dissection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Rubio, I.T.; Kovacs, T.; Klimberg, V.S.; Douek, M. Systematic review of axillary reverse mapping in breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.H.; Mougalian, S.S.; Soulos, P.R.; Smith, B.D.; Haffty, B.G.; Gross, C.P.; Yu, J.B. Adoption of intensity modulated radiation therapy for early-stage breast cancer from 2004 through 2011. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ma, P.; Li, S.; Dai, J.; Wang, S. Locoregional irradiation including internal mammary nodal region for left-sided breast cancer after breast conserving surgery: Dosimetric evaluation of 4 techniques. Med. Dosim. 2019, 44, e13–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkner, S.; Wieslander, E.; Lundstedt, D.; Berg, M.; Kristensen, I.; Andersson, Y.; Bergkvist, L.; Frisell, J.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Sund, M.; et al. Quality assessment of radiotherapy in the prospective randomized SENOMAC trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 197, 110372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offersen, B.V.; Boersma, L.J.; Kirkove, C.; Hol, S.; Aznar, M.C.; Sola, A.B.; Kirova, Y.M.; Pignol, J.P.; Remouchamps, V.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. ESTRO consensus guideline on target volume delineation for elective radiation therapy of early stage breast cancer, version 1.1. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 118, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.P.; Lynch, C.M.; Flores, A.M.; Jordan, S.W.; Helenowski, I.B.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Cutright, D.; Donnelly, E.D.; Strauss, J.B. Determining the Organ at Risk for Lymphedema After Regional Nodal Irradiation in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, K.; Huang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.A.; Moran, J.M.; Chen, G.P. NRG Protocol Radiation Therapy Template of Whole Breast Photon and Proton Therapy; Technical Report; 2022 Revised; NRG Oncology: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Suk Chang, J.; Ko, H.; Hee Im, S.; Sung Kim, J.; Kyung Byun, H.; Bae Kim, Y.; Jung, W.; Park, G.; Sun Lee, H.; Sung, W.; et al. Incorporating axillary-lateral thoracic vessel juncture dosimetric variables improves model for predicting lymphedema in patients with breast cancer: A validation analysis. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 41, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.I.; Chang, J.S.; Ko, H.; Im, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Byun, H.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Jung, W.; Kim, K.; Hong, C.S. Development and Validation of a Normal Tissue Complication Probability Model for Lymphedema After Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 116, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines® for Breast Cancer. NCCN; Version 4. 2025. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Loibl, S.; Andre, F.; Bachelot, T.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Burstein, H.J.; Cardoso, M.J.; Carey, L.A.; Dawood, S.; Del Mastro, L.; et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.G.; Lim, C.W.; Hur, S.M.; Kim, Z.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, M.J. Incidental Axillary Dose of Tomotherapy in Hypofractionated Whole Breast Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Dosimetrical Analysis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladbury, C.J.; Ridings, J.W.; Waxweiler, T.V.; Olsen, J.R. Regional Nodal Irradiation Targeting the Undissected Axilla Following Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND) Is Associated with Substantial Radiation Dose to the Dissected Axilla. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, E705–E706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldstein, C.; Moodie, T.; Ashworth, S.; Ahern, V.; Stuart, K.; Wang, W. Feasibility of arm-draining lymph node-sparing radiotherapy of breast cancer: A pilot planning study. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, E.; Beyer, S.; Jhawar, S.; White, J.R.; Bazan, J.G. The Axillary Lateral Vessel Thoracic Junction Is Not an Organ at Risk for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, J.E.; Chung, D.K.V.; Reynolds, H.M.; Jayathungage Don, T.D.; Suami, H.; Donohoe, K.J.; Singhal, D. Collateralization of the upper extremity lymphatic system after axillary lymph node dissection. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 131, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, A.J.; Dias, R.; Laurienzo, C.E.; Goncalves, M.C.; Dias, D.S.; Moriguchi, S.M. Arm lymphoscintigraphy after axillary lymph node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheville, A.L.; Das, I.; Srinivas, S.; Schuerman, J.; Velders, L.; Solin, L.J.; Basu, S.; Alavi, A. A pilot study to assess the utility of SPECT/CT-based lymph node imaging to localize lymph nodes that drain the arm in patients undergoing treatment for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 116, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.A.; Peng, J.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Cen, Y. Clinical application of axillary reverse mapping in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast 2020, 53, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennaro, M.; Maccauro, M.; Mariani, L.; Listorti, C.; Sigari, C.; De Vivo, A.; Chisari, M.; Maugeri, I.; Lorenzoni, A.; Aliberti, G.; et al. Occurrence of breast-cancer-related lymphedema after reverse lymphatic mapping and selective axillary dissection versus standard surgical treatment of axilla: A two-arm randomized clinical trial. Cancer 2022, 128, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ward, R.; Jia, D.; Ashworth, S.; Estoesta, E.; Moodie, T.; Ahern, V.; Stuart, K.; Ngui, N.; French, J.; et al. Location of arm draining lymph node in relation to breast cancer radiotherapy field and target volume. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 133, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.S.; Proulx, S.T.; Luciani, P.; Leroux, J.C.; Detmar, M. Dynamics of lymphatic regeneration and flow patterns after lymph node dissection. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheville, A.L.; Brinkmann, D.H.; Ward, S.B.; Durski, J.; Laack, N.N.; Yan, E.; Schomberg, P.J.; Garces, Y.I.; Suman, V.J.; Petersen, I.A. The addition of SPECT/CT lymphoscintigraphy to breast cancer radiation planning spares lymph nodes critical for arm drainage. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ALTJ | AXL1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Plan A | Plan B | p | Plan A | Plan B | p |
| V20Gy (%) | 100 ± 0 | 90.7 ± 9.3 | 0.018 | 97.2 ± 3.4 | 94.9 ± 4.7 | 0.011 |
| V30Gy (%) | 93.1 ± 7.1 | 28.5 ± 5.6 | 0.005 | 92.1 ± 6.6 | 75.6 ± 5.8 | 0.005 |
| V35Gy (%) | 82.7 ± 13.5 | 9.6 ± 4.7 | 0.005 | 87.5 ± 7.6 | 64.5 ± 6.2 | 0.005 |
| V40Gy (%) | 67.7 ± 18.0 | 2.6 ± 2.5 | 0.005 | 79.7 ± 7.3 | 50.2 ± 6.9 | 0.005 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 41.7 ± 3.4 | 27.2 ± 1.3 | 0.005 | 43.9 ± 2.0 | 37.7 ± 1.9 | 0.005 |
| Dmin (Gy) | 29.5 ± 5.9 | 18.0 ± 2.2 | 0.005 | 14.5 ± 6.5 | 13.0 ± 4.6 | 0.201 |
| Dmax (Gy) | 51.4 ± 2.1 | 44.0 ± 4.2 | 0.005 | 53.8 ± 0.9 | 54.1 ± 0.6 | 0.182 |
| OAR | Parameters | Plan A | Plan B | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ipsilateral Lung | V20Gy (%) | 22.3 ± 5.9 | 22.2 ± 5.6 | 0.233 |
| Heart | V5Gy (%) | 60.1 ± 14.4 | 57.2 ± 13.9 | 0.012 |
| V30Gy (%) | 2.6 ± 2.5 | 2.1 ± 2.3 | 0.043 | |
| Dmean (Gy) | 4.8 ± 1.7 | 4.8 ± 1.6 | 0.336 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.H.; Lim, C.W.; Hur, S.-M.; Kim, Z.; Jung, J.-H.; Kim, D.; Yeo, S.-G. Dosimetric Feasibility of Tomotherapy-Based Selective Axillary Sparing Regional Nodal Irradiation for Lymphedema Risk Reduction in Breast Cancer. Medicina 2025, 61, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122177
Cho KH, Lim CW, Hur S-M, Kim Z, Jung J-H, Kim D, Yeo S-G. Dosimetric Feasibility of Tomotherapy-Based Selective Axillary Sparing Regional Nodal Irradiation for Lymphedema Risk Reduction in Breast Cancer. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122177
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kwang Hwan, Cheol Wan Lim, Sung-Mo Hur, Zisun Kim, Jae-Hong Jung, Daegun Kim, and Seung-Gu Yeo. 2025. "Dosimetric Feasibility of Tomotherapy-Based Selective Axillary Sparing Regional Nodal Irradiation for Lymphedema Risk Reduction in Breast Cancer" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122177
APA StyleCho, K. H., Lim, C. W., Hur, S.-M., Kim, Z., Jung, J.-H., Kim, D., & Yeo, S.-G. (2025). Dosimetric Feasibility of Tomotherapy-Based Selective Axillary Sparing Regional Nodal Irradiation for Lymphedema Risk Reduction in Breast Cancer. Medicina, 61(12), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122177







