Acute Effects of Marathon and Ultramarathon Running on Body Composition in Trained Male Athletes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
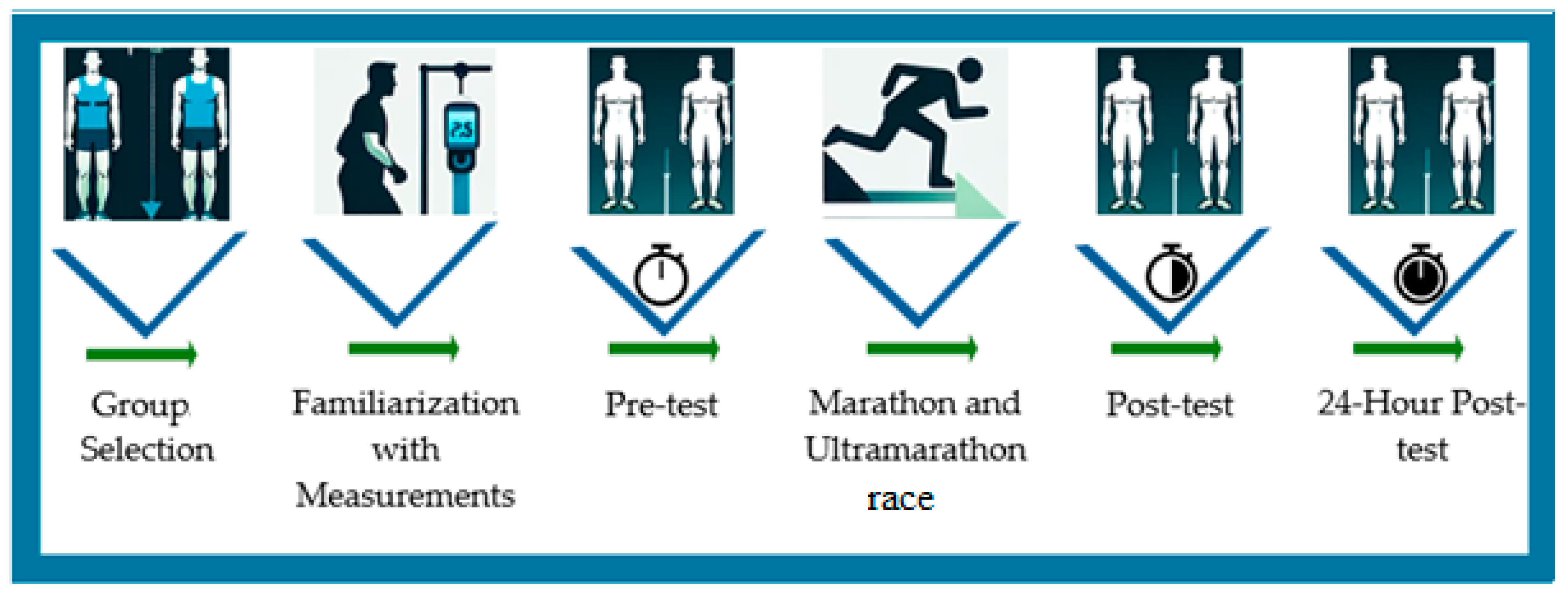
2.2. Study Design
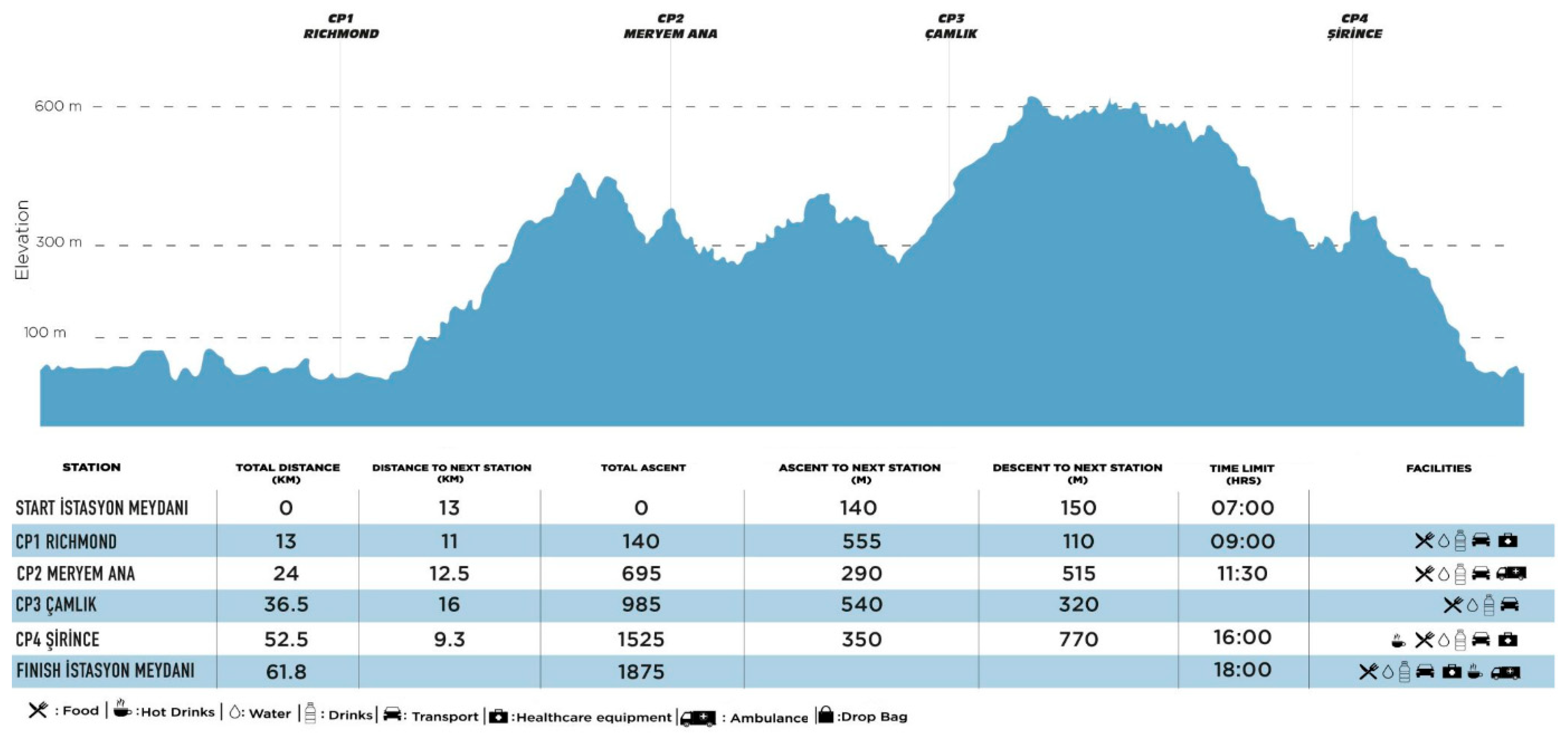
2.3. Marathon and Ultramarathon Courses
Race Characteristics
2.4. Body Composition Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landers-Ramos, R.Q.; Dondero, K.R.; Rowland, R.W.; Larkins, D.; Addison, O. Peripheral vascular and neuromuscular responses to ultramarathon running. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2022, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaryski, C.; Smith, D.J. Training principles and issues for ultra-endurance athletes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2005, 4, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechtle, B.; Nikolaidis, P.T. Physiology and pathophysiology in ultra-marathon running. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüst, C.A.; Knechtle, B.; Knechtle, P.; Rosemann, T. Similarities and differences in anthropometry and training between recreational male 100-km ultra-marathoners and marathoners. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüst, C.A.; Knechtle, B.; Knechtle, P.; Rosemann, T. Comparison of anthropometric and training characteristics between recreational male marathoners and 24-hour ultramarathoners. Open Access J Sports Med. 2012, 3, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-González, P.; Sedlacek, J. Effects of running-specific strength training, endurance training, and concurrent training on recreational endurance athletes’ performance and selected anthropometric parameters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knechtle, B. Ultramarathon runners: Nature or nurture? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2012, 7, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechtle, B.; Knechtle, P.; Wirth, A.; Rüst, C.A.; Rosemann, T. A faster running speed is associated with a greater body weight loss in 100-km ultra-marathoners. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O. Running Science; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sears, E.S. Running Through the Ages, 2nd ed.; McFarland: Jefferson, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Benyo, R.; Henderson, J. Running Encyclopedia; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Blagrove, R.; Hayes, P. The Science and Practice of Middle and Long Distance Running; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, R.J.S.; Gill, S.K.; Hankey, J.; Wright, A.; Marczak, S. Perturbed energy balance and hydration status in ultra-endurance runners during a 24 h ultramarathon. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živoder, I.; Hodić, V.; Degač, N.Z.; Potočnjak, J.; Arapović, M.; Kuzmić, A.; Jeleč, Ž.; Knežević, G.; Znika, M.; Meštrović, T. Motor capabilities and body composition in health vs. non-health university students: A pilot study. Life 2025, 15, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.B.; Ferguson, B.K.; Winter, I.P. Time of urine sampling may influence the association between urine specific gravity and body composition. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0333479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbant, Ö.; Süer, S.A. The effect of combined training on players’ body composition and their performance in beach soccer. Phys. Educ. Stud. 2025, 29, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioğlu, S.; Tekinalp, A.; Korkmaz, C.; Baylan, F.A.; Merter, M. Changes in body composition and their association with erythrocyte mass in regular exercisers: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2025, 104, e44065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizjak, D.A.; Schulz, S.V.W.; John, L.; Schellenberg, J.; Bizjak, R.; Witzel, J.; Valder, S.; Kostov, T.; Schalla, J.; Steinacker, J.M.; et al. Running for your life: Metabolic effects of a 160.9/230 km non-stop ultramarathon race on body composition, inflammation, heart function, and nutritional parameters. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, N.B.; Roberts, J.D.; Beasley, L.; Chapman, S.; Pinto, J.M.; Smith, L.; Wiffin, M.; Russell, M.; Sparks, S.A.; Duckworth, L.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Nutritional considerations for single-stage ultramarathon training and racing. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knechtle, B.; Duff, B.; Schulze, I.; Kohler, G. A multi-stage ultra-endurance run over 1200 km leads to a continuous accumulation of total body water. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2008, 7, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Knechtle, B.; Wirth, A.; Knechtle, P.; Rosemann, T. Increase of total body water with decrease of body mass while running 100 km nonstop—Formation of edema? Res. Q Exerc. Sport. 2009, 80, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaee, M.; Spittler, J.; VanBaak, K.; Changstrom, B.G.; Hill, J.C. Effects of running an ultramarathon on cardiac, hematologic, and metabolic biomarkers. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, C.K. Changes in serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), plasma CPK and plasma hs-CRP in relation to running distance in a marathon (42.195 km) and an ultramarathon (200 km) race. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernillo, G.; Savoldelli, A.; La Torre, A.; Skafidas, S.; Bortolan, L.; Schena, F. Injury and illness rates during ultratrail running. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videbæk, S.; Bueno, A.M.; Nielsen, R.O.; Rasmussen, S. Incidence of running-related injuries per 1000 hours of running in different types of runners: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstoft, K.; Solomon, T.P.; Laye, M.J.; Pedersen, B.K. Daily marathon running for a week—The biochemical and body compositional effects of participation. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, U.H.; Billich, C.; König, K.; Würslin, C.; Wiedelbach, H.; Brambs, H.-J.; Machann, J. Characteristics, changes and influence of body composition during a 4486 km transcontinental ultramarathon: Results from the Transeurope Footrace mobile whole body MRI project. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marathon (n = 8) | Age (year) | 38.00 | 53.00 | 45.25 | 5.77 |
| Body Height (cm) | 171.00 | 187.00 | 177.63 | 4.59 | |
| Body Weight (kg) | 66.40 | 99.20 | 80.31 | 11.39 | |
| Ultramarathon (n = 8) | Age (year) | 38.00 | 50.00 | 43.00 | 4.47 |
| Body Hight (cm) | 162.00 | 188.00 | 174.13 | 9.03 | |
| Body Weight (kg) | 59.90 | 90.20 | 74.70 | 11.06 |
| Dependent Variables (DV) | Independent Variables (IV) | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marathon | Ultramarathon | ||
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | Pre-test | 25.45 ± 3.49 | 24.56 ± 2.28 |
| Post-test | 25.02 ± 3.59 | 23.71 ± 2.32 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 25.33 ± 3.60 | 24.33 ± 2.24 | |
| Total Body Weight (kg) | Pre-test | 80.31 ± 11.39 | 74.70 ± 11.06 |
| Post-test | 78.90 ± 11.53 | 72.16 ± 11.03 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 79.98 ± 11.65 | 74.05 ± 10.61 | |
| Total Body Water (%) | Pre-test | 47.46 ± 4.85 | 44.36 ± 5.63 |
| Post-test | 47.65 ± 5.32 | 44.40 ± 5.95 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 48.02 ± 5.01 | 45.33 ± 6.31 | |
| Total Body Muscle (%) | Pre-test | 36.83 ± 3.99 | 34.32 ± 4.71 |
| Post-test | 37.16 ± 4.41 | 34.50 ± 5.01 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 37.32 ± 4.15 | 35.16 ± 5.32 | |
| Total Body Fat (%) | Pre-test | 18.57 ± 7.86 | 18.40 ± 3.58 |
| Post-test | 16.80 ± 7.52 | 15.58 ± 3.92 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 17.32 ± 7.30 | 16.07 ± 3.39 | |
| Lean Body Mass (kg) | Pre-test | 64.81 ± 6.54 | 60.73 ± 7.82 |
| Post-test | 65.15 ± 7.21 | 60.72 ± 8.27 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 65.61 ± 6.80 | 62.07 ± 8.79 | |
| Right Arm Fat (%) | Pre-test | 0.85 ± 0.79 | 0.75 ± 0.24 |
| Post-test | 0.68 ± 0.74 | 0.52 ± 0.23 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.75 ± 0.75 | 0.58 ± 0.20 | |
| Left Arm Fat (%) | Pre-test | 0.86 ± 0.79 | 0.77 ± 0.27 |
| Post-test | 0.73 ± 0.70 | 0.55 ± 0.27 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.77 ± 0.73 | 0.60 ± 0.20 | |
| Right Leg Fat (%) | Pre-test | 2.32 ± 1.13 | 2.20 ± 0.54 |
| Post-test | 1.96 ± 0.90 | 1.73 ± 0.48 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 2.15 ± 1.10 | 1.88 ± 0.41 | |
| Left Leg Fat (%) | Pre-test | 2.32 ± 1.14 | 2.18 ± 0.53 |
| Post-test | 1.96 ± 0.90 | 1.72 ± 0.47 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 2.12 ± 1.08 | 1.86 ± 0.42 | |
| Torso Fat (%) | Pre-test | 7.97 ± 4.78 | 6.98 ± 2.53 |
| Post-test | 7.26 ± 4.83 | 5.78 ± 2.58 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 7.26 ± 4.76 | 6.01 ± 2.17 | |
| Dependent Variables | Time | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | ηp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | Time | 3.49 | 2 | 1.74 | 37.19 | 0.01 ** | 0.72 |
| Time × Group | 0.38 | 2 | 0.19 | 4.13 | 0.05 | 0.22 | |
| Total Body Weight (kg) | Time | 33.87 | 2 | 16.93 | 33.05 | 0.01 ** | 0.70 |
| Time × Group | 2.68 | 2 | 1.34 | 2.61 | 0.09 | 2.68 | |
| Total Body Water (%) | Time | 5.51 | 2 | 2.75 | 5.30 | 0.01 * | 0.27 |
| Time × Group | 0.67 | 2 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.04 | |
| Total Body Muscle (%) | Time | 3.58 | 2 | 1.79 | 5.58 | 0.01 ** | 0.28 |
| Time × Group | 0.52 | 2 | 0.26 | 0.82 | 0.45 | 0.05 | |
| Total Body Fat (%) | Time | 39.08 | 2 | 19.54 | 20.30 | 0.01 ** | 0.59 |
| Time × Group | 1.80 | 2 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 0.06 | |
| Lean Body Mass (kg) | Time | 10.61 | 2 | 5.30 | 5.43 | 0.01 ** | 0.28 |
| Time × Group | 1.59 | 2 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.45 | 0.05 | |
| Right Arm Fat (%) | Time | 0.31 | 2 | 0.15 | 21.54 | 0.01 ** | 0.60 |
| Time × Group | 0.01 | 2 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.49 | 0.04 | |
| Left Arm Fat (%) | Time | 0.26 | 2 | 0.13 | 16.09 | 0.01 ** | 0.53 |
| Time × Group | 0.02 | 2 | 0.01 | 1.44 | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Right Leg Fat (%) | Time | 1.37 | 2 | 0.68 | 20.57 | 0.01 ** | 0.59 |
| Time × Group | 0.04 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.04 | |
| Left Leg Fat (%) | Time | 1.39 | 2 | 0.69 | 20.70 | 0.01 ** | 0.59 |
| Time × Group | 0.03 | 2 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.60 | 0.03 | |
| Torso Fat (%) | Time | 8.74 | 2 | 4.37 | 12.74 | 0.01 ** | 0.47 |
| Time × Group | 0.47 | 2 | 0.23 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.04 |
| Dependent Variables | Group | Time | Mean Difference | Std. Error | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.42 | 0.10 | 0.01 ** |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.11 | 0.12 | 1.00 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.85 | 0.10 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.22 | 0.12 | 0.26 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.62 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** | ||
| Total Body Weight (kg) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −1.41 | 0.37 | 0.01 ** |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.32 | 0.39 | 1.00 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 1.08 | 0.29 | 0.01 ** | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −2.53 | 0.37 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.65 | 0.39 | 0.37 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 1.88 | 0.29 | 0.01 ** | ||
| Total Body Water (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | 0.18 | 0.33 | 1.00 |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.63 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.70 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | 0.03 | 0.33 | 1.00 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.97 | 0.42 | 0.11 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.93 | 0.30 | 0.02 * | ||
| Total Body Muscle (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.73 |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.48 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.16 | 0.24 | 1.00 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | 0.17 | 0.26 | 1.00 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.07 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.66 | 0.24 | 0.05 | ||
| Lean Body Mass (kg) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | 0.33 | 0.45 | 1.00 |
| 24 h Post-test | 0.80 | 0.58 | 0.57 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.88 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.01 | 0.45 | 1.00 | |
| 24 h Post-test | 1.33 | 0.58 | 0.11 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 1.35 | 0.42 | 0.02 * | ||
| Dependent Variables | Group | Time | Mean Difference | Std. Error | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Body Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.33 | 0.45 | 1.00 |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.80 | 0.58 | 0.57 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.88 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.01 | 0.45 | 1.00 | |
| 24 h Post-test | −1.33 | 0.58 | 0.11 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 1.35 | 0.42 | 0.02 * | ||
| Right Arm Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.16 | 0.03 | 0.01 ** |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.10 | 0.05 | 0.24 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.28 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.22 | 0.03 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.16 | 0.05 | 0.02 * | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.28 | ||
| Left Arm Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.12 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.08 | 0.05 | 0.31 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.00 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.22 | 0.04 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.17 | 0.05 | 0.01 * | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.61 | ||
| Right Leg Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.36 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.17 | 0.10 | 0.30 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.11 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.46 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.31 | 0.10 | 0.02 * | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.26 | ||
| Left Leg Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.36 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.20 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.15 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.46 | 0.09 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.32 | 0.10 | 0.01 * | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.28 | ||
| Torso Fat (%) | Marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −0.71 | 0.31 | 0.11 |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.71 | 0.32 | 0.13 | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 8.88 | 0.23 | 1.00 | ||
| Ultra-marathon | Pre-test | Post-test | −1.20 | 0.31 | 0.01 ** | |
| 24 h Post-test | −0.97 | 0.32 | 0.02 * | |||
| Post-test | 24 h Post-test | 0.22 | 0.23 | 1.00 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Düz, S.; İlbak, İ.; Öğüt, A.E.K.; Sagat, P.; Bartik, P. Acute Effects of Marathon and Ultramarathon Running on Body Composition in Trained Male Athletes. Medicina 2025, 61, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122123
Düz S, İlbak İ, Öğüt AEK, Sagat P, Bartik P. Acute Effects of Marathon and Ultramarathon Running on Body Composition in Trained Male Athletes. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122123
Chicago/Turabian StyleDüz, Serkan, İsmail İlbak, Ayşe Eda Kınacı Öğüt, Peter Sagat, and Peter Bartik. 2025. "Acute Effects of Marathon and Ultramarathon Running on Body Composition in Trained Male Athletes" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122123
APA StyleDüz, S., İlbak, İ., Öğüt, A. E. K., Sagat, P., & Bartik, P. (2025). Acute Effects of Marathon and Ultramarathon Running on Body Composition in Trained Male Athletes. Medicina, 61(12), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122123









