Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
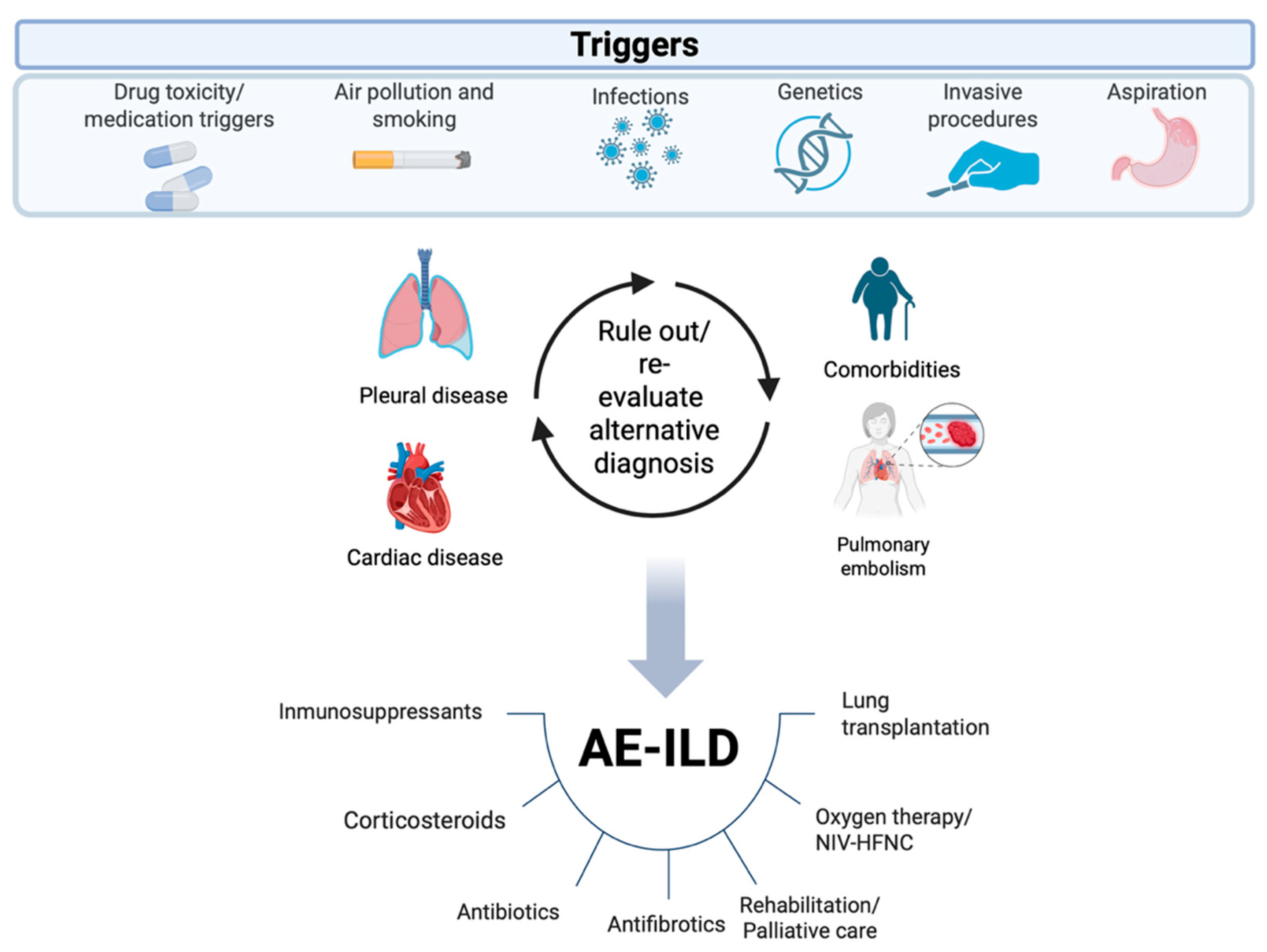
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Summary of Findings and Discussion
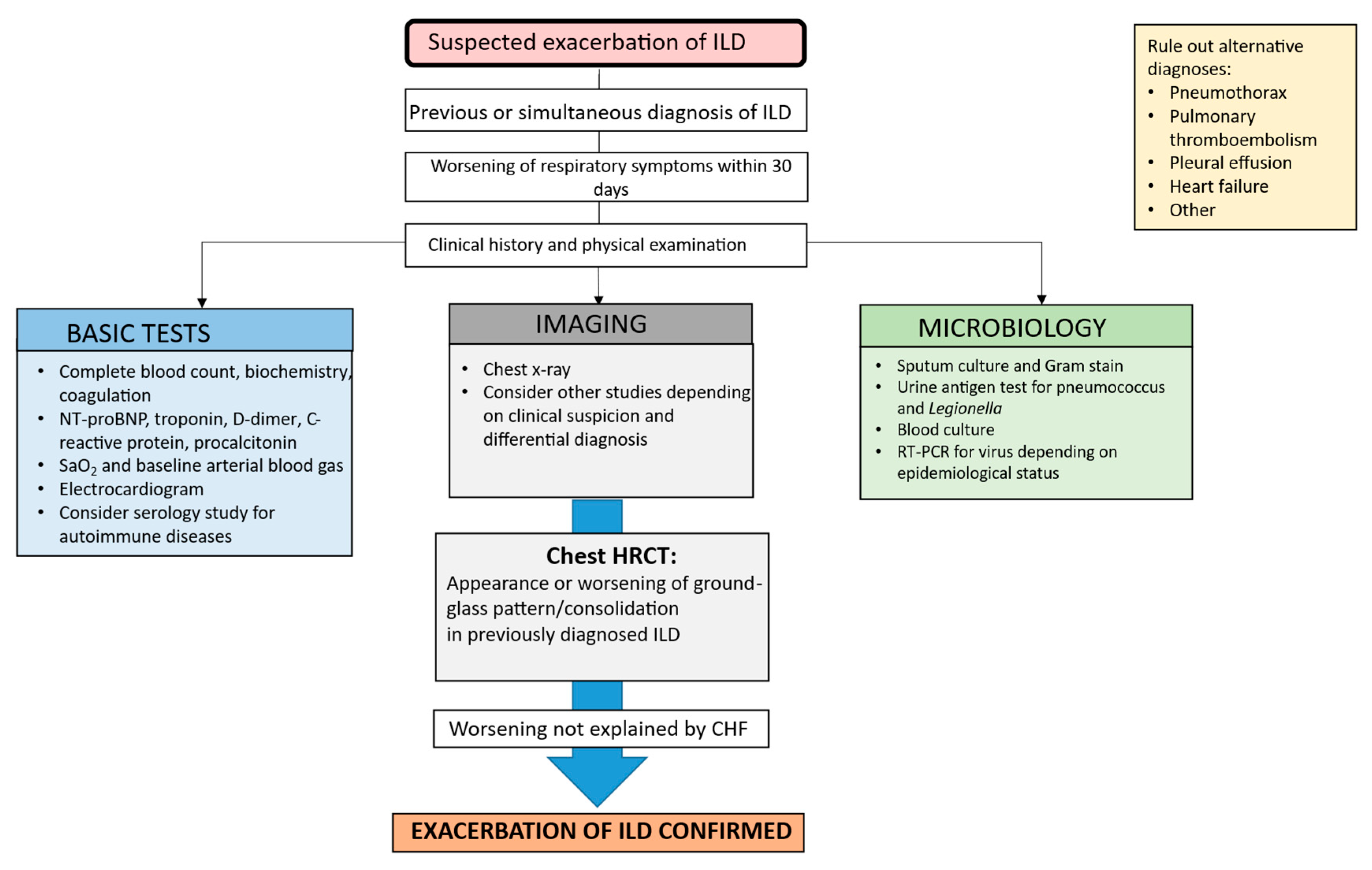
3.1. Diagnosis
3.1.1. Laboratory Tests
3.1.2. Microbiology
3.1.3. Imaging Tests
3.1.4. Electrocardiography and Echocardiography
3.2. Role of Immunological and Molecular Biomarkers
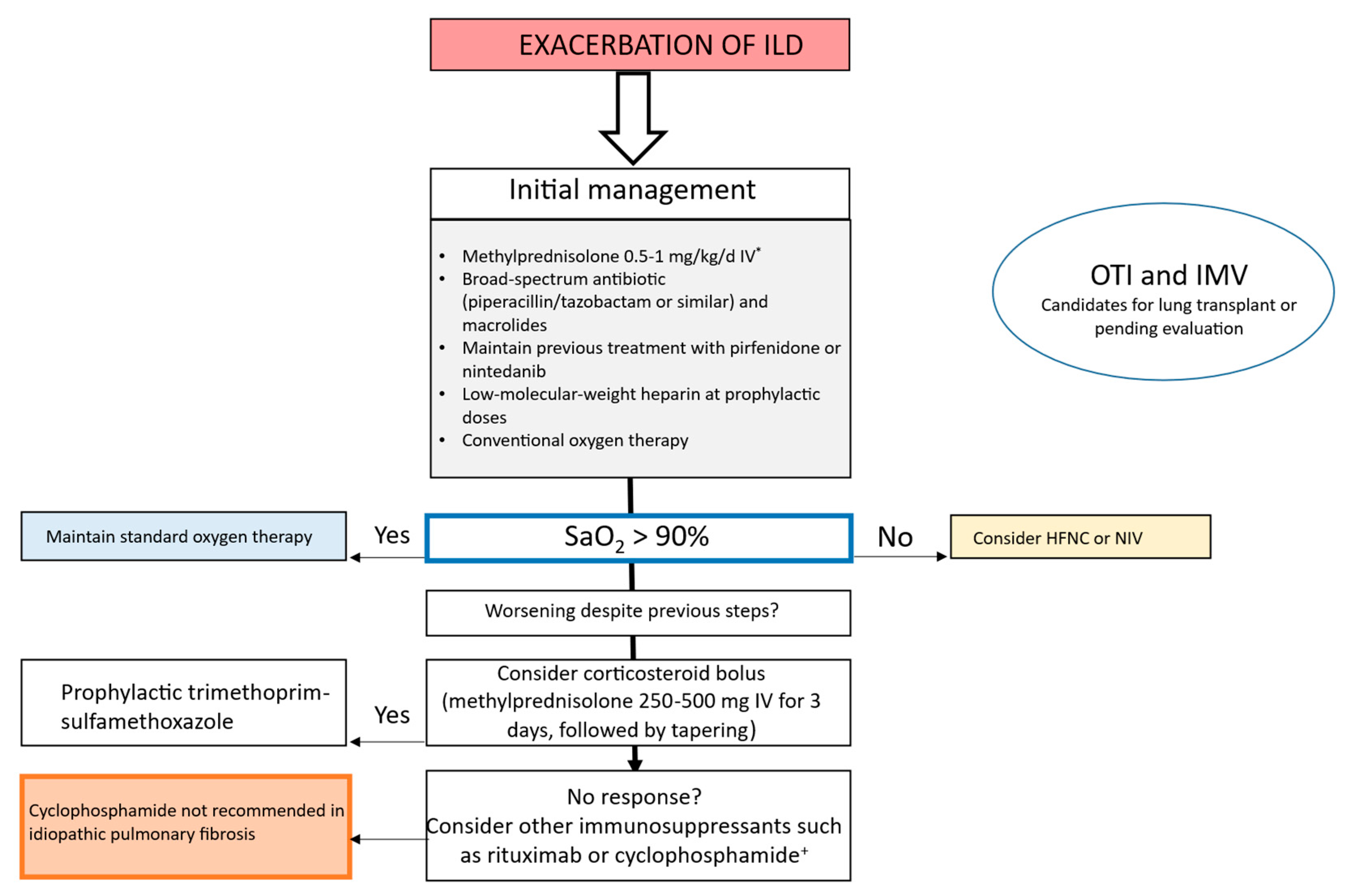
3.3. Management of AE in IPF and Other ILDs
3.4. Ventilatory Support in AE-ILD
3.5. Pharmacologic Treatment of AE-ILD
3.5.1. Corticosteroids
3.5.2. Antibiotics
3.5.3. Immunosuppressants
3.5.4. Other Treatments
4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An international working group report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Wuyts, W. Acute exacerbations of interstitial lung disease: Lessons from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 23, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, G.; Behr, J. Acute exacerbation in interstitial lung disease. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Panlaqui, O.M. A systematic review of the incidence, risk factors and prognosis of acute exacerbation of systemic autoimmune disease-associated interstitial lung disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Moore, B.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Kaner, R.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Loyd, J.E.; Noth, I.; Olman, M.A.; et al. Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Manfredi, A. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubouchi, K.; Hamada, N.; Tokunaga, S.; Ichiki, K.; Takata, S.; Ishii, H. Survival and acute exacerbation for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or non-IPF idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: 5-year follow-up analysis of a prospective multiinstitutional patient registry. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.I.; Park, S.H.; Dauti, S.; Park, B.J.; Lee, C.W. Interstitial lung disease and risk of mortality: 11-year nationwide population-based study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Calfee, C.S.; Wolters, P.J.; Song, J.W.; Hong, S.B.; Brady, S.; Ishizaka, A.; Jones, K.D.; King, T.E., Jr.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. Plasma biomarker profiles in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L3–L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivali, N.; De Giacomi, F. Procalcitonin in acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease: A systematic review of current evidence. Heart Lung. 2025, 73, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayeh, B.A.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Legué, S.; Luque Paz, D.; Plantier, L.; Flament, T. Thoracic Ultrasound for Acute Dyspnea in Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Markart, P.; Steiropoulos, P. Acute exacerbations of interstitial lung diseases: Focus on biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, P.; Duan, C.; Gao, L. KL-6 as an immunological biomarker predicts the severity, progression, acute exacerbation, and poor outcomes of interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Ji, J.; Zheng, D.; Luo, Z.; Luo, L.; Guo, L. Serum surfactant protein D as a significant biomarker for predicting occurrence, progression, acute exacerbation, and mortality in interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1450798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, G.; Acquah, S.O.; Salvatore, M.; Padilla, M.L. Elevated serum D-dimer level is associated with an increased risk of acute exacerbation in interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 2017, 128, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, R.; Raghu, G. Acute exacerbation of fibrotic interstitial lung disease beyond idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Time to intervene. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2300459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Polke, M.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Krisam, J.; Collard, H.R.; Chaudhuri, N.; Avdeev, S.; Behr, J.; Calligaro, G.; Corte, T.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: International survey and call for harmonisation. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizinga, M.; Machuca, T.N.; Shahmohammadi, A.; Patel, D.C.; Innabi, A.; Alzghoul, B.; Scheuble, V.; Pipkin, M.; Mehrad, B.; Pelaez, A.; et al. Lung transplantation for acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease. Thorax 2022, 77, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xiang, Z.; Dai, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Prognosis of Lung Transplantation in Patients with Acute Exacerbations of Interstitial Lung Disease: A Meta-Analysis Based on Cohort Studies. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2024, 30, 24-00086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat Syed, M.K.; Bruck, O.; Kumar, A.; Surani, S. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in the intensive care unit: Principles of diagnostic evaluation and management. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 12, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamami, A. Management strategies and outcomes predictors of interstitial lung disease exacerbation admitted to an intensive care setting: A narrative review. J. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 11, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo Pérez, A.; Aguado Ibáñez, S.; Salinas Castillo, S.; Pombo Lacaba, G.; Rodríguez Rubio, E.; Laporta Hernández, R.; Chinarro, B.J.; Sánchez, C.A. The Role of the Respiratory Intermediate Care Unit in Interstitial Lung Disease Exacerbations: A Bridge to Lung Transplantation. Open Respir. Arch. 2025, 7, 100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.J.; Dwyer, I.; Geoghegan, P. The use of mechanical ventilation in interstitial lung disease. Breathe 2025, 21, 240172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguanwong, N.; Jantarangsi, N.; Ngeyvijit, J.; Owattanapanich, N.; Phoophiboon, V. Effect of noninvasive respiratory support on interstitial lung disease with acute respiratory failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Respir. Ther. 2023, 59, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, P.V.; Coppola, A.; Carriera, L.; Macagno, F. The Impact of Corticosteroids on Mortality in Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Meta-Analysis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivali, N.; De Giacomi, F.; Moua, T.; Ryu, J.H. Corticosteroid therapy for treating acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases: A systematic review. Thorax 2025, 80, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Yamada, S.; Kushima, H.; Ishii, H.; Imanaga, T.; Harada, T.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Naito, K.; et al. Autopsy analyses in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, S.G.; O’Dwyer, D.N. The lung microbiome in interstitial lung disease. Breathe 2025, 21, 240167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Cox, M.J.; Wells, A.U.; Kim, H.C.; Ji, W.; Cookson, W.O.C.; Moffatt, M.F.; Kim, D.S.; Maher, T.M. Changes in the respiratory microbiome during acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Du, Y.; Yang, X. Treatment Strategies for Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases in Chinese Patients: A Scoping Review. Rheumatol Ther. 2025, 12, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Ichikado, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Anan, K.; Suga, M. Azithromycin for idiopathic acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective single-center study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, H.; Tong, X. The value of macrolides in the adjuvant treatment of pulmonary fibrosis: Maybe a panacea. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2025, 19, 17534666251346108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, J.-M.; Jouneau, S.; Didier, M.; Borie, R.; Cachanado, M.; Bourdin, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Bonniaud, P.; Israël-Biet, D.; Prévot, G.; et al. Cyclophosphamide added to glucocorticoids in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (EXAFIP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innabi, A.; Gomez-Manjarres, D.; Alzghoul, B.N.; Chizinga, M.; Mehrad, B.; Patel, D.C. Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: A Review of the Literature. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2021, 38, e2021002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luppi, F.; Manfredi, A.; Faverio, P.; Franco, G.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Sebastiani, M. Treatment of acute exacerbation in interstitial lung disease secondary to autoimmune rheumatic diseases: More questions than answers. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, T.; Valentine, V.G.; Fei, F.; Tran-Nguyen, T.K.; Quesada-Arias, L.D.; Mkorombindo, T.; Pham, H.P.; Simmons, S.C.; Dsouza, K.G.; Luckhardt, T.; et al. Correlates of survival after autoantibody reduction therapy for acute IPF exacerbations. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, T.; Criner, G.J.; Kass, D.J.; Rosas, I.O.; Scholand, M.B.; Dilling, D.F.; Summer, R.; Duncan, S.R. Design of the STRIVE-IPF trial- study of therapeutic plasma exchange, rituximab, and intravenous immunoglobulin for acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Román, F.; Pintado-Cort, B.; García-Casado, D.; Muñiz-González, F.; López García-Asenjo, J.A.; Díaz-Rodríguez, C. Rituximab for the treatment of acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. RMD Open. 2023, 9, e003479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, A.M.; Kremens, K. Rituximab for Salvage Therapy of Refractory Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. WMJ 2019, 118, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shitenberg, D.; Fruchter, O.; Fridel, L.; Kramer, M.R. Successful Rituximab Therapy in Steroid-Resistant, Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Series. Respiration 2015, 90, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkouan, Y.; Dury, S.; Perotin, J.M.; Picot, R.; Durlach, A.; Passouant, O.; Sandu, S.; Dewolf, M.; Dumazet, A.; Lebargy, F.; et al. Acute severe idiopathic lymphoid interstitial pneumonia: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e21473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Sato, S.; Ohta, H.; Kusano, K.; Nomaki, M.; Kawabe, R.; Uzuka, C.; Sasaki, H.; Amano, M.; Takemura, T.; et al. Baricitinib for acute exacerbation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: A preliminary study using propensity score matching. Respiration 2025, 104, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, N.; Akahane, M.; Okada, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Arai, T.; Amano, I.; Takezawa, T.; To, M.; To, Y. Tacrolimus and steroid treatment for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Homma, S.; Miyamoto, A.; Kurosaki, A.; Fujii, T.; Yoshimura, K. Cyclosporin A in the treatment of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ke, J.; Huang, S.; Lin, S.; Lei, S.; Huang, H.; Lei, L.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Duan, M. Acute exacerbation of anti-Ha antibody-positive antisynthetase syndrome-associated interstitial lung disease: A case report. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1614777. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, S.; Azuma, A.; Saito, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Kashiwada, T.; Tanaka, T.; Baba, T.; Sekine, A.; Kitamura, H.; Okuda, R.; et al. Direct hemoperfusion with polymyxin B immobilized fiber column (PMX) treatment for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Chung, C.; Park, D.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, J.E. Changes in Oxygenation and Serological Markers in Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Panlaqui, O.M. The efficacy of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (rhsTM) treatment for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Kida, H.; Ogata, Y.; Marumo, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Gohma, I.; Yamamoto, S.; Mori, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Tachibana, K.; et al. Recombinant thrombomodulin for acute exacerbation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Respirology 2019, 24, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnak, T.; Lertjitbanjong, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Moua, T. Impact of Antifibrotic Therapy on Mortality and Acute Exacerbation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2021, 160, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.Y.; Hang, W.L.; Yu, G.R.; Xu, Y. Impact of antifibrotic therapy on disease progression, all-cause mortality, and risk of acute exacerbation in non-IPF fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: Evidence from a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective controlled studies. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2024, 18, 17534666241232561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivali, N.; De Giacomi, F. Benefit of antifibrotic therapy initiated during acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease: A systematic review. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xiang, F. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis a narrative review primary focus on treatments. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 4727–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Román, F.; Pintado-Cort, B.; Máiz-Carro, L.; Almonacid-Sánchez, C.; Mercedes-Noboa, E.; Rodríguez-Calle, C.; Velasco-Álvarez, D.; Pérez-Figuera, A.; Retegui-García, A.; Durán-Barata, D. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An algorithmic approach to diagnosis and management. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Román, F.; Pintado-Cort, B.; Barberà, J.A.; Sellares, J.; Iturbe, D.; López-Zubizarreta, M.; Peña-Miguel, T.; Durán-Barata, D.; Jiménez, D. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la tromboembolia de pulmón y de la hipertensión pulmonar en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa [Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease]. Open Respir. Arch. 2025, 7, 100406. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- León-Román, F.; Pintado-Cort, B.; Largaespada-Pérez, G.; Khandji-Aslan, H.G.; Muñiz-González, F. Case Report: Inhaled treprostinil: An alternative for the treatment of refractory exacerbation of interstitial lung disease. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1639593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiropoulou, V.; Theochari, E.; Katsaras, M.; Tsiri, P.; Komninos, D.; Christopoulos, I.; Tsirikos, G.; Kalogeropoulou, C.; Daoussis, D.; Karkoulias, K.; et al. Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Acute Exacerbations of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective, Real-World Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Morita, T.; Koyauchi, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Mori, M.; Miyashita, M.; Tachikawa, R.; Tomii, K.; Tomioka, H.; et al. End-of-life care for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients with acute exacerbation. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlaja, H.; Piili, R.P.; Nuutinen, M.; Saarto, T.; Carpén, T.; Lehto, J.T. The use of specialist palliative care services differs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and interstitial lung disease: A national cohort study. Respir. Med. 2025, 240, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-Román, F.; Martínez-Besteiro, E.; Iturbe, D.; Peña-Miguel, T.; López-Zubizarreta, M.; Yerovi-Onofre, S.; Andrés-Porras, A.M.; Jerves-Donoso, D.; Martín-Carbajo, C.; López-Represa, C.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Medicina 2025, 61, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122097
León-Román F, Martínez-Besteiro E, Iturbe D, Peña-Miguel T, López-Zubizarreta M, Yerovi-Onofre S, Andrés-Porras AM, Jerves-Donoso D, Martín-Carbajo C, López-Represa C, et al. Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122097
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-Román, Francisco, Elisa Martínez-Besteiro, David Iturbe, Teresa Peña-Miguel, Marco López-Zubizarreta, Sofía Yerovi-Onofre, Ana María Andrés-Porras, David Jerves-Donoso, Cristina Martín-Carbajo, Carmen López-Represa, and et al. 2025. "Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: Early Diagnosis and Treatment" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122097
APA StyleLeón-Román, F., Martínez-Besteiro, E., Iturbe, D., Peña-Miguel, T., López-Zubizarreta, M., Yerovi-Onofre, S., Andrés-Porras, A. M., Jerves-Donoso, D., Martín-Carbajo, C., López-Represa, C., Jiménez-Romero, A., & Valenzuela, C. (2025). Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease: Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Medicina, 61(12), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122097






