Age-Related Variations in Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study in Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Body Composition and Anthropometrics
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
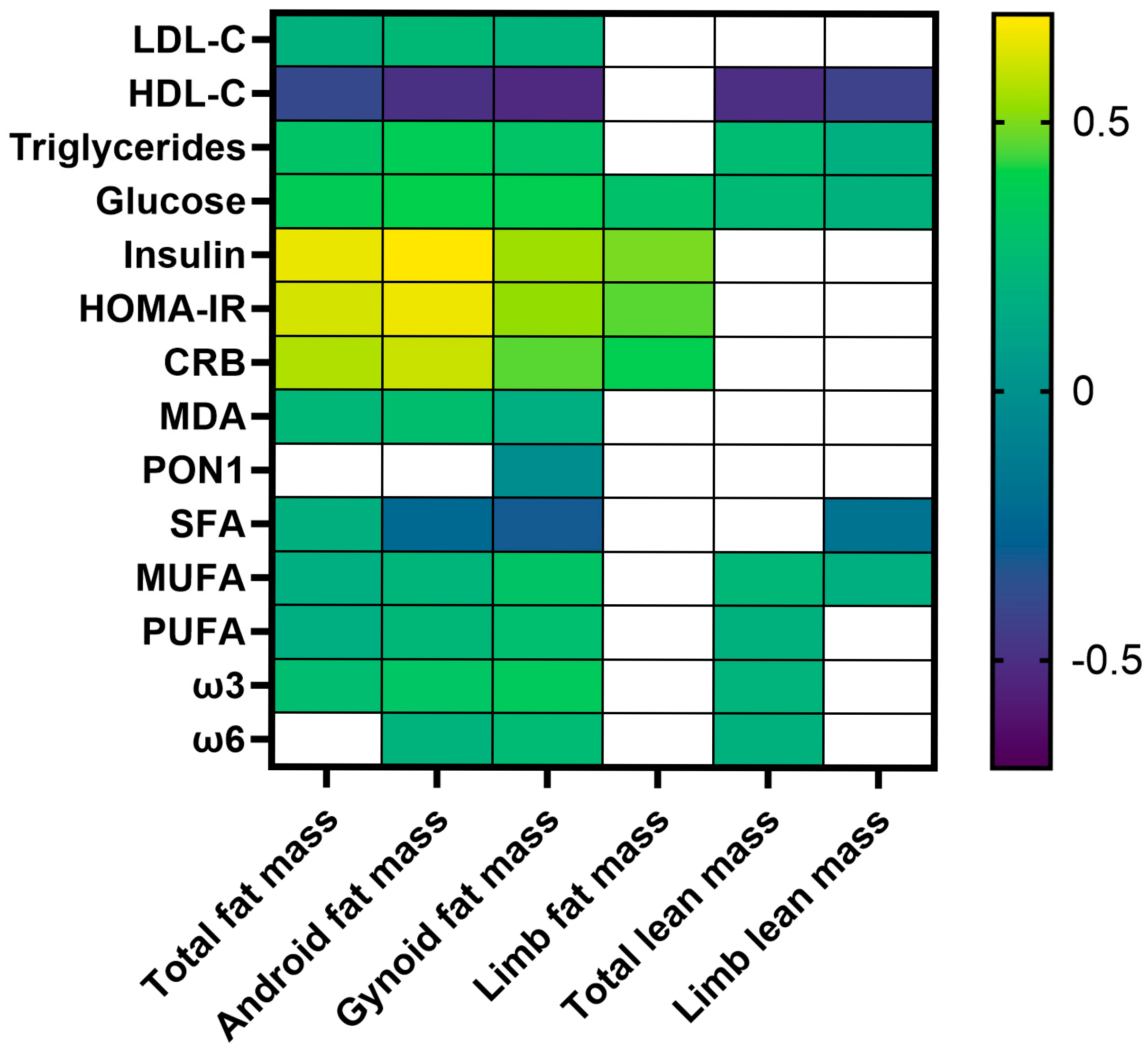
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | fatty acid |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TG | triglycerides |
| OxHDL | oxidized HDL |
| OxLDL | oxidized LDL |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| PON1 | human paraoxonase |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acid |
| MUFA | monounsaturated fatty acid |
| PUFA | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| BMI | body mass index |
| DXA | dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| FM | fat mass |
| FMI | fat mass index |
| LM | lean mass |
| LMI | lean mass index |
| A/G | android to gynoid ratio |
| T/L | trunk-to-leg ratio |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ALA | α-linolenic acid |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid |
| DPA | docosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| OA | oleic acid |
| LA | linoleic acid |
| ARA | arachidonic acid |
| SD | standard deviation |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
References
- Kammar-García, A.; Hernández-Hernández, M.E.; López-Moreno, P.; Ortíz-Bueno, A.M.; Martínez-Montaño Mde, L. Relation of body composition indexes to cardiovascular disease risk factors in young adults. Semergen 2019, 45, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Li, P.; Li, K. Metabolic health and cardiovascular disease across BMI categories: NHANES findings. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2025, 44, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, N.; Shao, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhong, H. The lean body mass to visceral fat mass ratio is negatively associated with cardiometabolic disorders: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, U.; Syauki, A.Y.; Taslim, N.A.; As’Ad, S.; Ashari, N.; Aminuddin, A. Body composition and cardiovascular risk: Correlation of fat mass, muscle mass, and visceral fat with atherogenic index of plasma in young adults. Nutr. Clínica Dietética Hosp. 2025, 45, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Cerjak, D.; Kent, J.W.; James, R.; Blangero, J.; Zhang, Y. Obesity, Central Adiposity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents: A Family-based Study. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, e58–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguso, C.A.; Kyle, U.; Kossovsky, M.P.; Roynette, C.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Hans, D.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. A 3-year longitudinal study on body composition changes in the elderly: Role of physical exercise. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.K.; Jensen, M.D. Metabolic changes in aging humans: Current evidence and therapeutic strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, F.; Santoro, A.; Mercatelli, D.; Gasperini, C.; Conte, M.; Martucci, M.; Sangiorgi, L.; Franceschi, C.; Bazzocchi, A. Aging and Imaging Assessment of Body Composition: From Fat to Facts. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da CPinaffi-Langley, A.C.; Pinto, C.B.; Mukli, P.; Peterfi, A.; Kaposzta, Z.; Owens, C.D.; Szarvas, Z.; Muranyi, M.; Adams, C.; Shahriari, A.; et al. Energy metabolism dysregulation, cerebrovascular aging, and time-restricted eating: Current evidence and proof-of-concept findings. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, V.A.; Frontera, W.R.; Roubenoff, R.; Evans, W.J.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A. Longitudinal changes in body composition in older men and women: Role of body weight change and physical activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Lipid accumulation product is associated with insulin resistance, lipid peroxidation, and systemic inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 29, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.T.; Wu, Y.J.; Yin, Q.; Chen, W.G.; Zuo, J. The Involvement of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Alteration in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Clinical Implication. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, R.M.; Al-Hashemi, W.K.; Al-Auqbi, T.F.R.; Jebali, J. Relation of MDA as Oxidative Stress Marker with Lipid Profile in a Diabetic Patient. Al Nahrain J. Sci. 2023, 26, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, N.; Rathnayake, H.; Lekamwasam, S. Age-Related Trends in Body Composition among Women Aged 20–80 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Obes. 2022, 2022, 4767793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.; Weber, D.; Kochlik, B.; Stuetz, W.; Toussaint, O.; Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Dollé, M.E.; Jansen, E.H.; Gonos, E.S.; Sikora, E.; et al. Gender- and age-dependencies of oxidative stress, as detected based on the steady state concentrations of different biomarkers in the MARK-AGE study. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petak, S.; Barbu, C.G.; Yu, E.W.; Fielding, R.; Mulligan, K.; Sabowitz, B.; Wu, C.-H.; Shepherd, J.A. The Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry: Body Composition Analysis Reporting. J. Clin. Densitom. 2013, 16, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.; Albano, D.; Gitto, S.; Tofanelli, L.; Bazzocchi, A.; Ulivieri, F.M.; Guglielmi, G.; Sconfienza, L.M. Body composition with dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: From basics to new tools. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchstone, J.C. Thin-layer chromatographic procedures for lipid separation. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 671, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadzadeh, M.; Valizadeh, M.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Momenan, A.; Mahdavi, M.; Barzin, M.; Azizi, F. Comprehensive evaluation of body composition in a wide age range of Iranian adults using bioelectrical impedance analysis: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Public Health Nutr. 2024, 27, e24–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Gallagher, D. Body composition changes with aging: The cause or the result of alterations in metabolic rate and macronutrient oxidation? Nutrition 2010, 26, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, M.; Raffin, J.; Gonzalez-Bautista, E.; Ritz, P.; Abellan Van Kan, G.; Pillard, F.; Faruch-Bilfeld, M.; Guyonnet, S.; Dray, C.; Vellas, B.; et al. Body composition and aging: Cross-sectional results from the INSPIRE study in people 20 to 93 years old. GeroScience 2025, 47, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontzer, H. Daily energy expenditure through the human life course. Yearb. Paediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 373, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbão, K.E.G.; Pavanello, A.; Oliveira, F.M.; Santos, N.Q.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Marchiori, L.L.M.; Franchini, E.; Branco, B.H.M. Variation in Body Composition Components Across Different Age Groups and Proposal of Age-Specific Normative Tables: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, J.L.; Saunders, T.J.; Davidson, L.E.; Ross, R. Age-related changes in total and regional fat distribution. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchkonia, T.; Morbeck, D.E.; Von Zglinicki, T.; Van Deursen, J.; Lustgarten, J.; Scrable, H.; Khosla, S.; Jensen, M.D.; Kirkland, J.L. Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Habib, A.; Sajjad, Z. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its association with CT-based central adiposity measures: A cross-sectional study at a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e082095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, Q.; Dong, J.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Xing, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, W.; Hou, H.; Wang, H.; et al. The association between normal BMI with central adiposity and proinflammatory potential immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlantis, E.; Martin, S.A.; Haren, M.T.; Taylor, A.W.; Wittert, G.A. Inverse associations between muscle mass, strength, and the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 2009, 58, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.W.; Tajar, A.; Pye, S.R.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.; Forti, G.; Giwercman, A.; et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis disruptions in older men are differentially linked to age and modifiable risk factors: The European male aging study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.R.; Gower, B.A.; Kane, B.L. Age Related Shift in Visceral Fat. Int. J. Body Compos. Res. 2010, 8, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Losev, V.; Lu, C.; Tahasildar, S.; Senevirathne, D.S.; Inglese, P.; Bai, W.; King, A.P.; Shah, M.; de Marvao, A.; O’rEgan, D.P. Sex-specific body fat distribution predicts cardiovascular ageing. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boneva-Asiova, Z.; Boyanov, M. Age-related changes of body composition and abdominal adipose tissue assessed by bio-electrical impedance analysis and computed tomography. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2011, 58, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čuprika, A.; Fernāte, A.; Čupriks, L. Physical Activities and Body Composition Among Women in Fitness. LASE J. Sport Sci. 2018, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooyens, A.C.; Visscher, T.L.; Verschuren, W.M.; Schuit, A.J.; Boshuizen, H.C.; van Mechelen, W.; Seidell, J.C. Age, period and cohort effects on body weight and body mass index in adults: The Doetinchem Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasiya, D.; Gupta, A.; Chauhan, S.; Patel, R.; Chaurasia, V. Age, period and birth cohort effects on prevalence of obesity among reproductive-age women in India. SSM Popul. Health 2019, 9, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, L.M.M.; Gordon, A.N.B.; Cabre Hannah, E.; Hoyle, A.T.; Ryan, E.; Hackney, A.C.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. Metabolic effects of menopause: A cross-sectional characterization of body composition and exercise metabolism. Menopause 2022, 29, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.J.; Tchernof, A.; Sites, C.K.; Poehlman, E.T. Effect of menopausal status on body composition and abdominal fat distribution. Int. J. Obes. Retal Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenner, M.; Shenouda, N.; Shoemaker, L. Characterizing vascular and hormonal changes in women across the life span: A cross-sectional analysis. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2024, 327, H1286–H1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvinen, S.; Jergenson, M.J.; Hyvärinen, M.; Aukee, P.; Tammelin, T.; Sipilä, S.; Kovanen, V.; Kujala, U.M.; Laakkonen, E.K. Menopausal status and physical activity are independently associated with cardiovascular risk factors of healthy middle-aged women: Cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb-Belkali, O.; Hadjer, C.; Lakhdar, Z.; Azzedine, F.; Belkacem, C.; Khedidja, M. Lipid profile, inflammation, and oxidative status in peri- and postmenopausal women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2016, 32, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.K.; Ahsan, M.; Das, B.; Saxena, S.; Samanta, S.; Kukreja, S. Study of Lipid Profile during Late Reproductive Phase, Perimenopause and Postmenopause in North Indian Women. Int. J. Med Res. Rev. 2015, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiger, K.J.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Toth, P.P.; Nasir, K.; Michos, E.D.; Gerstenblith, G.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Jones, S.R. Narrowing Sex Differences in Lipoprotein Cholesterol Subclasses Following Mid-Life: The Very Large Database of Lipids (VLDL-10B). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černiauskas, L.; Mažeikienė, A.; Mazgelytė, E.; Petrylaitė, E.; Linkevičiūtė-Dumčė, A.; Burokienė, N.; Karčiauskaitė, D. Malondialdehyde, Antioxidant Defense System Components and Their Relationship with Anthropometric Measures and Lipid Metabolism Biomarkers in Apparently Healthy Women. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; Kato, Y.; Imai, T.; Ando, F.; Shimokata, H. Higher serum EPA or DHA, and lower ARA compositions with age independent fatty acid intake in Japanese aged 40 to 79. Lipids 2013, 48, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, R.H.M.; Van Boxtel, M.P.J.; Schiepers, O.J.G.; Hornstra, G.; Jolles, J. Age dependence of plasma phospholipid fatty acid levels: Potential role of linoleic acid in the age-associated increase in docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid concentrations. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Medoro, A.; Accardi, G.; Calabrò, A.; Carru, C.; Cannavo, A.; Caruso, C.; Candore, G.; Scapagnini, G.; Corbi, G.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid status and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation across the lifespan: A cross-sectional study in a cohort with long-lived individuals. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 195, 112531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericel, E.; Croset, M.; Perrot, L.; Renaud, S.; Lagarde, M. Platelets and aging II-plasma lipoproteins and fatty acid profiles. Thromb. Res. 1988, 49, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisco, D.; Rogasi, P.G.; Matucci, M.; Paniccia, R.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Neri, S.G.G. Age related changes in platelet lipid composition. Thromb. Res. 1986, 44, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: New twists in an old tale. Biochimie 2009, 91, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, V.; Ingle, K.A.; Kachman, M.; Baum, H.; Shanmugam, G.; Rajasekaran, N.S.; Young, M.E.; Halade, G.V. Excess ω-6 fatty acids influx in aging drives metabolic dysregulation, electrocardiographic alterations, and low-grade chronic inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H160–H169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, F.; Yao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, N.; Huang, H.; Liang, J.; Lin, L. Body fat distribution and their associations with cardiovascular risk, insulin resistance and β-cell function: Are there differences between men and women? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2011, 65, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnick, K.E.; Nicholson, G.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; McQuaid, S.E.; Valet, P.; Frayn, K.N.; Denton, N.; Min, J.L.; Zondervan, K.T.; Fleckner, J.; et al. Distinct developmental profile of lower-body adipose tissue defines resistance against obesity-associated metabolic complications. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3785–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbetzova, M.; Koleva, D.; Mitkov, M.; Atanassova, I.; Nikolova, J.; Atanassova, P.; Genchev, G.D. Adipocytokines, neuropeptide Y and insulin resistance in overweight women with gynoid and android type of adipose tissue distribution. Folia Med. 2012, 54, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, V.; Khadilkar, A.; Chiplonkar, S.; Khadilkar, V. Dyslipidemia and Fat Distribution in Normal Weight Insulin Resistant Men. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2019, 67, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.M. Association of muscle mass and fat mass with insulin resistance and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouwborst, I.; Jardon, K.M.; Gijbels, A.; Hul, G.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Afman, L.A.; Linge, J.; Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. Body composition and body fat distribution in tissue-specific insulin resistance and in response to a 12-week isocaloric dietary macronutrient intervention. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Miller, E.; Dzongowski, E.; Miakisheva, K.; Ross, R. A compositional analysis study of body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors. Obesity 2022, 30, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, A.; D’Agostino, R.; Williams, K.; Karter, A.; Mayer-Davis, E.; Tracy, R.P.; Haffner, S. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rexrode, K.M.; Pradhan, A.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. Relationship of total and abdominal adiposity with CRP and IL-6 in women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hak, A.E.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Bots, M.L.; Polderman, K.H.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Westendorp, I.C.D.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.M. Associations of C-reactive protein with measures of obesity, insulin resistance, and subclinical atherosclerosis in healthy, middle-aged women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Body Composition | Mean ± SD | Biomarkers | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total body mass, kg | 82.29 ± 17.17 | Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.93 ± 0.87 |
| Total lean mass, kg | 51.33 ± 11.51 | LDL-cholesterol, mmol/L | 3.12 ± 0.83 |
| Total fat mass, kg | 28.13 ± 12.27 | HDL-cholesterol, mmol/L | 1.55 ± 0.41 |
| Trunk lean mass, kg | 22.32 ± 4.87 | Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.13 ± 0.70 |
| Trunk fat mass, kg | 13.61 ± 7.84 | Glucose, mmol/L | 5.36 ± 0.50 |
| Android fat mass, kg | 2.50 ± 1.49 | Insulin, mU/L | 10.52 ± 6.99 |
| Gynoid fat mass, kg | 5.39 ± 2.26 | HOMA-IR | 2.58 ± 1.94 |
| Legs lean mass, kg | 19.17 ± 4.53 | CRB, mg/L | 1.90 ± 2.66 |
| Legs fat mass, kg | 10.32 ± 3.97 | Oxidized LDL, ng/mL | 294.55 ± 148.61 |
| Arms lean mass, kg | 6.12 ± 2.38 | Oxidized HDL, ng/mL | 35.68 ± 52.82 |
| Arms fat mass, kg | 3.14 ± 1.33 | MDA, ng/L | 101.01± 19.02 |
| Total fat, % | 34.58 ± 10.31 | PON1, mcg/L | 10.75 ± 6.66 |
| Trunk fat, % | 35.53 ± 12.19 | SFA, % | 77.29 ± 12.93 |
| Android fat, % | 41.69 ± 14.19 | MUFA, % | 11.46 ± 6.20 |
| Gynoid fat, % | 42.55 ± 11.70 | PUFA, % | 11.12 ± 7.42 |
| Legs fat, % | 34.77 ± 10.25 | PUFA to SFA ratio | 0.17 ± 0.15 |
| Arms fat, % | 34.76 ± 12.85 | ω3 fatty acids, % | 1.46 ± 1.14 |
| Fat mass index, kg/m2 | 9.44 ± 4.41 | ω6 fatty acids, % | 9.76 ± 6.77 |
| Lean mass index, kg/m2 | 16.81 ± 2.68 | ω3-to-ω6 ratio | 0.22 ± 0.24 |
| Android-to-gynoid ratio | 0.45 ± 0.17 | ||
| Trunk-to-leg ratio | 1.31 ± 0.58 |
| Characteristic | <30 Years | 30–39 Years | 40–49 Years | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | ||||||
| Total body mass, kg | 88.01 ± 12.75 | 89.88 ± 14.59 | 92.92 ± 11.39 | 0.703 | 0.346 | 0.432 |
| Total lean mass, kg | 66.24 ± 11.31 | 62.75 ± 9.53 | 63.21 ± 7.43 | 0.303 | 0.399 | 0.861 |
| Total fat mass, kg | 18.30 ± 7.49 | 23.82 ± 10.47 | 26.36 ± 8.49 | 0.114 | 0.031 | 0.354 |
| Trunk lean mass, kg | 27.70 ± 4.44 | 26.78 ± 4.01 | 27.17 ± 3.26 | 0.516 | 0.721 | 0.731 |
| Trunk fat mass, kg | 8.34 ± 4.01 | 12.82 ± 7.76 | 14.81 ± 6.39 | 0.079 | 0.018 | 0.316 |
| Android fat mass, kg | 1.49 ± 0.92 | 2.35 ± 1.41 | 2.72 ± 1.22 | 0.071 | 0.017 | 0.331 |
| Gynoid fat mass, kg | 3.45 ± 1.82 | 4.04 ± 1.68 | 4.17 ± 1.19 | 0.301 | 0.240 | 0.787 |
| Legs lean mass, kg | 24.67 ± 5.32 | 23.31 ± 4.62 | 23.17 ± 3.24 | 0.395 | 0.378 | 0.914 |
| Legs fat mass, kg | 6.98 ± 2.99 | 7.41 ± 2.16 | 7.70 ± 1.73 | 0.592 | 0.397 | 0.644 |
| Arms lean mass, kg | 9.66 ± 1.93 | 8.46 ± 2.33 | 8.59 ± 1.40 | 0.107 | 0.174 | 0.824 |
| Arms fat mass, kg | 1.91 ± 0.81 | 2.46 ± 0.95 | 2.64 ± 0.75 | 0.091 | 0.034 | 0.459 |
| Total fat, % | 21.53 ± 7.70 | 26.86 ± 8.24 | 29.02 ± 7.29 | 0.068 | 0.017 | 0.346 |
| Trunk fat, % | 22.93 ± 9.43 | 30.41 ± 10.13 | 33.97 ± 10.12 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.224 |
| Android fat, % | 27.00 ± 13.06 | 36.26 ± 11.54 | 40.06 ± 12.38 | 0.040 | 0.007 | 0.279 |
| Gynoid fat, % | 26.43 ± 10.29 | 30.72 ± 7.53 | 31.98 ± 6.46 | 0.133 | 0.068 | 0.573 |
| Legs fat, % | 21.88 ± 7.85 | 24.36 ± 7.00 | 25.01 ± 5.01 | 0.305 | 0.222 | 0.732 |
| Arms fat, % | 16.65 ± 6.99 | 23.25 ± 9.90 | 23.64 ± 6.59 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.872 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.18 ± 4.18 | 27.49 ± 6.20 | 28.50 ± 3.75 | 0.229 | 0.104 | 0.502 |
| Fat mass index, kg/m2 | 5.28 ± 2.35 | 7.10 ± 3.03 | 8.03 ± 2.61 | 0.080 | 0.014 | 0.257 |
| Lean mass index | 18.90 ± 3.33 | 18.76 ± 2.54 | 19.19 ± 2.17 | 0.880 | 0.775 | 0.566 |
| Android-to-gynoid ratio | 0.42 ± 0.11 | 0.56 ± 0.16 | 0.63 ± 0.18 | 0.028 | 0.002 | 0.120 |
| Trunk-to-leg ratio | 1.22 ± 0.30 | 1.65 ± 0.59 | 1.88 ± 0.66 | 0.047 | 0.005 | 0.178 |
| Females | ||||||
| Total body mass, kg | 82.64 ± 18.70 | 71.91 ± 17.04 | 84.56 ± 14.20 | 0.016 | 0.683 | 0.001 |
| Total lean mass, kg | 45.70 ± 6.19 | 42.82 ± 5.62 | 47.12 ± 4.69 | 0.050 | 0.363 | <0.001 |
| Total fat mass, kg | 34.34 ± 13.87 | 26.62 ± 12.76 | 34.81 ± 10.97 | 0.022 | 0.893 | 0.003 |
| Trunk lean mass, kg | 20.21 ± 2.88 | 18.51 ± 2.76 | 21.39 ± 2.95 | 0.027 | 0.146 | <0.001 |
| Trunk fat mass, kg | 16.24 ± 9.02 | 11.62 ± 7.62 | 16.92 ± 7.72 | 0.031 | 0.763 | 0.003 |
| Android fat mass, kg | 2.97 ± 1.72 | 2.10 ± 1.45 | 3.19 ± 1.48 | 0.032 | 0.617 | 0.001 |
| Gynoid fat mass, kg | 7.07 ± 2.23 | 5.38 ± 2.16 | 6.93 ± 1.89 | 0.003 | 0.811 | 0.001 |
| Legs lean mass, kg | 17.36 ± 2.80 | 16.28 ± 2.21 | 17.38 ± 2.20 | 0.085 | 0.970 | 0.031 |
| Legs fat mass, kg | 13.17 ± 3.82 | 10.83 ± 3.89 | 12.96 ± 3.37 | 0.020 | 0.845 | 0.009 |
| Arms lean mass, kg | 4.61 ± 1.02 | 4.67 ± 0.90 | 4.81 ± 0.86 | 0.813 | 0.457 | 0.492 |
| Arms fat mass, kg | 3.87 ± 1.27 | 3.20 ± 1.52 | 3.88 ± 1.10 | 0.067 | 0.989 | 0.024 |
| Total fat, % | 41.38 ± 8.19 | 36.43 ± 9.50 | 41.52 ± 6.62 | 0.030 | 0.951 | 0.006 |
| Trunk fat, % | 41.46 ± 11.30 | 35.07 ± 13.15 | 42.04 ± 9.66 | 0.045 | 0.863 | 0.008 |
| Android fat, % | 48.70 ± 12.08 | 40.63 ± 15.66 | 49.38 ± 10.43 | 0.028 | 0.861 | 0.004 |
| Gynoid fat, % | 51.76 ± 6.11 | 47.21 ± 8.30 | 50.96 ± 5.31 | 0.018 | 0.692 | 0.016 |
| Legs fat, % | 42.50 ± 5.90 | 38.90 ± 7.25 | 42.19 ± 5.23 | 0.038 | 0.863 | 0.020 |
| Arms fat, % | 44.93 ± 9.15 | 38.88 ± 9.97 | 44.15 ± 5.80 | 0.010 | 0.753 | 0.006 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 29.53 ± 7.50 | 25.76 ± 6.58 | 30.36 ± 5.94 | 0.033 | 0.658 | 0.002 |
| Fat mass index, kg/m2 | 11.90 ± 4.87 | 9.46 ± 4.65 | 12.13 ± 3.84 | 0.042 | 0.852 | 0.007 |
| Lean mass index | 15.84 ± 2.29 | 15.14 ± 1.90 | 16.41 ± 1.61 | 0.167 | 0.292 | 0.002 |
| Android-to-gynoid ratio | 0.39 ± 0.12 | 0.35 ± 0.13 | 0.44 ± 0.14 | 0.244 | 0.167 | 0.001 |
| Trunk-to-leg ratio | 1.16 ± 0.40 | 0.99 ± 0.39 | 1.31 ± 0.55 | 0.144 | 0.273 | 0.002 |
| Characteristic | <30 Years, N = 28 | 30–39 Years, N = 82 | 40–49 Years, N = 53 | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.68 ± 1.07 | 4.85 ± 0.88 | 5.18 ± 0.68 | 0.355 | 0.014 | 0.033 |
| LDL cholesterol, mmol/L | 2.88 ± 0.94 | 3.05 ± 0.85 | 3.36 ± 0.66 | 0.346 | 0.013 | 0.031 |
| HDL cholesterol, mmol/L | 1.63 ± 0.49 | 1.59 ± 0.43 | 1.45 ± 0.31 | 0.645 | 0.063 | 0.058 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 0.99 ± 0.43 | 1.04 ± 0.59 | 1.34 ± 0.91 | 0.711 | 0.029 | 0.015 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 5.25 ± 0.44 | 5.30 ± 0.47 | 5.53 ± 0.53 | 0.620 | 0.013 | 0.007 |
| Insulin, mU/L | 10.40 ± 7.12 | 10.19 ± 6.29 | 11.09 ± 7.98 | 0.891 | 0.676 | 0.469 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.45 ± 1.71 | 2.46 ± 1.65 | 2.84 ± 2.42 | 0.964 | 0.388 | 0.276 |
| CRB, mg/L | 2.07 ± 2.77 | 1.82 ± 2.90 | 1.92 ± 2.23 | 0.680 | 0.816 | 0.840 |
| Oxidized LDL, ng/mL | 272.37 ± 146.85 | 289.31 ± 152.85 | 314.97 ± 143.16 | 0.617 | 0.242 | 0.350 |
| Oxidized HDL, ng/mL | 63.84 ± 121.71 | 28.71 ± 14.54 | 31.60 ± 12.13 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.761 |
| MDA, ng/L | 95.76 ± 21.55 | 99.72 ± 15.74 | 105.83 ± 21.38 | 0.882 | 0.085 | 0.034 |
| PON1, mcg/L | 12.02 ± 13.02 | 10.69 ± 4.69 | 10.52 ± 3.63 | 0.375 | 0.244 | 0.659 |
| SFA, % | 77.05 ± 13.21 | 79.13 ± 12.15 | 74.60 ± 13.71 | 0.470 | 0.427 | 0.054 |
| MUFA, % | 12.17 ± 7.31 | 10.73 ± 6.06 | 12.19 ± 5.75 | 0.302 | 0.985 | 0.196 |
| PUFA, % | 10.78 ± 6.39 | 10.14 ± 7.03 | 12.85 ± 8.33 | 0.699 | 0.243 | 0.046 |
| PUFA-to-SFA ratio | 0.16 ± 011 | 0.15 ± 0.15 | 0.20 ± 0.17 | 0.795 | 0.248 | 0.068 |
| ω3 fatty acids, % | 1.37 ± 0.78 | 1.35 ± 1.03 | 1.68 ± 1.41 | 0.924 | 0.248 | 0.104 |
| ω6 fatty acids, % | 9.41 ± 5.86 | 8.79 ± 6.49 | 11.44 ± 7.42 | 0.683 | 0.206 | 0.031 |
| ω3-to-ω6 ratio | 0.26 ± 0.33 | 0.23 ± 0.26 | 0.18 ± 0.13 | 0.665 | 0.187 | 0.229 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fomčenko, I.; Bikulčienė, I.; Karčiauskaitė, D.; Urbonas, M.; Alekna, V.; Šapoka, V. Age-Related Variations in Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study in Adults. Medicina 2025, 61, 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111951
Fomčenko I, Bikulčienė I, Karčiauskaitė D, Urbonas M, Alekna V, Šapoka V. Age-Related Variations in Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study in Adults. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111951
Chicago/Turabian StyleFomčenko, Inga, Inga Bikulčienė, Dovilė Karčiauskaitė, Mykolas Urbonas, Vidmantas Alekna, and Virginijus Šapoka. 2025. "Age-Related Variations in Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study in Adults" Medicina 61, no. 11: 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111951
APA StyleFomčenko, I., Bikulčienė, I., Karčiauskaitė, D., Urbonas, M., Alekna, V., & Šapoka, V. (2025). Age-Related Variations in Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study in Adults. Medicina, 61(11), 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111951






