Biomarkers to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Trauma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Selection
2.2. Data Collection and Definitions
2.3. Procedures for Sampling, DNA Extraction, and Quantification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Between Patients with and Without Acute Kidney Injury
3.2. Temporal Changes in Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number
3.3. Multivariate Analysis for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury
3.4. Optimal Cutoff Values for Hemoglobin and umtDNAcn
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| MODS | Multi-organ dysfunction syndrome |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial DNA |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular pattern |
| TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin |
| KIM-1 | Kidney injury molecule-1 |
| KDIGO | Kidney disease improving global outcomes |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Harrois, A.; Soyer, B.; Gauss, T.; Hamada, S.; Raux, M.; Duranteau, J.; Traumabase, G. Prevalence and risk factors for acute kidney injury among trauma patients: A multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golino, G.; Greco, M.; Rigobello, A.; Danzi, V.; De Cal, M.; Malchiorna, N.; Zannella, M.; Navalesi, P.; Costa-Pinto, R.; Ronco, C.; et al. Incidence of acute kidney injury in polytrauma patients and predictive performance of timp2× igfbp7 biomarkers for early identification of acute kidney injury. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Tam, D.; Bardia, A.; Bhasin, M.; Rowe, G.C.; Kher, A.; Zsengeller, Z.K.; Akhavan-Sharif, M.R.; Khankin, E.V.; Saintgeniez, M.; et al. Pgc-1alpha promotes recovery after acute kidney injury during systemic inflammation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emma, F.; Montini, G.; Parikh, S.M.; Salviati, L. Mitochondrial dysfunction in inherited renal disease and acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Agostinis, P.; Krysko, O.; Garg, A.D.; Bachert, C.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Vandenabeele, P. Emerging role of damage-associated molecular patterns derived from mitochondria in inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Raoof, M.; Chen, Y.; Sumi, Y.; Sursal, T.; Junger, W.; Brohi, K.; Itagaki, K.; Hauser, C.J. Circulating mitochondrial damps cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature 2010, 464, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.S.; Kim, D.K.; An, S.; Gong, S.C.; Kim, M.H.; Rahman, M.H.; Kim, C.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, K.; Ryu, H. Biomarkers to predict multiorgan distress syndrome and acute kidney injury in critically ill surgical patients. Medicina 2023, 59, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Ren, J.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Gu, G.; Ren, H.; Hong, Z.; et al. Urinary mitochondrial DNA levels identify acute kidney injury in surgical critical illness patients. Shock 2017, 48, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Geng, H.; Singha, P.K.; Saikumar, P.; Bottinger, E.P.; Weinberg, J.M.; Venkatachalam, M.A. Mitochondrial pathology and glycolytic shift during proximal tubule atrophy after ischemic aki. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3356–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, T.; Karbowski, M. Structural changes of mitochondria related to apoptosis. Biol. Signals Recept. 2001, 10, 26–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, Z. Mir-214 represses mitofusin-2 to promote renal tubular apoptosis in ischemic acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 318, F878–F887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Agborbesong, E.; Li, X. The role of mitochondria in acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease and its therapeutic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, R.M.; Stallons, L.J.; Kneff, J.E.; Alge, J.L.; Harmon, J.L.; Rahn, J.J.; Arthur, J.M.; Beeson, C.C.; Chan, S.L.; Schnellmann, R.G. Urinary mitochondrial DNA is a biomarker of mitochondrial disruption and renal dysfunction in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2012, 380, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Bellomo, R.; Devarajan, P.; Ma, Q.; Bennett, M.R.; Mockel, M.; Matalanis, G.; Dragun, D.; Haase-Fielitz, A. Novel biomarkers early predict the severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in adults. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 88, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: A final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Rivoli, L.; Garofalo, C.; Faga, T.; Pelagi, E.; Perticone, M.; Serra, R.; Michael, A.; Comi, N.; Andreucci, M. Renal resistive index in chronic kidney disease patients: Possible determinants and risk profile. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakar, C.V.; Yared, J.P.; Worley, S.; Cotman, K.; Paganini, E.P. Renal dysfunction and serious infections after open-heart surgery. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkouti, K.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; Yau, T.M.; McCluskey, S.A.; Chan, C.T.; Wong, P.Y.; Beattie, W.S. Influence of erythrocyte transfusion on the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery differs in anemic and nonanemic patients. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; McCulloch, C.E.; Fan, D.; Ordonez, J.D.; Chertow, G.M.; Go, A.S. Community-based incidence of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappitelli, M.; Washburn, K.K.; Arikan, A.A.; Loftis, L.; Ma, Q.; Devarajan, P.; Parikh, C.R.; Goldstein, S.L. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrois, A.; Libert, N.; Duranteau, J. Acute kidney injury in trauma patients. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2017, 23, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovik, S.; Isachsen, M.S.; Nordhuus, K.M.; Tveiten, C.K.; Eken, T.; Sunde, K.; Brurberg, K.G.; Beitland, S. Acute kidney injury in trauma patients admitted to the icu: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; The ADQI Workgroup. Acute renal failure—Definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The second international consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative (ADQI) group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Shah, S.V.; Molitoris, B.A.; Ronco, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Levin, A.; The Acute Kidney Injury Network. Acute kidney injury network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, J.; Uchino, S.; Takinami, M. A detailed evaluation of the new acute kidney injury criteria by kdigo in critically ill patients. J. Anesth. 2016, 30, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeze, J.; Keus, F.; Dieperink, W.; van der Horst, I.C.; Zijlstra, J.G.; van Meurs, M. Incidence, timing and outcome of aki in critically ill patients varies with the definition used and the addition of urine output criteria. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No AKI (n = 40) (%) | AKI (n = 25) (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.4 ± 18.0 | 64.7 ± 14.8 | 0.020 |
| Male sex | 32 (80.0) | 20 (80.0) | 1.000 |
| Known history | |||
| Hypertension | 12 (30.0) | 10 (40.0) | 0.576 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (12.5) | 4 (16.0) | 0.977 |
| Cerebrovascular disorder | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
| Liver disease | 1 (2.5) | 1 (4.0) | 1.000 |
| Respiratory disease | 2 (5.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.691 |
| Penetrating injury | 2 (5.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.691 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 117.5 ± 32.3 | 98.6 ± 34.8 | 0.030 |
| ISS | 14.9 ± 9.1 | 20.0 ± 8.7 | 0.030 |
| AIS1 | 0.6 ± 1.3 | 0.9 ± 1.2 | 0.382 |
| AIS2 | 0.3 ± 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 0.236 |
| AIS3 | 1.6 ± 1.5 | 2.3 ± 1.5 | 0.067 |
| AIS4 | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 0.635 |
| AIS5 | 1.0 ± 1.5 | 1.2 ± 1.7 | 0.591 |
| AIS6 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 0.6 ± 0.7 | 0.678 |
| Initial laboratory findings | |||
| DNI (%) | 2.1 ± 2.2 | 3.0 ± 3.2 | 0.201 |
| WBC (X3) (109/L) | 14.4 ± 4.7 | 15.0 ± 9.2 | 0.757 |
| Neutrophil (X3) (109/L) | 11.9 ± 4.2 | 12.4 ± 8.8 | 0.801 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.8 ± 1.8 | 11.4 ± 2.3 | 0.008 |
| Platelet (X3) (109/L) | 234.1 ± 111.5 | 192.6 ± 64.1 | 0.062 |
| INR | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.140 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 2.2 | 1.9 ± 5.9 | 0.477 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 3.0 ± 2.4 | 4.4 ± 3.2 | 0.054 |
| Procedure | 0.148 | ||
| Observation only | 22 (55.0) | 19 (76.0) | |
| Angioembolization | 3 (7.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Surgery | 15 (37.5) | 6 (24.0) | |
| Worst SOFA score | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 5.0 ± 3.0 | <0.001 |
| RBC transfusion ≤ 24 h | 1.8 ± 4.0 | 4.3 ± 5.3 | 0.037 |
| Hospital LOS | 19.9 ± 21.1 | 28.7 ± 22.5 | 0.118 |
| ICU LOS | 6.6 ± 11.0 | 7.8 ± 6.1 | 0.590 |
| Mortality | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.0%) | 0.811 |
| Day 0 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SmtDNAcn (copies/μL) | No AKI | 1114.7 ± 1996.2 | 1749.3 ± 3902.5 | 1024.7 ± 1207.5 | 1644.9 ± 1886.8 |
| AKI | 1594.5 ± 2341.6 | 677.3 ± 811.3 | 3567.3 ± 7328.4 | 2401.7 ± 3524.4 | |
| p-value | 0.381 | 0.154 | 0.140 | 0.387 | |
| UmtDNAcn (copies/μL) | No AKI | 1896.8 ± 2476.8 | 3482.4 ± 12,126.2 | 2472.2 ± 7167.9 | 3265.6 ± 12,817.8 |
| AKI | 3574.5 ± 3096.5 | 6040.7 ± 11,803.0 | 1106.4 ± 1371.5 | 5747.6 ± 22,591.1 | |
| p-value | 0.019 | 0.428 | 0.287 | 0.643 | |
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.70553 | 0.53281–0.93424 | 0.014 |
| Urine mitochondrial DNA copy number (copies/μL) | 1.00022 | 1.00002–1.00042 | 0.033 |
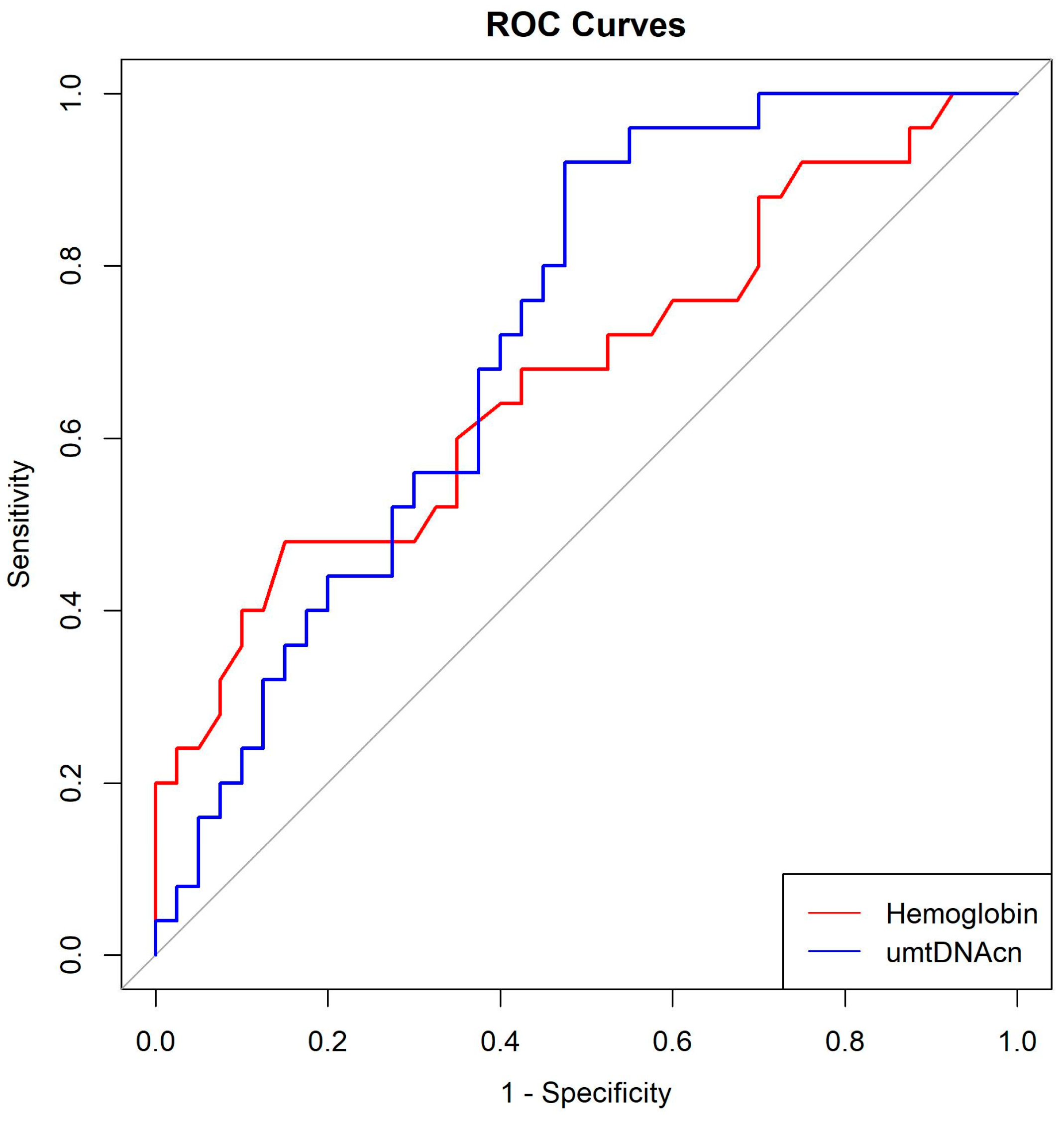
| AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Optimal Cut-Off Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.6735 | 0.48 | 0.850 | 10.9500 |
| Urine mitochondrial DNA copy number (copies/μL) | 0.7200 | 0.92 | 0.525 | 738.0013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, I.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.K.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, K. Biomarkers to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Trauma. Medicina 2025, 61, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101853
Shin IS, Kim MJ, Kim DK, Sohn JH, Kim K. Biomarkers to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Trauma. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101853
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, In Sik, Myoung Jun Kim, Da Kyung Kim, Joon Hyeong Sohn, and Kwangmin Kim. 2025. "Biomarkers to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Trauma" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101853
APA StyleShin, I. S., Kim, M. J., Kim, D. K., Sohn, J. H., & Kim, K. (2025). Biomarkers to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Trauma. Medicina, 61(10), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101853






