The Prognostic Immune and Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Baseline Clinical Characteristics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Study Participants
3.2. Cox Regression Analysis for Predictors of Overall Survival
3.3. Nomogram Derived from the FM to Predict 3- and 5-Year Survival
3.4. Model Comparison for Survival Prediction: FM vs. IM vs. BM
3.5. PINI vs. Established Biomarkers: Model Discrimination for Survival Outcomes
3.6. Factors Affecting the PINI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALB | Albumin |
| ALC | Absolute lymphocyte count |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AMC | Absolute monocyte count |
| ANC | Absolute neutrophil count |
| ASA | American society of anesthesiologists physical status |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CALLY | CRP-albumin-lymphocyte |
| C-index | Concordance index |
| cNRI | Continuous net reclassification improvement |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DCA | Decision curve analysis |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| FP | Fractional polynomial |
| HALP | Hemoglobin-albumin-lymphocyte-platelet |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| iAUC | Integrated AUC |
| IDI | Integrated discrimination improvement |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LASSO | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| LMR | Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| MCH | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin |
| MCHC | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration |
| MCV | Mean corpuscular volume |
| mSLI | Modified Shine–Lal index |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PINI | Prognostic immune and nutritional index |
| PL | Pleural invasion |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PNI | Prognostic nutritional index |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
References
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, D. Global burden of lung cancer in 2022 and projections to 2050: Incidence and mortality estimates from globocan. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 93, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majem, M.; Juan, O.; Insa, A.; Reguart, N.; Trigo, J.M.; Carcereny, E.; García-Campelo, R.; García, Y.; Guirado, M.; Provencio, M. Seom clinical guidelines for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (2018). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansky, K.; Detterbeck, F.C.; Nicholson, A.G.; Rusch, V.W.; Vallières, E.; Groome, P.; Kennedy, C.; Krasnik, M.; Peake, M.; Shemanski, L.; et al. The iaslc lung cancer staging project: External validation of the revision of the tnm stage groupings in the eighth edition of the tnm classification of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The iaslc lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the tnm stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the tnm classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, V.P.; Gonen, M.; Smith, J.J.; DeMatteo, R.P. Nomograms in oncology: More than meets the eye. Lancet. Oncol. 2015, 16, e173–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñate-Ocaña, L.F.; Aiello-Crocifoglio, V.; Gallardo-Rincón, D.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Brom-Valladares, R.; Carrillo, J.F.; Cervera, E.; Mohar-Betancourt, A. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ruan, G.T.; Liu, T.; Xie, H.L.; Ge, Y.Z.; Song, M.M.; Deng, L.; Shi, H.P. The value of crp-albumin-lymphocyte index (cally index) as a prognostic biomarker in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Sezaki, R.; Shinohara, H. Significance of preoperative evaluation of modified advanced lung cancer inflammation index for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2024, 72, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K.; Takamori, S.; Matsubara, T.; Haratake, N.; Akamine, T.; Kinoshita, F.; Ono, Y.; Wakasu, S.; Tanaka, K.; Oku, Y.; et al. Clinical significance of preoperative inflammatory markers in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A multicenter retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; Evison, M.; Michael, S.; Obale, E.; Fritsch, N.C.; Abah, U.; Smith, M.; Martin, G.P.; Shackcloth, M.; Granato, F.; et al. Pre-operative measures of systemic inflammation predict survival after surgery for primary lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 25, 460–467.e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellini, B.; Chaudhuri, A.A. Circulating tumor DNA minimal residual disease detection of non-small-cell lung cancer treated with curative intent. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balata, H.; Foden, P.; Edwards, T.; Chaturvedi, A.; Elshafi, M.; Tempowski, A.; Teng, B.; Whittemore, P.; Blyth, K.G.; Kidd, A.; et al. Predicting survival following surgical resection of lung cancer using clinical and pathological variables: The development and validation of the lnc-path score. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaitis, M.W.; Furnary, A.P.; Kosinski, A.S.; Kim, S.; Boffa, D.; Tong, B.C.; Cowper, P.; Jacobs, J.P.; Wright, C.D.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; et al. Prediction of long-term survival after lung cancer surgery for elderly patients in the society of thoracic surgeons general thoracic surgery database. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Shimuzu, T.; Tomita, M.; Ayabe, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Onitsuka, T. Preoperative serum C-reactive protein level in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2007, 27, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Motono, N.; Mizoguchi, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwai, S.; Iijima, Y.; Uramoto, H. Prognostic impact of cancer inflammation prognostic index for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung 2023, 201, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, M.; Shimizu, T.; Hara, M.; Ayabe, T.; Onitsuka, T. Preoperative leukocytosis, anemia and thrombocytosis are associated with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2009, 29, 2687–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.H.; Hao, J.; Shivakumar, M.; Nam, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.J.; Ryoo, S.B.; Choe, E.K.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, K.J.; et al. Development and validation of a novel strong prognostic index for colon cancer through a robust combination of laboratory features for systemic inflammation: A prognostic immune nutritional index. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wei, L.; Liu, M.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, X.; Tang, S.; Gan, J. Prognostic significance of preoperative prognostic immune and nutritional index in patients with stage i–iii colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibutani, M.; Kashiwagi, S.; Fukuoka, T.; Iseki, Y.; Kasashima, H.; Maeda, K. Significance of the prognostic immune and nutritional index in patients with stage i–iii colorectal cancer. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2023, 3, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Eo, W.; Lee, S. Prognostic immune and nutritional index as a predictor of survival in patients undergoing curative-intent resection for gastric cancer. Medicina 2025, 61, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Yonei, A.; Ayabe, T.; Tomita, M.; Nakamura, K.; Onitsuka, T. Postoperative serum c-reactive protein levels in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 16, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Alifano, M.; Falcoz, P.E.; Seegers, V.; Roche, N.; Schussler, O.; Younes, M.; Antonacci, F.; Forgez, P.; Dechartres, A.; Massard, G.; et al. Preresection serum c-reactive protein measurement and survival among patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Hamanaka, K.; Koizumi, T.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Terada, Y.; Nakamura, D.; Kumeda, H.; Agatsuma, H.; Hyogotani, A.; Kawakami, S.; et al. Clinical significance of preoperative serum albumin level for prognosis in surgically resected patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Comparative study of normal lung, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, O.; Avci, N.; Oktay, E.; Kalemci, S.; Pilanci, K.N.; Cokmert, S.; Menekse, S.; Kocar, M.; Sen, C.A.; Akman, T.; et al. Pretreatment serum albumin level is an independent prognostic factor in patients with stage iiib non-small cell lung cancer: A study of the turkish descriptive oncological researches group. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 5971–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Ikeo, S.; Morita, M.; Sone, N.; Niwa, T.; Nishiyama, A.; Yokoyama, T.; Sekine, A.; Ogura, T.; et al. Serum albumin level as a potential marker for deciding chemotherapy or best supportive care in elderly, advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with poor performance status. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, M.; Caro, A.A.; Raes, G.; Laoui, D. Systemic reprogramming of monocytes in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, J.; Gong, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, G.M.; et al. Ccl2/ccr2 pathway mediates recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells to cancers. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, L.; Pollard, J.W. Targeting macrophages: Therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, S.; Wirsik, N.M.; Kalkum, E.; Seide, S.E.; Nienhüser, H.; Müller, B.; Billeter, A.; Büchler, M.W.; Schmidt, T.; Probst, P. Systematic review of prognostic role of blood cell ratios in patients with gastric cancer undergoing surgery. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Eo, W.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.J. Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as a determinant of survival in patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy: A cohort study. Medicine 2023, 102, e33930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, W.K.; Jeong, D.W.; Chang, H.J.; Won, K.Y.; Choi, S.I.; Kim, S.H.; Chun, S.W.; Oh, Y.L.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, Y.O.; et al. Absolute monocyte and lymphocyte count prognostic score for patients with gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, H.; Yegen, S.C. Is systemic inflammatory response index (siri) a reliable tool for prognosis of gastric cancer patients without neoadjuvant therapy? Cureus 2023, 15, e36597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Eo, W.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S. Prognostic value of the noble and underwood score in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing surgical resection. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 6185–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.J.; Hur, J.Y.; Eo, W.; An, S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S. Clinical significance of c-reactive protein to lymphocyte count ratio as a prognostic factor for survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing curative surgical resection. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4497–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, W.K.; Chang, H.J.; Suh, J.; Ahn, J.; Shin, J.; Hur, J.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S. The prognostic nutritional index predicts survival and identifies aggressiveness of gastric cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D. The 2015 who classification of lung tumors. Pathologe 2014, 35 (Suppl. 2), 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Boffa, D.J.; Kim, A.W.; Tanoue, L.T. The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest 2017, 151, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanek, P.; Wittekind, C. The pathologist and the residual tumor (R) classification. Pathol. Res. Pract. 1994, 190, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriagada, R.; Bergman, B.; Dunant, A.; Le Chevalier, T.; Pignon, J.P.; Vansteenkiste, J. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, A.; Yoshida, J.; Miyaoka, E.; Asamura, H.; Fujii, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Mori, M.; Sawabata, N.; Okumura, M.; et al. Visceral pleural invasion classification in non-small-cell lung cancer in the 7th edition of the tumor, node, metastasis classification for lung cancer: Validation analysis based on a large-scale nationwide database. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Seishima, R.; Matsui, S.; Shigeta, K.; Okabayashi, K.; Kitagawa, Y. The prognostic impact of preoperative mean corpuscular volume in colorectal cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 52, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Eo, W.; Lee, S. Prognostic significance of modified shine and lal index in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing surgical resection. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.; Goodall, A.H. Studies on mean platelet volume (mpv)—New editorial policy. Platelets 2016, 27, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noris, P.; Melazzini, F.; Balduini, C.L. New roles for mean platelet volume measurement in the clinical practice? Platelets 2016, 27, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Fang, J.; Lee, D.S. Using fractional polynomials and restricted cubic splines to model non-proportional hazards or time-varying covariate effects in the cox regression model. Stat. Med. 2022, 41, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Cook, N.R.; Gerds, T.; Gonen, M.; Obuchowski, N.; Pencina, M.J.; Kattan, M.W. Assessing the performance of prediction models: A framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kyriss, T.; Dippon, J.; Hansen, M.; Boedeker, E.; Friedel, G. American society of anesthesiologists physical status facilitates risk stratification of elderly patients undergoing thoracoscopic lobectomy. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhang, T.; Ma, H.; Sui, P.; Du, J. Lower mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration is associated with unfavorable prognosis of resected lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Clinical significance of mean corpuscular volume as a prognostic indicator of radiotherapy for locally advanced lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 4916–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Qiao, H. Identification of prognostic nutritional index as a reliable prognostic indicator for advanced lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1213255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, F.; Takeoka, H.; Kozuma, Y.; Toyokawa, G.; Yamazaki, K.; Ichiki, M.; Takeo, S. Pretreatment prognostic nutritional index as a novel biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Lung Cancer 2019, 136, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Han, G.Y.; Eo, W.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S. Comparison of the geriatric nutritional risk index and the prognostic nutritional index in determining survival outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing surgical resection: A cohort study. Medicine 2022, 101, e31591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Niu, N.; Zhao, J.; Qi, W.; Xu, Y. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: A study based on the seer database and a Chinese cohort. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassir, N.; Chan, P.; Dang, S.; Bruno, R. External validation of a tumor growth inhibition-overall survival model in non-small-cell lung cancer based on atezolizumab studies using alectinib data. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2023, 92, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
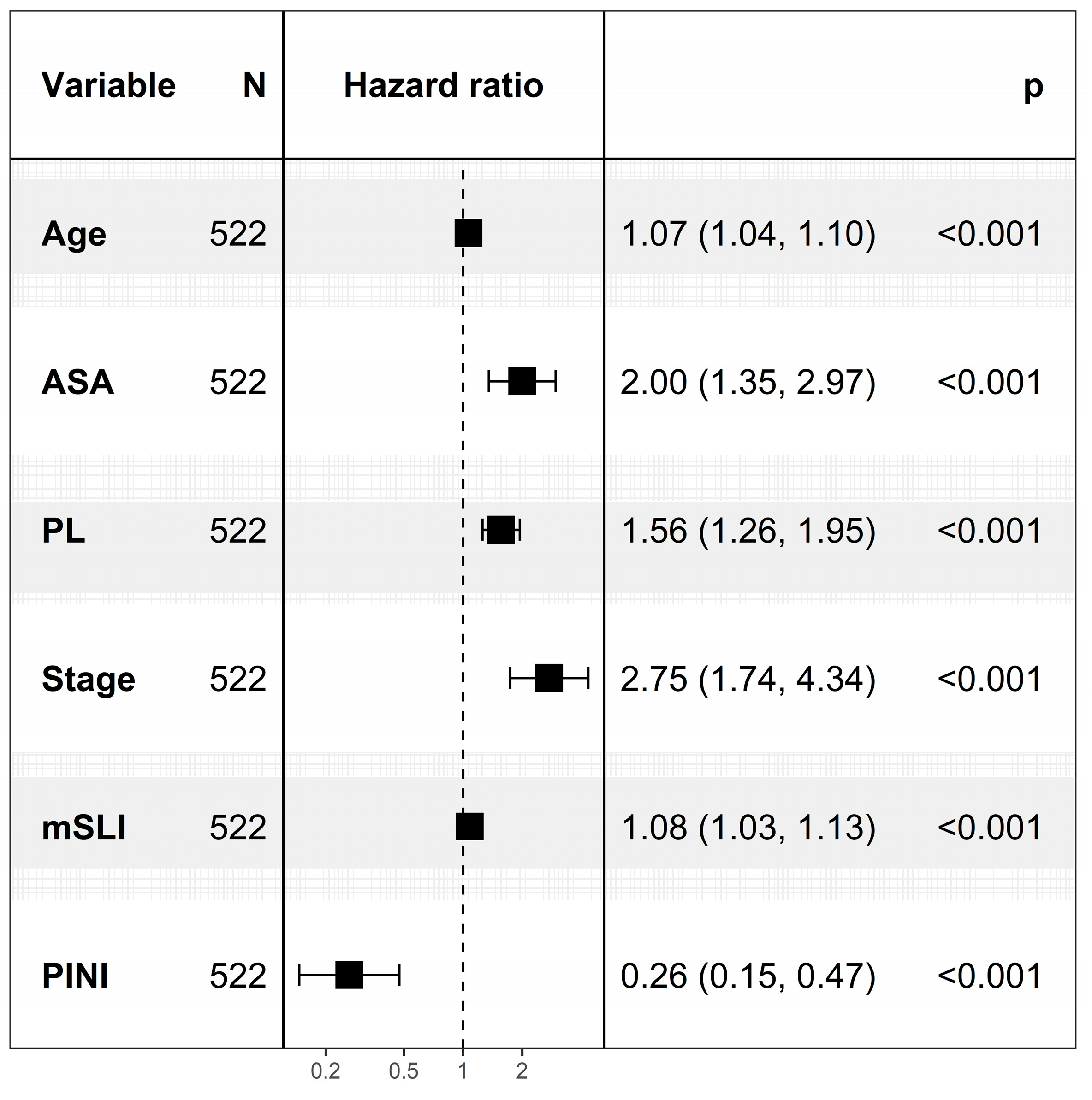





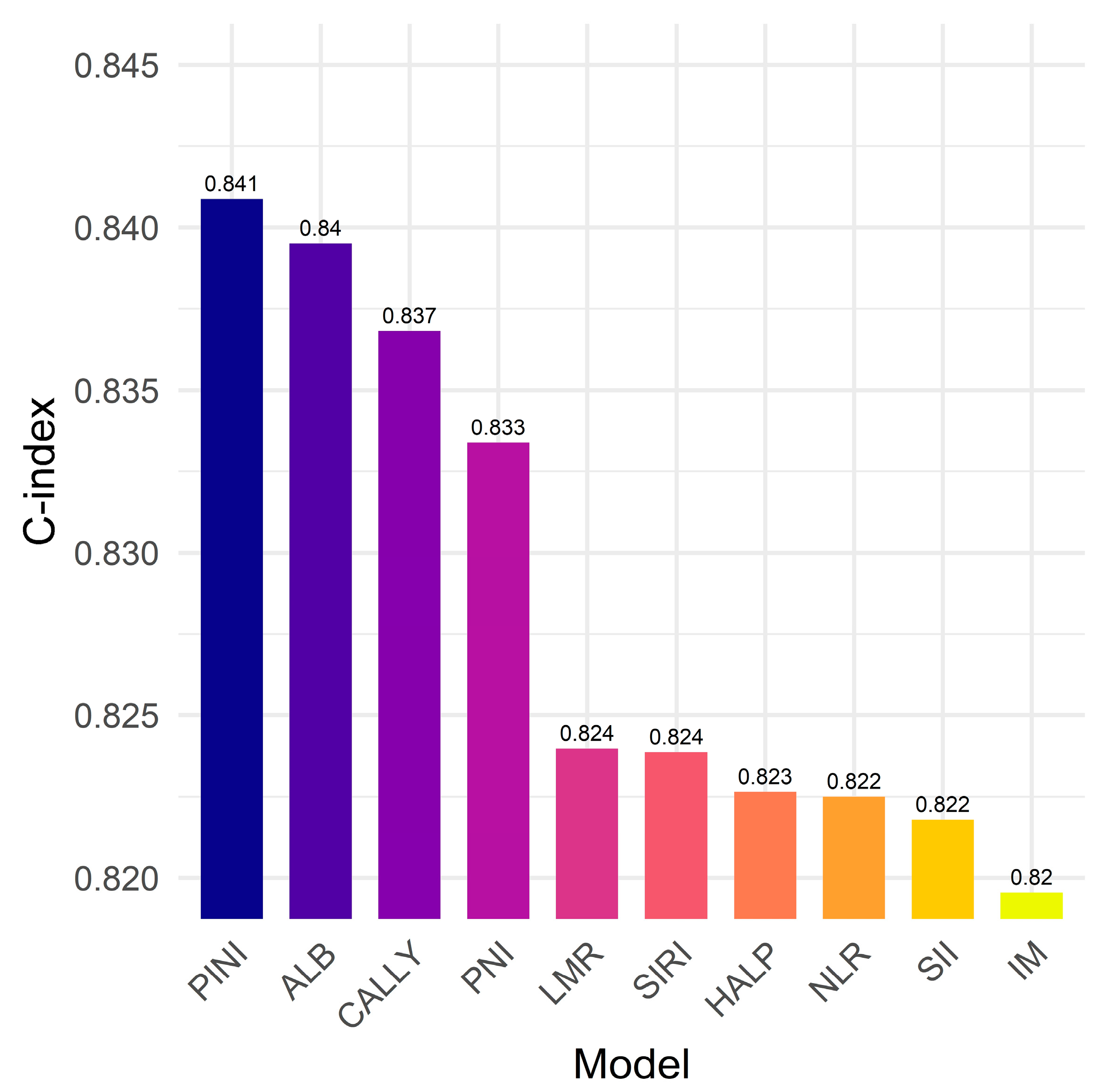
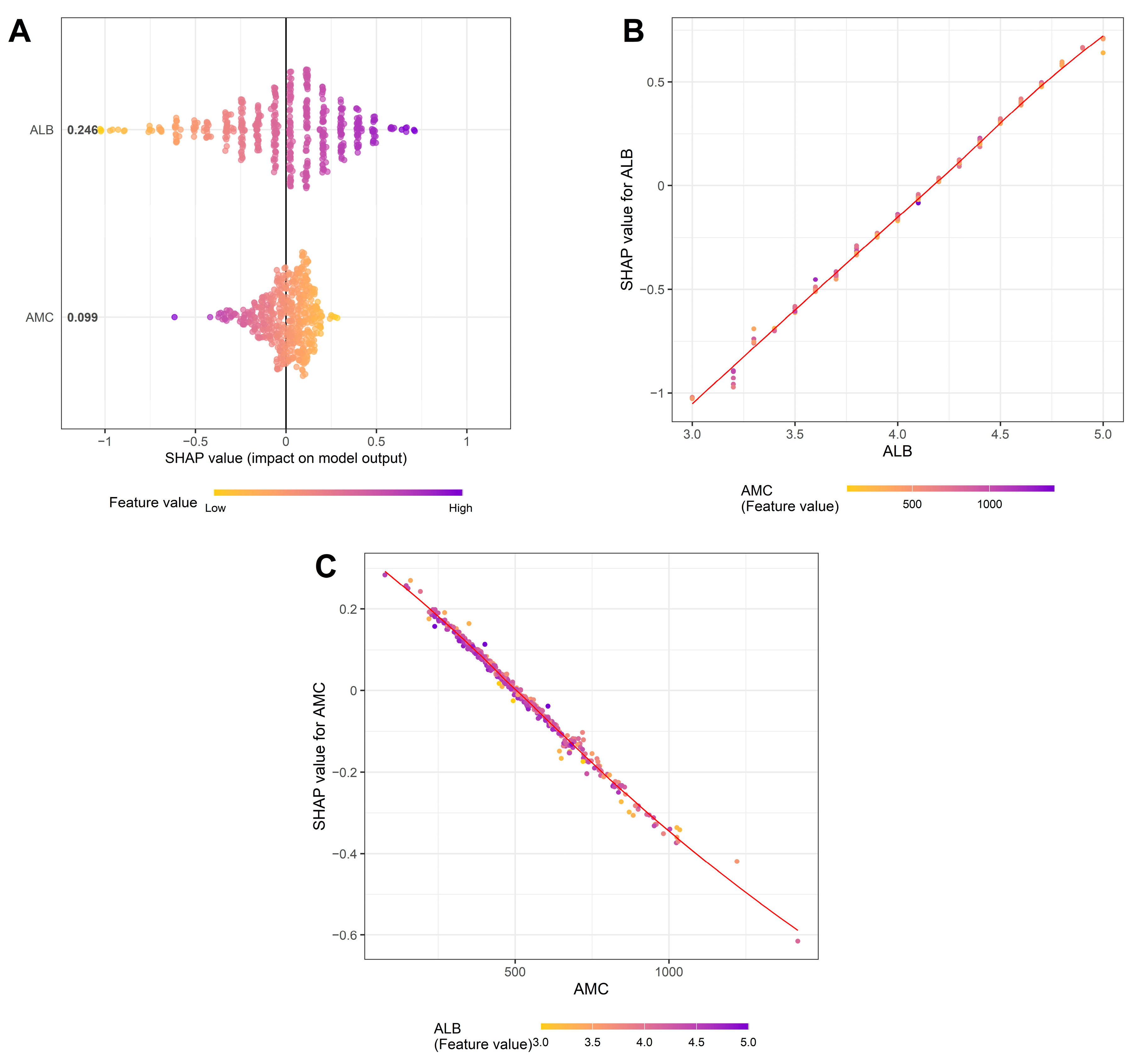
| Variables | N (%) or Median (IQR) | Variables | N (%) or Median (IQR) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 69.0 (62.0–74.0) | Vascular invasion | |||
| Sex | Yes | 28 (5.4%) | |||
| Men | 303 (58.0%) | No | 494 (94.6%) | ||
| Women | 219 (42.0%) | Perineural invasion | |||
| Smoking | Yes | 8 (1.5%) | |||
| Current/Past | 210 (40.2%) | No | 514 (98.5%) | ||
| Never | 312 (59.8%) | TNM stage | |||
| Alcohol consumption | IA/IB | 377 (72.2%) | |||
| Yes | 132 (25.3%) | IIA/IIB/IIIA | 145 (27.8%) | ||
| No | 390 (74.7%) | Protein, g/dL | 7.1 (6.8–7.5) | ||
| ASA-PS | Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 (4.0–4.4) | |||
| 1/2 | 428 (82.0%) | Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | ||
| 3/4 | 94 (18.0%) | AST, U/L | 22.0 (19.0–27.0) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.9 (21.9–26.2) | ALT, U/L | 17.0 (12.0–23.0) | ||
| Resection | CRP, mg/dL | 0.1 (0.1–0.3) | |||
| Sublobar resection | 194 (37.2%) | WBC, per μL | 6315.0 (5330.0–7460.0) | ||
| Lobectomy | 315 (60.3%) | ANC, per μL | 3622.0 (2920.0–4634.0) | ||
| Bilobectomy | 6 (1.1%) | AMC, per μL | 479.0 (382.0–610.0) | ||
| Pneumonectomy | 7 (1.3%) | ALC, per μL | 1831.5 (1532.0–2240.0) | ||
| Histology | RBC, ×106 per μL | 4.3 (3.9–4.6) | |||
| Squamous | 115 (22.0%) | Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.3 (12.1–14.2) | ||
| Non-squamous | 407 (78.0%) | MCV, fL | 91.8 (89.2–94.8) | ||
| Tumor size, cm | 2.5 (1.7–3.5) | MCH, g/dL | 30.9 (30.0–32.1) | ||
| Pleural invasion (PL) | MCHC, g/dL | 33.7 (33.1–34.3) | |||
| 0 | 417 (79.9%) | mSLI | 26.0 (24.1–28.8) | ||
| ≥1 | 105 (20.1%) | Platelet, ×103 per μL | 236.0 (202.0–278.0) | ||
| Lymphatic invasion | PINI | 3.4 (3.2–3.6) | |||
| Yes | 64 (12.3%) | ||||
| No | 458 (87.7%) | ||||
| Metrics | Improvement (FM vs. BM) | p Value (FM vs. BM) | Improvement (FM vs. IM) | p Value (FM vs. IM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-index | 0.153 (0.023) | <0.001 | 0.022 (0.012) | 0.012 |
| iAUC | 0.141 (0.009) | <0.001 | 0.013 (0.004) | 0.001 |
| IDI at 3 years | 0.252 (0.044) | <0.001 | 0.054 (0.024) | 0.008 |
| cNRI at 3 years | 0.502 (0.069) | <0.001 | 0.320 (0.088) | 0.020 |
| IDI at 5 years | 0.230 (0.042) | <0.001 | 0.039 (0.021) | 0.018 |
| cNRI at 5 years | 0.418 (0.068) | <0.001 | 0.238 (0.086) | 0.032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, S.; Kim, S.; Eo, W.; Lee, S. The Prognostic Immune and Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Medicina 2025, 61, 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101763
An S, Kim S, Eo W, Lee S. The Prognostic Immune and Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101763
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Soomin, Sehyun Kim, Wankyu Eo, and Sookyung Lee. 2025. "The Prognostic Immune and Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101763
APA StyleAn, S., Kim, S., Eo, W., & Lee, S. (2025). The Prognostic Immune and Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Medicina, 61(10), 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101763







