Abstract
Background and Objectives: Vision significantly contributes to postural control, balance, coordination, and body kinematics, thus deeply influencing everyday functionality. Sight-impaired subjects often show upper body anatomofunctional and kinetic chain alterations negatively impacting daily living efficiency and autonomy. The present study aimed to investigate and train, for the first time, upper body sensorimotor control in an Italian blind baseball team to boost global and segmental functionality while contemporarily prevent injuries. Materials and Methods: The whole team underwent a validated test battery using both quantitative traditional tools, such as goniometric active range of motion and muscular/functional tests, and an innovative biofeedback-based device, a Libra proprioceptive board. Consequently, a 6-week adapted training protocol was designed and leaded to improve sensorimotor control and, hence, counteract disability-related deficits and sport-specific overuse syndromes. Results: Statistically significant improvements were observed in all the investigated parameters. Noteworthy, an overall boost of global and segmental stability was detected through an orthostatic dynamic balance enhancement during the Y Balance test (p = 0.01) and trunk multiplanar control improvement on the Libra board (p = 0.01). Concurrently, the comparison of baseline vs. post-intervention outcomes revealed a consistent increase in upper body mobility (p < 0.05 for all the assessed districts), core recruitment (p = 0.01 for all the administered functional tests), and proprioceptive postural control (p = 0.01 for the Libra board validated test). Conclusions: Our findings suggest that a tailored sensorimotor training, conceived and led by an adapted physical activity kinesiologist, may effectively improve upper body functional prerequisites and global proprioceptive control, thus potentially promoting autonomy, quality of life, and physical activity/sport practice adherence in visually impaired individuals.
1. Introduction
Postural control requires a complex sensorimotor and cognitive input integration aimed to maintain balance and properly interact with the surrounding environment in response to external multimodal stimuli and perturbations [1,2,3]. Among these perceptual channels, vision plays a pivotal role in postural anchorage, spatial orientation, and movement accuracy, thus deeply conditioning daily living self-efficacy and autonomy [4,5]. Spatial representation through the selection and integration of multisensory signals is crucial to coherently perceive reality and interact with other individuals [6,7,8].
Vision, contemporarily providing spatial details and general background, deeply influences multisensory integration development and motivation/curiosity to explore the space-time dimension through movement during childhood [9,10,11,12]. In this regard, it has been demonstrated that the efficiency of multimodal interaction amongst different senses is mostly affected by perceptual and motor experiences during the aforementioned growth phase [13,14,15].
In case of early sight absence or loss, sensorimotor development delays and postural alterations may occur with a negative impact on stability, coordination, navigation, and socio-emotional wellbeing [9,16,17,18]. In this frame, even basic locomotor patterns become challenging tasks, hence increasing fall risk [19] and progressively discouraging self-engagement in recreational/sport activities, which triggers a vicious cycle toward sedentary habits able to jeopardize quality of life [20]. In order to perform daily living activities and sport practice safely and autonomously, visually impaired individuals count on vicariant senses, especially on the auditory and vestibular apparatus [21,22,23]. Both these sensory channels are anatomically located in the head, and therefore, head mobility and segmental control are essential to rapidly and efficiently respond to external stimuli without losing balance. Specifically, head–trunk separation is a sensorimotor development and visual anchorage-related skill and, consequently, upper body coordinative impairments are frequently detected in this target population [9,20,24,25,26]. Hip–trunk–head coordination allows the effective transfer of forces generated by lower body muscles along the total body kinetic chain underlying the main human motor patterns and balance control, which contributes to reducing joint overuse syndromes and injury risk [27,28,29]. Recent studies have highlighted the fact that trunk muscle strength and core stability/recruitment are associated with static and dynamic balance, daily living functional performance, and orientation skills in almost every age group, especially in visually impaired subjects [21,30,31,32]. Despite a remarkable lack of research specifically investigating this target population, it has been demonstrated that superior postural stability, gait efficiency, environmental mastery, and everyday functionality are directly related to higher levels of physical activity in those individuals [20,33,34,35]. Since visual input unavailability adversely affects kinesthesis abilities with consequent reduction in motor activity involvement and expertise of sight-impaired subjects [36,37], an intentional compensation/reeducation of these skills through targeted sensorimotor training protocols and regular sport practice are needed [21,38].
In this context, due to the performance model underlying the fundamental motor gestures and the multimodal input prevised by blind baseball (BXC) game dynamics and rules, such an adapted sport can significantly contribute to sensorimotor efficiency and quality of life improvement of regular practitioners [39,40]. As already detailed in our previous studies, the kinetic chain at the base of batting, running, and pitching requires finely orchestrated movements, muscle strength/power, proprioceptive postural control, global and segmental coordination, and sensory reactivity [21]. This blind-adapted discipline, conceived in Italy in the early 1990s, kept the dynamic features of the original sport played by sighted subjects, though introducing specific adaptations aimed to foster the safety and autonomy of disabled players during their athletic performance [41]. In particular, BXC players are driven by auditory and somatosensory input while performing all the above-mentioned technical gestures that involve complex cross-coordination skills and executive speed and, therefore, core recruitment and head–trunk separation become crucial for multisensory orientation and athletic efficiency during the game [21]. Batting and pitching gestures generally require a complex neuromuscular coordination and an effective sensorimotor timing/control to transfer ground reaction forces from the lower to upper body, thus conveying to the ball the maximal energy amount [42]. Within the kinetic chain on which these technical fundamentals are based, the swing movement represents the key ring, both for overload prevention and for athletic performance [43,44]. In sighted players, swing is mostly driven by visual input related to ball velocity or opponent batter running speed during the offensive and defensive phases of the game, respectively [45,46]. Conversely, in sight-impaired athletes, it primarily relies on proprioceptive information and involves upper body coordination/isolation patterns not naturally managed by those subjects. When consciously trained and acquired through a multimodal adapted approach, these motor skills can be easily transferred to daily life activities requiring multiplanar movements in the interaction with the tridimensional surrounding environment [21,39], hence counteracting disability-related deficits. Regarding BXC athletic performance, such prerequisites and motor abilities must be specifically trained during the whole sport season and especially boosted in the pre-season phase in order to prevent injuries and promote sport-specific body awareness and control [28,47,48].
On this basis, and taking advantage of the peculiar on-field expertise of our research team, the present study aimed to provide training methodological hints to improve the upper body sensorimotor control of visually impaired individuals through BXC anatomofunctional prerequisites and innovative workout tools. Among the latter, our investigation exploited a biofeedback-based proprioceptive tool (Libra sensorized board; Easytech, Borgo San Lorenzo, Florence, Italy) purposely designed to quantitatively assess postural control efficiency. The multisensory outputs provided by the digital interface allow the use of such an innovative device even in sight-impaired individuals, simply setting an auditory feedback instead of a visual one [21]. In addition, functional motor tests that are widely administered in healthy athletes were applied to reinforce the double aim, both re-educative and performative, of our proposal. Such a multiperspective tailored approach may help in boosting daily living functionality while contemporarily promoting sport practice and adherence in a non-medicalized enjoyable context in this vulnerable and under-investigated target population. In the wake of our previous studies addressing postural and motor control in visually impaired subjects [20,21], we expected that the proposed tailored training protocol could effectively improve the overall sensorimotor skills and the related anatomofunctional parameters in the investigated sample.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
The study participants included 8 visually impaired baseball players (mean ± SD age, 25.4 ± 9.1 years), 5 (62.5%) male and 3 (37.5%) female, from the Fiorentina BXC team regularly registered to Polisportiva Silvano Dani. In detail, 6 (75.0%) subjects were congenitally visually impaired while 2 (25.0%) had acquired vision loss. According to the Italian visual disability classification [49], blind and severely sight-impaired levels were the most equally represented categories (37.5%), followed by mildly sight-impaired (25.0%). Athletes were in possession of a valid sport medical certificate issued by a sports doctor, as mandatorily required by the Official Federation (FIBS), to take part in the regular competitive championship [41]. As commonly provided for Italian sport associations, in the act of renewing the annual membership to the team, each athlete signed informed consent and agreed to participate in the training and evaluation proposals promoted by the team management during the whole sport season. In such a perspective, with president’s approval, the training and evaluation protocol was conceived, supervised, and performed by the official technical staff of the team, specifically including the official adapted physical activity kinesiologist [21]. Since the sample consisted of a professional sport team whose athletes are regularly trained and measured at various stages of their competitive season, no formal approval by a properly constituted ethics committee was applicable. In agreement with the informed consent provided by all participants, the data were treated, processed, and stored in a completely anonymous form for the purposes of this study. The study was also performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki [50].
2.2. Participant Evaluations
Evaluation procedures were conducted before and after the ending of the adapted sensorimotor training (AST) protocol during the pre-season phase of the 2023 BXC regular championship, mostly applying validated quantitative tools, both traditional and innovative, to assess upper and lower body anatomofunctional prerequisites and global/segmental postural stability in the whole sample of visually impaired athletes.
All test batteries were performed strictly following the official guidelines available in the literature. Concerning the upper body, active range of motion (AROM) of the head was measured through the digital goniometer Easy Angle (Meloq AB, Stockholm, Sweden) in flexion, extension, bilateral rotation, and inclination movements [51]. Bilateral upper limb AROM was also assessed while performing flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and internal and external rotation movements. In addition, trunk AROM was evaluated during bilateral twist around the longitudinal axis, first placing the subject in a sitting and then in a half-kneeling position [51]. It has been demonstrated that such a digital goniometer meets the highest clinical standards and has an excellent reliability and validity compared to the widely used manual tools, allowing us to obtain fast, consistent, and accurate joint AROM data [52]. For the purpose of trunk functionality assessment, three out of the seven movement tasks prevised by the Functional Movement Screen (FMS™) test were used [53]. In particular, trunk extensor/abdominal/lateral muscle endurance tests were performed and estimated by measuring, in seconds, the skill of maintaining the specific isometric position without any postural compensation. Recently, it has been demonstrated that this widely applied screening test may be considered a valid and reliable tool for global and district functional assessment of athletes [54,55]. Furthermore, upper body sensorimotor stability was investigated and quantified through the Libra sensorized proprioceptive board, an innovative biofeedback-based tool previously described and applied in our recent studies [21,56]. In the context of the present investigation, Libra was leant on a wood jump box and the subject was asked to sit over it, keeping their arms crossed over their chest, with a 90° trunk–thigh angle and both legs orthogonal to the ground with feet on a skimmy proprioceptive cushion placed on the floor. Starting from this body attitude, two tests were performed, the first with the device straight-oriented and the second one transverse-oriented, thus allowing the board to tilt on frontal and sagittal plane, respectively. Setting the aforementioned board orientation allowed us to investigate trunk lateral and antero-posterior stability. During both 1 min tests, a linear pathway pattern, a maximum 10/10 difficulty level, and 10 cm tilting wedges were set (Figure 1), while the aim was to keep Libra in balance, parallel to the floor, following the auditory feedback provided by the software. In order to obtain reliable values, the validated performance index prevised by the manufacturer was recorded at the end of each test. Specifically, it is calculated by the digital interface through the weighted average of eight values and must be interpreted referring to the validated 0–100 preset cut-off; lower values correspond to a better sensorimotor control.
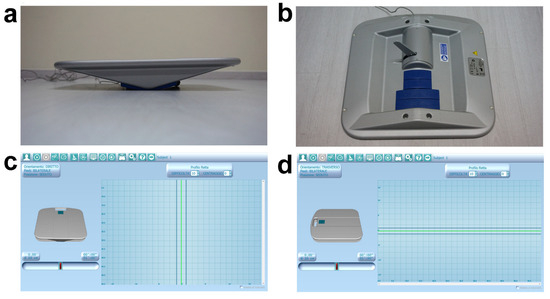
Figure 1.
Libra sensorized proprioceptive board. (a) Adjustable tilting radius. (b) Sensorized arm and interchangeable tilting wedges. (c,d) Digital interface and board settings during lateral (c) and antero-posterior (d) trunk stability test.
Regarding lower body district, the Thomas test was preliminarily performed to detect eventual lower limb anterior muscle chain retractions [57,58]; of note, no muscular deficits were observed in the whole sample. Additionally, bilateral hip goniometric AROM during internal and external rotation movements [51] were measured, as well as posterior muscle chain flexibility, through the well-known and validated sit-and-reach test [59]. Since orthostatic postural control plays a key role in daily living and sport functionality, the Libra Spielman-De Gunsch (SDG) test and the Y Balance test were also administered. This latter allows us to easily evaluate lower limb stability and functional symmetry through monopodalic multidirectional balance tasks performed following the three branches of a Y pattern drawn on the floor using a paper tape [60,61]. The subject, barefoot and placed in orthostatic position on the pivotal point of the Y with hands firmly on hips, was asked to keep monopodalic balance on the stance leg while sliding the controlateral foot as far as possible, subsequently following the different lines/directions of the drawn pattern. The required movement task must be executed by each lower limb following this mandatory direction order: right anterior, right posteromedial, left posteromedial, right posterolateral, and left posterolateral. Each monopodalic task was repeated for a total of three correct attempts; at the end of the whole test, the average achieved distance was recorded for each lower limb [60,61]. Since the sample consisted of visually impaired individuals, verbal explanation of the tasks followed by tactile exploration of the pathway were provided before performing the test. Finally, the SDG validated test was administered using the Libra sensorized proprioceptive board (Figure 1a,b) [62]. Such quantitative assessment has been purposely conceived to evaluate postural stability with respect to three different visual conditions, namely no gaze constraints, fixed gaze, and closed eyes. In case of sight-impaired subjects, the test can still be used simply applying head coordinative constraints (i.e., no head position constraint, straight head position constraint, and closed eyes). In detail, the SDG test previses three tasks of 30 s each with 25 s of recovery and repositioning in between, presetting a linear pathway pattern, a 9/10 difficulty level, and 10 cm tilting wedges. The subject, in orthostatic bipodalic stance, was asked to keep the board in balance, parallel to the floor, following the auditory feedback provided by the software. At the end of the whole test, the stability index obtained in each trial can be compared to the 0–100 cut-off values available in the digital database. Notably, lower scores correspond to higher postural stability.
2.3. Adapted Sensorimotor Training
The tailored training intervention was carried out on the whole Fiorentina BXC team during the pre-season stage of a regular sport season. Specifically, it was designed as two indoor 60 min workout sessions per week scheduled on non-consecutive days for a total protocol length of six weeks, from February to March 2023. The main objectives of our AST concerned trunk–head–pelvis coordination/separation, trunk stability and flexibility as well as global and segmental proprioceptive postural control. In order to improve these anatomofunctional prerequisites and sensorimotor skills contemporarily, respecting subjective fitness level and visual disability-related needs, a circuit training methodology was applied. As already reported in our previous studies addressing this target population, such an execution time-based methodological approach allows us to safely and individually adjust training load and to optimize communication and leading while taking advantage from the socio-emotional and motivational benefits of collective workout [20,21]. In detail, each training session was organized in three main phases, namely total body warm up, sensorimotor circuit training, and cool down. The first phase comprised aerobic activation through functional exercises such as skips, jumping jacks, burpees, squats, and push-ups along with breathing exercises with combined upper limb movements and upper body-focused dynamic stretching. The central phase consisted of an 8-station circuit training involving 2 min of work on each station for a total of two complete circuit rounds with no recovery between them. Particularly, exercises were focused on spine mobility on different anatomical planes, paravertebral and interscapular muscle strength/flexibility improvement, shoulder active mobility, anticipatory and reactive postural control, and core stability/endurance/recruitment. The third and final phase of each session was dedicated to total body static and dynamic stretching and breathing awareness, specifically focused on upper body muscle contraction/relaxation and diaphragm recruitment. Workout load was progressively increased by varying exercise executive positions, starting from unloaded ones until reaching BXC-specific body attitudes, introducing coordinative constraints and unstable surfaces (i.e., proprioceptive board, skimmy and hedgehog balance cushions, foam pad and fitball) and using small fitness tools such as sticks, elastic bands, ankle/wrist weights, light kettlebells, and dumbbells. In order to clearly summarize the training protocol design, an example workout session organization is graphically shown in Figure 2.
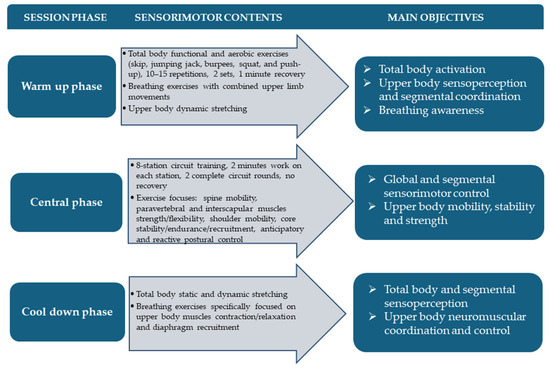
Figure 2.
Adapted sensorimotor training organization.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All data are represented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), or number/percentage of subjects. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare the baseline vs. post-adapted sensorimotor training (AST) intervention scores after verifying the normality of data with a Shapiro–Wilk test. The effect size of the comparisons (r) with 95% confidence interval was also determined. Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS version 29.0 (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical power was calculated with G*Power software (Version 3.1.9.7, Düsseldorf, Germany; online at http://www.psychologie.hhu.de/arbeitsgruppen/allgemeine-psychologie-und-arbeitspsychologie/gpower; accessed on 10 July 2024) [63]. The combined set of baseline and post-AST intervention variables provided a power of >80% for all comparisons.
3. Results
Results concerning the anatomofunctional assessment of upper body parameters at baseline and after ending the structured AST protocol are reported in Table 1. In detail, AROM values of head showed a post-intervention statistically significant improvement in flexion and extension, as well as in bilateral inclination and rotation movements (Table 1). Similarly, significant improvement in bilateral upper limb AROM was observed (Table 1). In addition, trunk AROM during right/left sitting and half-kneeling twist was significantly increased following the specific AST program (Table 1). Likewise, the trunk stability index, assessed by the sensorized Libra board on both the frontal and sagittal planes, resulted in significantly improved values (Table 1). Finally, core stability and recruitment, evaluated by the extensor/abdominal/lateral muscle isometric strength test, showed a statistically significant increase in all average scores (Table 1).

Table 1.
Anatomofunctional assessment of upper body parameters at baseline and post-AST protocol.
Table 2 shows the results of anatomofunctional assessment of lower body parameters at baseline and post-AST protocol. In particular, the posterior muscle chain flexibility, measured by the sit-and-reach test, was significantly increased following the specific AST program (Table 2). Moreover, bilateral hip AROM values showed also a statistically significant improvement at post-intervention respect to baseline in both external and internal rotation movements (Table 2).

Table 2.
Anatomofunctional assessment of lower body parameters at baseline and post-AST protocol.
Table 3 presents the data of postural stability, assessed either by Libra SDG or Y Balance test to provide an accurate assessment of the postural control quality, before and after the AST program in the study group. A statistically significant increase in all the postural stability test scores was observed (Table 3).

Table 3.
Mean scores of postural stability assessment at baseline and post-AST protocol.
4. Discussion
Research investigating sensorimotor control has often been focused on lower limb stability, given that the human body can be compared to an inverted pendulum with the ankles acting like a fulcrum [1,64]. However, since postural control efficiency is based on multisensory integration of the input provided by different perceptual channels, mainly located in the upper body [65,66,67], understanding the contribution of this anatomical district to such complex skills might be crucial to improving daily living functionality [68,69]. Despite the fact that it is well-known that vision significantly contributes to control/stability of trunk and upper extremities, existing literature on this topic in visually impaired individuals is still scarce [70].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study investigating upper body sensorimotor control in this target population through validated quantitative tools. By integrating BXC technical prerequisites within the herein-described AST intervention, we aimed to boost everyday functionality and autonomy, contemporarily preventing sport injuries and psychophysical overload [56]. The statistically significant results obtained in all the investigated parameters highlighted the preventive, re-educative, and training benefits of a tailored sensorimotor protocol on upper body functionality in physically active sight-impaired subjects. In particular, post-intervention trunk mobility/stability enhancement, detected through goniometric AROM and Libra proprioceptive board, might be strongly linked to core muscle recruitment and posterior muscle chain flexibility improvement observed in the FMS tasks and sit-and-reach test, respectively. The core includes trunk and pelvis muscles responsible for spine stability maintenance and force generation/transfer from large to small body districts during all human movements [71,72]. Furthermore, it connects upper and lower extremities via the abdominal fascial system, hence assuming not only a stabilizing but also a mobilizing function [73,74,75]. For such reasons, our AST protocol expressly focused on core recruitment and strengthening, also combined with upper and lower limb motion and unstable surface utilization [76,77,78], since it represents the fulcrum of the whole-body functional kinetic chain. Literature has repeatedly evidenced the importance of the core in optimizing force control and minimizing upper and lower body injuries, especially in overhead athletes [79,80]. Therefore, applying not only conventional but also sport-specific positions during the proposed workout tasks allowed subjects to easily transfer the acquired sensorimotor skills to BXC practice, thus preventing musculoskeletal overuse onset and improving the overall athletic performance.
The purposely designed exercises focused on upper body sensoperception and reactivity to external perturbations, as well as breathing awareness [81], might have effectively contributed to achieving our post-intervention positive findings regarding trunk stability and mobility [21,56,82]. It has been demonstrated that balance performance and trunk neuromuscular reactivity in sitting position may be considered reliable core stability and global functionality indicators [72,73,83]. In this perspective, such complex skills have been investigated by applying sensorimotor sitting tasks performed on the Libra proprioceptive board, which allowed us to test them in a multisensory and dynamic real context [62]. The post-intervention improvement in trunk sitting twist AROM and Libra performance index, on both the frontal and sagittal planes, highlighted the effectiveness of multimodal and unstable/tilting tools in boosting upper body sensorimotor control and core recruitment in visually impaired individuals [20,84,85]. Specifically, the biofeedback-based technology offered by the Libra digital interface provides high frequency real-time feedback by transducing specific functional parameters into multisensory signals. Such technology allows us to consciously perceive and progressively control the micromovements of the whole body or its segments, hence improving anticipatory/reactive sensorimotor control and motor learning processes [56]. Sensorized proprioceptive devices such as the Libra board also allow us to quantitatively evaluate the subjective motor skills, thus facilitating the workout load customization [86]. Moreover, introducing specific coordinative constraints and promoting proprioceptive postural control during complex and dynamic motor tasks can effectively counteract disability-related head–trunk–pelvis coordination deficits and upper body stiffness [21,87,88,89], as demonstrated by the statistically significant post-protocol SDG test outcomes and head, upper limb, and hip mobility values. Since hip AROM highly contributes to body load management during orthostatic motor tasks [90,91,92], the observed improvement may be also related to dynamic balance improvement detected at post-intervention through the Y Balance test. Regarding this evaluation tool, it is noteworthy that our AST effectively increased not only global postural control but also lower limb functional symmetry, consistently reducing right and left difference between the average distance achieved performing it [61].
The main limitations of the present investigation can be identified mainly in the small size of the sample and the shortness of the proposed AST protocol. Nonetheless, it is important to remark that adapted physical activity interventions for visually impaired subjects must be led in small groups in order to safeguard the disability-related needs and grant safety in this target population [20,21]. Moreover, given the BXC-specific frame in which the study was carried out, it is important to remark that workout duration was set according to the pre-season phase length of a regular championship. Even though they refer to a small sample, all these encouraging short-term obtained results may represent a promising innovative approach to effectively testing and training this vulnerable demographic of individuals.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings suggest that a tailored AST intervention designed and leaded by a kinesiologist may effectively improve upper body anatomofunctional prerequisites and proprioceptive postural control in sight-impaired subjects. We are confident that the present study could help spreading research interest and easily reproducible methodological hints to be applied to this under-investigated population [35] in order to improve global and segmental functionality. Moreover, combining and integrating re-educative and sport-inspired perspectives could help in counteracting the disability-related multidimensional deficits while fostering regular physical engagement in a non-medicalized enjoyable context [20]. Indeed, the evaluative procedures detailed in the present study highlight the growing necessity of both adapting validated tools and designing innovative ones to objectively and safely investigate visually impaired individuals, hence not limiting research to clinical and rehabilitation contexts [20,93].
Finally, given the growing athletic performance levels required of BXC players, as a future perspective, our study could help foster the necessity of applying an evidence-based workout programming. In fact, such a kinesiologist-led approach could effectively and safely adjust methodological and motor contents to the different sport season phases and each team’s peculiarities [21].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); methodology, G.C., F.S. and M.M. (Mirca Marini); formal analysis, G.C., E.S., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); investigation, G.C., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); data curation, G.C. and M.M. (Mirca Marini); visualization, G.C., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); writing—original draft preparation, G.C., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); writing—review and editing, G.C., F.S., E.S., M.M. (Mirko Manetti) and M.M. (Mirca Marini); supervision, M.M. (Mirca Marini). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Athletes were in possession of a valid sport medical certificate issued by a sports doctor as mandatorily required by the Official Federation (FIBS) to take part in the regular competitive championship. In addition, in the act of renewing the annual membership to the team, each athlete signed informed consent and agreed to participate in the training and evaluation proposals promoted by the Polisportiva Silvano Dani team management during the sport season. With such a perspective, the training and evaluation protocol was conceived, supervised, and performed by the official technical staff of the team after receiving the president’s approval. Since the sample consisted of a professional sport team whose athletes are regularly trained and measured at various stages of their competitive season, no formal approval by a properly constituted ethics committee was applicable. The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. For the purposes of this study, the data were treated and processed in a completely anonymous form.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all the visually impaired BXC athletes involved in the study for their committed participation and Polisportiva Silvano Dani team management and technical staff.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human Postural Control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.M. Multisensory Integration in Balance Control. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 137, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterka, R.J. Sensory Integration for Human Balance Control. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, M.P.; Villeneuve, P. Interaction between Feet and Gaze in Postural Control. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarlegna, F.R.; Sainburg, R.L. The Roles of Vision and Proprioception in the Planning of Reaching Movements. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 629, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, X.; Arnold, G.; Kirsch, L.P.; Auvray, M. Vision Shapes Tactile Spatial Perspective Taking. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2021, 150, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, A.; Proulx, M.J. The Role of Visual Experience for the Neural Basis of Spatial Cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouilloud, A.; Kauffmann, L.; Roux-Sibilon, A.; Rossel, P.; Boucart, M.; Mermillod, M.; Peyrin, C. Rapid Scene Categorization: From Coarse Peripheral Vision to Fine Central Vision. Vis. Res. 2020, 170, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, D.; Bollini, A.; Gori, M. Early Blindness Limits the Head-Trunk Coordination Development for Horizontal Reorientation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 699312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.F. Eye Movements and the Control of Actions in Everyday Life. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2006, 25, 296–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, P. Auditory Spatial Perception without Vision. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, N.; Haibach-Beach, P.; Knöpfle, I.; Neuberger, V. The Effects of Visual Impairment on Motor Imagery in Children and Adolescents. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 109, 103835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haibach, P.S.; Wagner, M.O.; Lieberman, L.J. Determinants of Gross Motor Skill Performance in Children with Visual Impairments. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogge, A.-K.; Hamacher, D.; Cappagli, G.; Kuhne, L.; Hötting, K.; Zech, A.; Gori, M.; Röder, B. Balance, Gait, and Navigation Performance Are Related to Physical Exercise in Blind and Visually Impaired Children and Adolescents. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.O.; Haibach, P.S.; Lieberman, L.J. Gross Motor Skill Performance in Children with and without Visual Impairments--Research to Practice. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 3246–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.; Wagels, L.; Neuschaefer-Rube, C.; Fels, J.; Gur, R.E.; Konrad, K. The Cross-Modal Effects of Sensory Deprivation on Spatial and Temporal Processes in Vision and Audition: A Systematic Review on Behavioral and Neuroimaging Research since 2000. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, e9603469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, N.; Davies, F.; Jones, L.; Castle, C.L.; Gomes, R.S.M. Conceptualizations of Well-Being in Adults with Visual Impairment: A Scoping Review. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 964537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, S.-M. Visual Impairment and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Follow-up Study Using a National Sample Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.K.; Rubin, G.S.; Broman, A.T.; Muñoz, B.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Turano, K. How Does Visual Impairment Affect Performance on Tasks of Everyday Life? The SEE Project. Salisbury Eye Evaluation. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretti, G.; Manetti, M.; Marini, M. Physical Activity and Sport Practice to Improve Balance Control of Visually Impaired Individuals: A Narrative Review with Future Perspectives. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1260942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretti, G.; Bianco, R.; Sgambati, E.; Manetti, M.; Marini, M. Reactive Agility and Pitching Performance Improvement in Visually Impaired Competitive Italian Baseball Players: An Innovative Training and Evaluation Proposal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak-Olejnik, M.; Loba, W.; Stieler, O.; Komar, D.; Majewska, A.; Marcinkowska-Gapińska, A.; Hojan-Jezierska, D. Body Balance Analysis in the Visually Impaired Individuals Aged 18-24 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, K.; Tokui, A. Audiospatial Cognitive Ability of Visually Impaired Athletes in Static and Dynamic Spatial Cognitive Tasks. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lewald, J. Opposing Effects of Head Position on Sound Localization in Blind and Sighted Human Subjects. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, R.A.; Pourmoghaddam, A.; Paloski, W.H. Sensorimotor Posture Control in the Blind: Superior Ankle Proprioceptive Acuity Does Not Compensate for Vision Loss. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, P.; Tabry, V.; Zatorre, R.J. Trade-off in the Sound Localization Abilities of Early Blind Individuals between the Horizontal and Vertical Planes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6051–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunik, E.; Poizner, H.; Levin, M.F.; Adamovich, S.V.; Messier, J.; Lamarre, Y.; Feldman, A.G. Arm-Trunk Coordination in the Absence of Proprioception. Exp. Brain Res. 2003, 153, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seroyer, S.T.; Nho, S.J.; Bach, B.R.; Bush-Joseph, C.A.; Nicholson, G.P.; Romeo, A.A. The Kinetic Chain in Overhand Pitching: Its Potential Role for Performance Enhancement and Injury Prevention. Sports Health 2010, 2, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetisli Korkmaz, N.; Can Akman, T.; Kilavuz Oren, G.; Bir, L.S. Trunk Control: The Essence for Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 24, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granacher, U.; Gollhofer, A.; Hortobágyi, T.; Kressig, R.W.; Muehlbauer, T. The Importance of Trunk Muscle Strength for Balance, Functional Performance, and Fall Prevention in Seniors: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, J.D.; Dougherty, C.P.; Ireland, M.L.; Davis, I.M. Core Stability and Its Relationship to Lower Extremity Function and Injury. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxel Bliven, K.C.; Anderson, B.E. Core Stability Training for Injury Prevention. Sports Health 2013, 5, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brian, A.; Pennell, A.; Haibach-Beach, P.; Foley, J.; Taunton, S.; Lieberman, L.J. Correlates of Physical Activity among Children with Visual Impairments. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 12, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegele, J.A.; Zhu, X. Physical Activity, Self-Efficacy and Health-Related Quality of Life among Adults with Visual Impairments. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 43, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeting, J.; Merom, D.; Astuti, P.A.S.; Antoun, M.; Edwards, K.; Ding, D. Physical Activity Interventions for Adults Who Are Visually Impaired: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoureux, E.L.; Hassell, J.B.; Keeffe, J.E. The Determinants of Participation in Activities of Daily Living in People with Impaired Vision. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Schrack, J.A.; Wang, H.; E, J.-Y.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Agrawal, Y.; Urbanek, J.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Swenor, B.K. Visual Impairment and Objectively Measured Physical Activity in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 2194–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz-Rodríguez, V.; Medina-Rebollo, D.; Muñoz-Llerena, A.; Fernández-Gavira, J. Influence of Physical Activity and Sport on the Inclusion of People with Visual Impairment: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, M.; Sarchielli, E.; Portas, M.F.; Ranieri, V.; Meli, A.; Piazza, M.; Sgambati, E.; Monaci, M. Can Baseball Improve Balance in Blind Subjects? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2011, 51, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Mirandola, D.; Monaci, M.; Miccinesi, G.; Vannuzzi, A.; Sgambati, E.; Manetti, M.; Marini, M. Psychological Well-Being and Quality of Life in Visually Impaired Baseball Players: An Italian National Survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency, L.W. Il Gioco e Le Regole—Baseball x Ciechi—AIBXC. Available online: https://www.aibxc.it/giocoregole/index.php?l=en (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Gray, R. Changes in Movement Coordination Associated With Skill Acquisition in Baseball Batting: Freezing/Freeing Degrees of Freedom and Functional Variability. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, T.; Maemichi, T.; Torii, S. Identification of Physical Characteristics Associated with Swing Velocity of Batting in Youth Baseball Players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrary, J.M.; Ackermann, B.J.; Halaki, M. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Upper Body Warm-up on Performance and Injury. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, A.J.; Fogt, N. Review: Head and Eye Movements and Gaze Tracking in Baseball Batting. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2021, 98, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishita, Y.; Ueda, H.; Kashino, M. Eye and Head Movements of Elite Baseball Players in Real Batting. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meron, A.; Saint-Phard, D. Track and Field Throwing Sports: Injuries and Prevention. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.J.; Winkelmann, Z.K.; Powden, C.J.; Games, K.E. Proprioceptive Training for the Prevention of Ankle Sprains: An Evidence-Based Review. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruciani, F.; Perilli, R.; Piccioni, M. Blindness and social security in Italy: Critical issues and proposals. Recent. Prog. Med. 2018, 109, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMA–The World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. Available online: https://www.wma.net/what-we-do/medicalethics/declaration-of-helsinki/ (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Kendall, F.P.; Kendall McCreary, E.; Geise Provance, P.; McIntyre Rodgers, M.; Romani, W.A. I muscoli. Funzioni e test con postura e dolore; Verduci Editore: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- EasyAngle Clinical Studies|Evidence Based Goniometry. Available online: https://meloqdevices.com/pages/completed-easyangle-clinical-studies (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Majewska, J.; Kołodziej-Lackorzyńska, G.; Cyran-Grzebyk, B.; Szymczyk, D.; Kołodziej, K.; Wądołkowski, P. Effects of Core Stability Training on Functional Movement Patterns in Tennis Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minthorn, L.M.; Fayson, S.D.; Stobierski, L.M.; Welch, C.E.; Anderson, B.E. The Functional Movement Screen’s Ability to Detect Changes in Movement Patterns After a Training Intervention. J. Sport. Rehabil. 2015, 24, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnacinski, S.L.; Cornell, D.J.; Meyer, B.B.; Arvinen-Barrow, M.; Earl-Boehm, J.E. Functional Movement Screen Factorial Validity and Measurement Invariance Across Sex Among Collegiate Student-Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3388–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretti, G.; Dabraio, A.; Manetti, M.; Marini, M. Biofeedback-Based Proprioceptive Training to Improve Functional Prerequisites of Dragon Boating in Breast Cancer Survivors. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2024, 14, 1351–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, K.; Powis, M.; Hopgood, K. Intrarater and Interrater Reliability of the Modified Thomas Test. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2022, 29, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Otoshi, K.-I.; Tominaga, R.; Kaga, T.; Igari, T.; Sato, R.; Konno, S.-I. Influences of Limited Flexibility of the Lower Extremities and Occurrence of Low Back Pain in Adolescent Baseball Players: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2022, 27, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga-Vega, D.; Merino-Marban, R.; Viciana, J. Criterion-Related Validity of Sit-and-Reach Tests for Estimating Hamstring and Lumbar Extensibility: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plisky, P.; Schwartkopf-Phifer, K.; Huebner, B.; Garner, M.B.; Bullock, G. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Y-Balance Test Lower Quarter: Reliability, Discriminant Validity, and Predictive Validity. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 16, 1190–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J.; Plisky, P. Using the Star Excursion Balance Test to Assess Dynamic Postural-Control Deficits and Outcomes in Lower Extremity Injury: A Literature and Systematic Review. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIBRA–Dispositivo Per Rieducazione Propriocettiva. Easytech. Available online: https://easytechitalia.com/libra/ (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, F. Physiology of Human Balance. Adv. Neurol. 2001, 87, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, T.C.K.; Schmuckler, M.A. Multisensory Postural Control in Adults: Variation in Visual, Haptic, and Proprioceptive Inputs. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 79, 102845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, P.A.; Chen, A.; Blouin, J.-S. Sensorimotor Control of Standing Balance. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodworth, A.D.; Mellodge, P.; Peterka, R.J. Stance Width Changes How Sensory Feedback Is Used for Multisegmental Balance Control. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 112, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mouchnino, L.; Aurenty, R.; Massion, J.; Pedotti, A. Coordination between Equilibrium and Head-Trunk Orientation during Leg Movement: A New Strategy Build up by Training. J. Neurophysiol. 1992, 67, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noamani, A.; Lemay, J.-F.; Musselman, K.E.; Rouhani, H. Postural Control Strategy after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury: Effect of Sensory Inputs on Trunk-Leg Movement Coordination. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaswinkel, E.; van Drunen, P.; Veeger, D.-J.H.E.J.; van Dieën, J.H. Effects of Vision and Lumbar Posture on Trunk Neuromuscular Control. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Clark, V.L.; Furlanetto, K.C.; Gibson, P.G.; McDonald, V.M. Core Function in Adults With Severe Asthma and Its Relationship With Breathing Symptoms. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2024, 12, 1254–1262.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Tsuda, E.; Yamamoto, Y.; Maeda, S.; Kimura, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Ishibashi, Y. Core-Muscle Training and Neuromuscular Control of the Lower Limb and Trunk. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Criekinge, T.; Truijen, S.; Schröder, J.; Maebe, Z.; Blanckaert, K.; van der Waal, C.; Vink, M.; Saeys, W. The Effectiveness of Trunk Training on Trunk Control, Sitting and Standing Balance and Mobility Post-Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dello Iacono, A.; Padulo, J.; Ayalon, M. Core Stability Training on Lower Limb Balance Strength. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupowitz, L.G. Comprehensive Approach to Core Training in Sports Physical Therapy: Optimizing Performance and Minimizing Injuries. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2023, 18, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Behm, D.G. The Impact of Instability Resistance Training on Balance and Stability. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreopoulou, G.; Maaswinkel, E.; Cofré Lizama, L.E.; van Dieën, J.H. Effects of Support Surface Stability on Feedback Control of Trunk Posture. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behm, D.G.; Muehlbauer, T.; Kibele, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of Strength Training Using Unstable Surfaces on Strength, Power and Balance Performance Across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, M.; Salesky, M.; Lansdown, D.A. Throwing Injury Prevention Strategies with a Whole Kinetic Chain-Focused Approach. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2022, 15, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, E.; Doty, S.; Lott, M.; Baker, J. Neuromechanical Integration of Pelvic-Thoracic Rotation among Youth Baseball Throwers. Sports Med. Int. Open 2022, 6, E47–E52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, L.; McConnell, A.K.; Pijnenburg, M.; Claeys, K.; Goossens, N.; Lysens, R.; Troosters, T.; Brumagne, S. Inspiratory Muscle Training Affects Proprioceptive Use and Low Back Pain. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surakka, A.; Kivelä, T. THE EFFECT OF A PHYSICAL TRAINING PROGRAMME ON FLEXIBILITY OF UPPER BODY AND TRUNK IN VISUALLY IMPAIRED AND DEAF-BLIND PERSONS. Eur. J. Adapt. Phys. Act. 2011, 4, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-Y.; Huang, J.-C.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-I. Effects of Trunk Exercise on Unstable Surfaces in Persons with Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghuis, J.; Hof, A.L.; Lemmink, K.A.P.M. The Importance of Sensory-Motor Control in Providing Core Stability: Implications for Measurement and Training. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 893–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Martel, V.; Santuz, A.; Bohm, S.; Arampatzis, A. Neuromechanics of Dynamic Balance Tasks in the Presence of Perturbations. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 560630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, D.; Fani, M.; Benedetti, M.G.; Scarsini, A.; Rocca, F.; Mamo, C. Effects of High-Frequency Proprioceptive Training on Single Stance Stability in Older Adults: Implications for Fall Prevention. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2382747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, S.; Ghai, I.; Effenberg, A.O. Effects of Dual Tasks and Dual-Task Training on Postural Stability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, S.; Schmitz, G.; Hwang, T.-H.; Effenberg, A.O. Training Proprioception with Sound: Effects of Real-Time Auditory Feedback on Intermodal Learning. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2019, 1438, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyquist, J.B.; Lappin, J.S.; Zhang, R.; Tadin, D. Perceptual Training Yields Rapid Improvements in Visually Impaired Youth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazennec, J.-Y.; Brusson, A.; Rousseau, M.-A. Hip–Spine Relations and Sagittal Balance Clinical Consequences. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talis, V.L.; Grishin, A.A.; Solopova, I.A.; Oskanyan, T.L.; Belenky, V.E.; Ivanenko, Y.P. Asymmetric Leg Loading during Sit-to-Stand, Walking and Quiet Standing in Patients after Unilateral Total Hip Replacement Surgery. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, S.; Kamali, F.; Bervis, S.; Razeghi, M. The Hip Joint Mobilization with Movement Technique Improves Muscle Activity, Postural Stability, Functional and Dynamic Balance in Hemiplegia Secondary to Chronic Stroke: A Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley-Holbrook, E.; Kang, M.; Morgan, D.W. Development and Evaluation of the Walk for Health Program: A Physical Activity Intervention for Adults with Visual Impairments. J. Vis. Impair. Blind. 2016, 110, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).