Long-Term Alterations in Motor Skills, Neurogenesis and Astrocyte Numbers following Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Chemicals and Antibodies
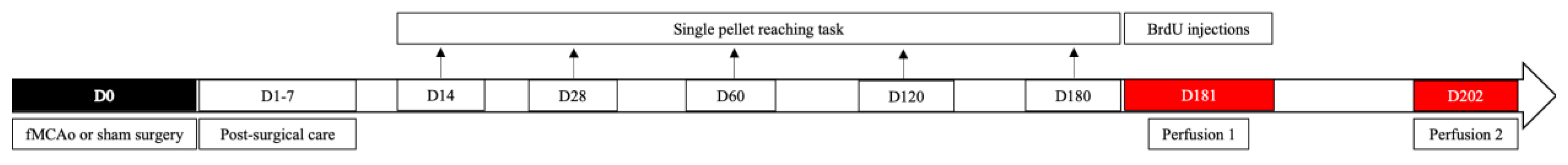
2.4. Filament Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (fMCAo) Model
2.5. Post-Operative Care
2.6. Single Pellet Reaching Task
2.7. BrdU Injections
2.8. Brain Tissue Preparation
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Image Acquisition and Processing
2.11. Statistical Analysis
- Sham ipsi against fMCAo ipsi group;
- Sham contra against fMCAo contra group;
- Sham ipsi against Sham contra group;
- fMCAo ipsi against fMCAo contra group.
3. Results
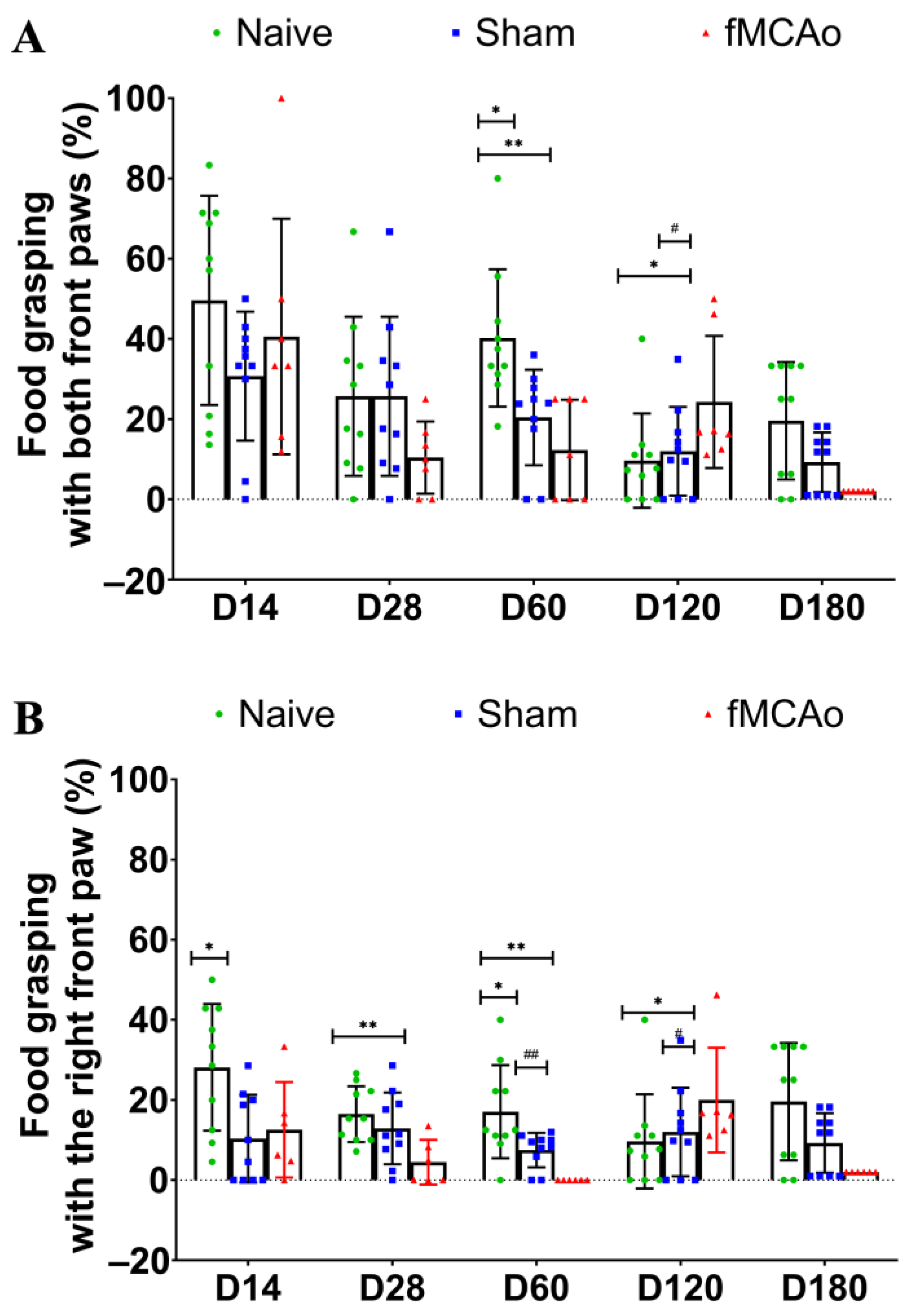
3.1. Impaired Reaching Ability of fMCAo Mice
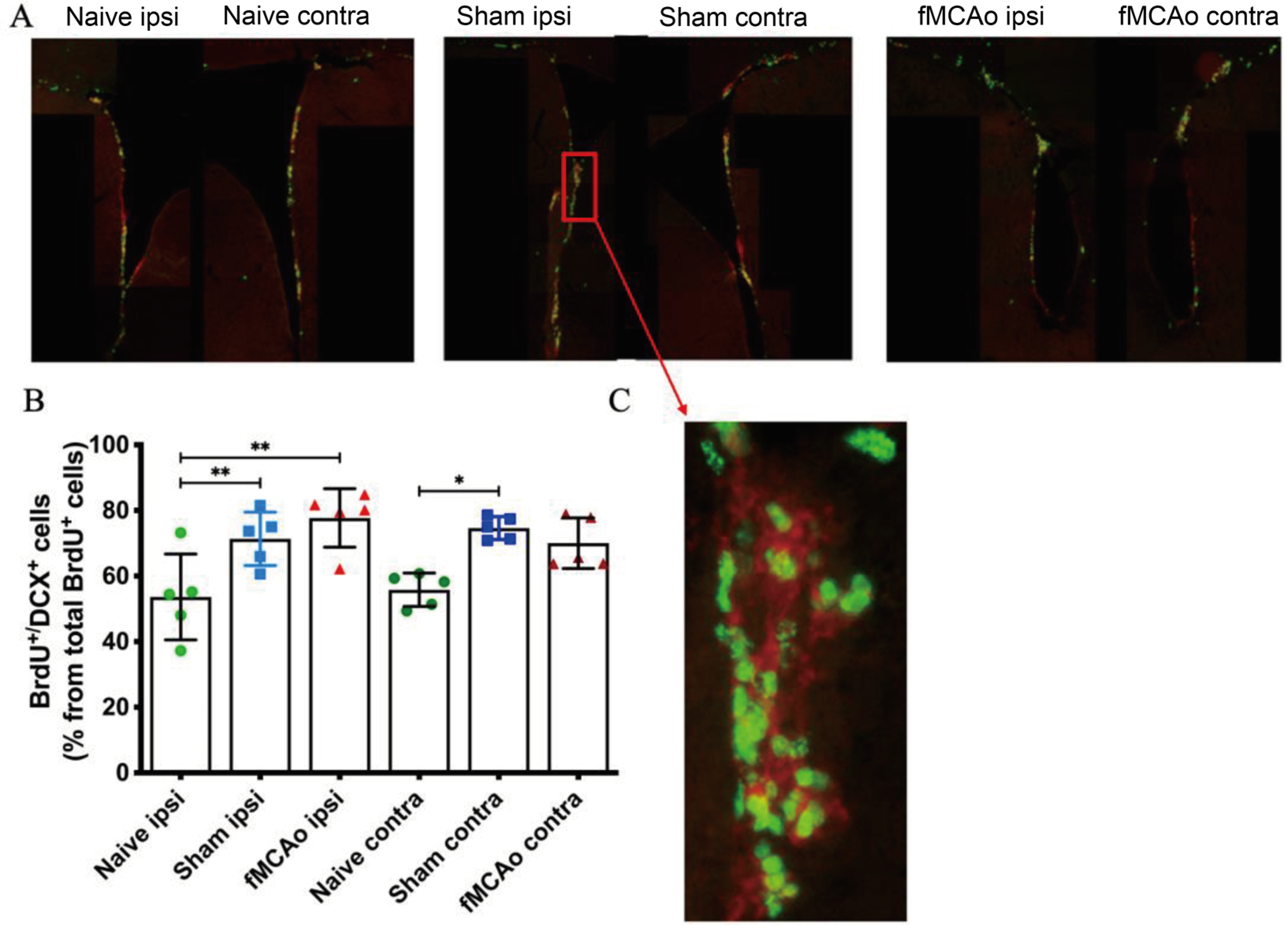
3.2. Altered BrdU+/DCX+ Cell Numbers in the SVZ Region
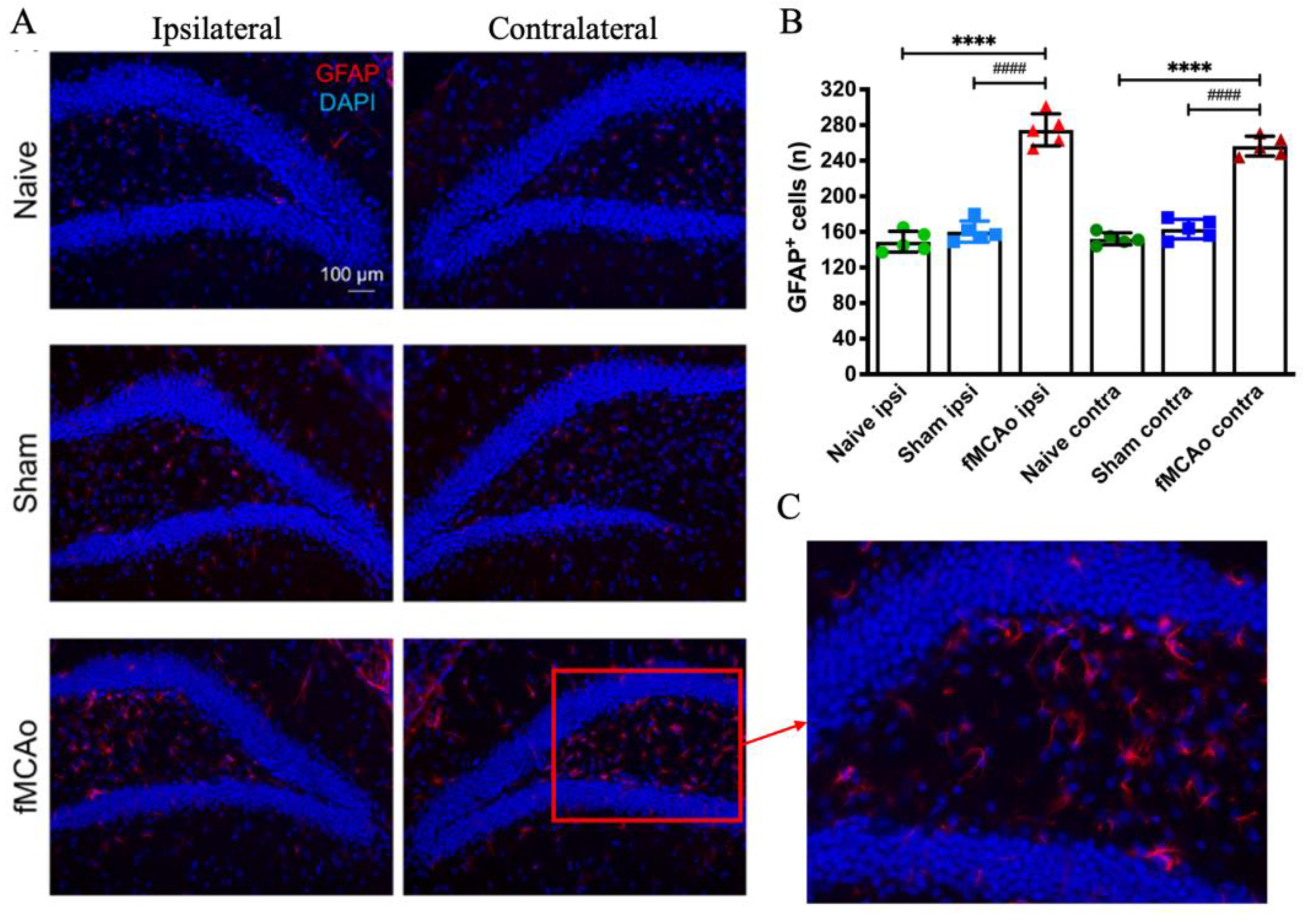
3.3. Changes in GFAP+ Cells in the Hippocampal DG
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holloway, P.M.; Gavins, F.N.E. Modeling Ischemic Stroke In Vitro: Status Quo and Future Perspectives. Stroke 2016, 47, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auriel, E.; Bornstein, N.M. Neuroprotection in acute ischemic stroke—Current status. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2200–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarczyk, L.; Szelenberger, R.; Cichon, N.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M.; Miller, E. Biomarkers of angiogenesis and neuroplasticity as promising clinical tools for stroke recovery evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, B.L.; Carvalho, G.A.; Freitas, E.M.M.; Chiareli, R.A.; Barbosa, T.G.; Di Araújo, A.G.P.; Nogueira, Y.L.; Ribeiro, R.I.; Parreira, R.C.; Vieira, M.S.; et al. The role of neurogenesis in neurorepair after ischemic stroke. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 95, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Wang, B.; Zhuge, Q.; Jin, K. Coupling of neurogenesis and angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 2015, 1623, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.P.; Couillard-Després, S.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.M.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L.; Kuhn, H.G. Transient Expression of Doublecortin during Adult Neurogenesis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 467, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Jin, K. Current perspectives on the link between neuroinflammation and neurogenesis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Mao, X.O.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Mao, Y.; Banwait, S.; Greenberg, D.A. Evidence for stroke-induced neurogenesis in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13198–13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Minami, M.; Lan, J.Q.; Mao, X.O.; Batteur, S.; Simon, R.P.; Greenberg, D.A. Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4710–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Hirota, Y.; Ema, M.; Takahashi, S.; Miyoshi, I.; Okano, H.; Sawamoto, K. Subventricular zone-derived neural progenitor cells migrate along a blood vessel scaffold toward the post-stroke striatum. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, S.-W.; Chang, D.; Jenkins, A.; Bensoussan, A.; Kiat, H. Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke and Angiogenic Effects of Chinese Herbal Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, E.S.; Coshall, C.; Dundas, R.; Stewart, J.; Rudd, A.G.; Howard, R.; Wolfe, C.D. Estimates of the Prevalence of Acute Stroke Impairments and Disability in a Multiethnic Population. Stroke 2001, 32, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.B.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Chang, W.N.; Yeom, J.W.; Kim, Y.D.; Hwang, B.Y. Six-month functional recovery of stroke patients. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2015, 38, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols-Larsen, D.S.; Clark, P.C.; Zeringue, A.; Greenspan, A.; Blanton, S. Factors Influencing Stroke Survivors’ Quality of Life during Subacute Recovery. Stroke 2005, 36, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potente, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 2011, 146, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroud, A.; Whishaw, I.Q. Changes in the kinematic structure and non-kinematic features of movements during skilled reaching after stroke: A Laban Movement Analysis in two case studies. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 158, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, E.; Uswatte, G.; Mark, V.W. The functional significance of cortical reorganization and the parallel development of CI therapy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jickling, G.C.; Sharp, F.R. Improving the translation of animal ischemic stroke studies to humans. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, J.; Van de Beeck, L.; Plumier, J.C.; Ferrara, A. Procedural learning as a measure of functional impairment in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 307, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.; Agin, V.; Rahman, M.; Morancho, A.; Ali, C.; Koistinaho, J.; Wang, X.; Vivien, D.; Schwaninger, M.; Montaner, J. Distal Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery in Mice: Are We Ready to Assess Long-Term Functional Outcome? Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Yao, Y. Behavioral tests in rodent models of stroke. Brain Hemorrhages 2020, 1, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Sacrey, L.-A.R.; Whishaw, I.Q.; Dunnett, S.B. The use of rodent skilled reaching as a translational model for investigating brain damage and disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Min, J.-W.; Munshi, Y.; Lai, Y.-J.; Qi, L.; Urayama, A.; McCullough, L.D.; Li, J. Activation of endothelial ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) improves post-stroke recovery and angiogenesis via activating Pak1 in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 322, 113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; Gilmore, A.; Zuo, Y. Study Motor Skill Learning by Single-pellet Reaching Tasks in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 85, e51238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipenko, V.; Dzirkale, Z.; Rozkalne, R.; Upite, J.; Hellal, F.; Plesnila, N.; Jansone, B. Focal Cerebral Ischemia Induces Global Subacute Changes in the Number of Neuroblasts and Neurons and the Angiogenic Factor Density in Mice. Medicina (B Aires) 2023, 59, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates BT—123Library, 6th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.D.; Whishaw, I.Q. Quantitative and Qualitative Impairments in Skilled Reaching in the Mouse (Mus musculus) After a Focal Motor Cortex Stroke. Stroke 2002, 33, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLellan, C.L.; Gyawali, S.; Colbourne, F. Skilled reaching impairments follow intrastriatal hemorrhagic stroke in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 175, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkaya, M.; Kröber, J.M.; Rex, A.; Endres, M. Assessing Post-Stroke Behavior in Mouse Models of Focal Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2013, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, S.; Murray, K.N.; Rothwell, N.J.; Metz, G.A.S.; Allan, S.M. Long-term functional recovery and compensation after cerebral ischemia in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 270, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Ruhoff, A.M.; Fath, T.; Jones, N.M. Hypoxic postconditioning enhances functional recovery following endothelin-1 induced middle cerebral artery occlusion in conscious rats. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 306, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankhong, S.; Kim, S.; Moon, S.; Lee, K.-H.; Jeon, H.-E.; Hwang, B.-H.; Beak, J.-W.; Joa, K.-L.; Kang, J.-H. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Tau and Related Proteins in Rats with the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thored, P.; Arvidsson, A.; Cacci, E.; Ahlenius, H.; Kallur, T.; Darsalia, V.; Ekdahl, C.T.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Persistent Production of Neurons from Adult Brain Stem Cells During Recovery after Stroke. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, S.P.; Ogle, M.E.; Ding, X.S.; Wei, L. Enhanced neurogenesis and cell migration following focal ischemia and peripheral stimulation in mice. Dev. Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Qin, L.; Kim, E.; Bhosle, S.; Guo, H.; Febbraio, M.; Haskew-Layton, R.E.; Ratan, R.; Cho, S. CD36 is Involved in Astrocyte Activation and Astroglial Scar Formation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2012, 32, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestriner, R.G.; Saur, L.; Bagatini, P.B.; Baptista, P.P.A.; Vaz, S.P.; Ferreira, K.; Machado, S.A.; Xavier, L.L.; Netto, C.A. Astrocyte morphology after ischemic and hemorrhagic experimental stroke has no influence on the different recovery patterns. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 278, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaverdashvili, M.; Whishaw, I.Q. A behavioral method for identifying recovery and compensation: Hand use in a preclinical stroke model using the single pellet reaching task. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 950–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.B.; Lee, J.; McCullough, L.D. Sex differences in the inflammatory response to stroke. Semin. Immunopathol. 2023, 45, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Manufacturer | Concentration | Cat. No. | RRID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse anti-BrdU | Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) | 1:4000 | MA3-071 | AB_10986341 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG2A (AlexaFluor® 488-conjugated) | 1:1000 | A21131 | AB_2535771 | |
| Rabbit anti-DCX | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | 1:50 | ab207175 | AB_2894710 |
| Rabbit anti-GFAP | 1:250 | ab68428 | AB_1209224 | |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG (AlexaFluor® 594-conjugated) | 1:1000 | ab150084 | AB_2734147 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilipenko, V.; Upite, J.; Revina, B.L.; Jansone, B. Long-Term Alterations in Motor Skills, Neurogenesis and Astrocyte Numbers following Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Medicina 2024, 60, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040658
Pilipenko V, Upite J, Revina BL, Jansone B. Long-Term Alterations in Motor Skills, Neurogenesis and Astrocyte Numbers following Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Medicina. 2024; 60(4):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040658
Chicago/Turabian StylePilipenko, Vladimirs, Jolanta Upite, Beatrise Luize Revina, and Baiba Jansone. 2024. "Long-Term Alterations in Motor Skills, Neurogenesis and Astrocyte Numbers following Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Mice" Medicina 60, no. 4: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040658
APA StylePilipenko, V., Upite, J., Revina, B. L., & Jansone, B. (2024). Long-Term Alterations in Motor Skills, Neurogenesis and Astrocyte Numbers following Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Medicina, 60(4), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60040658






