The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
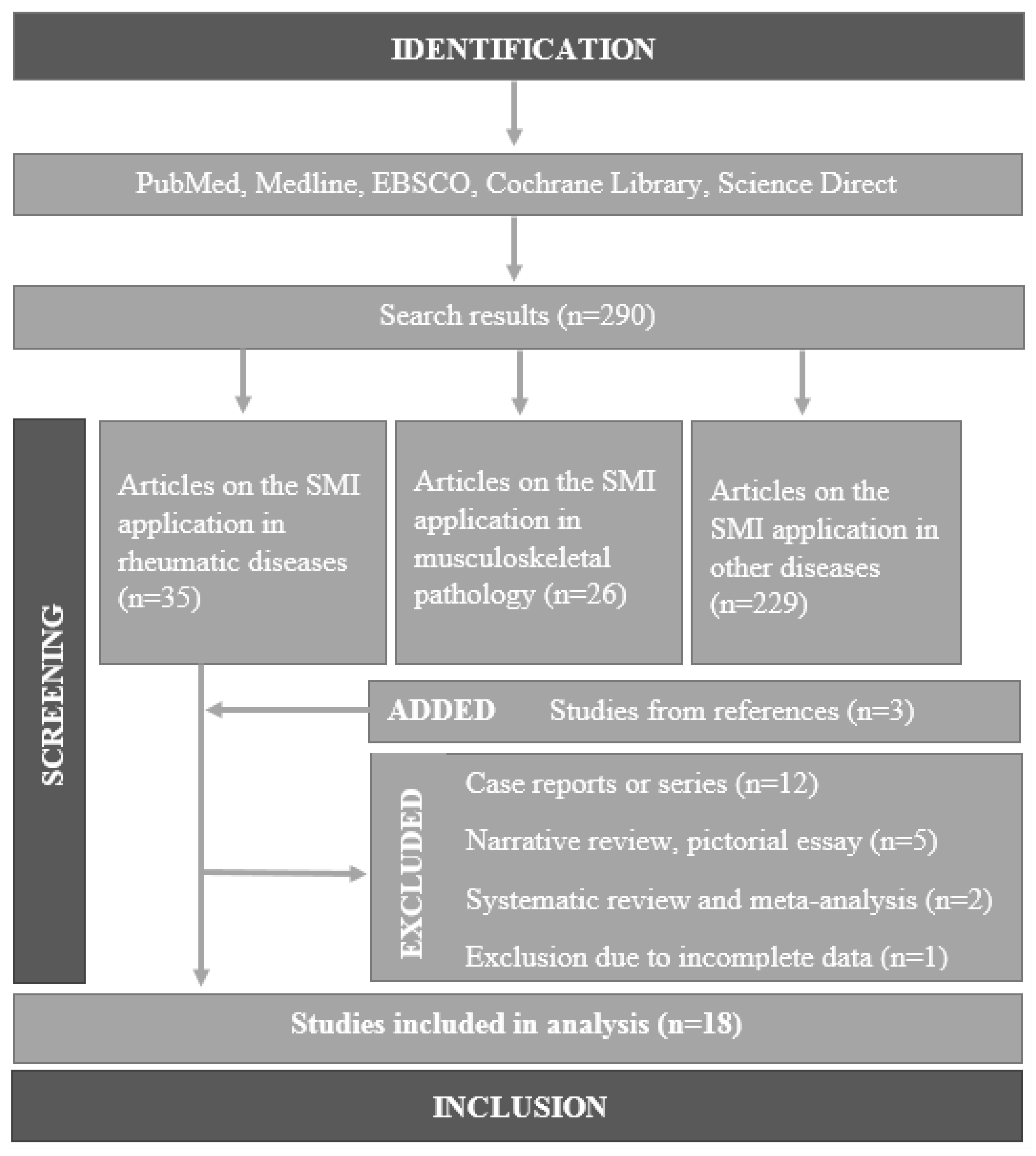
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Analysis
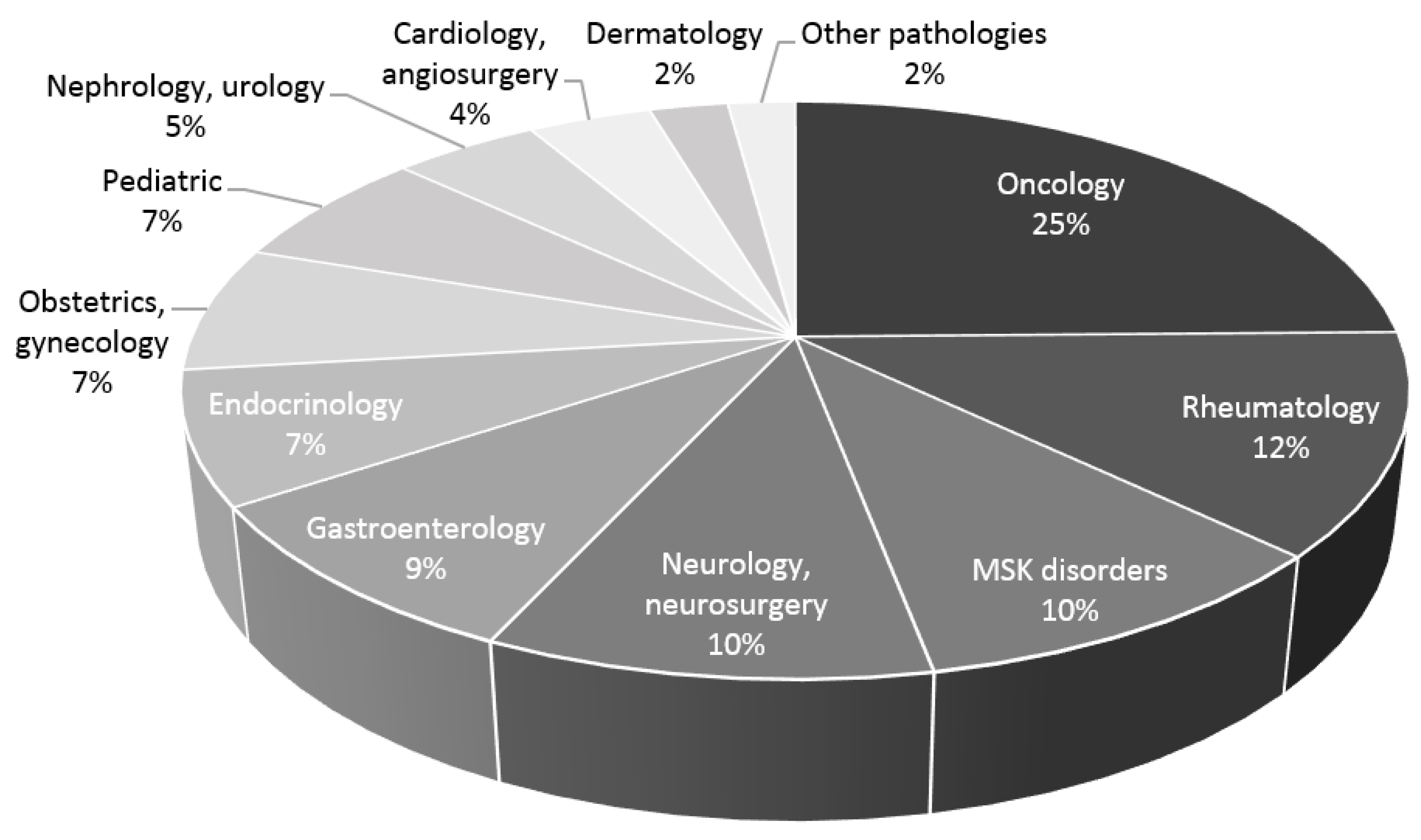
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torp-Pedersen, S.T.; Terslev, L. Settings and artefacts relevant in colour/power Doppler ultrasound in rheumatology. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 67, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, S.; Cheung, P.P. The Role of Power Doppler Ultrasonography as Disease Activity Marker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 325909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.J.; Hao, Y.Z.; Zhou, C.W. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in thyroid lesions. Chin. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2006, 41, 415s. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Li, J.C.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.; Su, N.; Yang, M. Role of Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Inflammatory Arthritis. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauser, A.; Demharter, J.; De Marchi, A.; Sureda, D.; Barile, A.; Masciocchi, C.; Faletti, C.; Schirmer, M.; Kleffel, T.; Bohndorf, K. Contrast enhanced gray-scale sonography in assessment of joint vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the IACUS study group. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rednic, N.; Tamas, M.M.; Rednic, S. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in inflammatory arthritis. Med. Ultrason. 2011, 13, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, J. Seeing the Unseen: New Techniques in Vascular Imaging Superb Microvascular Imaging. Toshiba Med Rev P:1–8. 2014. Available online: https://global.medical.canon/publication/index (accessed on 1 November 2014).
- Lim, A.K. The Clinical Utility of Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI) for Assessing Musculoskeletal Inflammation. Toshiba Medical Systems. 2014. Available online: https://global.medical.canon/publication/index (accessed on 1 February 2014).
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.L.; Liu, X.T. Clinical Applications of Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Liver, Breast, Thyroid, Skeletal Muscle, and Carotid Plaques. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H.; Kamada, M.; Imamura, A.; Shimizu, M.; Inagaki, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ito, H.; Fujii, Y. Machine learning-based prediction of relapse in rheumatoid arthritis patients using data on ultrasound examination and blood test. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H.; Tabuchi, Y.; Yukimatsu, R.; Imamura, A.; Shimizu, M.; Inagaki, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Nakabo, S.; Tsuji, H.; Nakajima, T.; et al. Positive rate and prognostic significance of the superb microvascular imaging signal in joints of rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission with normal C-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rates. J. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 48, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H.; Imamura, A.; Shimizu, M.; Inagaki, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Nakabo, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Ito, H.; Tanaka, S.; Mimori, T.; et al. Prediction of recurrence and remission using superb microvascular imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 47, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Nishida, M.; Tanimura, S.; Kamishima, T.; Tamai, E.; Morimura, Y.; Nishibata, Y.; Masuda, S.; Nakazawa, D.; Tomaru, U.; et al. Detection of Increased Vascular Signal in Arthritis-Prone Rats Without Joint Swelling Using Superb Microvascular Imaging Ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Tsuzuki Wada, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Mimura, T. Detection of synovial inflammation in rheumatic diseases using superb microvascular imaging: Comparison with conventional power Doppler imaging. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, X.H.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhan, J.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, Y. Superb microvascular imaging is as sensitive as contrast-enhanced ultrasound for detecting synovial vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 2866–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Fu, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z. SWE and SMI ultrasound techniques for monitoring needling treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: Study protocol for a single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Du, J. Comparison of three ultrasonographic examinations on the synovial membrane vascularity of RA patients. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, M.; Xi, J.; Wu, J.; Ji, Y. Superb microvascular imaging (SMI) for evaluating hand joint lesions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical remission. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, F.; Zhu, J.; Wei, X.; Chen, Z. Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging improving inflammatory flow blood sensitivity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. For. 2016, 9, 19930–19934. [Google Scholar]
- Kandemirli, S.G.; Cicek, F.; Erdemli Gursel, B.; Bilgin, C.; Kilic, S.S.; Yazici, Z. Superb Microvascular Imaging in Assessment of Synovitis and Tenosynovitis in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Ultrasound Q. 2021, 37, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, O.F.; Kandemirli, S.G.; Erdemli Gursel, B.; Bilgin, C.; Korkmaz, B.; Yolgosteren, A.; Inecikli, M.F. Diagnostic utility of superb microvascular imaging in depiction of corkscrew collaterals in Buerger’s disease. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2020, 49, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, M.F.; Bayramoglu, Z.; Adaletli, B. Evaluation of Periarticular Soft Tissues in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis by Superb Microvascular Imaging and Shear Wave Elastography. Arch. Rheumatol. 2020, 35, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustabasioglu, F.E.; Korkmaz, S.; Ilgen, U. Quantitative Assessment of Salivary Gland Parenchymal Vascularization Using Power Doppler Ultrasound and Superb Microvascular Imaging: A Potential Tool in the Diagnosis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Balk. Med. J. 2021, 37, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oo, W.M.; Linklater, J.M.; Bennell, K.L.; Yu, S.; Fu, K.; Wang, X.; Duong, V.; Hunter, D.J. Superb Microvascular Imaging in Low-Grade Inflammation of Knee Osteoarthritis Compared with Power Doppler: Clinical, Radiographic and MRI Relationship. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, D.; Gitto, S.; Perugin Bernardi, S.; Corazza, A.; De Flaviis, L.; Silvestri, E.; Cimmino, M.A.; Sconfienza, L.M. Advanced Power Doppler Technique Increases Synovial Vascularity Detection in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.T.; Song, J.S. The superb microvascular imaging is more sensitive than conventional power Doppler imaging in detection of active synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.K.P.; Satchithananda, K.; Dick, E.A.; Abraham, S.; Cosgrove, D.O. Microflow imaging: New Doppler technology to detect low-grade inflammation in patients with arthritis. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.A.; Navarro, S.M.; Kambala, S.; Tan, G.; Poondla, R.; Lederman, S.; Barbour, K.; Lavy, C. Trends in Ultrasound Use in Low and Middle Income Countries: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Matern. Child Health AIDS (IJMA) 2020, 9, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.; Purves, D.; McConnachie, A.; McInnes, I.; Porter, D. Tightening Up? Impact of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Disease Activity Assessment on Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated Using a Treat to Target Strategy. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 66, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeganova, S.; Huizinga, T. Sustained remission in rheumatoid arthritis: Latest evidence and clinical considerations. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2017, 9, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenic, P.; Aletaha, D.; de Wit, M.; Stamm, T.A.; Alasti, F.; Lacaille, D.; Smolen, J.S.; Felson, D.T. American College of Rheumatology/EULAR remission criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 2022 revision. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippou, G.; Sakellariou, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Carrara, G.; Rumi, F.; Bellis, E.; Adinolfi, A.; Batticciotto, A.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Cagnotto, G.; et al. The predictive role of ultrasound-detected tenosynovitis and joint synovitis for flare in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in stable remission. Results of an Italian multicentre study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology Group for Ultrasound: The STARTER study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Geng, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Subclinical synovitis assessed by ultrasound predicts flare and progressive bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis patients with clinical remission: A systematic review and metaanalysis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larché, M.J.; Seymour, M.; Lim, A.; Eckersley, R.J.; Pétavy, F.; Chiesa, F.; Rioja, I.; Lukey, P.T.; Binks, M.; McClinton, C.; et al. Quantitative Power Doppler Ultrasonography Is a Sensitive Measure of Metacarpophalangeal Joint Synovial Vascularity in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Declines Significantly Following a 2-week Course of Oral Low-dose Corticosteroids. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudlarek, M.; Narvestad, E.; Klarlund, M.; Court-Payen, M.; Thomsen, H.S.; Østergaard, M. Ultrasonography of the metatarsophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography, and clinical examination. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Lambrecht, S.; Verheugen, E.; Pauwels, E.; Kollias, G.; Armaka, M.; Verhoye, M.; Van der Linden, A.; Achten, R.; Lories, R.J.; et al. Proof of concept: Enthesitis and new bone formation in spondyloarthritis are driven by mechanical strain and stromal cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, A.S.; Corr, M.; Weisman, M.H. Review: Enthesitis: New Insights into Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Modalities, and Treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Karahan, A.Y.; Oncu, F.; Bakdik, S.; Durmaz, M.S.; Tolu, I. Diagnostic Performance of Superb Microvascular Imaging and Other Sonographic Modalities in the Assessment of Lateral Epicondylosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Kang, C.H.; Hong, S.J.; Jeong, W.K. Ultrasound elastography of lateral epicondylosis: Clinical feasibility of quantitative elastographic measurements. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, K.; Bai, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Assessment of neovascularization of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques using superb microvascular imaging: A comparison with contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging and histology. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, H.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. Study of Vertebral Artery Dissection by Ultrasound Superb Microvascular Imaging Based on Deep Neural Network Model. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich-Zbroja, A.; Kuczyńska, M.; Majdan, A.; Majdan, M. A rare case of aortic involvement in microscopic polyangiitis evaluated using contrast-enhanced ultrasound, superb microvascular imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 132, 16231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakellariou, G.; Giovannini, I.; Grignaschi, S.; Zabotti, A.; Iagnocco, A. Reply to: Superb microvascular imaging in giant cell arteritis by Conticini et al. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Tahara, N.; Hirakata, S.; Kaieda, S.; Tahara, A.; Maeda-Ogata, S.; Bekki, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Honda, A.; Igata, S.; et al. Signal intensity of superb micro-vascular imaging associates with the activity of vascular inflammation in Takayasu arteritis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, W.; Sato, T.; Iino, T.; Seki, K.; Watanabe, H. Visualization of arterial wall vascularization using superb microvascular imaging in active-stage Takayasu arteritis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudlarek, M.; Court-Payen, M.; Jacobsen, S.; Klarlund, M.; Thomsen, H.S.; Østergaard, M. Interobserver agreement in ultrasonography of the finger and toe joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wang, C. Superb microvascular imaging evaluating joint lesion scores in rheumatoid arthritis compared with power Doppler imaging. Medicine 2020, 99, e22185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, E.Y.; Yoon, G.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, H.H. Added Value of the Vascular Index on Superb Microvascular Imaging for the Evaluation of Breast Masses. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 40, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.N.; Lv, K.; Jiang, Y.X.; Jiang, T.A. Application of superb microvascular imaging in focal liver lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7765–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artul, S.; Nseir, W.; Armaly, Z.; Soudack, M. Superb Microvascular Imaging: Added Value and Novel Applications. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2017, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, O.; Corvino, A.; Basile, L.; Catalano, F.; Varelli, C. Use of new microcirculation software allows the demonstration of dermis vascularization. J. Ultrasound. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, A.; Varelli, C.; Cocco, G.; Corvino, F.; Catalano, O. Seeing the unseen with superb microvascular imaging: Ultrasound depiction of normal dermis vessels. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 2022, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Bruni, C.; Cuomo, G.; Delle Sedie, A.; Gargani, L.; Gutierrez, M.; Lepri, G.; Ruaro, B.; Santiago, T.; Suliman, Y.; et al. The role of ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: On the cutting edge to foster clinical and research advancement. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021, 6, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shung, K.K. High Frequency Ultrasonic Imaging. J. Med. Ultrasound 2009, 17, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzetti, R.; Vitali, S.; Aringhieri, G.; Nisi, M.; Oranges, T.; Dini, V.; Ferro, F.; Baldini, C.; Romanelli, M.; Caramella, D.; et al. Ultra-High Frequency Ultrasound, A Promising Diagnostic Technique: Review of the Literature and Single-Center Experience. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2020, 72, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, C.G.; Ioannidis, J.P. Reproducibility in Science. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seskute, G.; Jasionyte, G.; Rugiene, R.; Butrimiene, I. The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091641
Seskute G, Jasionyte G, Rugiene R, Butrimiene I. The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Medicina. 2023; 59(9):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091641
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeskute, Goda, Gabija Jasionyte, Rita Rugiene, and Irena Butrimiene. 2023. "The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review" Medicina 59, no. 9: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091641
APA StyleSeskute, G., Jasionyte, G., Rugiene, R., & Butrimiene, I. (2023). The Use of Superb Microvascular Imaging in Evaluating Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Medicina, 59(9), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091641




