ACE2-Inhibitory Effects of Bromelain and Ficin in Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.4. Cell-ELISA Method
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
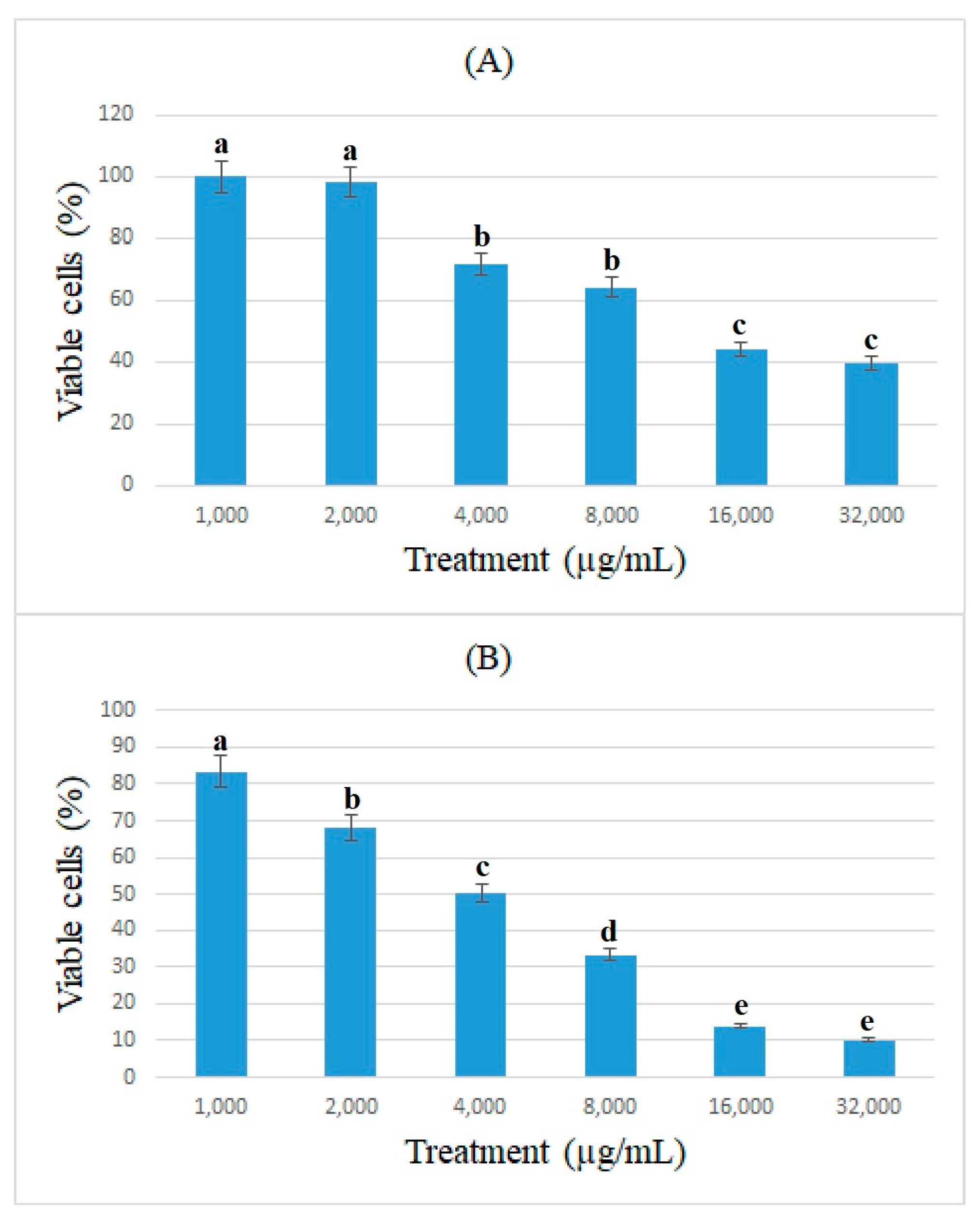
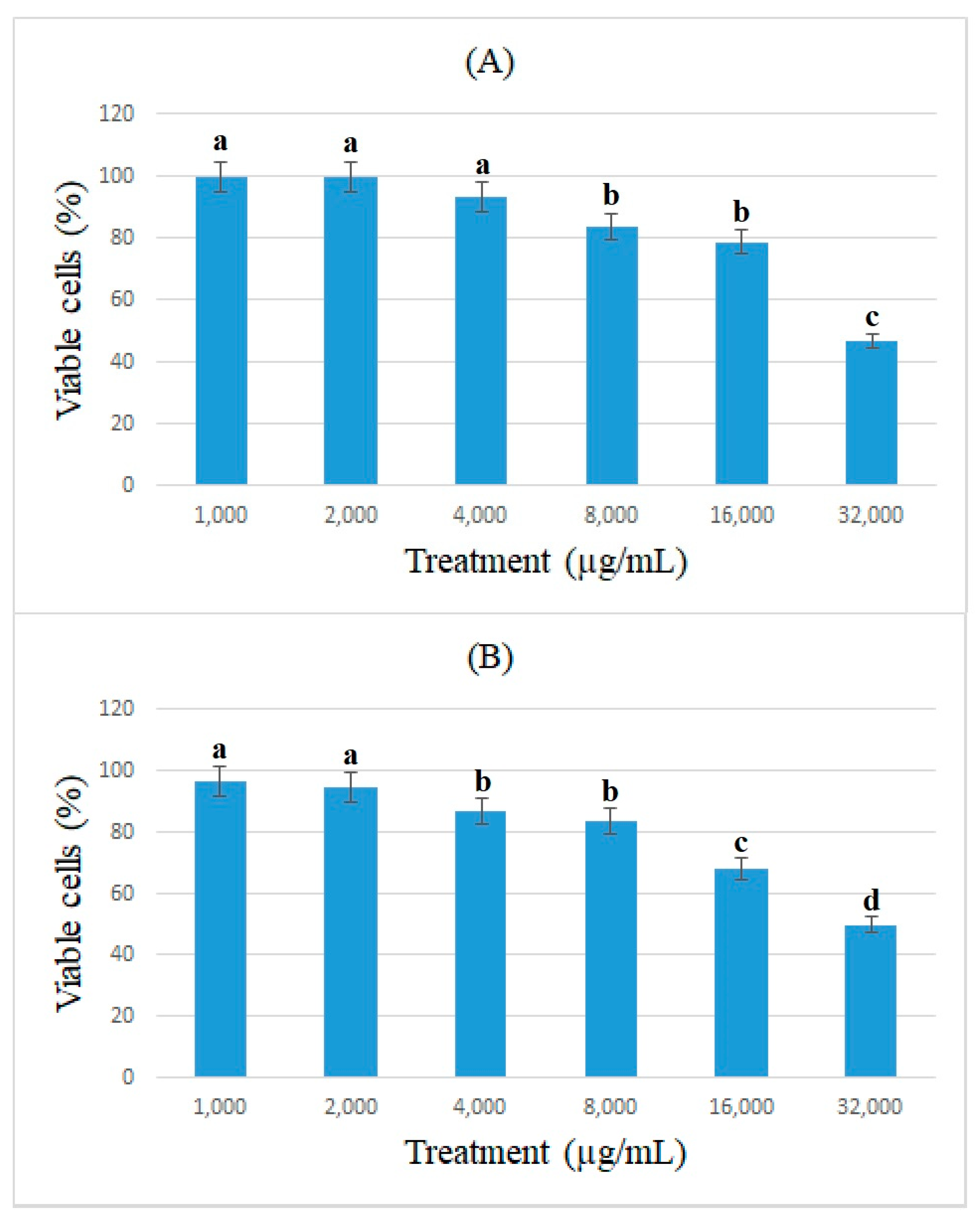
3.1. Antiproliferation Assay (MTT)
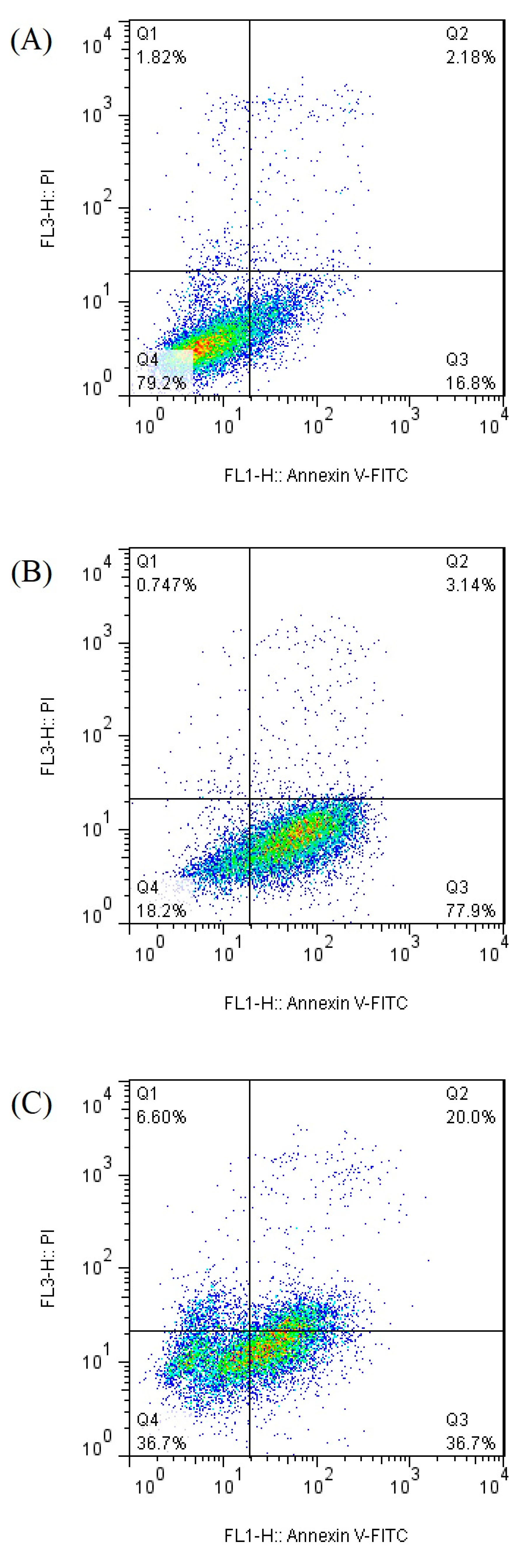
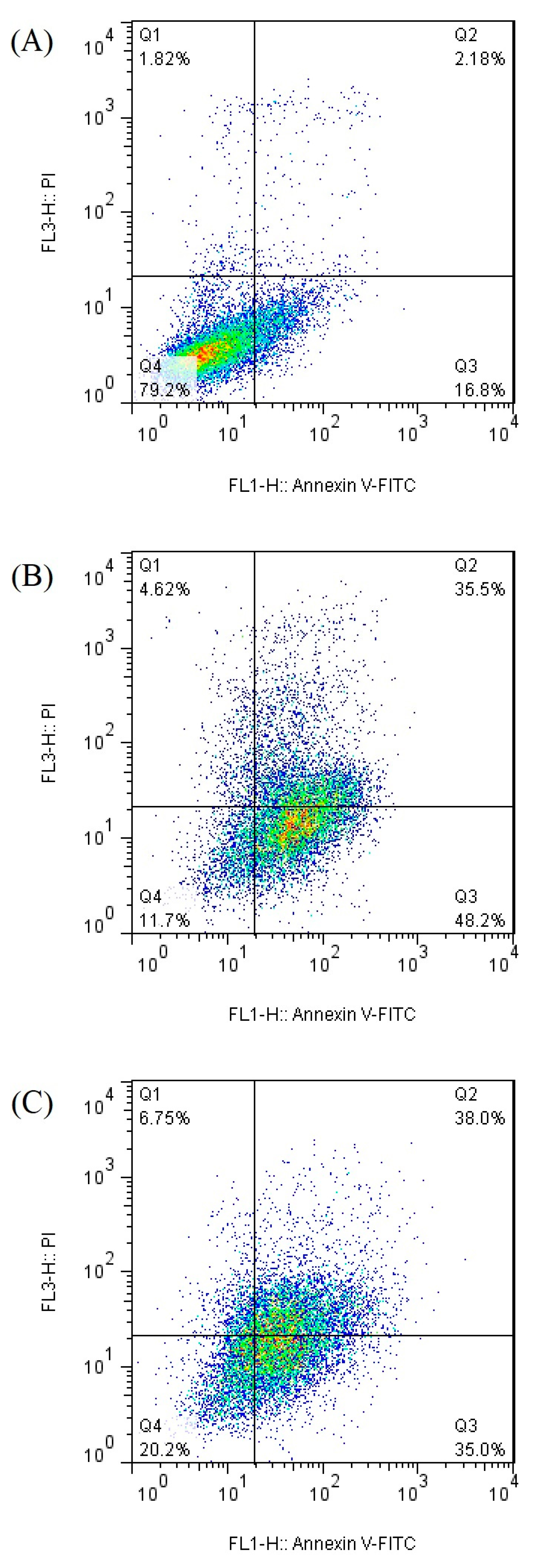
3.2. Apoptosis Analysis
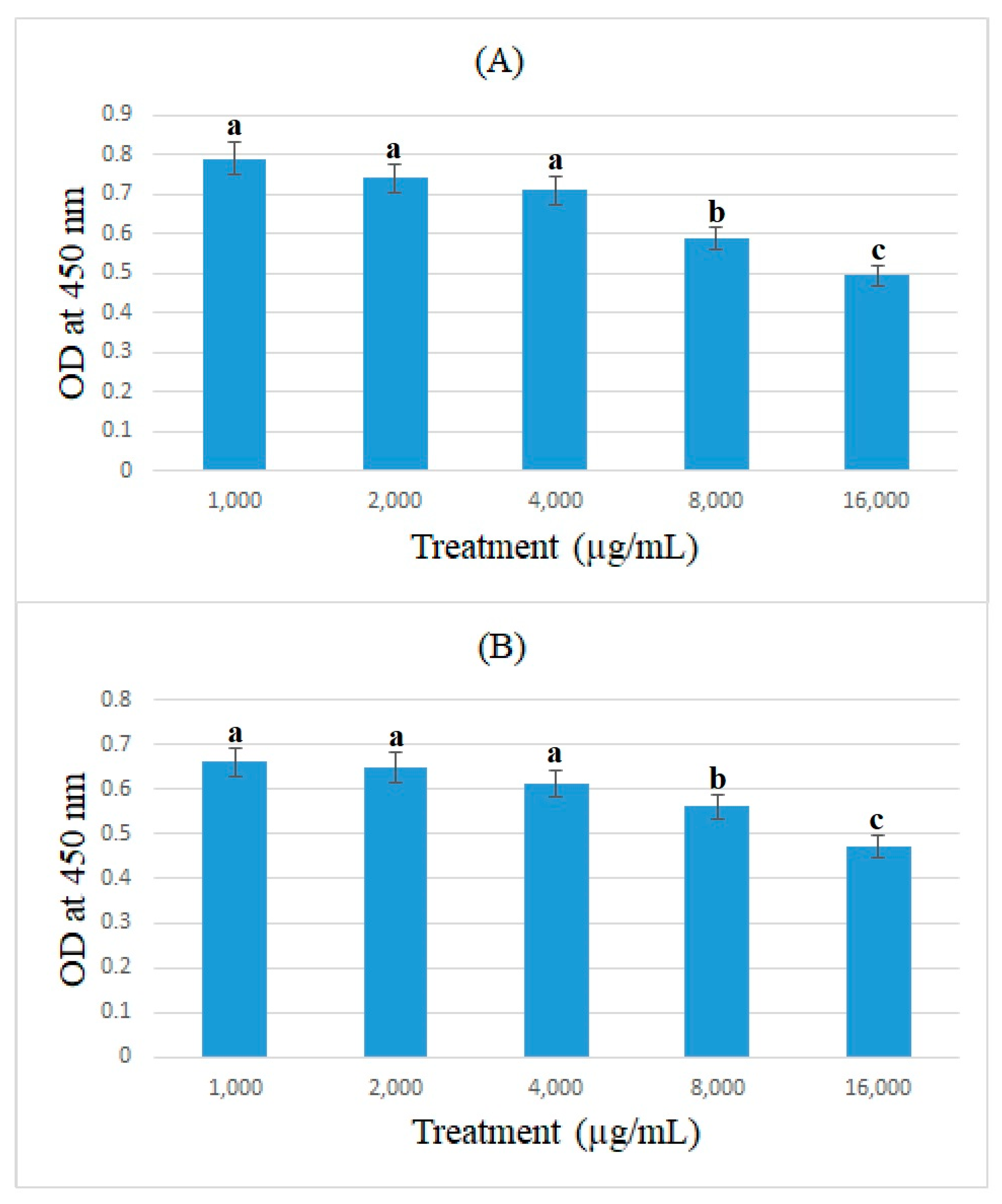
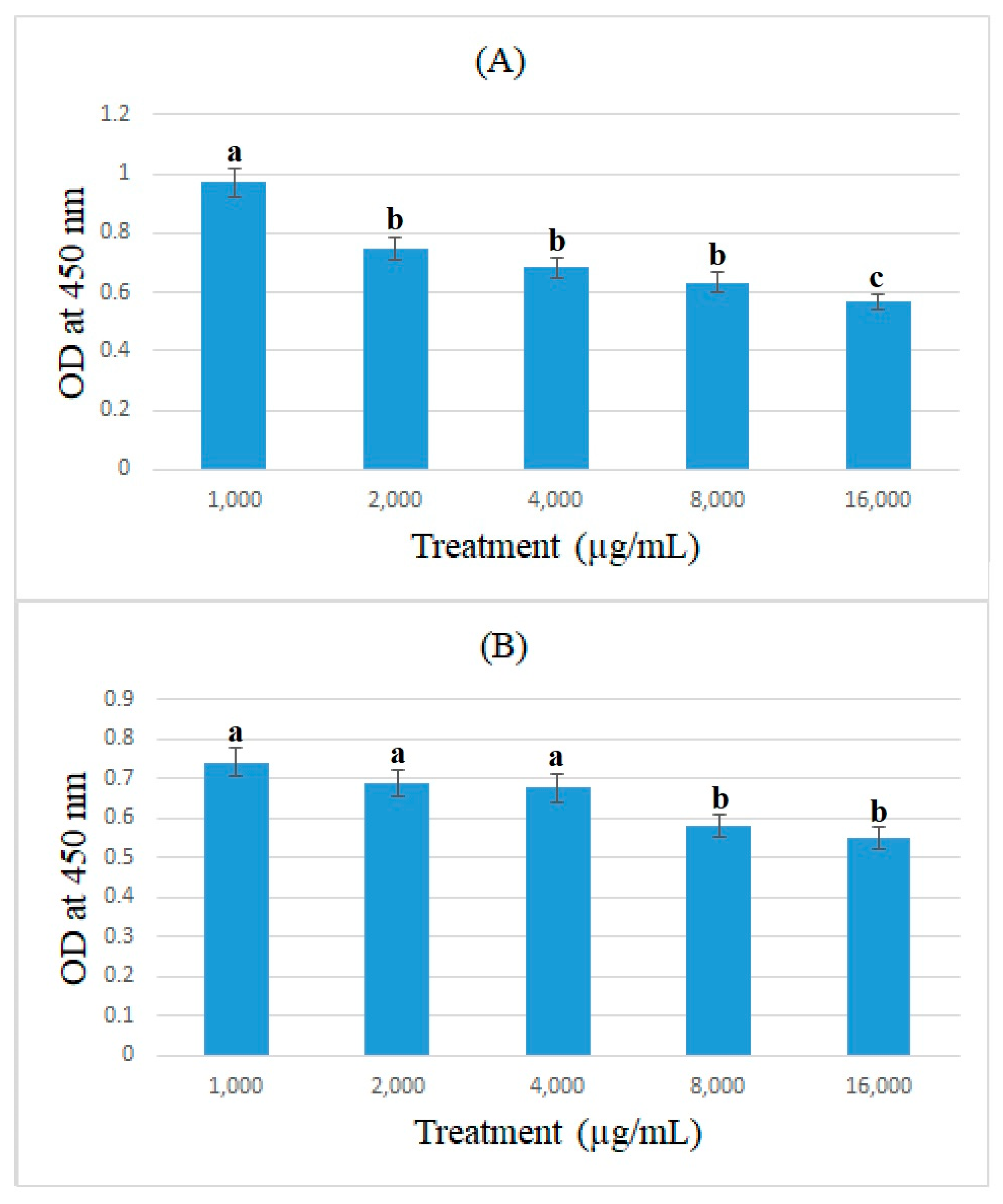
3.3. Cell-ELISA Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hikmet, F.; Méar, L.; Edvinsson, Å.; Micke, P.; Uhlén, M.; Lindskog, C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol. Syst. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, I.; Cooper, M.E.; Haagmans, B.L.; Hooper, N.M.; Korstanje, R.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Timens, W.; Turner, A.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. The emerging role of ACE2 in physiology and disease. J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2007, 212, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuiri, S.; Ohashi, Y. ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Jeffrey, C.T.; Liu, M.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Shenoy, V. ACE2 and microbiota: Emerging targets for cardiopulmonary disease therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.A.F.; de Brito, B.B.; Santos, M.L.C.; Marques, H.S.; da Silva Júnior, R.T.; de Carvalho, L.S.; Vieira, E.S.; Oliveira, M.V.; de Melo, F.F. COVID-19 gastrointestinal manifestations: A systematic review. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanopoulos, M.; Gkeros, F.; Doukatas, A.; Karianakis, G.; Pontas, C.; Tsoukalas, N.; Viazis, N.; Liatsos, C.; Mantzaris, G.J. COVID-19 pandemic: Pathophysiology and manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Potential role of ACE2 in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) prevention and management. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2020, 8, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, L.; You, R. Physiological and pathological regulation of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Expression of ACE2 in airways: Implication for COVID-19 risk and disease management in patients with chronic inflammatory respiratory diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.; Rathinavel, A.K.; Lutz, W.E.; Struble, L.R.; Khurana, S.; Schnaubelt, A.T.; Mishra, N.K.; Guda, C.; Palermo, N.Y.; Broadhurst, M.J. Bromelain inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection via targeting ACE-2, TMPRSS2, and spike protein. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeesan, P.; Jagadeesan, R.; Ramachandran, R. Bromelain: A Potential Therapeutic Solution For COVID-19. International J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2021, 12, 487–541. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, K.; Bid, H.K.; Konwar, R. Reinventing the ACE inhibitors: Some old and new implications of ACE inhibition. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, R.; Baruwa, A. Pharmacological review on natural ACE inhibitors. Pharm. Lett. 2010, 2, 273–293. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, R.; Jain, S.; Kumar, A. Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 976203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, A.; Natoli, V.; Casu, C. Bromelain: An Overview of Applications in Medicine and Dentistry. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 8165–8170. [Google Scholar]
- Baidamshina, D.R.; Trizna, E.Y.; Holyavka, M.G.; Bogachev, M.I.; Artyukhov, V.G.; Akhatova, F.S.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Kayumov, A.R. Targeting microbial biofilms using Ficin, a nonspecific plant protease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep46068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Chen, G.; Li, Y. Production and characterization of antioxidative hydrolysates and peptides from corn gluten meal using papain, ficin, and bromelain. Molecules 2020, 25, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakbin, B.; Pishkhan Dibazar, S.; Allahyari, S.; Javadi, M.; Farasat, A.; Darzi, S. Probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii supernatant inhibits survivin gene expression and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbin, B.; Dibazar, S.P.; Allahyari, S.; Javadi, M.; Amani, Z.; Farasat, A.; Darzi, S. Anticancer Properties of Probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii Supernatant on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhoi, S.K.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Ranjbar, S.; Khaleghi, S.; Farasat, A. Liposomal nanoparticle armed with bivalent bispecific single-domain antibodies, novel weapon in HER2 positive cancerous cell lines targeting. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 96, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnavelu, V.; Alitheen, N.B.; Sohila, S.; Kanagesan, S.; Ramesh, R. Potential role of bromelain in clinical and therapeutic applications. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, B.K. Bromelain: An overview. Nat. Prod. Radiance 2008, 7, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- de Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Lopes, A.M.; de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma, V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa Junior, A. Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MüLLER, A.; Barat, S.; Chen, X.; Bui, K.C.; Bozko, P.; Malek, N.P.; Plentz, R.R. Comparative study of antitumor effects of bromelain and papain in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2025–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeisi, F.; Raeisi, E.; Heidarian, E.; Shahbazi-Gahroui, D.; Lemoigne, Y. Bromelain inhibitory effect on colony formation: An In vitro Study on human AGS, PC3, and MCF7 cancer cells. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2019, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badgujar, S.B.; Patel, V.V.; Bandivdekar, A.H.; Mahajan, R.T. Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Ficus carica: A review. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barolo, M.I.; Mostacero, N.R.; López, S.N. Ficus carica L. (Moraceae): An ancient source of food and health. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, M.; Qiu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, L. The Inhibitory Effects of Ficin on Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Formation. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6692328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.; Abediankenari, S.; Ghasemi, M.; Azadbakht, M.; Yousefzadeh, Y.; Dehpour, A. The effect of fig tree latex (Ficus carica) on stomach cancer line. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2011, 13, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, B.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Han, S.H.; Hwang, E.J.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, B.-R.; Kim, C.S. Latex of Ficus carica L. induces apoptosis through caspase and Bcl-2 family in FaDu human hypopharynx squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oral Biol. 2017, 42, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, A.D.; Janiak, M.C.; Marrone, F.; Arora, P.S.; Higham, J.P. Comparative ACE2 variation and primate COVID-19 risk. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Xie, X. Reply to:‘Interaction between RAAS inhibitors and ACE2 in the context of COVID-19′. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Neptune, E.; Cui, H. Targeting ACE2 for COVID-19 therapy: Opportunities and challenges. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoufaly, A.; Poglitsch, M.; Aberle, J.H.; Hoepler, W.; Seitz, T.; Traugott, M.; Grieb, A.; Pawelka, E.; Laferl, H.; Wenisch, C. Human recombinant soluble ACE2 in severe COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, Z.; Higazi, A.A.R.; Kinaneh, S.; Armaly, Z.; Skorecki, K.; Heyman, S.N. ACE2, COVID-19 infection, inflammation, and coagulopathy: Missing pieces in the puzzle. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritis, P.; Karampela, I.; Kokoris, S.; Dalamaga, M. The combination of bromelain and curcumin as an immune-boosting nutraceutical in the prevention of severe COVID-19. Metab. Open 2020, 8, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, S.; Kumkum, F.A.; Bashar, F.; Rahman, A. Exploring the lived experiences of pregnant women and community health care providers during the pandemic of COVID-19 in Bangladesh through a phenomenological analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Yuan, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, Y. ACE inhibitory activity in vitro and antihypertensive effect in vivo of LSGYGP and its transepithelial transport by Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103488. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, Y. Preparation and identification of novel inhibitory angiotensin-I-converting enzyme peptides from tilapia skin gelatin hydrolysates: Inhibition kinetics and molecular docking. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5251–5259. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pakbin, B.; Dibazar, S.P.; Allahyari, S.; Shariatifar, H.; Brück, W.M.; Farasat, A. ACE2-Inhibitory Effects of Bromelain and Ficin in Colon Cancer Cells. Medicina 2023, 59, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020301
Pakbin B, Dibazar SP, Allahyari S, Shariatifar H, Brück WM, Farasat A. ACE2-Inhibitory Effects of Bromelain and Ficin in Colon Cancer Cells. Medicina. 2023; 59(2):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020301
Chicago/Turabian StylePakbin, Babak, Shaghayegh Pishkhan Dibazar, Samaneh Allahyari, Hanifeh Shariatifar, Wolfram Manuel Brück, and Alireza Farasat. 2023. "ACE2-Inhibitory Effects of Bromelain and Ficin in Colon Cancer Cells" Medicina 59, no. 2: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020301
APA StylePakbin, B., Dibazar, S. P., Allahyari, S., Shariatifar, H., Brück, W. M., & Farasat, A. (2023). ACE2-Inhibitory Effects of Bromelain and Ficin in Colon Cancer Cells. Medicina, 59(2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020301






