Combining Surgical Innovations in Amputation Surgery—Robotic Harvest of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle, Transplantation and Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Improves Myocontrol Capability and Pain in a Transradial Amputee
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Prosthetic Hand Replacement and Control
1.2. The Rectus Abdominis (RA) Muscle in Reconstructive Surgery
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case
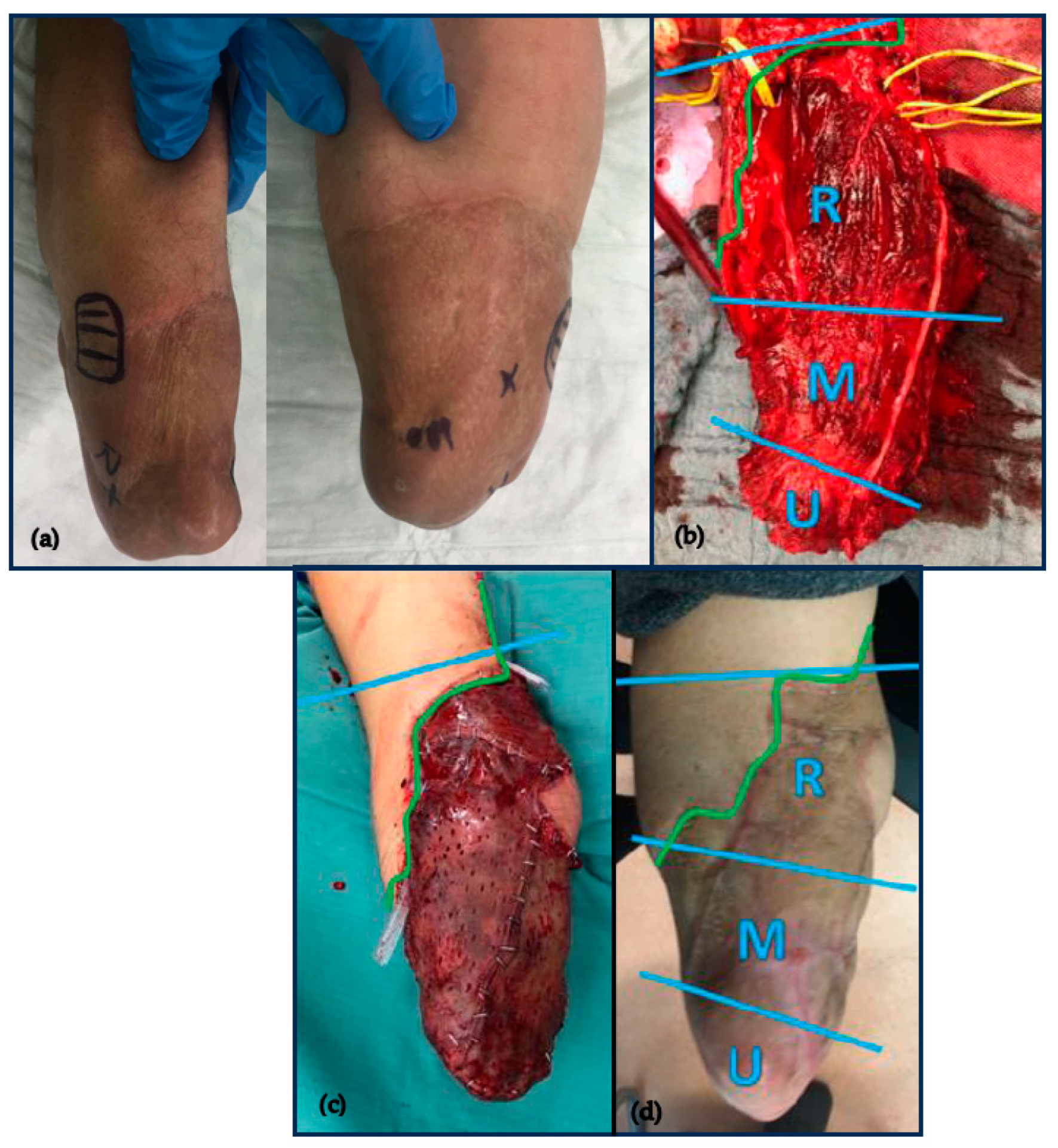
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Rehabilitation Protocol
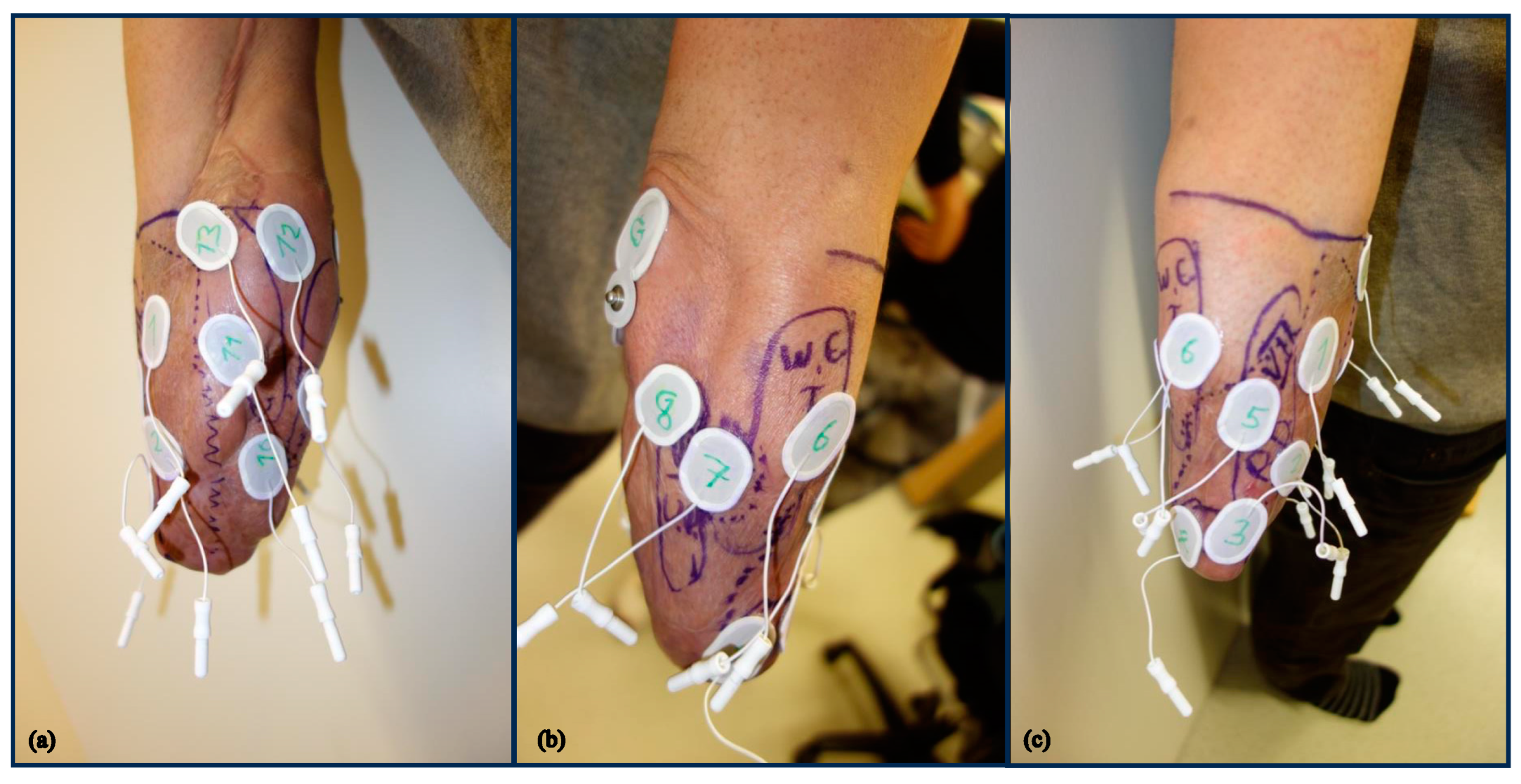
2.4. Myoelectric and Sensory Assessment
2.5. EMG Analysis
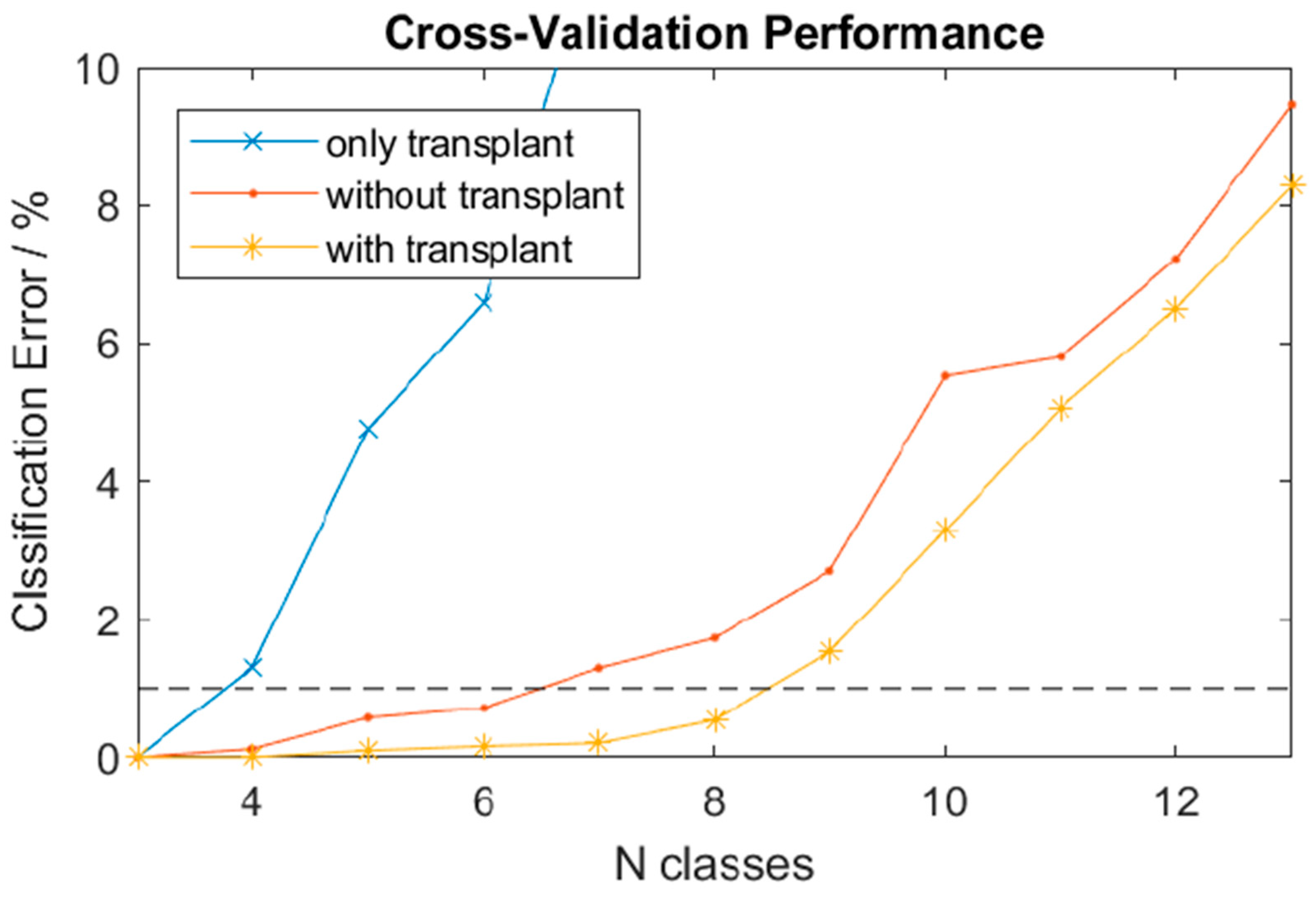
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Course
3.1.1. Wound Healing
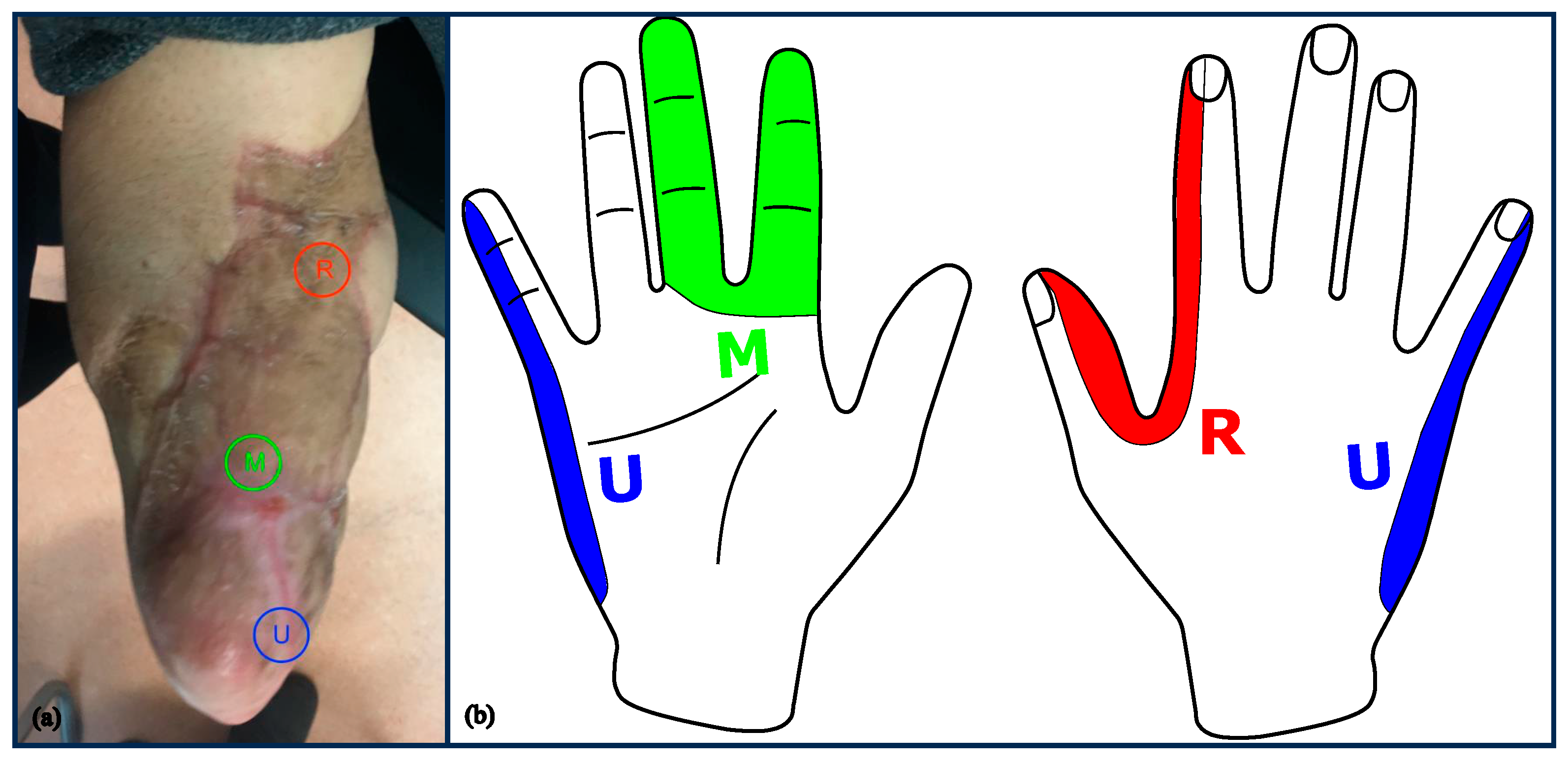
3.1.2. Residual Limb Pain (RLP)
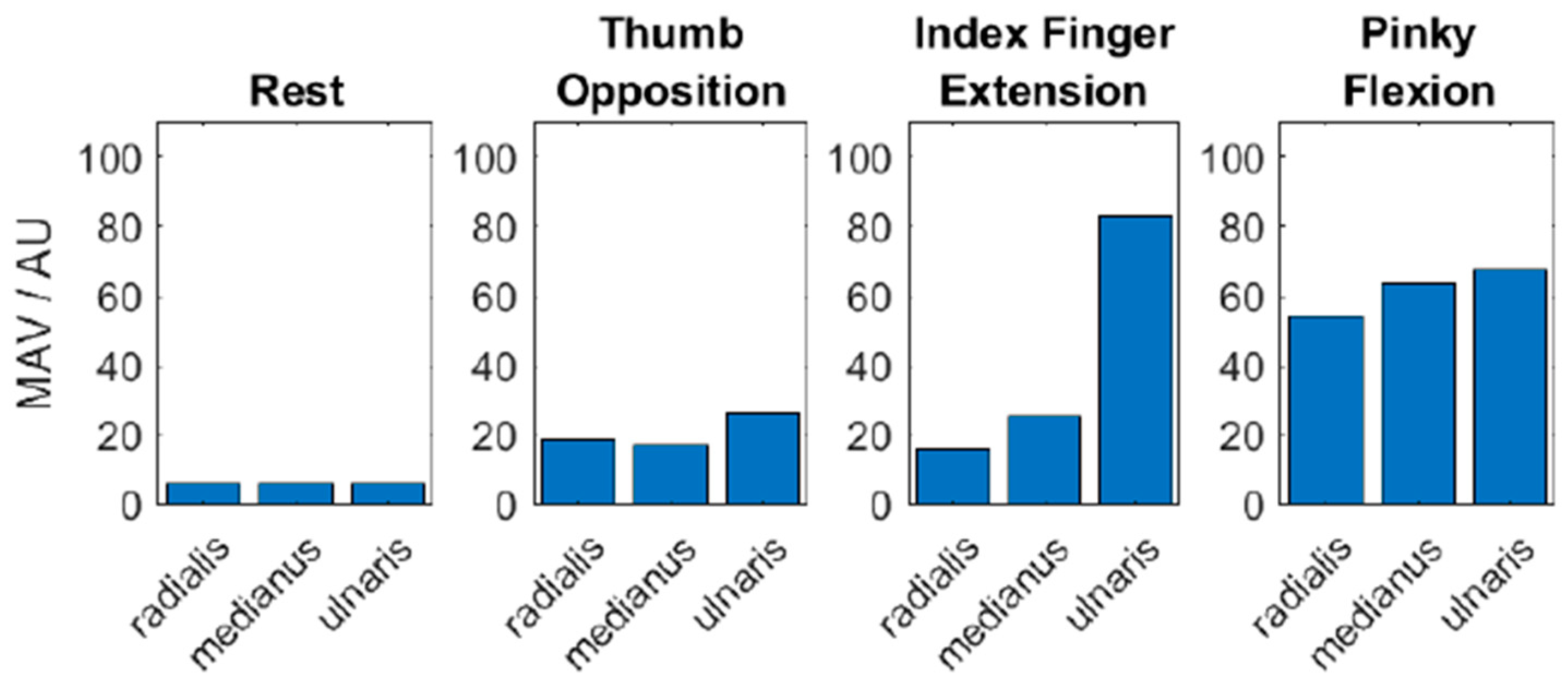
3.2. EMG-Activity Patterns of the Transplant
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, L.A.; Lederman, S.J. Human Hand Function; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, D. The World of Touch; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Muzumdar, A. Powered Upper Limb Prostheses: Control, Implementation and Clinical Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Dosen, S.; Muller, K.-R.; Farina, D. Myoelectric Control of Artificial Limbs—Is There a Need to Change Focus? [In the Spotlight]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 152-150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwell, A.; Kenney, L.; Thies, S.; Galpin, A.; Head, J. The Reality of Myoelectric Prostheses: Understanding What Makes These Devices Difficult for Some Users to Control. Front. Neurorobot. 2016, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiken, T.A.; Li, G.; Lock, B.A.; Lipschutz, R.D.; Miller, L.A.; Stubblefield, K.A.; Englehart, K.B. Targeted muscle reinnervation for real-time myoelectric control of multifunction artificial arms. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 301, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiken, T.A.; Miller, L.A.; Lipschutz, R.D.; Lock, B.A.; Stubblefield, K.; Marasco, P.D.; Dumanian, G.A. Targeted reinnervation for enhanced prosthetic arm function in a woman with a proximal amputation: A case study. Lancet 2007, 369, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheesborough, J.E.; Smith, L.H.; Kuiken, T.A.; Dumanian, G.A. Targeted muscle reinnervation and advanced prosthetic arms. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2015, 29, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A.D.; Lakey, B.; Mendez, I.; Vujaklija, I.; Farina, D.; Aszmann, O.C. Clinical Perspectives in Upper Limb Prostheses: An Update. Curr. Surg. Reports 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, D.M.; MacLachlan, M. Prevalence and characteristics of phantom limb pain and residual limb pain in the long term after upper limb amputation. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2010, 33, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.M.; Cheesborough, J.E.; Ko, J.H.; Cho, M.S.; Kuiken, T.A.; Dumanian, G.A. Targeted Muscle Reinnervation: A Novel Approach to Postamputation Neuroma Pain. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlenwein, J.; Diers, M.; Ernst, J.; Schulz, F.; Petzke, F. Clinical updates on phantom limb pain. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.N.; Potter, B.K.; Souza, J.M.; Tintle, S.M.; Nanos, G.P. Targeted muscle reinnervation for transradial amputation: Description of operative technique. Tech. Hand Up. Extrem. Surg. 2016, 20, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, D.; Reissis, D.; Sadri, A.; Sadigh, P. Targeted muscle reinnervation for pain control in an elective transradial amputation. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2018, 71, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipschutz, R. Impact of Emerging Technologies on Clinical Considerations: Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Surgeries, Pattern Recognition, Implanted Electrodes, Osseointegration, and Three-Dimensional Printed Solutions. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2017, 29, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horch, R.E.; Stark, G.B. The rectus abdominis free flap as an emergency procedure in extensive upper extremity soft-tissue defects. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 103, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whetzel, T.P.; Huang, V. The vascular anatomy of the tendinous intersections of the rectus abdominis muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1996, 98, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchateau, J.; Declety, A.; Lejour, M. Innervation of the rectus abdominis muscle: Implications for rectus flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1988, 82, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.I.; Corlett, R.J.; Boyd, J.B. The versatile deep inferior epigastric (inferior rectus abdominis) flap. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1984, 37, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Ko, J.H.; O’Shaughnessy, K.K.; Kuiken, T.A.; Pohlmeyer, E.A.; Dumanian, G.A. The effects of targeted muscle reinnervation on neuromas in a rabbit rectus abdominis flap model. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2012, 37, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeel, P.N.; Vanderstraeten, G.G.; Monstrey, S.J.; Van Landuyt, K.; Tonnard, P.; Lysens, R.; Matton, G. The donor site morbidity of free DIEP flaps and free TRAM flaps for breast reconstruction. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1997, 50, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.V.; Pedersen, J.C. Robotic harvest of the rectus abdominis muscle: A preclinical investigation and case report. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2012, 28, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.; Song, D.H.; Selber, J.C. Robotic, intraperitoneal harvest of the rectus abdominis muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Sarhane, K.A.; Pederson, J.C.; Selber, J.C. Robotic harvest of the rectus abdominis muscle: Principles and clinical applications. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2014, 28, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck-Gramcko, D.; Lubahn, J.D. The hoffmann-tinel sign. J. Hand Surg. 1993, 18, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, T.R.; Weir, R.F. The optimal controller delay for myoelectric prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, D.J.; Heard, D.C.Y.; Donovan, W.H. Epidemiologic overview of individuals with upper-limb loss and their reported research priorities. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 1996, 8, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.W.; Hagen, A.D.; Wood, M.B. Prosthetic Usage in Major Upper Extremity Amputations. J. Hand Surg. Am. Vol. 1995, 20, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanchek, M.G.; Wei, B.; Baghmanli, Z.; Sugg, K.; Cederna, P.S. Long-term stability of regenerative peripheral nerve interfaces (RPNI). Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128 (Suppl. S4), 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ernst, J.; Hahne, J.M.; Markovic, M.; Schilling, A.F.; Lorbeer, L.; Grade, M.; Felmerer, G. Combining Surgical Innovations in Amputation Surgery—Robotic Harvest of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle, Transplantation and Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Improves Myocontrol Capability and Pain in a Transradial Amputee. Medicina 2023, 59, 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122134
Ernst J, Hahne JM, Markovic M, Schilling AF, Lorbeer L, Grade M, Felmerer G. Combining Surgical Innovations in Amputation Surgery—Robotic Harvest of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle, Transplantation and Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Improves Myocontrol Capability and Pain in a Transradial Amputee. Medicina. 2023; 59(12):2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122134
Chicago/Turabian StyleErnst, Jennifer, Janne M. Hahne, Marko Markovic, Arndt F. Schilling, Lisa Lorbeer, Marian Grade, and Gunther Felmerer. 2023. "Combining Surgical Innovations in Amputation Surgery—Robotic Harvest of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle, Transplantation and Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Improves Myocontrol Capability and Pain in a Transradial Amputee" Medicina 59, no. 12: 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122134
APA StyleErnst, J., Hahne, J. M., Markovic, M., Schilling, A. F., Lorbeer, L., Grade, M., & Felmerer, G. (2023). Combining Surgical Innovations in Amputation Surgery—Robotic Harvest of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle, Transplantation and Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Improves Myocontrol Capability and Pain in a Transradial Amputee. Medicina, 59(12), 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122134







