Swallowing Exercise Evaluated Using High-Density Surface Electromyography in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Supplementary Analysis of an Exploratory Phase II Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Objectives and Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Measurement Items
2.3.1. Physical Status
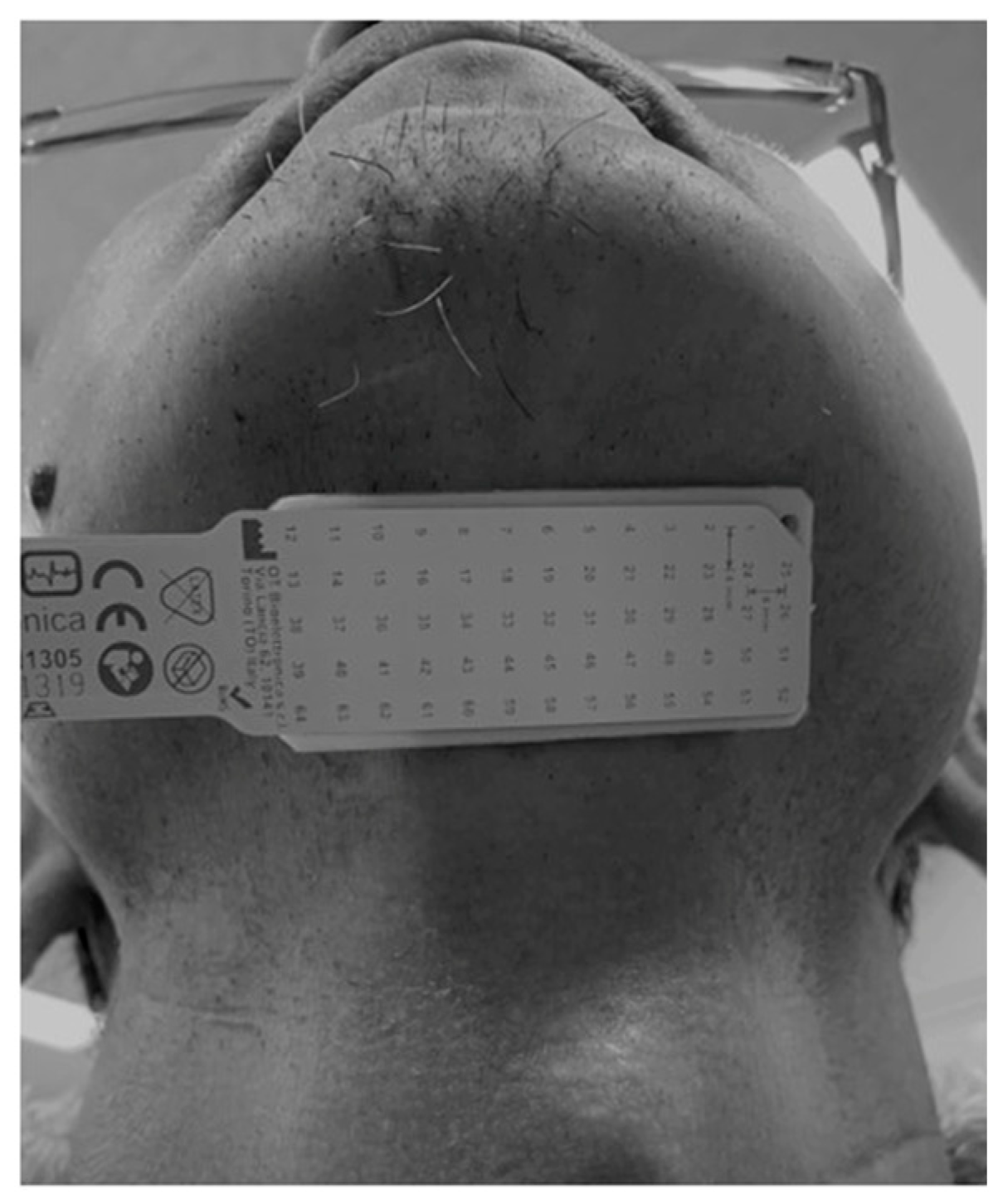
2.3.2. HD-sEMG
2.3.3. Measurements of Tongue Muscle Strength
2.3.4. Tongue Pressure
2.4. Swallowing Muscle Exercise
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Head and Neck Cancers. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-process/transparency-process-and-recommendations/GetFileFromFileManagerGuid?FileManagerGuidId=c0d39f8d-46a2-4662-b373-467ca4cacd96 (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Pignon, J.; Le Maître, A.; Maillard, E.; Maillard, E.; Bourhis, J.; MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer: An update on 93 randomised trials and 17346 patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Nie, W.; Zhou, X.; Guo, W.; Mou, J.; Yong, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, X. Review of prophylactic swallowing interventions for head and neck cancer. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 123, 104074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotz, T.; Federman, A.D.; Kao, J.; Milman, L.; Packer, S.; Lopez-Prieto, C.; Forsythe, K.; Genden, E.M. Prophylactic swallowing exercises in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing chemoradiation: A randomized trial. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnaby-Mann, G.; Crary, M.A.; Schmalfuss, I.; Amdur, R. ‘Pharyngocise’: Randomized controlled trial of preventative exercises to maintain muscle structure and swallowing function during head-and-neck chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. A randomized prospective study of rehabilitation therapy in the treatment of radiation-induced dysphagia and trismus. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2011, 187, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, R.; Loenneke, J.P.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Abe, T. Low-load bench press training to fatigue results in muscle hypertrophy similar to high-load bench press training. Int. J. Clin. Med. 2013, 4, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; West, D.W.; Burd, N.A.; Breen, L.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance exercise load does not determine training-mediated hypertrophic gains in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtermann, A.; Grönlund, C.; Stefan Karlsson, J.S.; Roeleveld, K. Spatial distribution of active muscle fibre characteristics in the upper trapezius muscle and its dependency on contraction level and duration. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtermann, A.; Roeleveld, K. EMG amplitude distribution changes over the upper trapezius muscle are similar in sustained and ramp contractions. Acta Physiol. 2006, 186, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Holobar, A.; Farina, D. Analysis of motor units with high-density surface electromyography. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Hamano, T.; Kasahara, T.; Toyokura, M.; Masakado, Y. Proposal for a modified jaw opening exercise for dysphagia: A randomized, controlled trial. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2017, 42, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Yumii, K.; Chikuie, N.; Taruya, T.; Horibe, Y.; Ishino, T.; Ueda, T.; Takeno, S.; Yoshimura, K. Evaluation of the safety of percutaneous sensory nerve stimulation in patients with head and neck cancer receiving chemoradiotherapy. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Koehler, K.M.; Gallagher, D.; Romero, L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R.R.; Garry, P.J.; Lindeman, R.D. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Komiya, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Morikawa, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Tashiro, T.; Fukui, K.; Kimura, H.; Urabe, Y. Effect of acute static stretching on the activation patterns using high-density surface electromyography of the gastrocnemius muscle during ramp-up task. Sensors 2021, 21, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, L.R.; Ward, E.C.; Cartmill, B.; Hill, A.J. Physiological changes to the swallowing mechanism following (chemo)radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Summary comments. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, H.M.; Daubert, C.R.; Mills, R.H. The interdependency of protein-energy malnutrition, aging, and dysphagia. Dysphagia 2000, 15, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.; Gangnon, R.E.; Theis, S.M.; Kays, S.A.; Hewitt, A.L.; Hind, J.A. The effects of lingual exercise on swallowing in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kuroda, R. Relationship between thinness and swallowing function in Japanese older adults: Implications for sarcopenic dysphagia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1785–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, I.; Fujiu-Kurachi, M.; Arai, H.; Hyodo, M.; Kagaya, H.; Maeda, K.; Mori, T.; Nishioka, S.; Oshima, F.; Ogawa, S.; et al. Sarcopenia and dysphagia: Position paper by four professional organizations. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hayashi, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Yagihashi, F.; Oikawa, L.O.; Ota, T. A significant association of malnutrition with dysphagia in acute patients. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, M.; Ireland, A.; Piasecki, J.; Stashuk, D.W.; Swiecicka, A.; Rutter, M.K.; Jones, D.A.; McPhee, J.S. Failure to expand the motor unit size to compensate for declining motor unit numbers distinguishes sarcopenic from non-sarcopenic older men. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momosaki, R.; Yasunaga, H.; Matsui, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Fushimi, K.; Abo, M. Effect of dysphagia rehabilitation on oral intake in elderly patients with aspiration pneumonia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Uchida, K.; Jeong, S.; Yamaga, M. Effects of nutritional supplements on muscle mass and activities of daily living in elderly rehabilitation patients with decreased muscle mass: A randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, P.M.; Luschei, E.S.; Jaffe, D.; McCulloch, T.M. Contributions of individual muscles to the submental surface electromyogram during swallowing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1999, 42, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | No. of Patients (n = 10) | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 10 | 100 |
| Female | 0 | 0 |
| Age, years | ||
| Median | 67 | |
| Range | 45–76 | |
| ECOG PS | ||
| 0 | 10 | 100 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Primary sites of cancer | ||
| Nasopharyngeal | 1 | 10 |
| Hypopharyngeal | 7 | 70 |
| Laryngeal | 1 | 10 |
| Unknown primary | 1 | 10 |
| TNM stage | ||
| II | 2 | 20 |
| ⅣA | 4 | 40 |
| ⅣB | 4 | 40 |
| Diabetes | ||
| + | 1 | 10 |
| − | 9 | 90 |
| Radiation therapy | ||
| 70 Gy/35 fractions | 9 | 90 |
| 66 Gy/33 fractions | 1 | 10 |
| Concurrent Chemotherapy | ||
| Cisplatin | 9 | 90 |
| Cetuximab | 1 | 10 |
| No. | Age/Sex | Primary Site | TNM/Stage | Treatment | Chemo Agent/Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70/male | Hypopharynx | T1N2bM0/Stage IVA | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/3 cycles |
| 2 | 59/male | Nasopharynx | T1N1M0/Stage II | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/2 cycles |
| 3 | 73/male | Primary Unknown | T0N3bM0/Stage IVB | CRT | Cisplatin/3 cycles |
| 4 | 76/male | Hypopharynx | T4aN2bM0/Stage IVA | BRT | Cetuximab/7 cycles |
| 5 | 72/male | Hypopharynx | T2N3bM0/Stage IVB | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/3 cycles |
| 6 | 64/male | Hypopharynx | T4aN2cM0/Stage IVA | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/2 cycles |
| 7 | 45/male | Hypopharynx | T4bN3bM0/Stage IVB | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/2 cycles |
| 8 | 74/male | Hypopharynx | T4aN3bM0/Stage IVB | CRT after IC 2cycles | Cisplatin/2 cycles |
| 9 | 51/male | Larynx | T2N0M0/Stage II | CRT | Cisplatin/3 cycles |
| 10 | 64/male | Hypopharynx | T1N2bM0/Stage IVA | CRT | Cisplatin/3 cycles |
| Indicator | Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.06 ± 3.61 | 20.99 ± 3.14 | 0.486 |
| SMI, kg/m2 | 7.67 ± 1.07 | 7.24 ± 1.15 | 0.399 |
| MTP, kpa | 33.39 ± 4.87 | 30.80 ± 5.90 | 0.298 |
| Coefficient of variation (50%), median [IQR] | 6.47 (3.95–13.82) | 5.89 (3.57–6.71) | 0.405 |
| Coefficient of variation (60%), median [IQR] | 8.95 (5.39–16.26) | 6.31(3.67–7.35) | 0.256 |
| Coefficient of variation (65%), median [IQR] | 7.42 (3.72–11.33) | 6.71 (5.51–7.93) | 0.939 |
| Root mean square (50%), median [IQR] | 1.14 (1.06–1.25) | 1.17 (0.95–1.24) | 0.496 |
| Root mean square (60%), median [IQR] | 1.24 (1.12–1.31) | 1.26 (0.95–1.39) | 0.570 |
| Root mean square (65%), median [IQR] | 1.26 [1.18–1.33] | 1.35 [1.02–1.42] | 0.969 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshikawa, K.; Hamamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Yumii, K.; Chikuie, N.; Taruya, T.; Ishino, T.; Horibe, Y.; Takemoto, K.; Nishida, M.; et al. Swallowing Exercise Evaluated Using High-Density Surface Electromyography in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Supplementary Analysis of an Exploratory Phase II Trial. Medicina 2023, 59, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122120
Yoshikawa K, Hamamoto T, Sato Y, Yumii K, Chikuie N, Taruya T, Ishino T, Horibe Y, Takemoto K, Nishida M, et al. Swallowing Exercise Evaluated Using High-Density Surface Electromyography in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Supplementary Analysis of an Exploratory Phase II Trial. Medicina. 2023; 59(12):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122120
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshikawa, Kohei, Takao Hamamoto, Yuki Sato, Kohei Yumii, Nobuyuki Chikuie, Takayuki Taruya, Takashi Ishino, Yuichiro Horibe, Kota Takemoto, Manabu Nishida, and et al. 2023. "Swallowing Exercise Evaluated Using High-Density Surface Electromyography in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Supplementary Analysis of an Exploratory Phase II Trial" Medicina 59, no. 12: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122120
APA StyleYoshikawa, K., Hamamoto, T., Sato, Y., Yumii, K., Chikuie, N., Taruya, T., Ishino, T., Horibe, Y., Takemoto, K., Nishida, M., Kawasumi, T., Ueda, T., Nishikawa, Y., Mikami, Y., & Takeno, S. (2023). Swallowing Exercise Evaluated Using High-Density Surface Electromyography in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Supplementary Analysis of an Exploratory Phase II Trial. Medicina, 59(12), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122120







