Analysis of Medication Errors Reported by Community Pharmacists in the Republic of Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohn, L.T.; Corrigan, J.M.; Donaldson, M.S. (Eds.) To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Launches Global Effort to Halve Medication-Related Errors in 5 Years. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-03-2017-who-launches-global-effort-to-halve-medication-related-errors-in-5-years (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Aronson, J.K. Medication errors: What they are, how they happen, and how to avoid them. Q. J. Med. 2009, 102, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Conceptual Framework for the International Classification for Patient Safety Version 1.1: Final Technical Report January 2009. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/70882 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- World Health Organization. Medication Errors: Technical Series on Safer Primary Care. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/252274 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Azar, C.; Thomas, L.; Gras-Champel, V.; Laroche, M.L.; Grau, M.; Allué, D.; Saleh, N.; Maison, P. Patterns of Medication Errors Involving Older Adults Reported to the French Medication Error Guichet. J. Patient Saf. 2022, 18, e514–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronovost, P.J.; Morlock, L.L.; Sexton, J.B.; Miller, M.R.; Holzmueller, C.G.; Thompson, D.A.; Lubomski, L.H.; Wu, A.W. Improving the Value of Patient Safety Reporting Systems. In Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches (Vol. 1: Assessment); Henriksen, K., Battles, J.B., Keyes, M.A., Grady, M.L., Eds.; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E. Safety climate and attitude toward medication error reporting after hospital accreditation in South Korea. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2016, 28, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.J.; Lee, H.; Son, Y.J. Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Medication Error Reporting among Early- and Mid-Career Female Nurses in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Suh, H.S. Current state of medication error in Korea: Analysis of medication injury relief in Korea Consumer Agency. J. Health Technol. Assess 2019, 7, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Yug, J.S.; Ki, D.Y.; Yoon, J.E.; Kang, S.W.; Chung, E.K. Characterization of Medication Errors in a Medical Intensive Care Unit of a University Teaching Hospital in South Korea. J. Patient Saf. 2022, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Kim, H.E.; Chung, S.; Park, B.J. Pediatric medication error reports in Korea adverse event reporting system database, 1989–2012: Comparing with adult reports. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. Available online: https://www.koiha.or.kr/web/kr/index.do (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, M. Community Pharmacy-based Patient Safety Activities: Focused on the Regional Patient Safety Center of the Korean Pharmaceutical Association. Yakhak Hoeji 2020, 64, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knottnerus, A.; Tugwell, P. STORBE—A checklist to STrengthen the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. About Medication Errors. Available online: https://www.nccmerp.org/about-medication-errors (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- World Health Organization. Reporting and Learning Systems for Medication Errors: The Role of Pharmacovigilance Centres. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/137036 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Aspden, P.W.J.; Bootman, J.L.; Cronenwett, L.R. Preventing Medication Errors: Quality Chasm Series; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 463. [Google Scholar]
- National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. NCC MERP Taxonomy of Medication Errors. Available online: https://www.nccmerp.org/taxonomy-medication-errors-now-available (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- De Las Mercedes Martínez Sánchez, A. Medication errors in a Spanish community pharmacy: Nature, frequency and potential causes. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 35, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adie, K.; Fois, R.A.; McLachlan, A.J.; Walpola, R.L.; Chen, T.F. The nature, severity and causes of medication incidents from an Australian community pharmacy incident reporting system: The QUMwatch study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4809–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, G.; Phillips, R.; Graham, D.; Hickner, J. Medication errors reported by US family physicians and their office staff. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2008, 17, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, J.C.; Story, J.L.; Hicks, R.W.; Shore, A.D.; Morlock, L.L.; Cheung, D.S.; Kelen, G.D.; Pronovost, P.J. National Study on the Frequency, Types, Causes, and Consequences of Voluntarily Reported Emergency Department Medication Errors. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, D.H.; Gerrett, D.; Warner, B. A review of medication incidents reported to the National Reporting and Learning System in England and Wales over 6 years (2005–2010). Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, M.J.; Evans, S.M.; Smith, B.J.; Berry, J.G. Attitudes of doctors and nurses towards incident reporting: A qualitative analysis. Med. J. Aust. 2004, 181, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.J.; Patel, M.; Martin, J.R.; Hincapie, A.L.; Axon, D.R.; Warholak, T.L.; Slack, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of community pharmacy error rates in the USA: 1993–2015. BMJ Open Qual. 2018, 7, e000193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, D.L.; Tam, W.V.; Ashcroft, D.M. Integrating Data from the UK National Reporting and Learning System with Work Domain Analysis to Understand Patient Safety Incidents in Community Pharmacy. J. Patient Saf. 2017, 13, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.L.; Barlow, D.; McArtney, R.; Hiom, S.; Roberts, D.; Whittlesea, C. Incidence, type and causes of dispensing errors: A review of the literature. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2010, 17, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynskey, D.; Haigh, S.J.; Patel, N.; Macadam, A.B. Medication errors in community pharmacy: An investigation into the types and potential causes. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2010, 15, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Hong, Y.D.; Cooke, C.E. Medication errors in community pharmacies: The need for commitment, transparency, and research. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Barker, K.A. Out-of-hospital medication errors: A 6-year analysis of the national poison data system. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2009, 18, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Practices, I.f.S.M. ISMP’s List of High Alert Medications in Community/Ambulatory Healthcare. Available online: https://www.ismp.org/recommendations/high-alert-medications-community-ambulatory-list (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Tariq, R.A.; Vashisht, R.; Sinha, A.; Scherbak, Y. Medication Dispensing Errors and Prevention; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, C.; Smith, S.R.; Keyes, M.A.; Hicks, R.W.; Cousins, D.D.; Clancy, C.M. How useful are voluntary medication error reports? The case of warfarin-related medication errors. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2008, 34, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
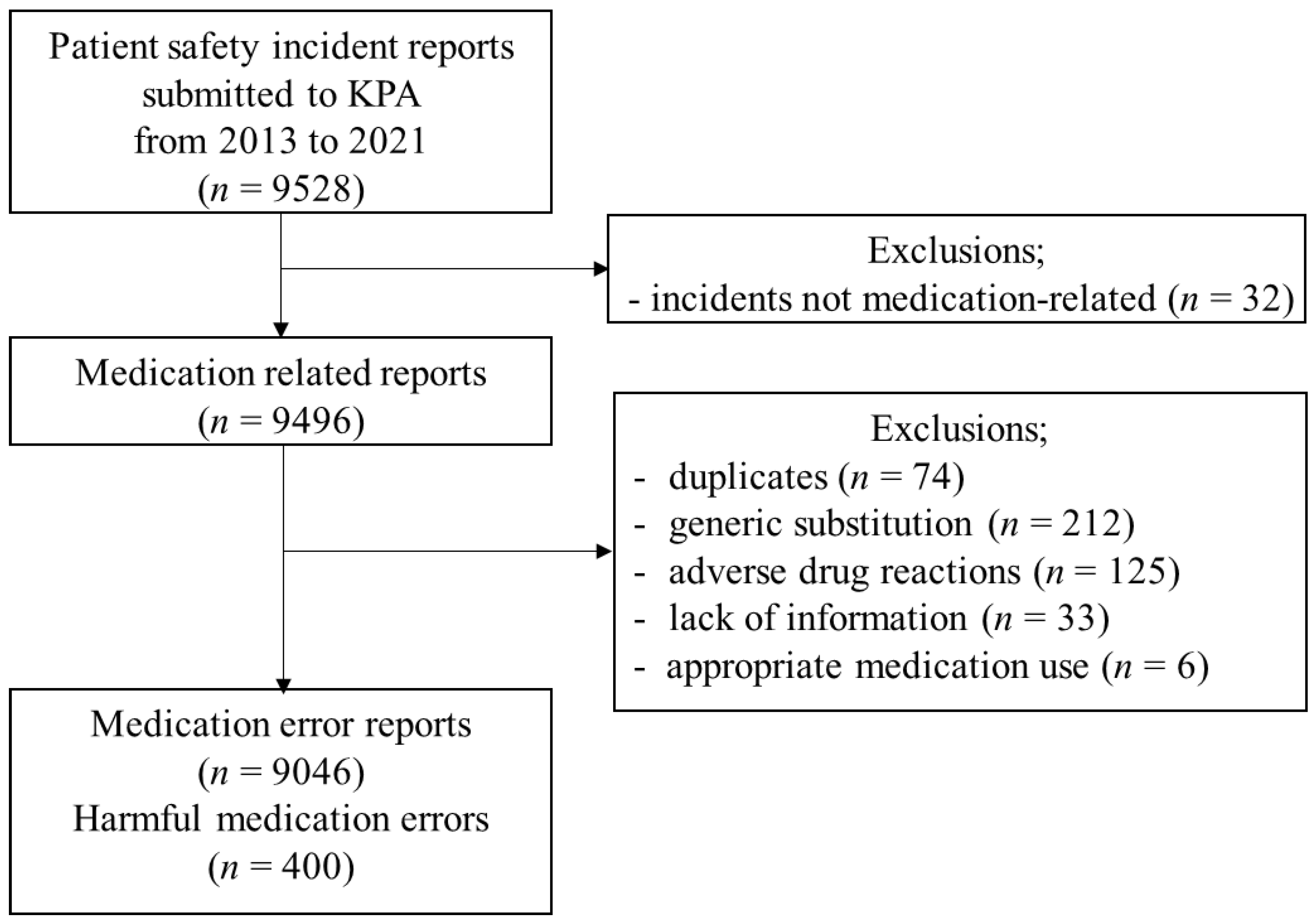
| Medication Use Process | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Prescribing | Dispensing | Administering | Others | Missing | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
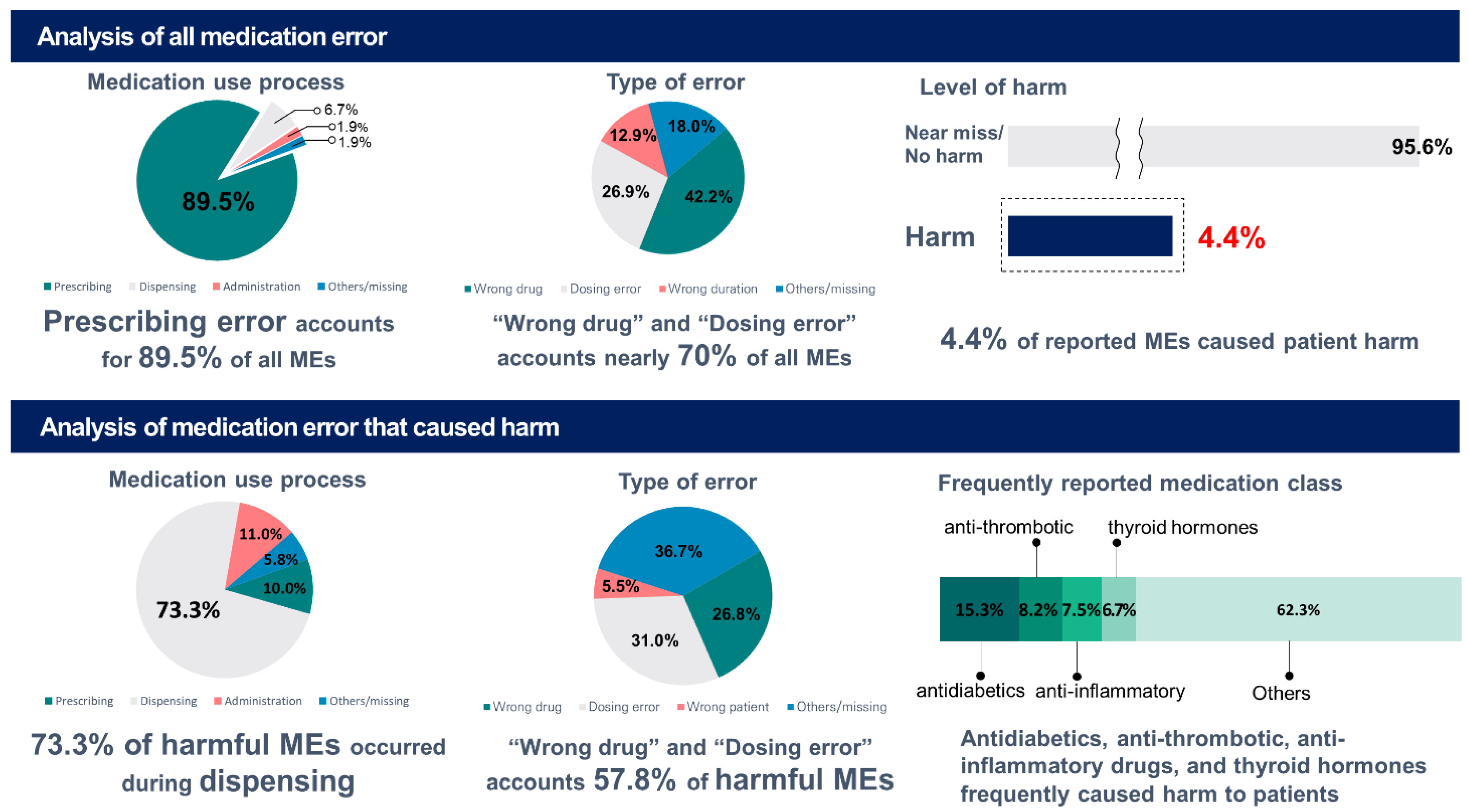
| Total | 9046 | 8098 | 605 | 171 | 72 | 100 |
| (100) | (89.5) | (6.7) | (1.9) | (0.8) | (1.1) | |
| Level of harm | ||||||
| Near miss | 7985 (88.3) | 7819 (86.4) | 109 (1.2) | 30 (0.3) | 17 (0.2) | 10 (0.1) |
| No harm | 121 (1.3) | 17 (0.2) | 43 (0.5) | 37 (0.4) | 24 (0.3) | 0 |
| Mild harm | 259 (2.9) | 25 (0.3) | 186 (2.1) | 34 (0.4) | 6 (0.1) | 9 (0.1) |
| Moderate harm | 135 (1.5) | 16 (0.2) | 101 (1.1) | 10 (0.1) | 0 | 8 (0.1) |
| Severe harm | 6 (0.1) | 0 | 6 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Missing | 540 (6.0) | 222 (2.5) | 160 (1.8) | 60 (0.7) | 25 (0.3) | 73 (0.8) |
| Type of error | ||||||
| Wrong drug | 3815 (42.2) | 3628 (40.1) | 149 (1.6) | 27 (0.3) | 0 | 11 (0.1) |
| Dosing error | 2437 (26.9) | 2193 (24.2) | 153 (1.7) | 86 (1.0) | 0 | 5 (0.1) |
| Wrong duration | 1136 (12.9) | 1136 (12.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Omission error | 513 (5.7) | 474 (5.2) | 20 (0.2) | 18 (0.2) | 0 | 1 (0.0) |
| Wrong form/route | 296 (3.3) | 272 (3.0) | 20 (0.2) | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Wrong patient | 157 (1.7) | 116 (1.3) | 41 (0.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wrong count | 58 (0.6) | 0 | 58 (0.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wrong storage | 11 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 11 (0.1) | 0 | 0 |
| Expired medication | 12 (0.1) | 0 | 11 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.0) |
| Mislabeling | 14 (0.2) | 0 | 14 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Others | 360 (4.0) | 237 (2.6) | 29 (0.3) | 22 (0.2) | 72 (0.8) | 0 |
| Missing | 237 (2.6) | 42 (0.5) | 110 (1.2) | 3 (0.0) | 0 | 82 (0.9) |
| Medication Use Process | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Prescribing | Dispensing | Administering | Others | Missing | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| Harmful MEs | 400 | 40 | 293 | 44 | 6 | 17 |
| (100) | (10.0) | (73.3) | (11.0) | (1.5) | (4.3) | |
| Level of harm | ||||||
| Mild harm | 259 (64.8) | 24 (6.0) | 186 (46.5) | 34 (8.5) | 6 (1.5) | 9 (2.3) |
| Moderate harm | 135 (33.8) | 16 (4.0) | 101 (25.3) | 10 (2.5) | 0 | 8 (2.0) |
| Severe harm | 6 (1.5) | 0 | 6 (1.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Type of error | ||||||
| Dosing error | 124 (31.0) | 9 (2.3) | 83 (20.8) | 27 (6.8) | 0 | 5 (1.3) |
| Wrong drug | 107 (26.8) | 20 (5.0) | 86 (21.5) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| Wrong patient | 22 (5.5) | 3 (0.8) | 19 (4.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Omission error | 14 (3.5) | 1 (0.3) | 9 (2.3) | 3 (0.8) | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| Wrong count | 13 (3.3) | 0 | 13 (3.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mislabeling | 6 (1.5) | 0 | 6 (1.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Expired medication | 6 (1.5) | 0 | 5 (1.3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.3) |
| Wrong storage | 5 (1.3) | 0 | 0 | 5 (1.3) | 0 | 0 |
| Wrong form/route | 2 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 0 | 0 |
| Others | 24 (6.0) | 0 | 13 (3.3) | 5 (1.3) | 6 (1.5) | 0 |
| Missing | 77 (19.3) | 7 (1.8) | 58 (14.5) | 3 (0.8) | 0 | 9 (2.3) |
| Harmful Medication Errors (N = 255) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Subgroup (ATC Level 2) a | N | % | Chemical Substance | N | % | |
| (ATC Level 5) a,b | ||||||
| A10 | Drugs used in diabetes | 39 | 15.3 | Warfarin | 15 | 5.9 |
| B01 | Anti-thrombotic agents | 21 | 8.2 | Levothyroxine sodium | 13 | 5.1 |
| M01 | Anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic products | 19 | 7.5 | Glimepiride | 9 | 3.5 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 5 | 2 | ||||
| H03 | Thyroid therapy | 17 | 6.7 | Clonazepam | 5 | 2 |
| N05 | Psycholeptics | 16 | 6.3 | Loxoprofen | 5 | 2 |
| C09 | Agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system | 14 | 5.5 | Atorvastatin | 4 | 1.6 |
| N03 | Anti-epileptics | 11 | 4.3 | Dexibuprofen | 4 | 1.6 |
| C10 | Lipid-modifying agents | 8 | 3.1 | Metformin | 4 | 1.6 |
| N02 | Analgesics | 8 | 3.1 | Naproxen | 4 | 1.6 |
| N06 | Psychoanaleptics | 8 | 3.1 | Pregabalin | 4 | 1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.-H.; Heo, K.-N.; Han, J.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Min, S.; Ah, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y. Analysis of Medication Errors Reported by Community Pharmacists in the Republic of Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2023, 59, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010151
Han J-H, Heo K-N, Han J, Lee M-S, Kim S-J, Min S, Ah Y-M, Lee J-Y. Analysis of Medication Errors Reported by Community Pharmacists in the Republic of Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina. 2023; 59(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ju-Hee, Kyu-Nam Heo, JiMin Han, Mo-Se Lee, Su-Jin Kim, Sangil Min, Young-Mi Ah, and Ju-Yeun Lee. 2023. "Analysis of Medication Errors Reported by Community Pharmacists in the Republic of Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study" Medicina 59, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010151
APA StyleHan, J.-H., Heo, K.-N., Han, J., Lee, M.-S., Kim, S.-J., Min, S., Ah, Y.-M., & Lee, J.-Y. (2023). Analysis of Medication Errors Reported by Community Pharmacists in the Republic of Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina, 59(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010151





