Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
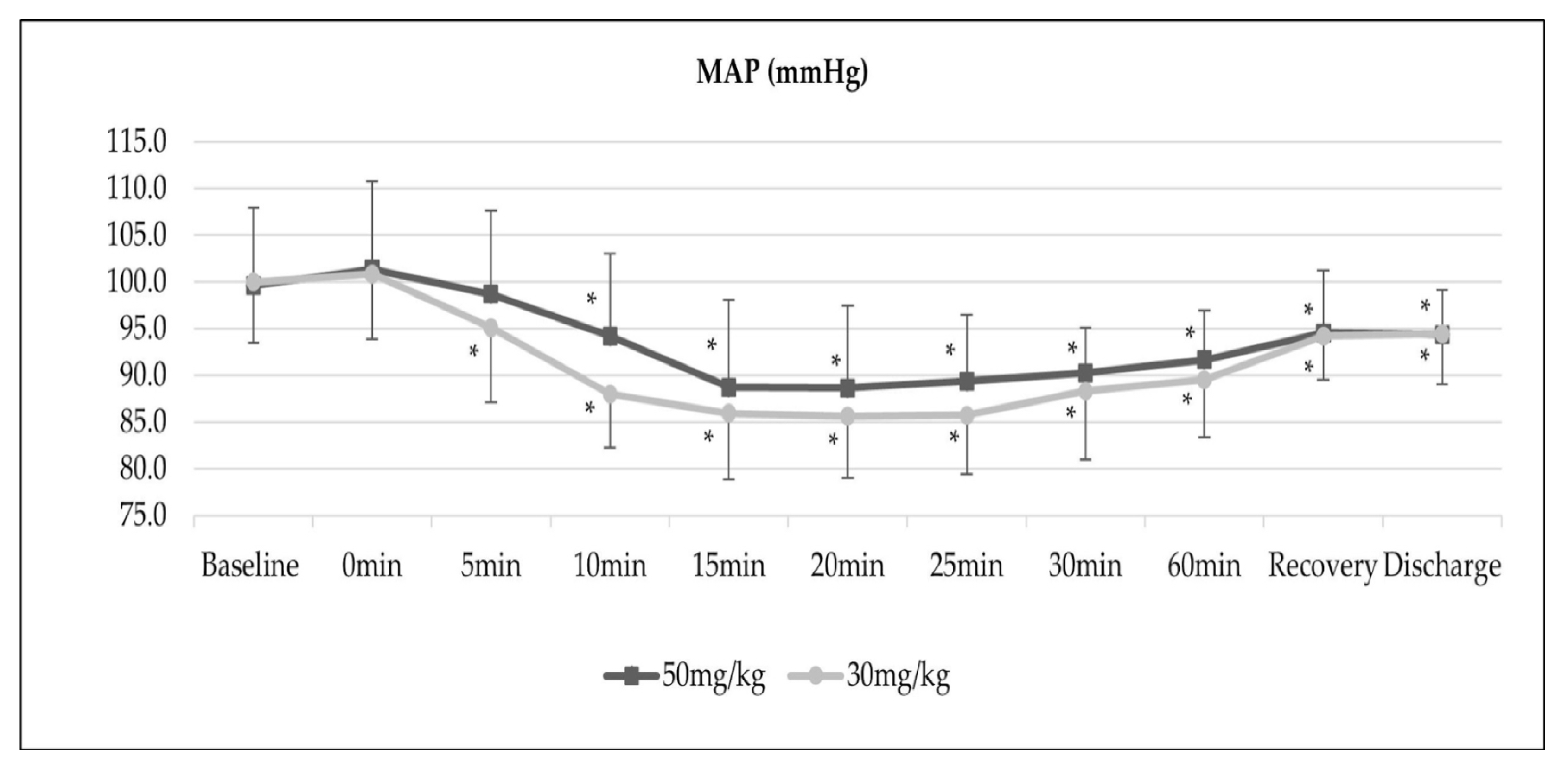
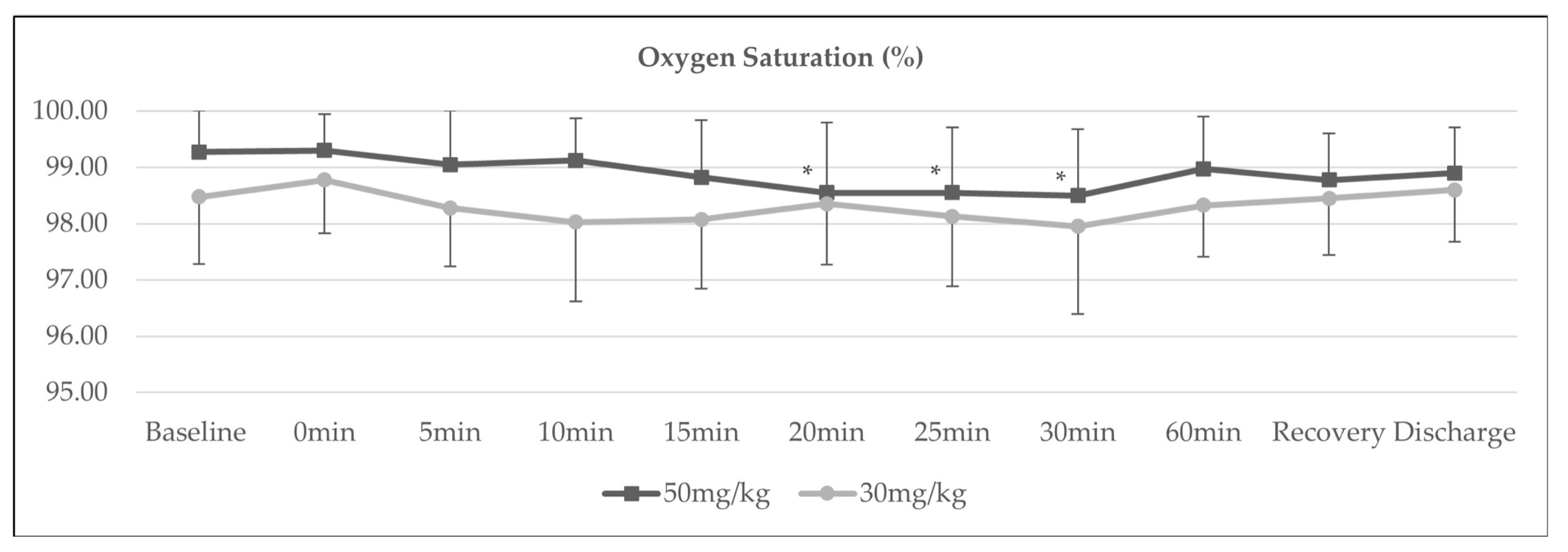
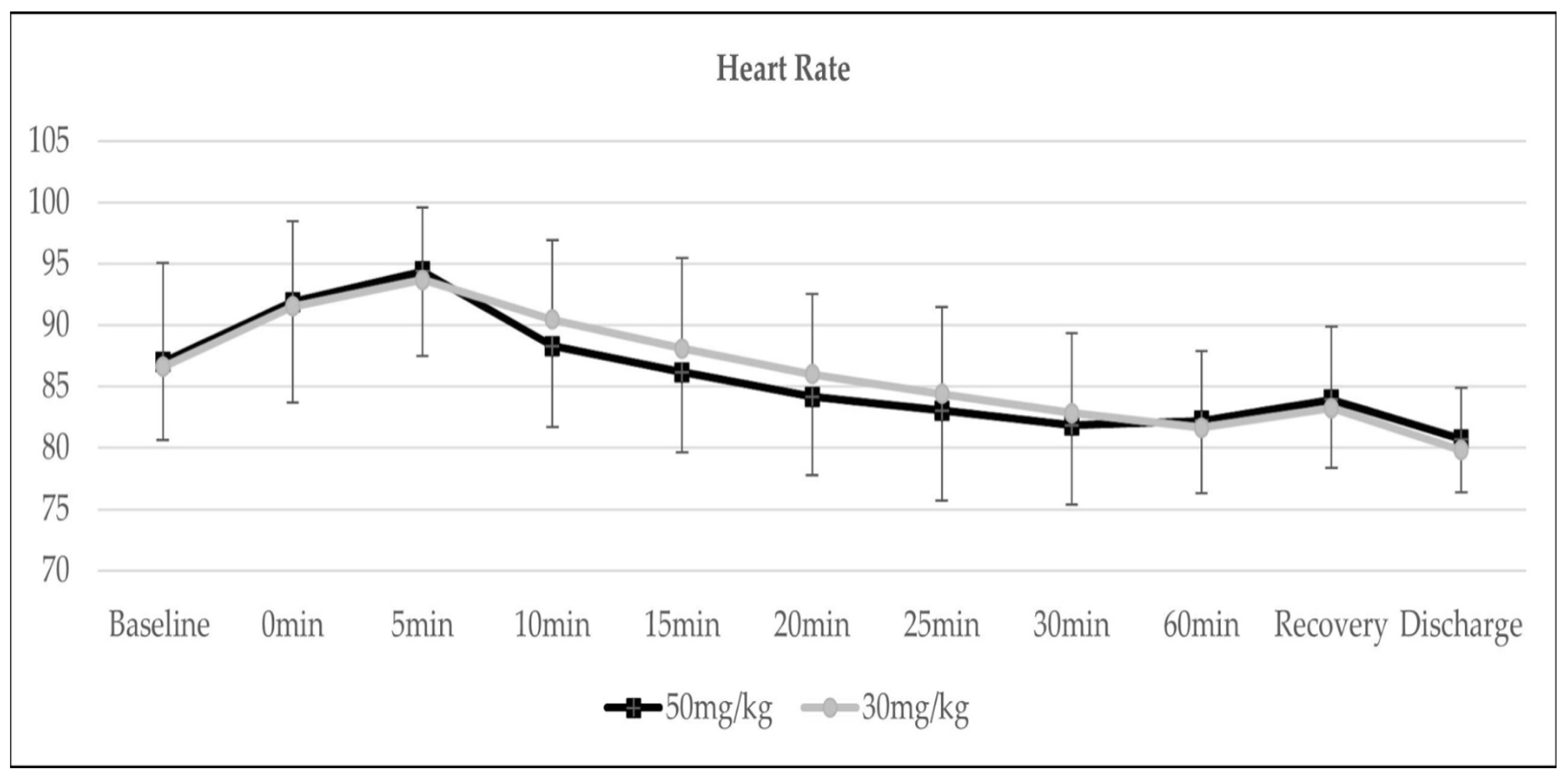
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, U.; Malhotra, K.; Prabhakar, T. A comparative study of the effect of clonidine and tramadol on post-spinal anaesthesia shivering. Indian J. Anaesth. 2011, 55, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.B. Postanaesthetic shivering—From pathophysiology to prevention. Rom. J. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2018, 25, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Witte, J.; Sessler, D.I. Perioperative shivering: Physiology and pharmacology. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.S. Magnesium sulphate vsersus meperidine for prevention of shivering in patients scheduled for elective orthopedic surgery under spinal anesthesia. AAMJ 2010, 8, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Luggya, T.S.; Kabuye, R.N.; Mijumbi, C.; Tindimwebwa, J.B.; Kintu, A. Prevalence, associated factors and treatment of post spinal shivering in a Sub-Saharan tertiary hospital: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2016, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiran, K.; Aziz, F.Z. Effectiveness of low-dose midazolam plus ketamine in the prevention of shivering during spinal anaesthesia for emergency lower limb surgery. S. Afr. J. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 19, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundra, T.S.; Kuthiala, G.; Shrivastava, A.; Kaur, P. A comparative study on the efficacy of dexmedetomidine and tramadol on post-spinal anesthesia shivering. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2017, 11, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.J.; Shah, N.K. Effects of motion on the performance of pulse oximeters in volunteers. Anesthesiology 1996, 85, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrench, I.; Cavill, G.; Ward, J.; Crossley, A. Comparison between alfentanil, pethidine and placebo in the treatment of post-anaesthetic shivering. Br. J. Anaesth. 1997, 79, 541–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Do, S.H. Magnesium Sulfate: A Versatile Anesthetic Adjuvant. Anesth. Intensive Care 2017, 4, 555646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawakami, H.; Nakajima, D.; Mihara, T.; Sato, H.; Goto, T. Effectiveness of magnesium in preventing shivering in surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossley, A.; Mahajan, R. The intensity of postoperative shivering is unrelated to axillary temperature. Anaesthesia 1994, 49, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozdemir, M.; Usta, B.; Demircioglu, R.I.; Muslu, B.; Sert, H.; Karatas, O.F. Magnesium sulfate infusion prevents shivering during transurethral prostatectomy with spinal anesthesia: A randomized, double-blinded, controlled study. J. Clin. Anesth. 2010, 22, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.T.; Megalla, S.A.; Khalifa, O.S.M.; El Deen, H.M.S. Prophylactic vs. therapeutic magnesium sulfate for shivering during spinal anesthesia. Egypt J. Anaesth. 2014, 30, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasem, O.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Abd Elasttar, M.N. Comparative study between dexmedetomidine, magnesium sulphate and meperidine as anti-shivering agent following neuraxial anesthesia. Egypt J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 75, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsonbaty, M.; Elsonbaty, A.; Saad, D. Is this the time for Magnesium sulfate to replace Meperidine as an antishivering agent in spinal anesthesia? Egypt J. Anaesth. 2013, 29, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Qian, D.C.; Zheng, M.M.; Lu, X.; Han, Y.; Qi, D.Y. Effects of different doses of magnesium sulphate on pneumoperitoneum-related hemodynamic changes in patients undergoing gastrointestinal laparoscopy: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachidananda, R.; Basavaraj, K.; Shaikh, S.I.; Umesh, G.; Bhat, T.; Arpitha, B. Comparison of prophylactic intravenous magnesium sulfate with tramadol for postspinal shivering in elective cesarean section: A placebo controlled randomized double-blind pilot study. Anesth. Essays Res. 2018, 12, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Na, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-T.; Ro, Y.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Do, S.-H. IV infusion of magnesium sulphate during spinal anaesthesia improves postoperative analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Zhang, W. Effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate on bupivacaine spinal anesthesia in preeclamptic patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaigawa, Y.; Akazawa, S.; Shimizu, R.; Ishii, R.; Ikeno, S.; Inoue, S.; Yamato, R. Effects of magnesium sulphate on the cardiovascular system, coronary circulation and myocardial metabolism in anaesthetized dogs. Br. J. Anaesth. 1997, 79, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, M.R.; Gordon, G.; Salem, M.; Chernow, B. Magnesium administration and dysrhythmias after cardiac surgery: A placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. JAMA 1992, 268, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanian, F.; Khatir, I.G.; Ahidashti, H.A.; Amirifard, S. The Effect of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate as an Adjuvant in the Treatment of Acute Exacerbations of COPD in the Emergency Department: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2021, 31, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, J.A.; Neimark, M.; Poskin, M. Maternal oxygen desaturation with intravenous magnesium therapy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 89, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Group A (50 mg/kg) | Group B (30 mg/kg) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 40) | (n = 40) | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 26 (65.0) | 25 (62.5) | 0.816 |
| Female | 14 (35.0) | 15 (37.5) | |
| Age (years) | 40.9 ± 12.9 | 46.4 ± 12.8 | 0.948 |
| Discipline | |||
| Orthopaedic | 21 (52.5) | 25 (62.5) | 0.267 |
| Surgery | 12 (30.0) | 8 (20.0) | |
| Urology | 6 (15.0) | 3 (7.5) | |
| Gynaecology | 1 (2.5) | 4 (10.0) | |
| ASA class | |||
| ASA I | 18 (45.0) | 15 (37.5) | 0.496 |
| ASA II | 22 (55.0) | 25 (62.5) | |
| Weight (kg) | 71.1 ± 10.2 | 69.1 ± 9.5 | 0.653 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 2.8 | 26.2 ± 2.2 | 0.143 |
| Duration of Surgery (minutes) | 62.8 ± 7.9 | 64.2 ± 7.4 | 0.44 |
| OR Temperature (°C) | 19.3 ± 1.2 | 19.5 ± 1.1 | 0.624 |
| Shivering Grade | Group A (n = 40) | Group B (n = 40) | p-Value | p-Value (Post-Hoc Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No shivering (grade 0) | 18 (45.0) | 8 (20.0) | 0.016 * | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 17 (42.5) | 16 (40.0) | 0.008 * | 0.82 |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 5 (12.5) | 16 (40.0) | 0.002 * |
| Time Point | Shivering Grade | Group A (n = 40) | Group B (n = 40) | p-Value | p-Value (Post-Hoc Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15th min | No shivering (grade 0) | 33 (82.5) | 36 (90.0) | - | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 7 (17.5) | 4 (10.0) | 0.117 | - | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 0 (0) | 0 | - | ||
| 20th min | No shivering (grade 0) | 24 (60.0) | 16 (40.0) | - | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 15 (37.5) | 22 (55.0) | 0.196 | - | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 1 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | - | ||
| 25th min | No shivering (grade 0) | 23 (57.5) | 12 (30.0) | 0.013 * | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 14 (35.0) | 19 (47.5) | 0.027 * | 0.256 | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 3 (7.5) | 9 (22.5) | 0.041 * | ||
| 30th min | No shivering (grade 0) | 24 (60.0) | 10 (25.0) | 0.002 * | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 11 (27.5) | 15 (37.5) | 0.003 * | 0.34 | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 5 (12.5) | 15 (37.5) | 0.010 * | ||
| 60th min | No shivering (grade 0) | 20 (50.0) | 8 (20.0) | 0.005* | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 15 (37.5) | 17 (42.5) | 0.006 * | 0.648 | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 5 (12.5) | 15 (37.5) | 0.010 * | ||
| Recovery bay | No shivering (grade 0) | 21 (52.5) | 9 (22.5) | 0.006 * | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 17 (42.5) | 26 (65.0) | 0.019 * | 0.044 * | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 2 (5.0) | 5 (12.5) | 0.235 | ||
| Upon discharge | No shivering (grade 0) | 26 (65.0) | 15 (37.5) | - | |
| Mild (grade 1–2) | 14 (35.0) | 25 (62.5) | 0.014 * | - | |
| Severe (grade 3–4) | 0 | 0 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Low, R.G.; Izaham, A.; Zain, J.M.; Nor, N.M.; Low, H.J.; Yusof, A.M. Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate. Medicina 2022, 58, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58081046
Low RG, Izaham A, Zain JM, Nor NM, Low HJ, Yusof AM. Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate. Medicina. 2022; 58(8):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58081046
Chicago/Turabian StyleLow, Ren Geng, Azarinah Izaham, Jaafar Md Zain, Nadia Md Nor, Hsueh Jing Low, and Aliza Mohamad Yusof. 2022. "Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate" Medicina 58, no. 8: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58081046
APA StyleLow, R. G., Izaham, A., Zain, J. M., Nor, N. M., Low, H. J., & Yusof, A. M. (2022). Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate. Medicina, 58(8), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58081046






