Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electronic Database Search
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
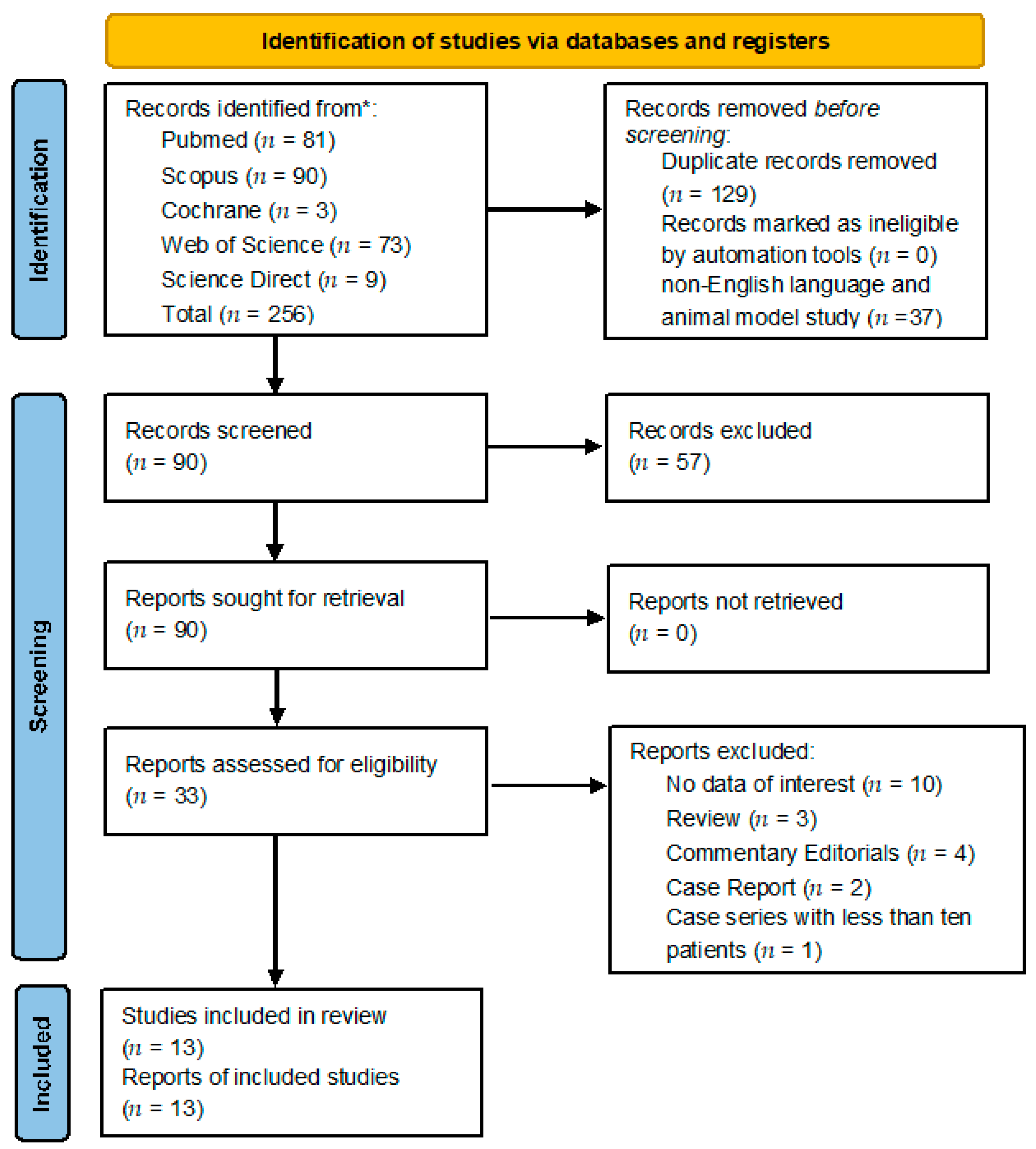
3.1. Retrieving Studies
3.2. Assessing of Quality
3.3. Qualitative Synthesis
3.3.1. Biomarkers in SSNHL vs. Control Groups
3.3.2. Treatment, Outcome, and Prognosis
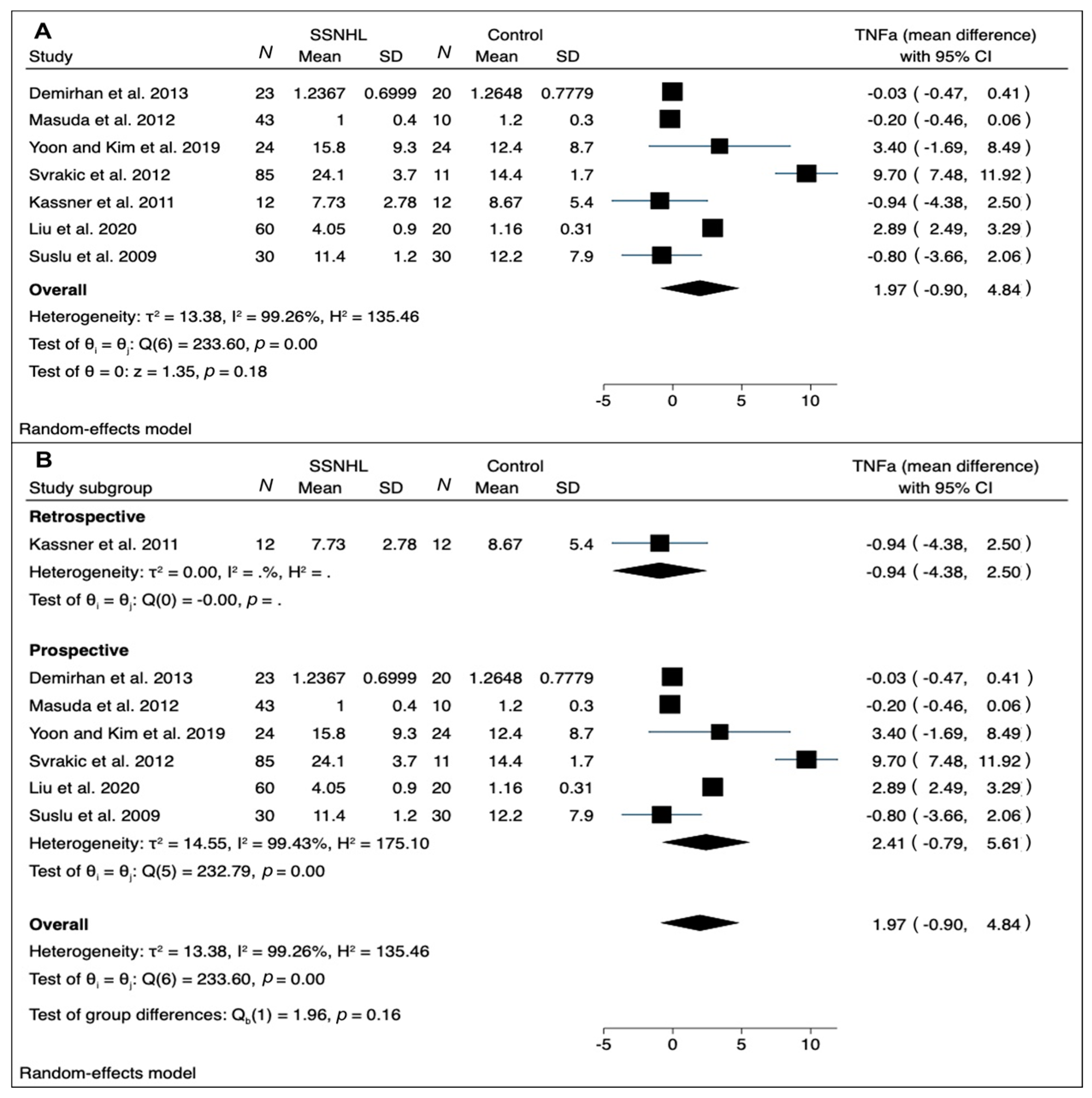
3.4. Quantitative Synthesis
4. Discussion
4.1. The Reason for Investigating Biomarkers in SSNHL
4.2. The Role of Circulating Biomarkers in SSNHL
4.3. Analyzing CRP and TNF-α Trends
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of Current Data and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss (update) executive summary. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lionello, M.; Staffieri, C.; Breda, S.; Turato, C.; Giacomelli, L.; Magnavita, P.; de Filippis, C.; Staffieri, A.; Marioni, G. Uni- and multivariate models for investigating potential prognostic factors in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. OtoRhinoLaryngol. 2015, 272, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and Other Tools) Resource; FDA-NIH Biomark Work Group: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK402289/#Co-published (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Ni, W.; Song, S.P.; Jiang, Y.D. Association between routine hematological parameters and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. J. Otol. 2021, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, J. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts diagnosis and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiang, H.; Huang, S.; Gao, J.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, B. Prognostic role of haematological indices in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, R.; Takenaka, Y.; Imai, T.; Sato, T.; Osaki, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Inohara, H. Serum fibrinogen as a prognostic factor in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e929–e935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doo, J.G.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, M.C.; Kim, S.S.; Ryu, J.; Yeo, S.G. Biomarkers suggesting favorable prognostic outcomes in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Robertson, J.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca//programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Göde, S.; Turhal, G.; Kaya, İ.; Mavili, H.İ.; Kirazlı, T. Evaluation of procalcitonin and hs-CRP levels in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2018, 14, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öçal, R.; Akın Öçal, F.C.; Güllüev, M.; Alataş, N. Is the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio a prognostic and predictive factor in sudden hearing loss? Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassner, S.S.; Schöttler, S.; Bonaterra, G.A.; Stern-Sträter, J.; Sommer, U.; Hormann, K.; Kinscherf, R.; Gössler, U.R. Proinflammatory and proadhesive activation of lymphocytes and macrophages in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol. Neurotol. 2011, 16, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süslü, N.; Yilmaz, T.; Gürsel, B. Utility of anti-HSP 70, TNF-α, ESR, antinuclear antibody, and antiphospholipid antibodies in the diagnosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Liang, F.; Jia, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improves hearing level via attenuating TLR4/NF-κB mediated inflammation in sudden sensorineural hearing loss patients. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, J. The roles played by blood inflammatory parameters in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 014556132096035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayir, S.; Kayabasi, S.; Hizli, O. Predictor parameters for poor prognosis in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Fibrinogen to albumin ratio vs. C-reactive protein to albumin ratio. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 87, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadoni, G.; Scorpecci, A.; Cianfrone, F.; Giannantonio, S.; Paludetti, G.; Lippa, S. Serum fatty acids and cardiovascular risk factors in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A case-control study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, M.; Kanzaki, S.; Minami, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Kanzaki, J.; Sato, H.; Ogawa, K. Correlations of inflammatory biomarkers with the onset and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.H.; Kim, M.E.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, C.H. Inflammatory cytokines and mononuclear cells in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaranfar, M.; Dadgarnia, M.; Zand, V.; Vaziribozorg, S.; Mirzade, F.S.; Mirzade, M. The role of immunological factors on sudden sensoryneural hearing loss. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 30, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svrakic, M.; Pathak, S.; Goldofsky, E.; Hoffman, R.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Sperling, N.; Alexiades, G.; Ashbach, M.; Vambutas, A. Diagnostic and prognostic utility of measuring tumor necrosis factor in the peripheral circulation of patients with immune-mediated sensorineural hearing loss. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirhan, E.; Eskut, N.P.; Zorlu, Y.; Cukurova, I.; Tuna, G.; Kirkali, F.G. Blood levels of TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-12 in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1778–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Sommerlad, A.; Orgeta, V.; Costafreda, S.G.; Huntley, J.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet 2017, 390, 2673–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandavia, R.; Horstink, Y.M.; Grutters, J.P.C.; Landry, E.; May, C.; Rovers, M.; Schilder, A.G.M.; Scholte, M. The potential added value of novel hearing therapeutics: An early health economic model for hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Pepys, M.B.; Wood, S.P. The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine. Structure 1999, 7, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.W.; Yang, H.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsieh, M.C.; Chou, H.H.; Chen, K.S. Prognostic value of c-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zeng, X.; Tu, W.J.; Zhao, J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: The next marker of stroke. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2395269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Firestein, G.S.; Billings, P.B.; Harris, J.P.; Keithley, E.M. Proinflammatory cytokine expression in the endolymphatic sac during inner ear inflammation. JARO J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2003, 4, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharaf, K.; Ihler, F.; Bertlich, M.; Reichel, C.A.; Berghaus, A.; Canis, M. Tumor necrosis factor-induced decrease of cochlear blood flow can be reversed by etanercept or JTE-013. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, e203–e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, L.; Frosolini, A.; Parrino, D.; Lovato, A.; de Filippis, C.; Marioni, G. Ototoxicity of immunosuppressant drugs: A systematic review. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Fujioka, M.; Kanzaki, S.; Okano, H.J.; Shibata, S.; Yamashita, D.; Masuda, M.; Mihara, M.; Ohsugi, Y.; Ogawa, K.; et al. Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling suppressed cochlear inflammatory response and improved hearing impairment in noise-damaged mice cochlea. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Type | Country | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Adequacy | Represen- tativeness | Selection | Definition | Ascertainment | Same method | Non-response rate | Total (9/9) | |||
| Göde et al. 2018 [11] | Observational retrospective case-control | Turkey | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Öçal et al. 2020 [12] | Longitudinal retrospective case-control | Turkey | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Kassner et al. 2011 [13] | Observational retrospective case-control | Germany | * | * | ** | * | 5 | ||||
| Cayir et al. 2021 [17] | Cross-sectional retrospective case-control | Turkey | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 8 | |
| Guo et al. 2021 [16] | Observational retrospective case-control | China | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Cadoni et al. 2010 [18] | Observational prospective case-control | Italy | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | 8 | |
| Yoon et al. 2018 [20] | Observational prospective case-control | South Korea | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Svakic et al. 2012 [22] | Longitudinal prospective case-control | USA | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Baradaranfar et al. 2018 [21] | Observational prospective case-control | Iran | * | * | ** | * | 5 | ||||
| Demirhan et al. 2013 [23] | Prospective clinical trial | Turkey | * | * | * | * | * | 5 | |||
| Suslu et al. 2009 [14] | Prospective clinical trial | Turkey | * | * | * | ** | * | 6 | |||
| Masuda et al. 2012 [19] | Observational longitudinal prospective cohort | Japan | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 7 | ||
| Liu et al. 2020 [15] | Observational prospective case-control | China | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| Study | Years of Age (Mean and Standard Deviation) | Sex (Male/Female) | Time Intervals Elapsed from the Onset of SSNHL to Blood Sampling | Diagnostic Value (p < 0.05 SSNHL vs. Control Group) | Prognostic Value (p < 0.05 Good Prognosis vs. Poor Prognosis) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cayir et al. 2020 [17] | 42.29 ± 9.2 | 24/23 | <5 days; blood sampling on the first day of admission, before corticosteroid treatment | CAR; FAR; NLR; PLR; Hgb; WBC | CAR; FAR; NLR; PLR; Hgb; WBC |
| Öçal et al. 2020 [12] | 44.1 ± 14.2 | 24/16 | Admission time | CAR | CAR; NLR |
| Masuda et al. 2012 [19] | 57 ± 15 | 23/20 | <7 days; blood sampling at the first visit, before corticosteroid treatment | TNF-α; CRP; N; L; M; IL-6; NKCA | TNF-α; CRP; N; L; M; IL-6; NKCA |
| Liu et al. 2020 [15] | ND | 41/79 | ND | TNF-α;TLR-4; NFKB | ND |
| Kassner et al. 2011 [13] | 45.4 ± 4.1 | ND | 6–24 h; blood sampling before corticosteroid treatment | TNF-α; CRP; WBC; N; L; E; B; LDL; HDL; CD40 | ND |
| Cadoni et al. 2010 [18] | 50 ± 14 | 19/24 | Admission time | Q10; Cholesterol; LDL; Nervonic acid | ND |
| Yoon and Kim et al. 2019 [20] | 46.91 ± ND | 15/9 | Before corticosteroid treatment | TNF-α; M; CD86 | ND |
| Baradaranfar et al. 2018 [21] | 40.80 ± 13.37 | 26/30 | ND | ESR; Anti CCP; Anti-dsDNA; ANA; C3 and C4; WBC; N; L; E; P; M | ND |
| Svrakic et al. 2012 [22] | 52.51 ± 16.08 | 35/50 | Before corticosteroid treatment | TNF-α | TNF-α |
| Göde et al. 2018 [11] | 47.91 ± 15.73 | 14/0 | Before corticosteroid treatment | CRP; Procalcitonin | CRP; Procalcitonin |
| Demirhan et al. 2013 [23] | 52 ± ND | 13/10 | Before corticosteroid treatment | TNF-α; IL-10; IL-12 | TNF-α; IL-10; IL-12 |
| Guo et al. 2021 [16] | 46.69 ± 16.76 | 80/89 | Before corticosteroid treatment | CRP; CAR; NLR | CRP; CAR; NLR |
| Suslu et al. 2009 [14] | 42 ± ND | 11/19 | ND | ESR; TNF-α; Anti HSP-70; ANA | ESR; TNF-α; Anti HSP-70; ANA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frosolini, A.; Franz, L.; Daloiso, A.; Lovato, A.; de Filippis, C.; Marioni, G. Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2022, 58, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070963
Frosolini A, Franz L, Daloiso A, Lovato A, de Filippis C, Marioni G. Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina. 2022; 58(7):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070963
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrosolini, Andrea, Leonardo Franz, Antonio Daloiso, Andrea Lovato, Cosimo de Filippis, and Gino Marioni. 2022. "Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Medicina 58, no. 7: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070963
APA StyleFrosolini, A., Franz, L., Daloiso, A., Lovato, A., de Filippis, C., & Marioni, G. (2022). Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina, 58(7), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070963










