Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins (LMWH) and Synthetic Factor X Inhibitors Can Impair the Osseointegration Process of a Titanium Implant in an Interventional Animal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Ovariectomy (OVX) Procedure
2.3. Intramedullary Nail
2.4. Treatment
2.5. Collection of Samples
2.6. Serum Analysis
2.7. Micro-CT Examination
2.8. Mechanical Pull-Out Test
2.9. Histological Examination
2.10. SEM/EDX Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weight
3.2. Serum Analysis
3.3. Micro-CT Examination
3.4. Mechanical Pull-Out Test
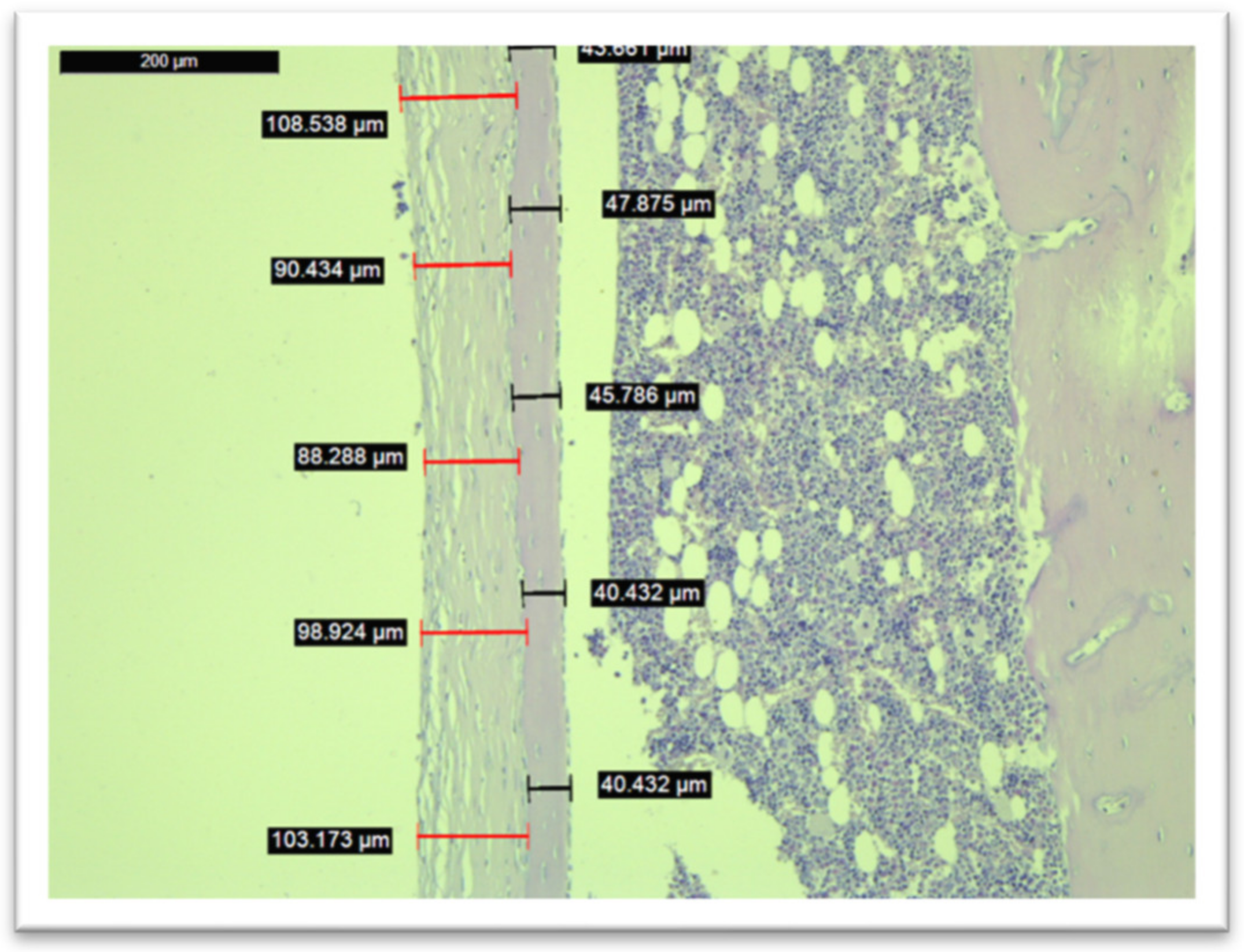
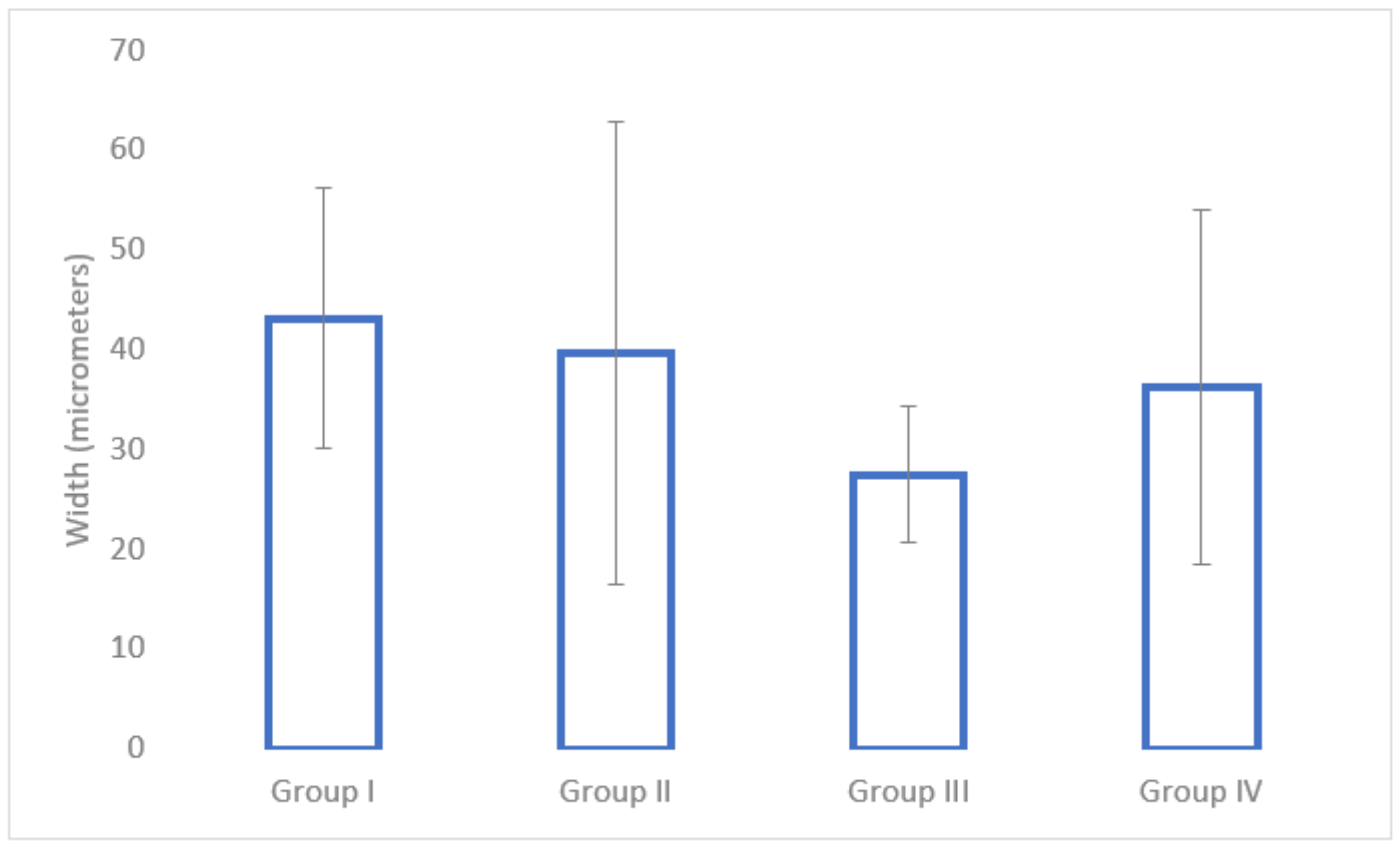
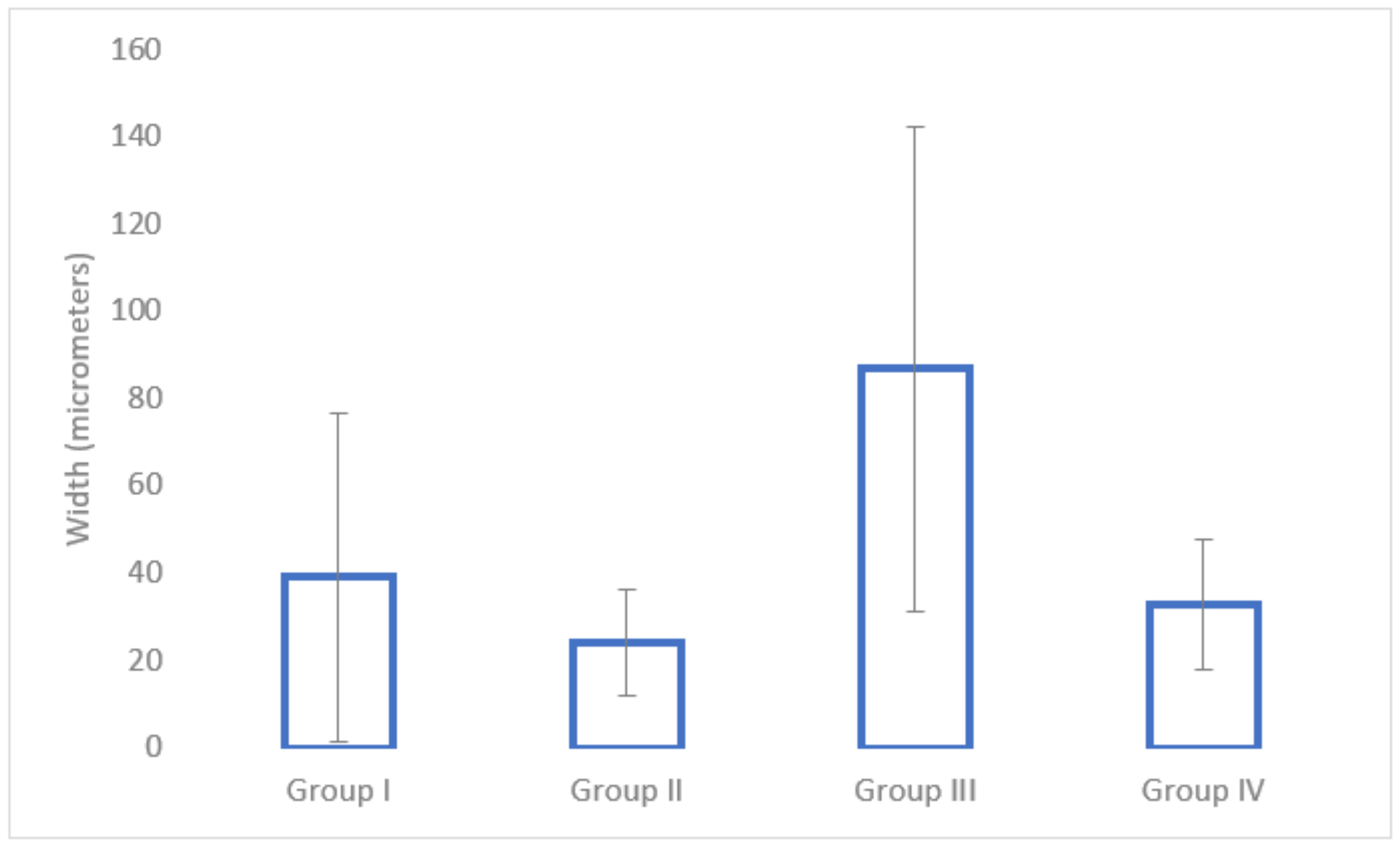
3.5. Histological Analysis
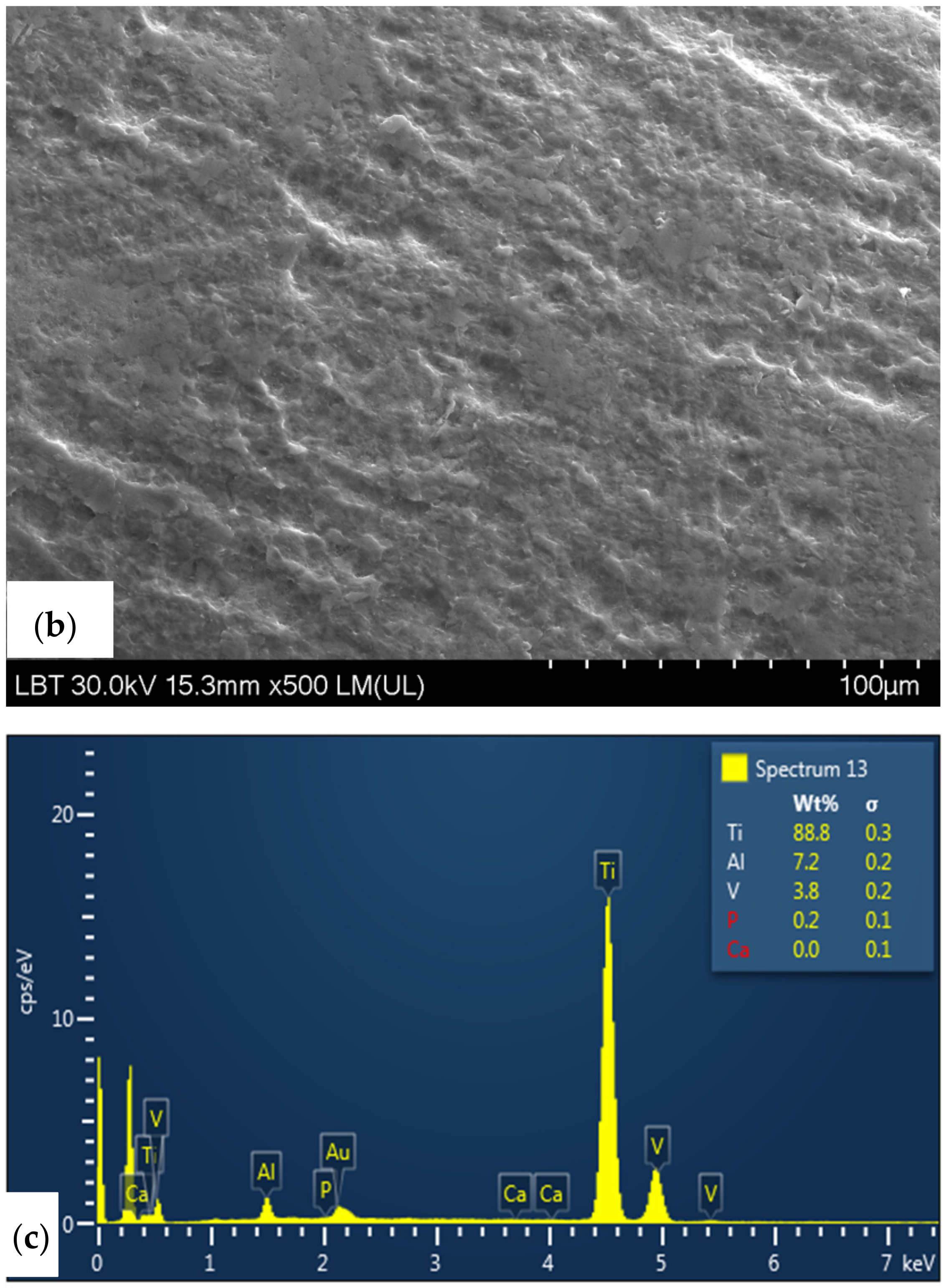
3.6. SEM/EDX Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS | Bone surface |
| BS/VR | Bone surface/volume ratio |
| BV | Bone volume |
| BV% | Percent bone volume |
| DVT | Deep vein thrombosis |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LMWH | Low-molecular-weight heparins |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cell |
| M-CSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| OVX | Ovariectomy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TD | Trabecular diameter |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 |
| TN | Trabecular number |
| TNF | Tumour necrosis factor |
| TS | Tissue surface |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Jordan, J.M. Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochbati, R.; Rbai, H.; Jlailia, M.; Makhlouf, H.; Bouguira, A.; Daghfous, M.S. Predictive factors of aseptic loosening of cemented total hip prostheses. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2016, 24, 260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanhegan, I.S.; Malik, A.K.; Jayakumar, P.; Islam, S.; Haddad, F.S. A financial analysis of revision hip arthroplasty: The economic burden in relation to the national tariff. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelani, M.A.; Crook, K.; Barrack, R.L.; Maloney, W.J.; Clohisy, J.C. What is the Prognosis of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients 55 Years and Younger? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, P.G.; Jimbo, R. Osseointegration of metallic devices: Current trends based on implant hardware design. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 561, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostu, D.; Lucaciu, O.; Lucaciu, G.D.; Crisan, B.; Crisan, L.; Baciut, M.; Onisor, F.; Baciut, G.; Campian, R.S.; Bran, S. Systemic drugs that influence titanium implant osseointegration. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, G.; Del Mondo, D.; Russo, D.; Cervino, G.; D’Amico, C.; Fiorillo, L. Stem Cells in Temporomandibular Joint Engineering: State of Art and Future Persectives. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2022, 33, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, G.; Romano, A.; Petruzzi, M.; Maio, C.; Serpico, R.; Lucchese, A.; Candotto, V.; Di Stasio, D. Telescopic overdenture on natural teeth: Prosthetic rehabilitation on (OFD) syndromic patient and a review on available literature. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Minervini, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Russo, D.; Lanza, A.; D’Amico, C.; Cervino, G.; Meto, A.; Di Francesco, F. Prosthodontic Treatment in Patients with Temporomandibular Disorders and Orofacial Pain and/or Bruxism: A Review of the Literature. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostu, D.; Lucaciu, O.; Mester, A.; Oltean-Dan, D.; Gheban, D.; Benea, H.R.C. Tibolone, alendronate, and simvastatin enhance implant osseointegration in a preclinical in vivo model. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, H.J.; Handschin, A.E. Osteoblast Growth Inhibition by Unfractioned Heparin and by Low molecular Weight Heparins: An In-Vitro Investigation. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 8, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osip, S.L.; Butcher, M.; Young, E.; Yang, L.; Shaughnessy, S.G. Differential effects of heparin and low molecular weight heparin on osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis in vitro. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, M.; Hirsh, J.; Weitz, J.I.; Young, E.; Venner, T.J.; Shaughnessy, S.G. The effects of standard and low molecular weight heparin on bone nodule formation in vitro. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 80, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, J.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kapetanakis, S.; Nastoulis, E.; Demesticha, T.; Demetriou, T. The Effect of Low Molecular Weight Heparins on Fracture Healing. Open Orthop. J. 2015, 9, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudrova, M.; Kvasnicka, J.; Kudrnova, Z.; Zenahlikova, Z.; Mazoch, J. Influence of long-term thromboprophylaxis with low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin) on changes of bone metabolism markers in pregnant women. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2011, 17, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarahrudi, K.; Kaizer, G.; Thomas, A. The influence of low molecular weight heparin on the expression of osteogenic growth factors in human fracture healing. Int. Orthop. 2011, 36, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Folwarczna, J.; Janiec, W.; Gavor, M. Effects of enoxaparin on bone histomorphometric parameters in rats. Pol. J. Pharm. 2004, 56, 451–457. [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzynska, L.; Tomkowski, W.Z.; Przedlacki, J.; Hajduk, B.; Torbicki, A. Changes in bone density during long term administration of low molecular weights heparins or acenocoumarol for secondary prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2003, 33, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matziolis, G.; Perka, C.; Disch, A.; Zippel, H. Effects of fondaparinus compared with dalteparin, enoxaparin and unfractionated heparin on human osteoblasts. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 73, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folwarczna, J.; Sliwinski, L.; Janiec, W.; Pikul, M. Effects of standard heparin and low molecular weight heparins on the formation of murine osteoclasts in vitro. Pharm. Rep 2005, 57, 635–645. [Google Scholar]
- Handschin, A.E.; Trenz, O.A.; Hoerstrup, S.; Kock, H.J.; Wanner, G.A.; Trentz, O. Effect of low molecular weight heparin (dalteparin) and fondaparinux (arixtra) on human osteoblasts in vitro. Br. J. Surg. 2005, 92, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, J.T.; Mc Grath, M.; Regan, K. Thromboprophylaxis using a low molecular weight heparin delays fracture repair. Clin. Orthop. 2000, 381, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Wang, D. Impaired bone healing by enoxaparin via inhibiting the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, M.S.; Vidigal, L.; Canova, A.R. The effects of low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin) on bony callus formation in rats femurs—An experimental study. Acta Orthop. Bras. 2006, 14, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Demirtas, A.; Azboy, I.; Bulut, M.; Ucar, B.Y.; Alabalik, U.; Necmioglou, N.M. Investigation of the effects of Enoxaparin, Fondaparinux, and Rivaroxaban used in thromboembolism prophylaxis on fracture healing in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 17, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, B. Enhanced osseointegration of titanium implants in a rat model of osteoporosis using multilayer bone mesenchymal stem cell sheets. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaras, N.; Rezvani, A. Diffuse skeletal pain after administration of alendronate. Indian J. Pharm. 2010, 42, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Mello, A.S.; dos Santos, P.L.; Marquesi, A.; Queiroz, T.P.; Margonar, R.; de Souza Faloni, A.P. Some aspects of bone remodeling around dental implants. Rev. Clin. Periodoncia Implantol. Rehabil. Oral 2016, 11, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.C.; Moon, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.B.; Kim, J.-H. Effects of alendronate on the peri-implant bone in rats. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuero-Filho, E.A.; Aydos, R.D.; Senefonte, F.R.; Ferreira, C.M.; Pereira, E.F.; de Oliveire, V.M.; de Menezes, G.P.; Bosio, M.A.C. Effects of enoxaparin and unfractioned heparin in prophylactic and therapeutic doses on the fertility of female Wistar rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2014, 29, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiebert, L.M.; Ping, T.; Wice, S.M. Repeated doses of oral and subcutaneous heparins have similar antithrombotic effect in rat carotid arterial model of thrombosis. J Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2012, 17, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklosz, J.; Kalaska, B.; Kaminski, K.; Szczubialka, K.; Pawlak, D.; Nowakowska, M.; Mogielnicki, A. Heparin binding copolymer reverses the anticoagulant activity of low molecular weight heparins: Safety and efficacy data in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114 (Suppl. 1), S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Group I (Control) n = 3 | Group II (Enoxaparin) n = 3 | Group III (Nadroparin) n = 3 | Group IV (Fondaparinux) n = 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone volume (BV) | 0.21 (±0.02) b | 0.20 (±0.04) | 0.12 (±0.06) a | 0.22 (±0.03) |
| Percent bone volume (BV%) | 1.93 (±0.15) b | 1.72 (±0.5) | 1.46 (±0.2) a | 1.75 (±0.4) |
| Bone surface (BS) | 39.46 (±6.5) | 38.54 (±7.5) | 32.23 (±9.2) | 40.21 (±4.8) |
| Tissue surface (TS) | 43.21 (±2.4) | 45.32 (±4.2) | 56.56 (±7.1) | 43.32 (±5.3) |
| Bone surface/volume ratio (BS/VR) | 207.68 | 226.7 | 230.21 | 236.52 |
| Mean total cross-sectional bone area | 0.038 (±0.02) | 0.034 (±0.025) | 0.029 (±0.05) | 0.036 (±0.045) |
| Cross-sectional thickness | 0.013 (±0.002) | 0.014 (±0.004) | 0.010 (±0.004) | 0.016 (±0.002) |
| Trabecular diameter | 0.020 (±0.003) | 0.023 (±0.0025) | 0.016 (±0.005) | 0.021 (±0.002) |
| Trabecular number | 8.82 (±0.53) | 9.2 (±0.63) | 7.52 (±0.78) | 8.26 (±0.32) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostu, D.; Berechet, B.; Oltean-Dan, D.; Mester, A.; Petrushev, B.; Popa, C.; Gherman, M.L.; Tigu, A.B.; Tomuleasa, C.I.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; et al. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins (LMWH) and Synthetic Factor X Inhibitors Can Impair the Osseointegration Process of a Titanium Implant in an Interventional Animal Study. Medicina 2022, 58, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111590
Apostu D, Berechet B, Oltean-Dan D, Mester A, Petrushev B, Popa C, Gherman ML, Tigu AB, Tomuleasa CI, Barbu-Tudoran L, et al. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins (LMWH) and Synthetic Factor X Inhibitors Can Impair the Osseointegration Process of a Titanium Implant in an Interventional Animal Study. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111590
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostu, Dragos, Bianca Berechet, Daniel Oltean-Dan, Alexandru Mester, Bobe Petrushev, Catalin Popa, Madalina Luciana Gherman, Adrian Bogdan Tigu, Ciprian Ionut Tomuleasa, Lucian Barbu-Tudoran, and et al. 2022. "Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins (LMWH) and Synthetic Factor X Inhibitors Can Impair the Osseointegration Process of a Titanium Implant in an Interventional Animal Study" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111590
APA StyleApostu, D., Berechet, B., Oltean-Dan, D., Mester, A., Petrushev, B., Popa, C., Gherman, M. L., Tigu, A. B., Tomuleasa, C. I., Barbu-Tudoran, L., Benea, H. R. C., & Piciu, D. (2022). Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins (LMWH) and Synthetic Factor X Inhibitors Can Impair the Osseointegration Process of a Titanium Implant in an Interventional Animal Study. Medicina, 58(11), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111590









