Comparison of Long-Term Skin Quality and Scar Formation in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds Treated with Suprathel® and epicitehydro® Wound Dressings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Wound Regime
2.3. Assessment of Scar Quality
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Skin Elasticity
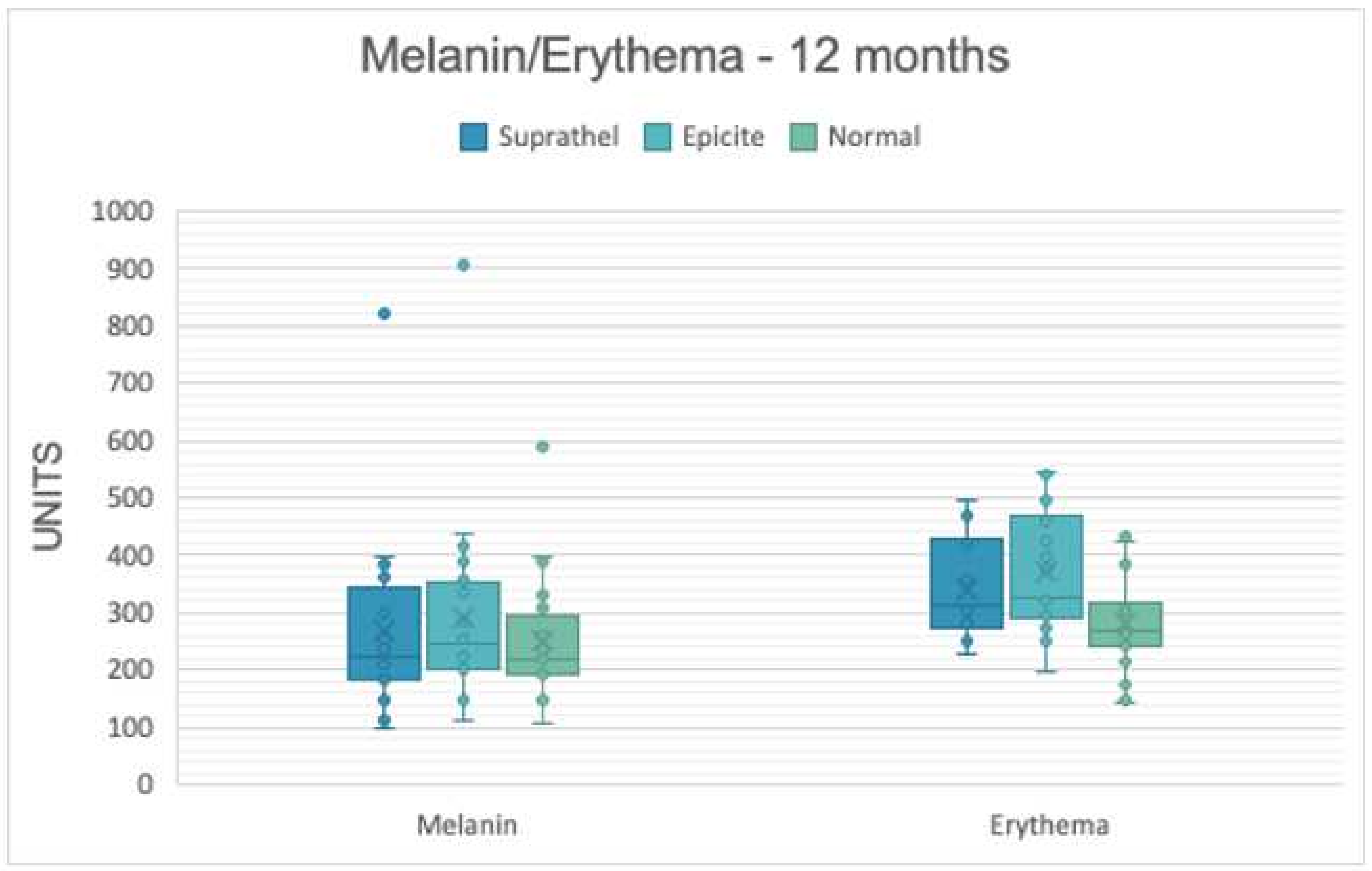
3.2. Skin Pigmentation
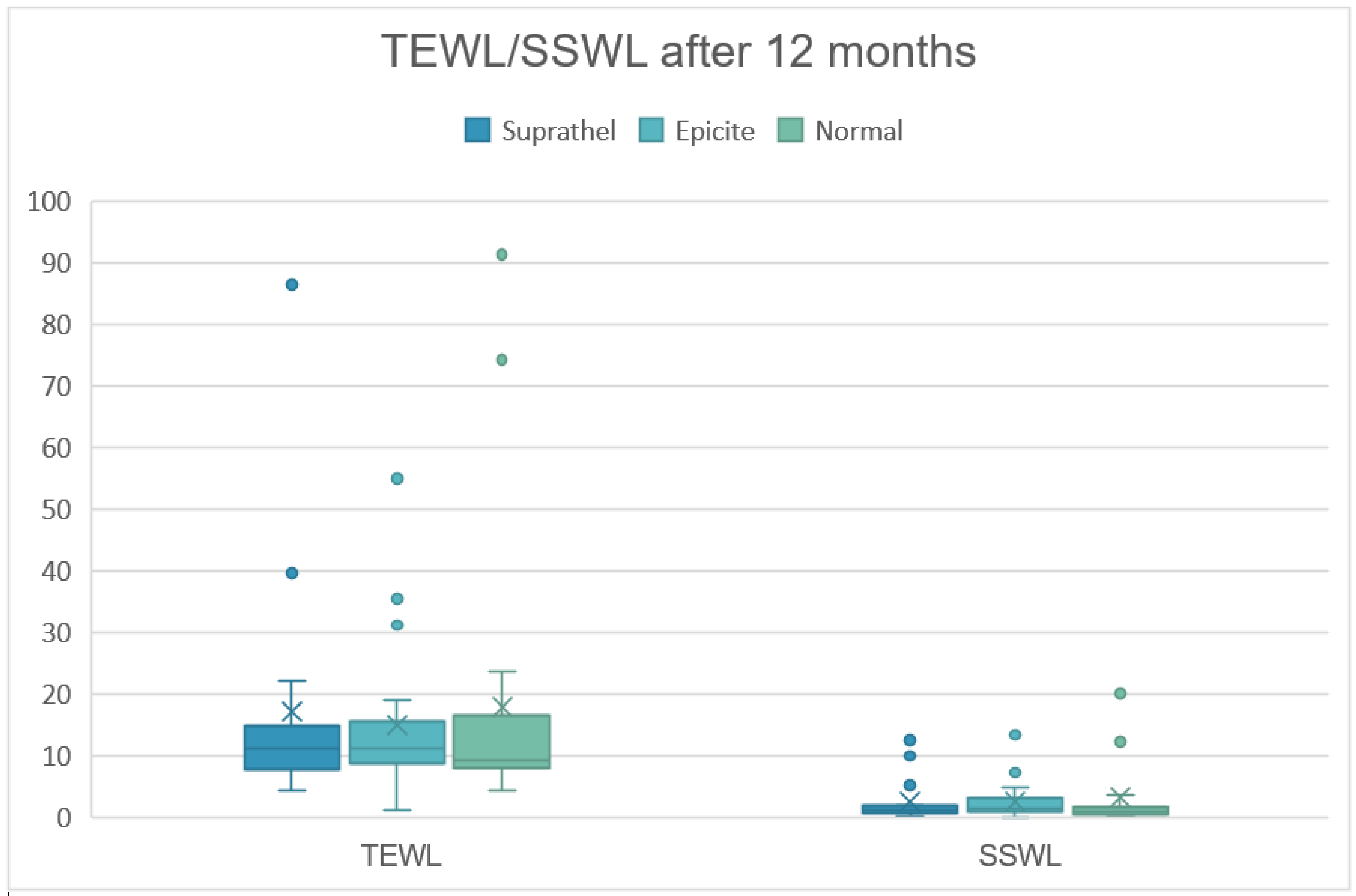
3.3. Trans-Epidermal Water Loss (in g/h/m2)
3.4. Skin Evaluation with Lightguide Spectrophotometry
3.5. Vancouver Scar Scale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peck, M.D. Epidemiology of burns throughout the world. Part I: Distribution and risk factors. Burns 2011, 37, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolle, C.; Cambiaso-Daniel, J.; Forbes, A.A.; Wurzer, P.; Hundeshagen, G.; Branski, L.K.; Huss, F.; Kamolz, L.-P. Recent trends in burn epidemiology worldwide: A systematic review. Burns 2017, 43, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Perbix, W.; Grigutsch, D.; Zinser, M.; Demir, E.; Fuchs, P.C.; Schulz, A. Etiology, incidence and gender-specific patterns of severe burns in a German Burn Center—Insights of 25 years. Burns 2016, 42, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guideline: Treatments of thermal injuries oft he adult; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Verbrennungsmedizin; S2k Leitlinie Behandlung thermischer Verletzungen des Erwachsenen AWMF-Register-Nr.: 044-001. 2021. Available online: https://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/044-001l_S2k_Behandlung-thermischer-Verletzungen-des-Erwachsenen_2021-07.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Karlsson, M.; Steinvall, I.; Sjöberg, F.; Olofsson, P.; Elmasry, M. Burn scar outcome at six and 12 months after injury in children with partial thickness scalds: Effects of dressing treatment. Burns 2020, 46, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Wal, M.B.A.; Vloemans, J.F.P.M.; Tuinebreijer, W.E.; van de Ven, P.; van Unen, E.; van Zuijlen, P.P.M.; Middelkoop, E. Outcome after burns: An observational study on burn scar maturation and predictors for severe scarring. Wound Repair Regen. 2012, 20, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beele, H. Artificial skin: Past, present and future. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2002, 25, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybilski, M.; Deb, R.; Erdmann, D.; Germann, G. New developments in skin replacement materials. Chirurg 2004, 75, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Daniels, M.; Grigutsch, D.; Fuchs, P.C.; Schulz, A. Feasibility of Pure Silk for the Treatment of Large Superficial Burn Wounds Covering Over 10% of the Total Body Surface. J. Burn Care Res. 2020, 41, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, H.L.; Blome-Eberwein, S.E.; Branski, L.K.; Carson, J.S.; Crombie, R.E.; Hickerson, W.L.; Kamolz, L.P.; King, B.T.; Nischwitz, S.P.; Popp, D.; et al. Porcine Xenograft and Epidermal Fully Synthetic Skin Substitutes in the Treatment of Partial-Thickness Burns: A Literature Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Andreae, J.; Fuchs, P.C.; Lefering, R.; Heidekrueger, P.I.; Schulz, A.; Bagheri, M. Evaluation of Scar Quality after Treatment of Superficial Burns with Dressilk® and Suprathel®-In an Intraindividual Clinical Setting. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Arens, E.; Grigutsch, D.; Rath, R.; Hoffmann, A.; Fuchs, P.C.; Schulz, A. A prospective intra-individual evaluation of silk compared to Biobrane for the treatment of superficial burns of the hand and face. Burns 2017, 43, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.K.; Martin, H.C.; Holland, A.J. Medical management of paediatric burn injuries: Best practice. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 48, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, K.; Renkert, M.; Duis, M.; Weiss, C.; Wessel, L.M.; Lange, B. Application of bacterial nanocellulose-based wound dressings in the management of thermal injuries: Experience in 92 children. Burns 2021, 48, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashaan, Z.M.; Krijnen, P.; Allema, J.H.; Vloemans, A.F.; Schipper, I.B.; Breederveld, R.S. Usability and effectiveness of Suprathel® in partial thickness burns in children. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2017, 43, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vloemans, A.F.P.M.; Hermans, M.H.E.; van der Wal, M.B.A.; Liebregts, J.; Middelkoop, E. Optimal treatment of partial thickness burns in children: A systematic review. Burns 2014, 40, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundeshagen, G.; Collins, V.N.; Wurzer, P.; Sherman, W.; Voigt, C.D.; Cambiaso-Daniel, J.; Lopez, O.N.; Sheaffer, J.; Herndon, D.N.; Finnerty, C.C.; et al. A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing the Outpatient Treatment of Pediatric and Adult Partial-Thickness Burns with Suprathel or Mepilex Ag. J. Burn Care Res. 2018, 39, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highton, L.; Wallace, C.; Shah, M. Use of Suprathel® for partial thickness burns in children. Burns 2013, 39, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, M.; Selig, H.F.; Lumenta, D.B.; Kamolz, L.P.; Mittlböck, M.; Frey, M. The use of Suprathel® in deep dermal burns: First results of a prospective study. Burns 2012, 38, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, H.; Küntscher, M.; Uhlig, C.; Hierlemann, H.; Prantl, L.; Ottomann, C.; Hartmann, B. Suprathel, a new skin substitute, in the management of partial-thickness burn wounds: Results of a clinical study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2008, 60, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, C.; Rapp, M.; Hartmann, B.; Hierlemann, H.; Planck, H.; Dittel, K.-K. Suprathel-an innovative, resorbable skin substitute for the treatment of burn victims. Burns 2007, 33, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattelaens, J.; Turco, L.; Berclaz, L.M.; Huelsse, B.; Hitzl, W.; Vollkommer, T.; Bodenschatz, K.J. The Impact of a Nanocellulose-Based Wound Dressing in the Management of Thermal Injuries in Children: Results of a Retrospective Evaluation. Life 2020, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, J.C.J.; Tiffner, K.; Kainz, S.; Reisenegger, P.; Bernardelli de Mattos, I.; Funk, M.; Lemarchand, T.; Laaff, H.; Bal, A.; Birngruber, T.; et al. A novel human ex-vivo burn model and the local cooling effect of a bacterial nanocellulose-based wound dressing. Burns 2020, 46, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nischwitz, S.P.; Bernardelli de Mattos, I.; Hofmann, E.; Groeber-Becker, F.; Funk, M.; Mohr, G.J.; Branski, L.K.; Mautner, S.I.; Kamolz, L.P. Continuous pH monitoring in wounds using a composite indicator dressing—A feasibility study. Burns 2019, 45, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mattos, I.B.; Holzer, J.C.J.; Tuca, A.-C.; Groeber-Becker, F.; Funk, M.; Popp, D.; Mautner, S.; Birngruber, T.; Kamolz, L.-P. Uptake of PHMB in a bacterial nanocellulose-based wound dressing: A feasible clinical procedure. Burns 2019, 45, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, S.; Wiegand, C.; Wesarg, F.; Hessler, N.; Müller, F.A.; Kralisch, D.; Hipler, U.-C.; Fischer, D. Active wound dressings based on bacterial nanocellulose as drug delivery system for octenidine. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Aretz, G.F.; Fuchs, P.C.; Bagheri, M.; Funk, M.; Schulz, A.; Daniels, M. Comparison of wound healing and patient comfort in partial-thickness burn wounds treated with SUPRATHEL and epicte(hydro) wound dressings. Int. Wound J. 2021, 19, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.N.; Thraen, A.-C.J.; Gohritz, A.; Rennekampff, H.-O.; Vogt, P.M. Burn Scar Evaluation Using the Cutometer® MPA 580 in Comparison to “Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale” and “Vancouver Scar Scale”. J. Burn Care Res. 2018, 39, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draaijers, L.J.; Botman, Y.A.; Tempelman, F.R.; Kreis, R.W.; Middelkoop, E.; van Zuijlen, P.P. Skin elasticity meter or subjective evaluation in scars: A reliability assessment. Burns 2004, 30, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Dretzke, J.; Grover, L.; Logan, A.; Moiemen, N. A systematic review of objective burn scar measurements. Burns Trauma 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.E.; DeBruler, D.M.; Blackstone, B.N.; Coffey, R.A.; Boyce, S.T.; Supp, D.M.; Bailey, J.K.; Powell, H.M. Direct comparison of reproducibility and reliability in quantitative assessments of burn scar properties. Burns 2021, 47, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, B.; Correa, J.A.; Rachelska, G.; Armour, A.; LaSalle, L. Quantitative measurement of hypertrophic scar: Intrarater reliability, sensitivity, and specificity. J. Burn Care Res. 2008, 29, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.N.; Roettger, A.; Herold, C.; Vogt, P.M.; Rennekampff, H.-O. Evaporative Water Loss in Superficial to Full Thickness Burns. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 77, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardien, K.L.; Baas, D.C.; de Vet, H.C.; Middelkoop, E. Transepidermal water loss measured with the Tewameter TM300 in burn scars. Burns 2016, 42, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, K.M.; Pfau, M.; Blumenstock, G.; Tenenhaus, M.; Schaller, H.E.; Rennekampff, H.O. Cutaneous microcirculatory assessment of the burn wound is associated with depth of injury and predicts healing time. Burns 2010, 36, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Lucassen, G.W.; Houben, A.J.; Neumann, M.H. Vasoconstrictive effect of topical applied corticosteroids measured by laser doppler imaging and reflectance spectroscopy. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 65, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, D.; Spilker, G.; Lefering, R.; Weinand, C. O2C Laser Doppler and Digital Photo Analysis for Treatment Evaluation of Beta-Glucan versus Provitamin Pantothenic Acid of Facial Burns. Facial Plast. Surg. 2016, 32, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryza, M.J.; Baryza, G.A. The Vancouver Scar Scale: An administration tool and its interrater reliability. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 1995, 16, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, V.; Burrows, S.; Kendell, R.; Berghuber, A.; Chong, V.; Tan, J.; Edgar, D.W.; Wood, F. Modified Vancouver Scar Scale score is linked with quality of life after burn. Burns 2017, 43, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, C.C.; Jeschke, M.G.; Branski, L.K.; Barret, J.P.; Dziewulski, P.; Herndon, D.N. Hypertrophic scarring: The greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet 2016, 388, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.L.; Rath, R.; Ahrens, E.; Grigutsch, D.; Gräff, I.; Stromps, J.-P.; Fuchs, P.C.; Schulz, A. Evaluation of scar quality after treatment of superficial burns of the hands and face with Dressilk or Biobrane-An intra-individual comparison. Burns 2018, 44, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartinen, I.S.; Kuokkanen, H.O. Suprathel(®) causes less bleeding and scarring than Mepilex(®) Transfer in the treatment of donor sites of split-thickness skin grafts. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2011, 45, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkarainen, T.; Koivuniemi, R.; Kosonen, M.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Vuola, J.; Valtonen, J.; Tammela, P.; Mäkitie, A.; Luukko, K.; et al. Nanofibrillar cellulose wound dressing in skin graft donor site treatment. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubison, T.C.; Pape, S.A.; Parkhouse, N. Evidence for the link between healing time and the development of hypertrophic scars (HTS) in paediatric burns due to scald injury. Burns 2006, 32, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitch, E.A.; Wheelahan, T.M.; Rose, M.P.; Clothier, J.; Cotter, J. Hypertrophic burn scars: Analysis of variables. J. Trauma. 1983, 23, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
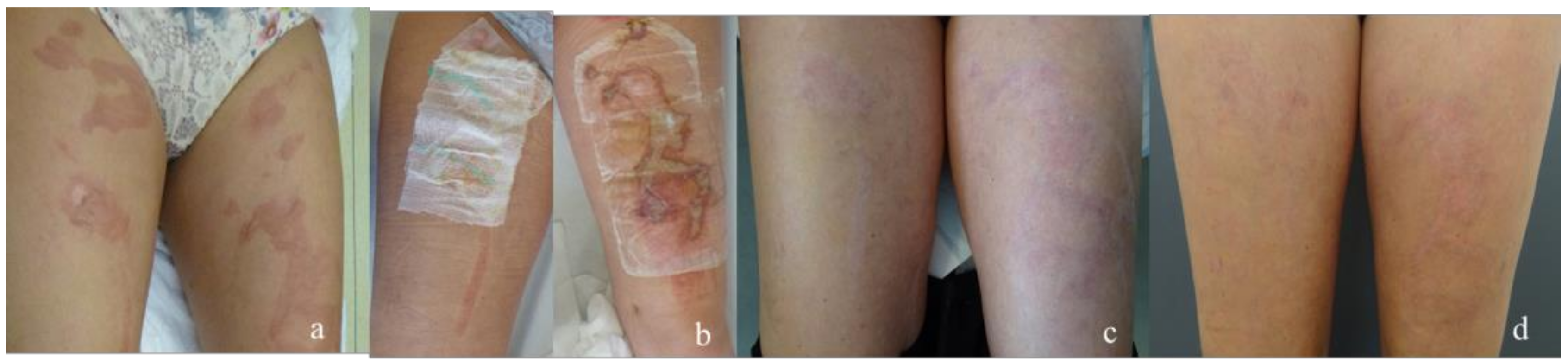
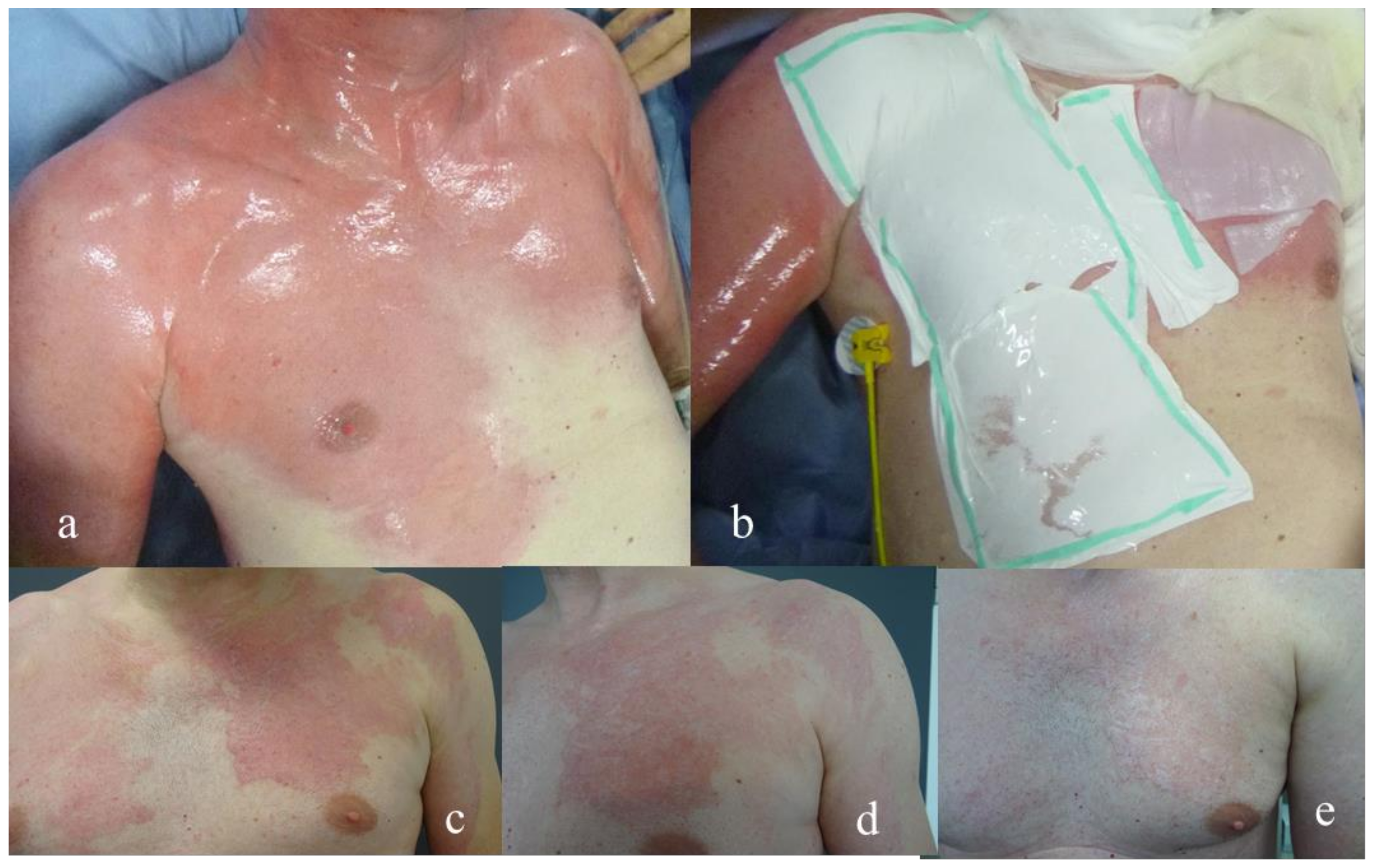
| Dressing | Suprathel® | epicitehydro® | Normal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
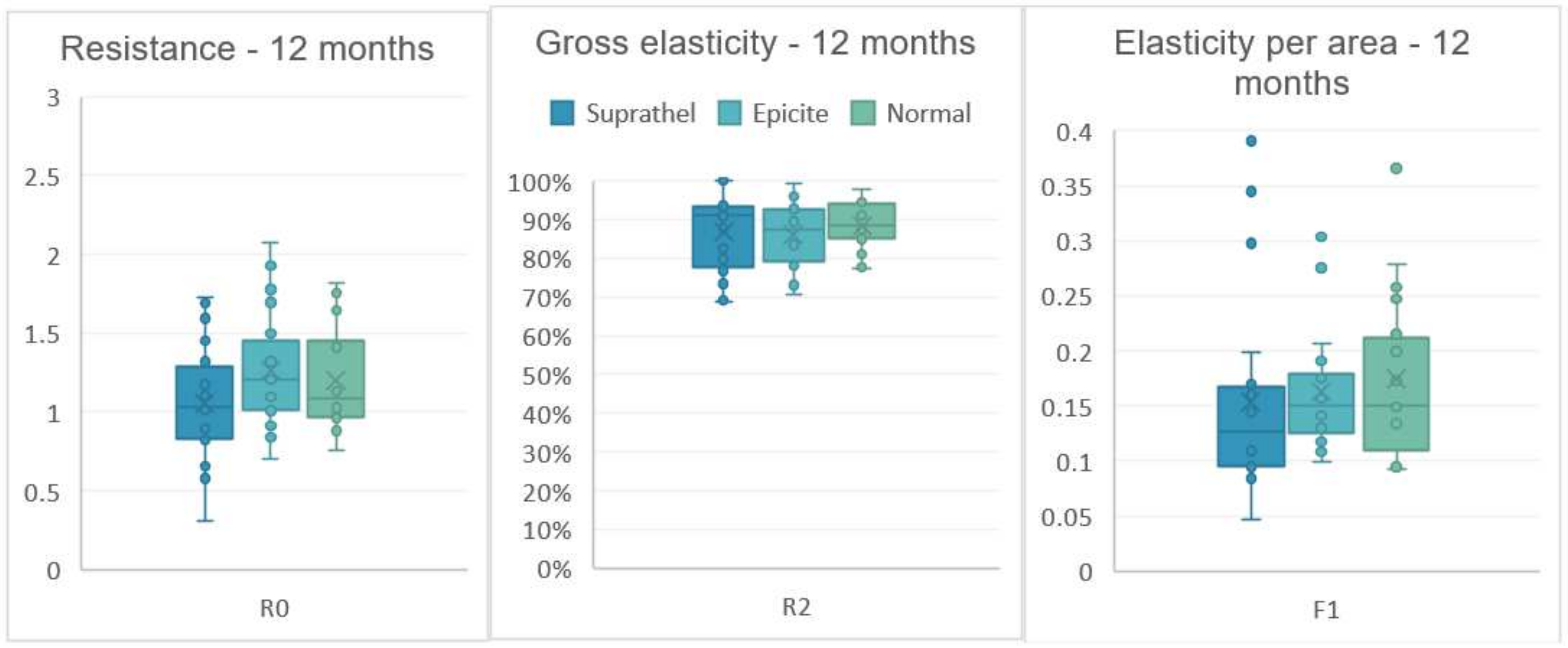
| Cutometer | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| R0 Resistence | 3 months | 0.94 | 0.22 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 1.08 | 0.25 |
| 6 months | 1.06 | 0.32 | 1.16 | 0.36 | 1.10 | 0.24 | |
| 12 months | 1.05 | 0.37 | 1.25 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.31 | |
| R2 Gross Elasticity | 3 months | 0.83 | 0.1 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 0.1 |
| 6 months | 0.85 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 0.08 | |
| 12 months | 0.87 | 0.1 | 0.85 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.05 | |
| F1 Elasticity | 3 months | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.06 |
| 6 months | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.05 | |
| 12 months | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.06 | |
| Dressing | Suprathel® | epicitehydro® | Normal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mexameter | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Melanin | 3 months | 237.1 | 125.8 | 244.6 | 105.3 | 251.2 | 90.7 |
| 6 months | 247.7 | 131.1 | 268.3 | 151.4 | 249.1 | 102.2 | |
| 12 months | 265.6 | 156.5 | 288.7 | 170.5 | 249.3 | 111.0 | |
| Erythema | 3 months | 378.6 | 77.1 | 390.7 | 89.8 | 299.0 | 91.2 |
| 6 months | 359.1 | 85.3 | 376.3 | 72.1 | 270.2 | 93.6 | |
| 12 months | 341.3 | 85.5 | 368.6 | 104.6 | 282.6 | 86.7 | |
| Dressing | Suprathel® | epicitehydro® | Normal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tewameter | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| TEWL | 3 months | 18.8 | 15.5 | 18.3 | 16.2 | 17.8 | 19.8 |
| 6 months | 16.5 | 11.3 | 16.2 | 11.7 | 13.0 | 11.6 | |
| 12 months | 17.1 | 19.1 | 15.0 | 12.4 | 18.0 | 22.7 | |
| SSWL | 3 months | 2.0 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.0 |
| 6 months | 2.0 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 1.8 | |
| 12 months | 2.5 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 5.4 | |
| Dressing | Suprathel® | epicitehydro® | Normal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
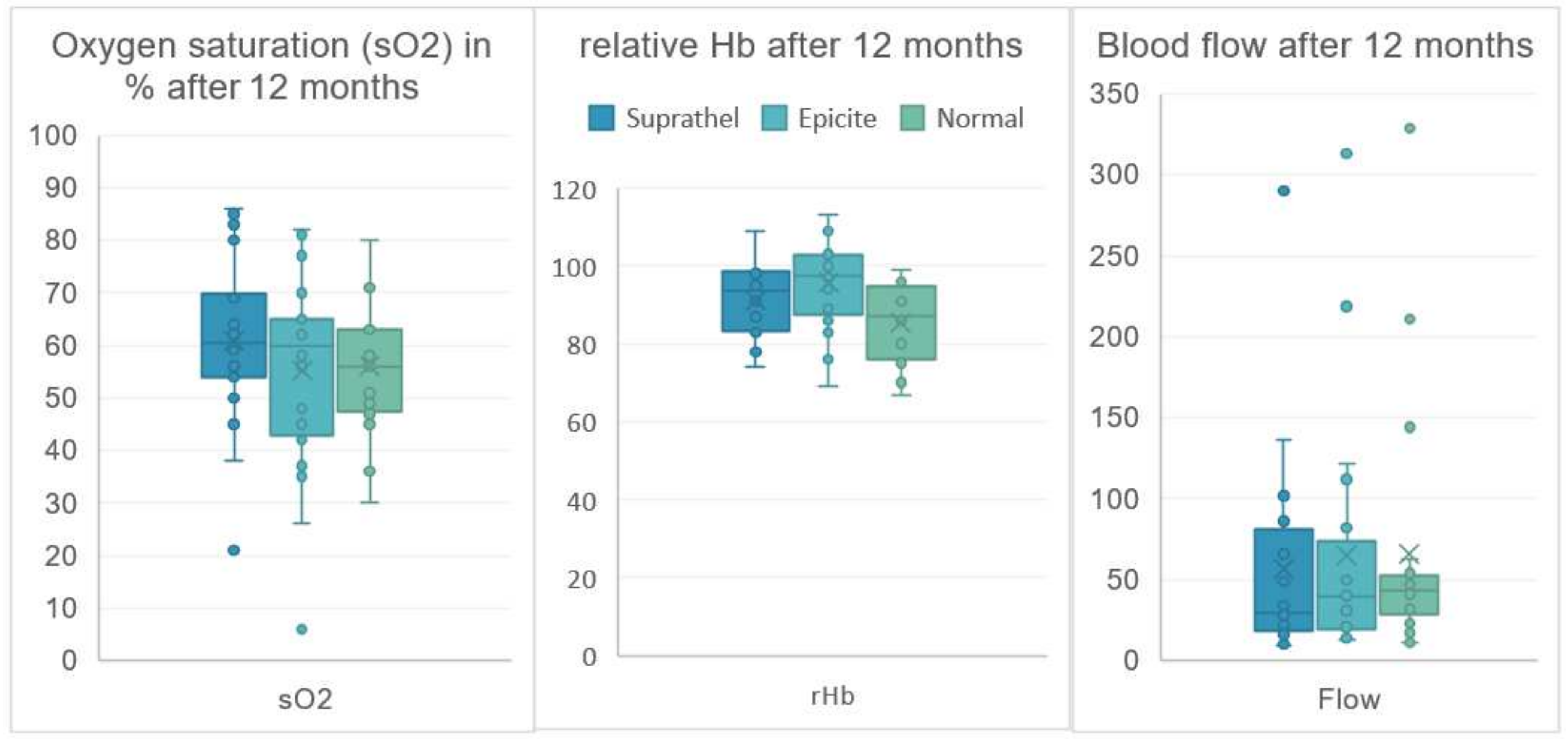
| Oxygen2See | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| sO2 | 3 months | 74.2 | 11.5 | 68.1 | 14.1 | 58.2 | 14.1 |
| 6 months | 73.3 | 17.3 | 61.3 | 16.0 | 63.0 | 12.8 | |
| 12 months | 61.0 | 16.2 | 55.2 | 19.1 | 56.1 | 12.5 | |
| rHb | 3 months | 94.6 | 11.8 | 97.5 | 11.5 | 82.1 | 11.2 |
| 6 months | 95.2 | 11.0 | 97.5 | 8.5 | 85.2 | 10.1 | |
| 12 months | 91.3 | 9.1 | 95.8 | 11.6 | 85.3 | 10.0 | |
| Flow | 3 months | 72.1 | 57.1 | 74.3 | 64.0 | 57.6 | 58.0 |
| 6 months | 73.2 | 69.4 | 77.5 | 102.9 | 42.2 | 30.8 | |
| 12 months | 57.1 | 65.7 | 64.9 | 76.6 | 65.6 | 77.4 | |
| Dressing | Suprathel® | epicitehydro® | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSS Parameter | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Pigmen-tation | 3 months | 1.5 | 0.607 | 1.45 | 0.686 |
| 6 months | 1.05 | 0.887 | 1.25 | 0.851 | |
| 12 months | 0.90 | 0.912 | 0.95 | 0.887 | |
| Vasculartity | 3 months | 1.25 | 0.444 | 1.15 | 0.366 |
| 6 months | 0.70 | 0.657 | 0.60 | 0.503 | |
| 12 months | 0.35 | 0.587 | 0.30 | 0.571 | |
| Pliability | 3 months | 0.00 | 0.000 | 0.05 | 0.224 |
| 6 months | 0.15 | 0.671 | 0.10 | 0.447 | |
| 12 months | 0.30 | 0.733 | 0.25 | 0.639 | |
| Height | 3 months | 0.15 | 0.366 | 0.10 | 0.447 |
| 6 months | 0.10 | 0.308 | 0.10 | 0.308 | |
| 12 months | 0.25 | 0.550 | 0.10 | 0.308 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiefer, J.L.; Aretz, F.G.; Fuchs, P.C.; Lefering, R.; Yary, P.; Opländer, C.; Schulz, A.; Daniels, M. Comparison of Long-Term Skin Quality and Scar Formation in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds Treated with Suprathel® and epicitehydro® Wound Dressings. Medicina 2022, 58, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111550
Schiefer JL, Aretz FG, Fuchs PC, Lefering R, Yary P, Opländer C, Schulz A, Daniels M. Comparison of Long-Term Skin Quality and Scar Formation in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds Treated with Suprathel® and epicitehydro® Wound Dressings. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111550
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiefer, Jennifer Lynn, Friederike Genoveva Aretz, Paul Christian Fuchs, Rolf Lefering, Pouyan Yary, Christian Opländer, Alexandra Schulz, and Marc Daniels. 2022. "Comparison of Long-Term Skin Quality and Scar Formation in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds Treated with Suprathel® and epicitehydro® Wound Dressings" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111550
APA StyleSchiefer, J. L., Aretz, F. G., Fuchs, P. C., Lefering, R., Yary, P., Opländer, C., Schulz, A., & Daniels, M. (2022). Comparison of Long-Term Skin Quality and Scar Formation in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds Treated with Suprathel® and epicitehydro® Wound Dressings. Medicina, 58(11), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111550






