Procoagulant Disorders in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
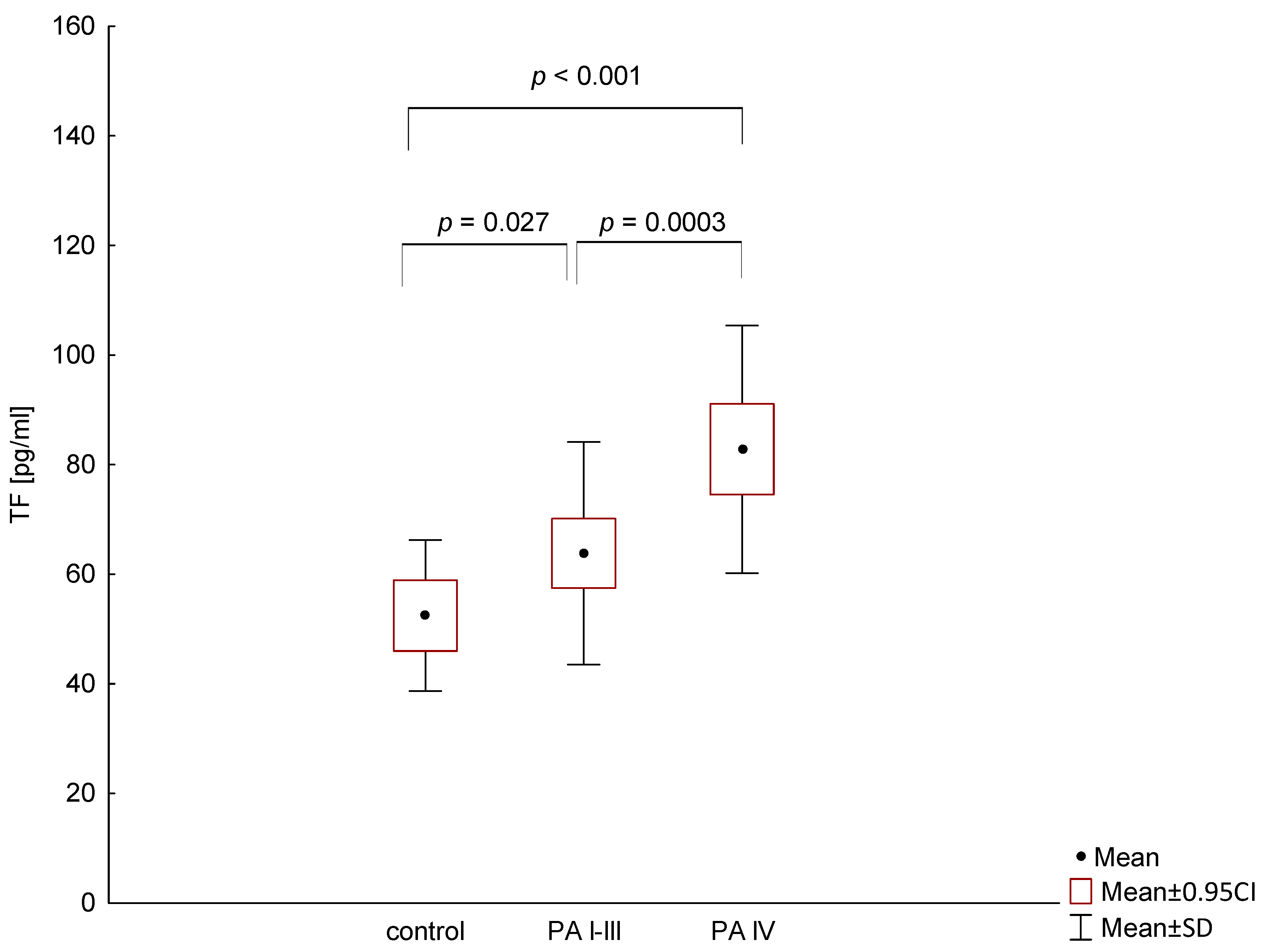
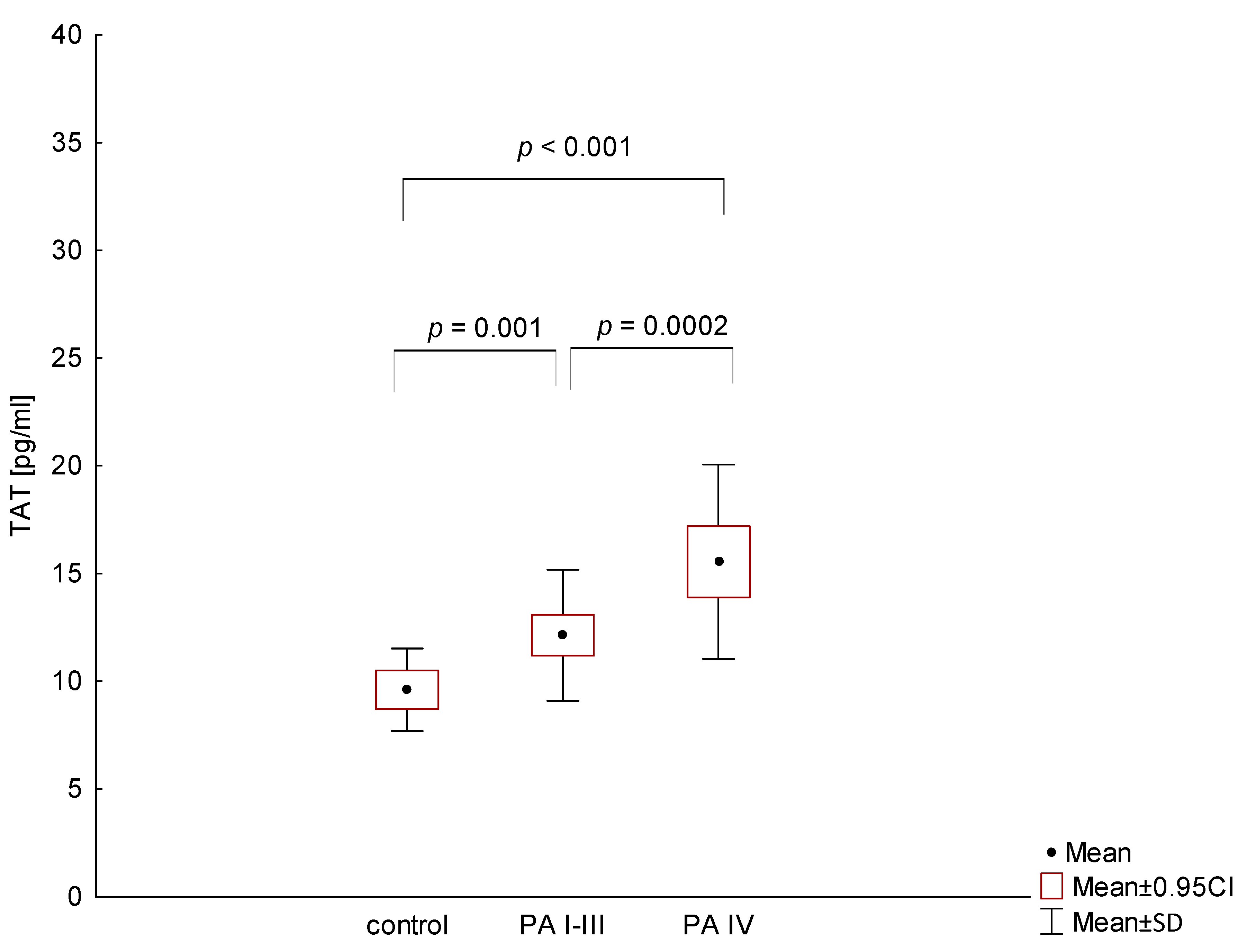
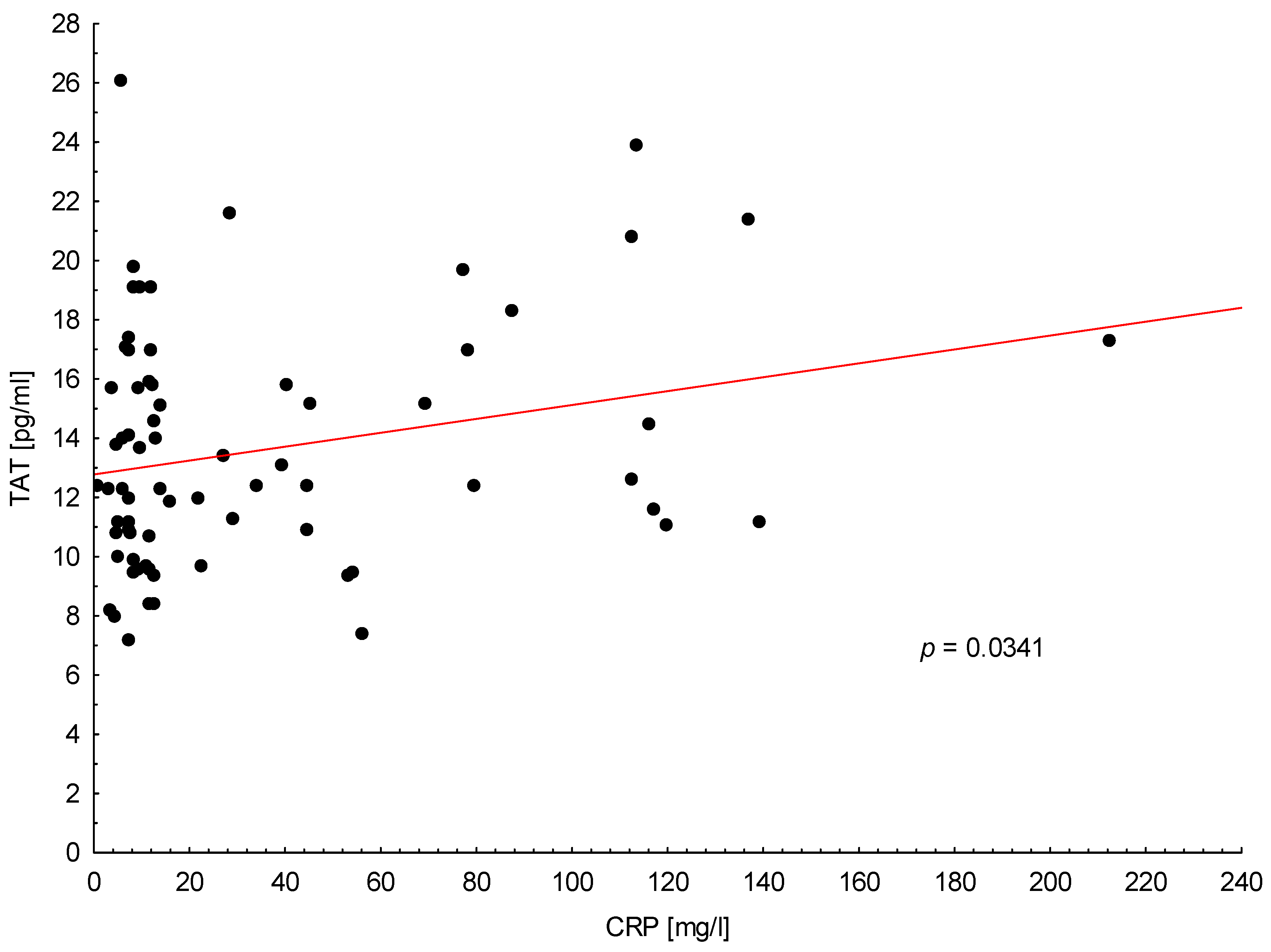
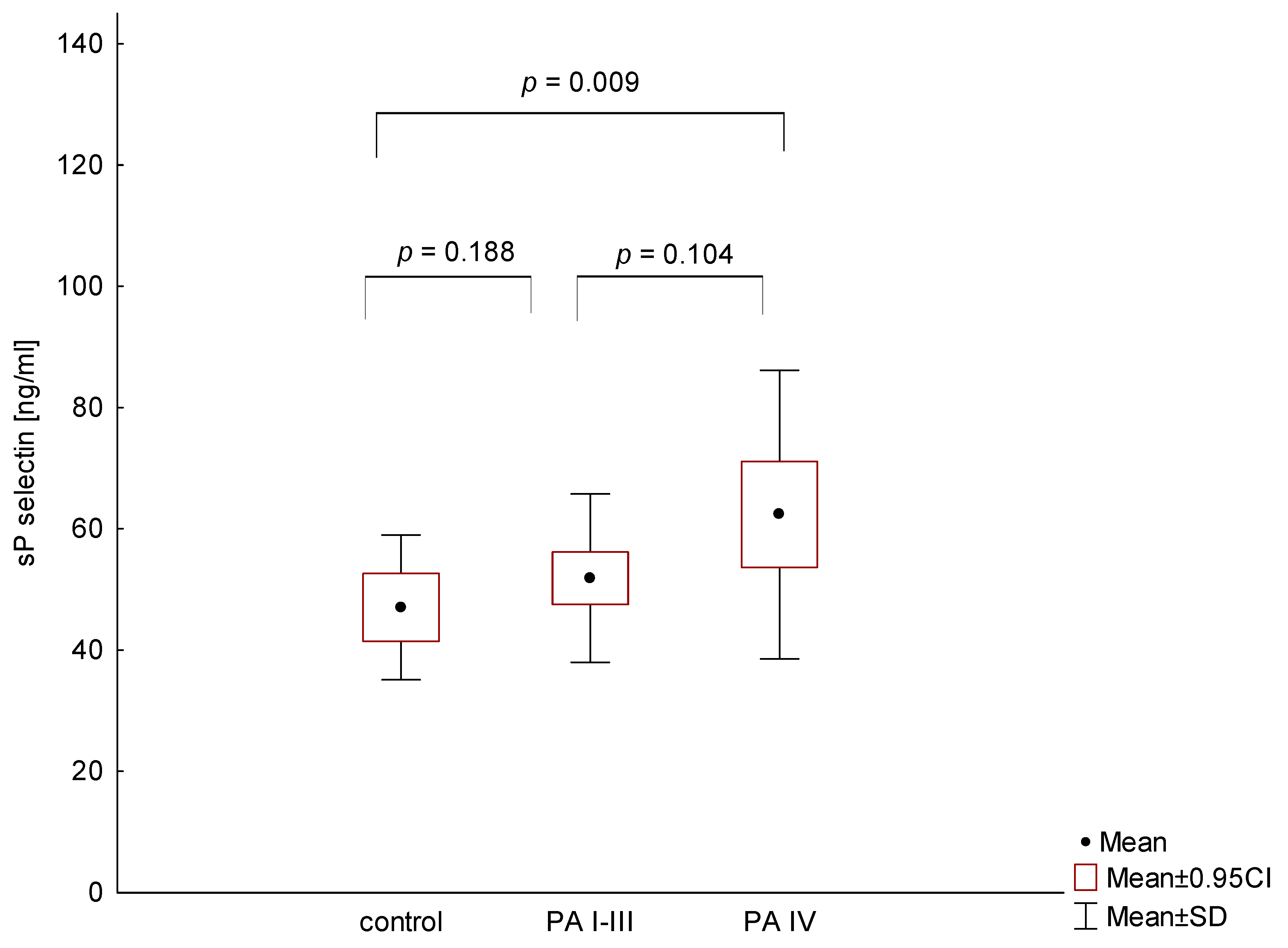
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emmerich, J. Epidemiology of venous thrombosis. Bull. Acad. Natl. Med. 2003, 187, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Falanga, A.; Russo, L.; Milesi, V. The coagulopathy of cancer. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, K.; Nakai, Y.; Isayama, H.; Saito, K.; Hamada, T.; Takahara, N.; Mizuno, S.; Mohri, D.; Kogure, H.; Matsubara, S.; et al. Thromboembolisms in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis of 475 Patients. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, O.; Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J. Adjuvant, neoadjuvant, and experimental regimens in overcoming pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2016, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, L.A.; Peterson, D.R.; Berry, A.; Sousou, T.; Khorana, A.A. Symptomatic and incidental thromboembolism are both associated with mortality in pancreatic cancer. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 106, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Dalal, M.; Lin, J.; Connolly, G.C. Incidence and predictors of venous thromboembolism (VTE) among ambulatory high-risk cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in the United States. Cancer 2013, 119, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Guo, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B. Tissue factor in tumor microenvironment: A systematic review. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, G.; Tan, Y.; Wei, J.; Wu, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, N. Immunolocalisation of tissue factor in esophageal cancer is correlated with intratumoral angiogenesis and prognosis of the patient. Acta Histochem. 2010, 112, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, K.; Homma, S.; Satoh, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Abe, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Oki, A.; Tsunoda, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Nagasawa, T.; et al. Tissue factor expression as a possible determinant of thromboembolism in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Toi, M.; Koike, M.; Nakamura, S.; Tominaga, T. Tissue factor expression in breast cancer tissues: Its correlation with prognosis and plasma concentration. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitori, N.; Ino, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Honda, K.; Yanagihara, K.; Kosuge, T.; Kanai, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Hirohashi, S. Prognostic significance of tissue factor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Menzies, K.E.; Wang, J.G.; Hyrien, O.; Hathcock, J.; Mackman, N.; Taubman, M.B. Plasma tissue factor may be predictive of venous thromboembolism in pancreatic cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1983–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Ahrendt, S.A.; Ryan, C.K.; Francis, C.W.; Hruban, R.H.; Hu, Y.C.; Hostetter, G.; Harvey, J.; Taubman, M.B. Tissue factor expression, angiogenesis, and thrombosis in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2870–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Gąsiorowska, A.; Olakowski, M.; Lekstan, A.; Lampe, P.; Małecka-Panas, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) genotype and serum concentration in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Fidan, E.; Kavgaci, H.; Orem, A.; Yilmaz, M.; Yildiz, B.; Fidan, S.; Akcan, B.; Ozdemir, F.; Aydin, F. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and thrombin-antithrombin-III-complex levels in patients with gastric cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2012, 33, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyilkan, O.; Baltali, E.; Ozdemir, O.; Tekuzman, G.; Kirazli, S.; Firat, D. Haemostatic changes; plasma levels of alpha2-antiplasmin-plasmin complex and thrombin-antithrombin III complex in female breast cancer. Tumori J. 1998, 84, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadducci, A.; Marrai, R.; Baicchi, U.; Gagetti, O.; Facchini, V.; Genazzani, A.R. Prothrombin fragment F1+2 and thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT) plasma levels in patients with gynecological cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 1996, 61, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Sasaki, M.; Hosoi, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Morizane, C.; Ueno, N.; Okusaka, T. Incidence and risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with pretreated advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16883–16890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, H.R.; Van Doormaal, F.F.; Van Sluis, G.L.; Kamphuisen, P.W. Cancer and thrombosis: From molecular mechanisms to clinical presentations. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Reyes, M.E.; George, M.D.; Roberts, J.D.; Akiyama, S.K. P-selectin activates integrinmediated colon carcinoma cell adhesion to fibronectin. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 4056–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, N.; Vella, K.; Hickey, K.; Bertù, L.; Zammit, D.; Spiteri, S.; Kitchen, S.; Makris, M.; Ageno, W.; Gatt, A. Biomarkers for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism: D-dimer, thrombin generation, procoagulant phospholipid and soluble P-selectin. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.G.; Chen, M.; Chou, K.C. P-selectin cell adhesion molecule in inflammation, thrombosis, cancer growth and metastasis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.E.; Sookthai, D.; Johnson, T.; Schübel, R.; González Maldonado, S.; Pletsch-Borba, L.; Katzke, V.; Bugert, P.; Hoffmeister, M.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Pre-diagnostic plasma concentrations of Fibrinogen, sGPIIb/IIIa, sP-selectin, sThrombomodulin, Thrombopoietin in relation to cancer risk: Findings from a large prospective study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.; Cheung, W.Y. Evolving treatment landscape for early and advanced pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2017, 9, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.S.; Soff, G.A.; Capanu, M.; Crosbie, C.; Shah, M.A.; Kelsen, D.P. Analysis of incidence and clinical outcomes in patients with thromboembolic events and invasive exocrine pancreatic cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 3053–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Kitayama, J.; Ishikawa, M.; Nagawa, H. Tissue factor expression is a clinical indicator of lymphatic metastasis and poor prognosis in gastric cancer with intestinal phenotype. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 95, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandoj, C.; Pizzuti, L.; Sergi, D.; Sperduti, I.; Mazzotta, M.; Di Lauro, L. Observational study of coagulation activation in early breast cancer: Development of a prognostic model based on data from the real world setting. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komala, A.S.; Rachman, A. Association of Peripheral Monocyte Count with Soluble P-Selectin and Advanced Stages in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Adv. Hematol. 2018, 3864398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantur, M.; Koper, O.; Snarska, J.; Sidorska, A.; Kruszewska-Wnorowska, K. Evaluation of PDGF-AB and sP-selectin concentrations in relation to platelet mount in patients with colorectal cancer before and after surgical treatment. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2008, 118, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Alban, S.; Bistrian, R.; Boehncke, W.H.; Kaufmann, R.; Henschler, R.; Gille, J. The ability of different forms of heparins to suppress P-selectin function in vitro correlates to their inhibitory capacity on blond borne metastasis in vivo. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Boehme, B.; Podda, M.; Henschler, R.; Jager, E.; Tandi, C.; Boehncke, W.H.; Zollner, T.M.; Kaufmann, R.; Gille, J. Endothelial P-selectin as a target of heparin action in experimental melanoma lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, C.; Simanek, R.; Vormittag, R.; Dunkler, D.; Alguel, G.; Koder, S.; Kornek, G.; Marosi, C.; Wagner, O.; Zielinski, C.; et al. High plasma levels of soluble P-selectin are predictive of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: Results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS). Blood 2008, 112, 2703–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman-Zawadzka, A.; Łukaszewicz-Zając, M.; Gryko, M.; Kulczyńska-Przybik, A.; Mroczko, B. Serum chemokine CXCL8 as a better biomarker for diagnosis and prediction of pancreatic cancer than its specific receptor CXCR2, C-reactive protein, and classic tumor markers CA 19-9 and CEA. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2018, 128, 524–531. [Google Scholar]
- Babic, A.; Schnure, N.; Neupane, N.P.; Zaman, M.M.; Rifai, N.; Welch, M.W. Plasma inflammatory cytokines and survival of pancreatic cancer patients. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Gryko, M.; Kemona-Chetnik, I.; Kemona, H. Relationship between soluble P-selectin and inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein) in colorectal cancer. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanz, R.; Vukovich, T.; Vormittag, R.; Dunkler, D.; Ay, C.; Thaler, J.; Haselböck, J.; Scheithauer, W.; Zielinski, C.; Pabinger, I. Thrombosis risk and survival in cancer patients with elevated C-reactive protein. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group of PA Patients | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I-III | Stage IV | ||
| n = 42 | n = 31 | ||
| Mean age (years) | 66.1 ± 4.1 | 69.2 ± 4.3 | NS |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 25 | 18 | NS |
| Female | 17 | 13 | |
| Tumor size | |||
| <3 cm | 24 | 9 | <0.05 |
| ≥3 cm | 19 | 22 | |
| Tumor location | |||
| Head of pancreas | 32 | 23 | NS |
| Body or tail | 10 | 8 | |
| Histological differentiation | |||
| G1 + G2 | 27 | 14 | NS |
| G3 | 16 | 17 | |
| Lymph node involvement | <0.001 | ||
| positive | 18 | 29 | |
| negative | 25 | 2 | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.3 ± 1.3 | 9.6 ± 1.5 | NS |
| Platelet (G/L) | 251.2 ± 7.9 | 253.9 ± 9.1 | NS |
| CRP (mg/L) | 25.0 ± 2.7 | 46.7 ± 4.1 | NS |
| D-dimers (ng/mL) | 2162.2 ± 17.9 | 3475.5 ± 21.9 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Woźniak, M.; Borkowska, A.; Cypryk, K.; Olakowski, M.; Małecka-Panas, E. Procoagulant Disorders in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Medicina 2020, 56, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120677
Talar-Wojnarowska R, Woźniak M, Borkowska A, Cypryk K, Olakowski M, Małecka-Panas E. Procoagulant Disorders in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Medicina. 2020; 56(12):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120677
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalar-Wojnarowska, Renata, Małgorzata Woźniak, Anna Borkowska, Katarzyna Cypryk, Marek Olakowski, and Ewa Małecka-Panas. 2020. "Procoagulant Disorders in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma" Medicina 56, no. 12: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120677
APA StyleTalar-Wojnarowska, R., Woźniak, M., Borkowska, A., Cypryk, K., Olakowski, M., & Małecka-Panas, E. (2020). Procoagulant Disorders in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Medicina, 56(12), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120677







