Association between SNPs of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels, Hypercholesterolemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Clinical and Biological Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
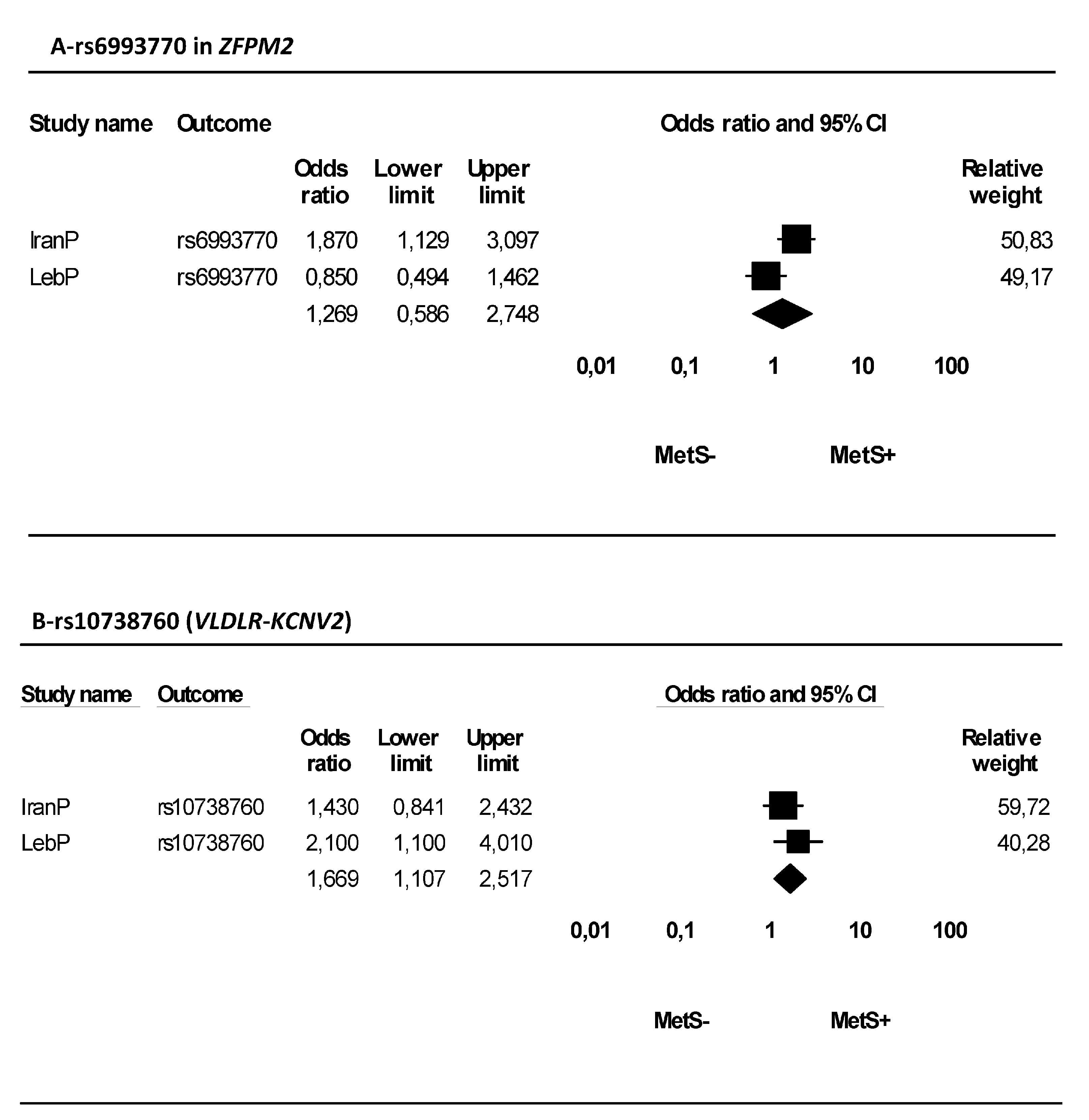
2.5. Meta-Analysis with Metabolic Syndrome
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karr, S. Epidemiology and management of hyperlipidemia. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, T.; Castelli, W.P.; Hjortland, M.C.; Kannel, W.B.; Dawber, T.R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. Am. J. Med. 1977, 62, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.-P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Rissanen, T.T.; Vajanto, I.; Hartikainen, J. Vascular endothelial growth factors: Biology and current status of clinical applications in cardiovascular medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, K.S.; Vakili, K.; Zurakowski, D.; Soliman, M.; Butterfield, C.; Sylvin, E.; Lo, K.-M.; Gillies, S.; Javaherian, K.; Folkman, J. Inhibition of plaque neovascularization reduces macrophage accumulation and progression of advanced atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4736–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukardali, Y.; Aydogdu, S.; Ozmen, N.; Yonem, A.; Solmazgul, E.; Ozyurt, M.; Cingozbay, Y.; Aydogdu, A. The relationship between severity of coronary artery disease and plasma level of vascular endothelial growth factor. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2008, 9, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Belgore, F.M.; Constans, J.; Conri, C.; Lip, G.Y. Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor Flt-1 in patients with hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis and the effects of fluvastatin or fenofibrate. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, C.B.; Gramling, R.; Parker, D.R.; Roberts, M.B.; Lu, B.; Ridker, P.M. Prospective association of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) with coronary heart disease mortality in Southeastern New England. Atherosclerosis 2008, 200, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrahmoune, H.; Herbeth, B.; Lamont, J.V.; Masson, C.; Fitzgerald, P.S.; Visvikis-Siest, S.; Visvikis-Siest, S. Heritability for Plasma VEGF Concentration in the Stanislas Family Study. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2007, 71, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Chen, M.H.; Destefano, A.; Choi, S.H.; Yang, Q.; Vasan, R.S.; Seshadri, S.; Visvikis-Siest, S.; Nezhad, M.A.; Marteau, J.B.; et al. Identification of cis-and trans-acting genetic variants explaining up to half the variation in circulating vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, M.G.; Bonnefond, A.; Ndiaye, N.C.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; El Shamieh, S.; Saleh, A.; Rancier, M.; Siest, G.; Lamont, J.; Fitzgerald, P.; et al. A common variant highly associated with plasma VEGFA levels also contributes to the variation of both LDL-C and HDL-C. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Mirhafez, S.R.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; Murray, H.; Ndiaye, N.C.; Bahrami, A.; Varasteh, A.; Avan, A.; Bonnefond, A.; Rancier, M.; et al. The relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor cis- and trans-acting genetic variants and metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Med Sci. 2018, 355, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaad, S.; Costanian, C.; Jaffal, L.; Tannous, F.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; El Shamieh, S. Association of TLR4 Polymorphisms, Expression, and Vitamin D with Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghalyini, B.; El Shamieh, S.; Salami, A.; Siest, S.V.; Fakhoury, H.M.; Fakhoury, R. Effect of SLCO1B1 gene polymorphisms and vitamin D on statin-induced myopathy. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2018, 33, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shamieh, S.; Costanian, C.; Kassir, R.; Visvkis-Siest, S.; Bissar-Tadmouri, N.; Siest, S.V. APOE genotypes in Lebanon: Distribution and association with hypercholesterolemia and Alzheimer’s disease. Pers. Med. 2019, 16, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br. Med. J. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Nguyen, D.T. Total and High-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults: United States, 2015–2016. NCHS Data Brief 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.M.; Khan, S.A.; Jackson, R.T.; Duane, M. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Central and South American Immigrant Residents of the Washington, DC, Area. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017, 9531964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibai, A.-M.; Obeid, O.; Batal, M.; Adra, N.; El Khoury, D.; Hwalla, N. Prevalence and correlates of metabolic syndrome in an adult Lebanese population. CVD Prev. Control. 2008, 3, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogan, K.; Bayram, F.; Capak, M.; Tanriverdi, F.; Karaman, A.; Ozturk, A.; Altunbas, H.; Gokce, C.; Kalkan, A.; Yazici, C. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the Mediterranean region of Turkey: Evaluation of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lawati, J.A.; Mohammed, A.J.; Al-Hinai, H.Q.; Jousilahti, P. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome Among Omani Adults. Diabet. Care 2003, 26, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovar, R.; Kiani, F.; Sayehmiri, F.; Yasemi, M.; Mohsenzadeh, Y.; Mohsenzadeh, Y. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Iran: A meta-analysis. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 5402–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kivelä, A.M.; Heinonen, S.E.; Huusko, J.; Dijkstra, M.H.; Gurzeler, E.; Mäkinen, P.I.; Leppänen, P.; Olkkonen, V.M.; Eriksson, U.; Jauhiainen, M.; et al. The effects of VEGF-A on atherosclerosis, lipoprotein profile, and lipoprotein lipase in hyperlipidaemic mouse models. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, O.; Nanchen, D.; Cornuz, J.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Gmel, G.; Daeppen, J.-B.; Paccaud, F.; Mooser, V.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; et al. Alcohol drinking, the metabolic syndrome and diabetes in a population with high mean alcohol consumption. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Rubbiati, L.; Bagnardi, V.; Zambon, A.; Poikolainen, K. Alcohol and coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis. Addict. 2000, 95, 1505–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, K.A.; Whelan, E.M.; Kava, R. The Health effects of moderate alcohol intake in humans: An epidemiologic review. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2000, 37, 261–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, K. Association of alcohol consumption with lipid profile in hypertensive men. Alcohol Alcohol. 2012, 47, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Participants (n = 460) |
|---|---|
| Age | 40.60 ± 14.16 |
| Gender n (%) | |
| Male | 168 (36.5) |
| Female | 292 (63.5) |
| Education Level n (%) | |
| None | 3 (0.7) |
| School | 194 (42.2) |
| University | 263 (57.2) |
| Marital Status n (%) | |
| Single | 121 (26.3) |
| Married | 321 (69.8) |
| Divorced | 18 (3.9) |
| Characteristics | Participants (n = 460) |
|---|---|
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 25.71 ± 4.98 |
| Alcohol consumption (current drinker) n (%) | 162 (35.3) |
| Smoker n (%) | 122 (26.5) |
| Physical activity (more than once per week) n (%) | 115 (25.0) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 181.41 ± 40.94 |
| High n (%) | 351 (76.3) |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 117.39 ± 33.52 |
| High n (%) | 347 (75.4) |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 45.53 ± 14.61 |
| Low n (%) | 270 (58.7) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 145.96 ± 124.34 |
| High n (%) | 174 (37.8) |
| SBP (mmHg) | 132.07 ± 15.89 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 67.82 ± 9.12 |
| Hypertension n (%) | 255 (55.4) |
| MAF | |
| rs6921438G > A | 0.34 |
| rs4416670C > T | 0.49 |
| rs6993770A > T | 0.34 |
| rs10738760A > G | 0.46 |
| Variables | SNP | Ancestral Alleles | MAF | p | Beta | SE | Trait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | 0.68 | 0.15 | Tchol | |||
| <0.001 | 2.07 | 0.45 | HDL-C | ||||
| <0.001 | 0.53 | 0.13 | LDL-C | ||||
| Gender | <0.001 | 14.10 | 4.49 | Tchol | |||
| <0.001 | 5.93 | 1.56 | HDL-C | ||||
| <0.001 | 11.15 | 3.75 | LDL-C | ||||
| VLDLR-KCNV2 | rs10738760 | A | 0.46 | 0.01 | –5.53 | 2.62 | Tchol |
| ZFPM2 | rs6993770 | A | 0.34 | 0.007 | 7.89 | 2.90 | Tchol |
| 0.01 | 6.20 | 2.42 | LDL-C | ||||
| ZFPM2 | rs6993770 x Gender | A | 0.02 | 3.661 | 1.58 | Tchol | |
| 0.03 | 2.795 | 1.31 | LDL-C |
| Risk Factors | Total Cholesterol | LDL-C | MetS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% C.I.) | p | OR (95% C.I.) | p | OR (95% C.I.) | p | |
| Age | ||||||
| <40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| ≥40 | 22.67 (9.70–53.02) | <0.001 | - | ns | - | ns |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| BMI | ||||||
| <25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 25–29.9 | - | ns | - | ns | 2.44 (1.29–4.62) | 0.006 |
| ≥30 | 3.03 (1.16–7.92) | 0.02 | 2.78 (1.06–7.33) | 0.04 | - | ns |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Non-married | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Married | 0.16 (0.07–0.35) | <0.001 | - | ns | 0.54 (0.28–1.03) | 0.06 |
| Divorced | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| Widowed | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Non smoker | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Past smoker | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| Current smoker | 2.24 (1.08–4.64) | 0.03 | - | ns | - | ns |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||
| Non drinker | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Past drinker | 0.01 (0–0.07) | <0.001 | 0.01 (0.001–0.11) | <0.001 | - | ns |
| Current drinker | 0.47 (0.25–0.88) | 0.01 | - | ns | - | ns |
| Physical activity | 1 | |||||
| <1 per week | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 per week | 0.291 (0.12–0.68) | 0.004 | 0.24 (0.10–0.58) | 0.001 | - | ns |
| ≥2 per week | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| rs6993770 AA | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| AT | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
| TT | 2.61 (0.94–7.19) | 0.01 | 4.30 (1.37–13.51) | 0.01 | - | ns |
| rs10738760 AA | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| GA | - | ns | - | ns | 2.10 (1.10–4.01) | 0.02 |
| GG | - | ns | - | ns | - | ns |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salami, A.; El Shamieh, S. Association between SNPs of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels, Hypercholesterolemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina 2019, 55, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55080464
Salami A, El Shamieh S. Association between SNPs of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels, Hypercholesterolemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina. 2019; 55(8):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55080464
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalami, Ali, and Said El Shamieh. 2019. "Association between SNPs of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels, Hypercholesterolemia and Metabolic Syndrome" Medicina 55, no. 8: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55080464
APA StyleSalami, A., & El Shamieh, S. (2019). Association between SNPs of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels, Hypercholesterolemia and Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina, 55(8), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55080464






