Salt Consumption in Latvian Population: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Record
2.3. 24-h Urinary Collection
2.4. Anthropometric Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Mapping Salt Reduction Initiatives in the Who European Region; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, C.; Webster, J. National approaches to monitoring population salt intake: A trade-off between accuracy and practicality? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Veterinary Service Food Centre. Comprehensive Study on Food Consumption of Latvian Population 2007–2009; Food and Veterinary Service Food Centre: Riga, Latvia, 2009.
- The European Parliament. Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods. OJ 2006, 404, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Guidance Document for Competent Authorities for the Control of Compliance with EU Legislation on: Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers, Amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and Repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004 and Council Directive 90/496/EEC of 24 September 1990 on Nutrition Labelling of Foodstuffs and Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 June 2002 on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States Relating to Food Supplements with Regard to the Setting of Tolerances for Nutrient Values Declared on a Label; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- Ji, C.; Sykes, L.; Paul, C.; Dary, O.; Legetic, B.; Campbell, N.R.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sub-Group for Research and Surveillance of the PAHO–WHO Regional Expert Group for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention through Population-wide Dietary Salt Reduction. Systematic review of studies comparing 24-h and spot urine collections for estimating population salt intake. Pan Am. J. Public Health 2012, 32, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Strategies to Monitor and Evaluate Population Sodium Consumption and Sources of Sodium in the Diet; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guideline: Potassium Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. General principles for the collection of national food consumption data in the view of a pan-European dietary survey. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. How to Obtain Measures of Population Level Sodium Intake in 24-h Urine Samples; WHO: Warwick, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Ji, C.; Donfrancesco, C.; Palmieri, L.; Ippolito, R.; Vanuzzo, D.; Giampaoli, S.; Strazzullo, P. Geographic and socioeconomic variation of sodium and potassium intake in Italy: results from the MINISAL-GIRCSI programme. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frese, E.M.; Fick, A.; Sadowsky, H.S. Blood pressure measurement guidelines for physical therapists. Cardiopulm. Phys. Ther. J. 2011, 22, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortega, R.M.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Ballesteros, J.M.; Pérez-Farinós, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Aparicio, A.; Perea, J.M.; Andrés, P. Estimation of salt intake by 24 h urinary sodium excretion in a representative sample of Spanish adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandevijvere, S.; De Keyzer, W.; Chapelle, J.-P.; Jeanne, D.; Mouillet, G.; Huybrechts, I.; Hulshof, P.; van Oyen, H. Estimate of total salt intake in two regions of Belgium through analysis of sodium in 24-h urine samples. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, B.; Cox, L.; Maplethorpe, N.; Mazumder, A.; Nicholson, S.; Page, P.; Prentice, A.; Rooney, K.; Ziauddeen, N.; Swan, G. National Diet and Nutrition Survey—Assessment of Dietary Sodium in Adults (Aged 19 to 64 Years) in England, 2014; Public Health England: London, UK, 2016.
- Reicks, M.; Trofholz, A.C.; Stang, J.S.; Laska, M.N. Impact of cooking and home food preparation interventions among adults: Outcomes and implications for future programs. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2014, 46, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Nago, E.; Verstraeten, R.; Roberfroid, D.; van Camp, J.; Kolsteren, P. Eating out of home and its association with dietary intake: A systematic review of the evidence. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeland, M.A.; Kumanyika, S.; Wilson, A.C.; Reboussin, D.M.; Easter, L.; Self, M.; Robertson, J.; Brown, W.M.; McFarlane, M. TONE Cooperative Research Group. Statistical issues in analyzing 24-h dietary recall and 24-h urine collection data for sodium and potassium intakes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo, K.; Pizarro, F.; Atalah, E.; Galgani, J.E. Assessment of dietary intake and urinary excretion of sodium and potassium in adults. Rev. Med. Chil. 2014, 142, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, A.A.; Fransen, H.; Jenab, M.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Tumino, R.; Agnoli, C.; Ericson, U.; Johansson, I.; Ferrari, P.; Engeset, D.; et al. Variation in intakes of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron and potassium in 10 countries in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, S101–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Fagard, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Redon, J.; Zanchetti, A.; Bohm, M.; Christiaens, T.; Cifkova, R.; De Backer, G.; Dominiczak, A. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1281–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Language Centre. Cabinet regulation No. 172. Regulations regarding nutritional norms for educatees of educational institutions, clients of social care and social rehabilitation institutions and patients of medical treatment institutions. Latvijas Vēstnesis 2012, 43, 4646. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuklina, E.V.; Flanders, W.D.; Hong, Y.; Gillespie, C.; Chang, M.H.; Gwinn, M.; Dowling, N.; Khoury, M.J. Sodium and potassium intake and mortality among US adults. Prospective data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Okamura, T.; Miura, K.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueshima, H.; Nakagawa, H. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Uezono, K.; Sasaki, H. A simple method for estimating 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion from second morning voiding urine specimen in adults. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1993, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakova, N.; Jüttner, K.; Dahlmann, A.; Schröder, A.; Linz, P.; Kopp, C.; Rauh, M.; Goller, U.; Beck, L.; Agureev, A.; et al. Long-term space flight simulation reveals infradian rhythmicity in human Na(+) balance. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerchl, K.; Rakova, N.; Dahlmann, A.; Rauh, M.; Goller, U.; Basner, M.; Dinges, D.F.; Beck, L.; Agureev, A.; Larina, I.; et al. Agreement between 24-h salt ingestion and sodium excretion in a controlled environment. Hypertension 2015, 66, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birukov, A.; Rakova, N.; Lerchl, K.; Engberink, R.H.; Johannes, B.; Wabel, P.; Moissl, U.; Rauh, M.; Luft, F.C.; Titze, J. Ultra-long-term human salt balance studies reveal interrelations between sodium, potassium, and chloride intake and excretion. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Sodium intake and all-cause mortality over 20 years in the trials of hypertension prevention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Men (n = 15) | Women (n = 15) | Total (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 44.5 (11.8) | 42.8 (12.8) | 43.6 (12.1) |
| Age, % | |||
| 19–35 years | 26.7 | 33.3 | 30.0 |
| 36–50 years | 33.3 | 33.3 | 33.3 |
| 51–64 years | 40.0 | 33.3 | 36.7 |
| Height, mean (SD), cm | 181.9 (3.9) | 165.8 (6.9) | 173.9 (9.9) |
| Weight, mean (SD), kg | 95.0 (18.3) | 74.5 (16.4) | 84.7 (20.0) |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 28.7 (5.8) | 27.2 (5.9) | 27.9 (5.8) |
| BMI category, % | |||
| Underweight (16–18.49 kg/m2) | 0 | 6.7 | 3.35 |
| Normal weight (18.5–24.9 kg/m2) | 33.3 | 33.3 | 33.3 |
| Overweight (25–45 kg/m2) | 66.7 | 60 | 63.4 |
| Waist-hip ratio, mean (SD) | 0.96 (0.08) | 0.83 (0.12) | 0.89 (0.12) |
| Education, % | |||
| Tertiary | 26.7 | 66.7 | 46.7 |
| Other | 73.3 | 33.3 | 53.3 |
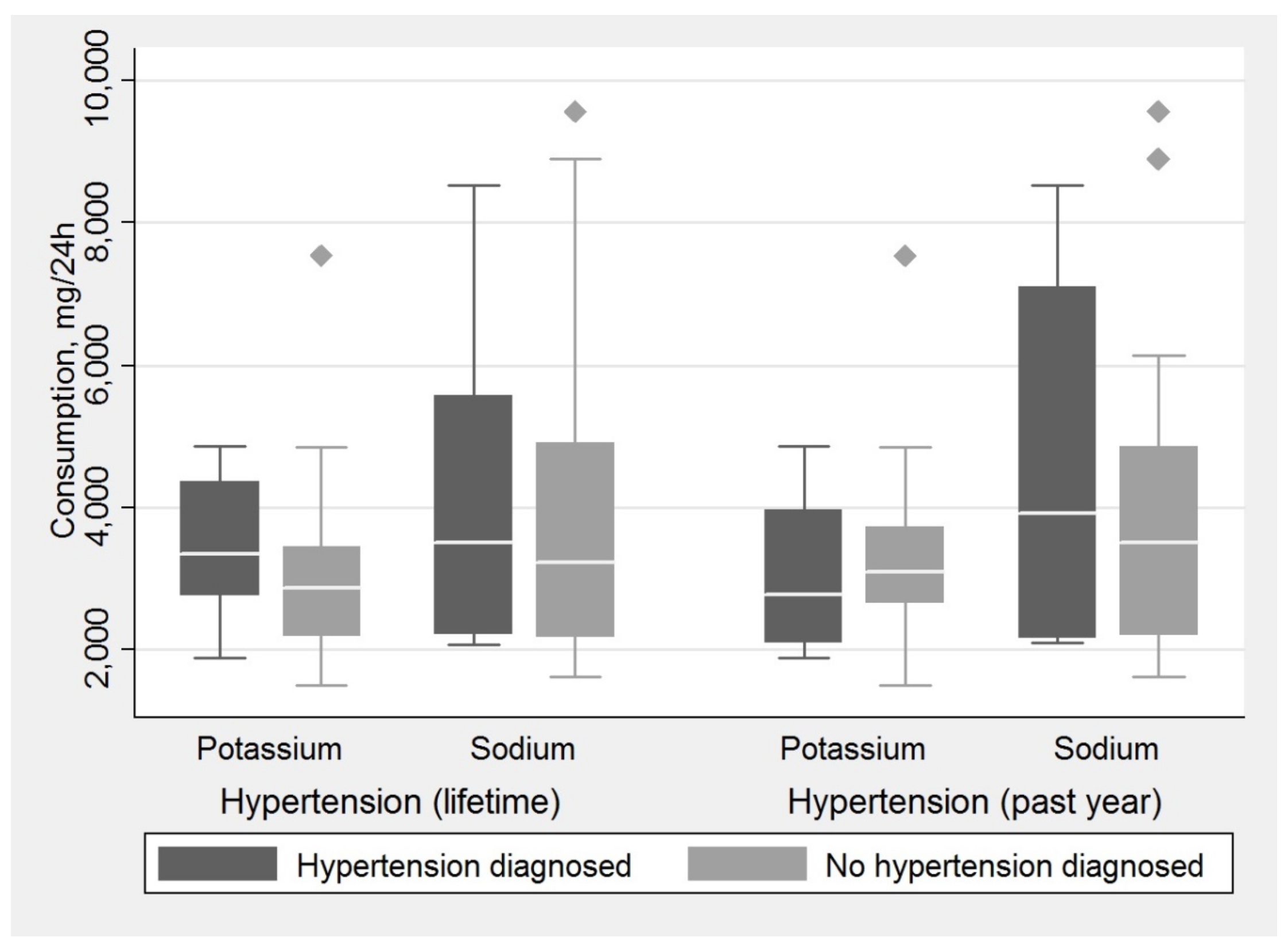
| Ever-diagnosed hypertension, % | |||
| Yes | 46.7 | 33.3 | 40.0 |
| No | 53.3 | 66.7 | 60.0 |
| Hypertension diagnosed in past year, % | |||
| Yes | 26.7 | 13.3 | 20.0 |
| No | 73.3 | 86.7 | 80.0 |
| Analyzed criterion | Men (n = 15) | Women (n = 15) | Total (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
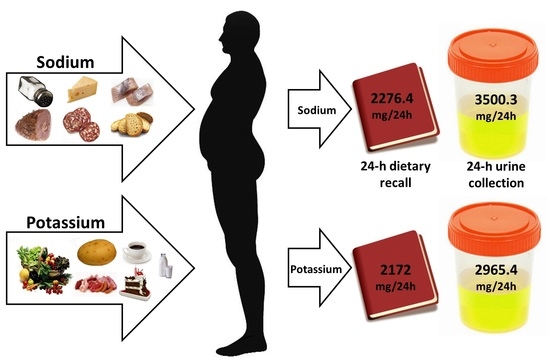
| Sodium, medium (IQR), mg/day | 3142.9 (1875.5–4814.0) | 1900.1 (1507.9–3080.8) | 2276.4 (1683.3–3979.4) |
| % of subjects consuming no more than 2000 mg/day * | 33.3 | 53.3 | 43.3 |
| Potassium, medium (IQR), mg/day | 2151.2 (1779.6–3586.5) | 2421.4 (1489.1–3323.7) | 2172.0 (1740.6–3506.5) |
| % of subjects consuming at least 3510 mg/day ** | 26.7 | 20.0 | 23.3 |
| Analyzed criterion | Men (n = 15) | Women (n = 15) | Total (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium, medium (IQR), mg/day | 4299.8 (2245.1–5579.2) | 2487.6 (2074.3–4345.1) | 3500.3 (2191.0–5535.0) |
| % of subjects consuming no more than 2000 mg/day * | 6.7 | 20.0 | 13.3 |
| Potassium, medium (IQR), mg/day | 3420.8 (2932.0–3960.9) | 2787.0 (2131.9–3598.0) | 2965.4 (2530.2–3749.9) |
| % of subjects consuming at least 3510 mg/day ** | 40.0 | 26.7 | 33.3 |
| Analyzed Criterion | Ion-Selective Electrode Method (n = 30) | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium level, mean (SD), mmol/L | 103.6 (55.3) | 102.2 (58.2) |
| Analyzed criterion | Ion-Selective Electrode Method (n = 30) | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|
| Potassium level, mean (SD), mmol/L | 40.7 (18.4) | 39.8 (15.7) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazda, I.; Goldmanis, M.; Siksna, I. Salt Consumption in Latvian Population: A Pilot Study. Medicina 2018, 54, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina54010010
Lazda I, Goldmanis M, Siksna I. Salt Consumption in Latvian Population: A Pilot Study. Medicina. 2018; 54(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina54010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazda, Ilva, Māris Goldmanis, and Inese Siksna. 2018. "Salt Consumption in Latvian Population: A Pilot Study" Medicina 54, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina54010010
APA StyleLazda, I., Goldmanis, M., & Siksna, I. (2018). Salt Consumption in Latvian Population: A Pilot Study. Medicina, 54(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina54010010