Keratinocytes: An Enigmatic Factor in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Factors Triggering Keratinocyte Activation
2.1. Cytokines
2.2. Immunologic Triggers—Allergens
2.2.1. Contact Allergens
2.2.2. Food Allergens
2.2.3. Inhalant Allergens
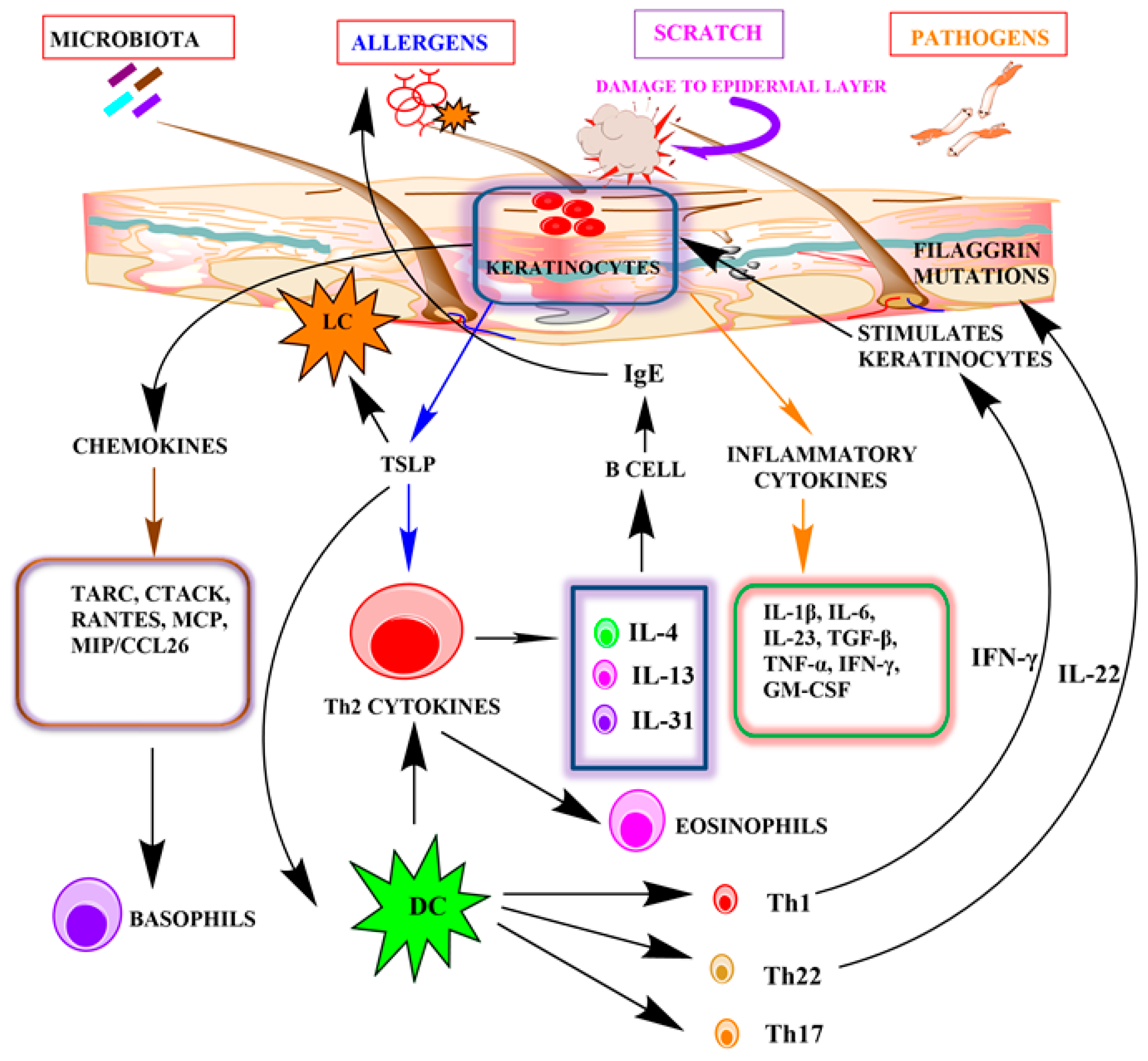
3. Possible Role of Keratinocytes in AD
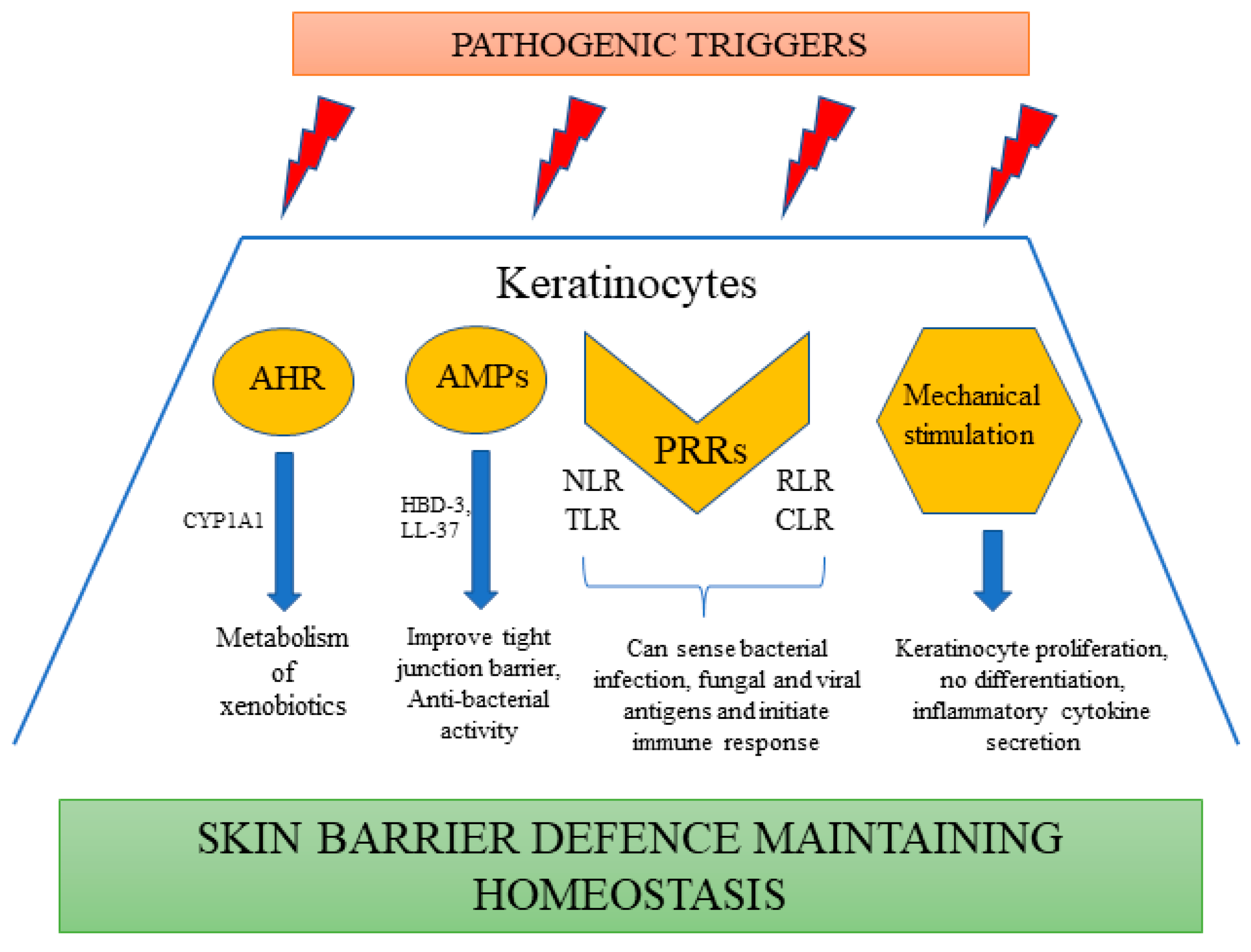
4. Keratinocytes as a Guardian of Skin Immune Defense
5. Keratinocytes as a Contributor to Pathogenesis in AD
6. Therapeutic Implications
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, J.N.W.N.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Mitra, R.S.; Dixit, V.M.; Nickoloff, B.J. Keratinocytes as Initiators of Inflammation. Lancet 1991, 337, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieosilapatham, P.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Umehara, Y.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Peng, G.; Yue, H.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Niyonsaba, F. Keratinocytes: Innate Immune Cells in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 204, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorschner, R.A.; Lopez-Garcia, B.; Massie, J.; Kim, C.; Gallo, R.L. Innate Immune Defense of the Nail Unit by Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 50, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolomoni, G.; Pastore, S. The Role of Keratinocytes in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esche, C.; de Benedetto, A.; Beck, L.A. Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis: Inflammatory Signals. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004, 4, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werfel, T. The Role of Leukocytes, Keratinocytes, and Allergen-Specific IgE in the Development of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, R.; Werfel, T.; Wittmann, M. IL-13-Stimulated Human Keratinocytes Preferentially Attract CD4+ CCR4+ T Cells: Possible Role in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Scarponi, C.; Giustizieri, M.L.; Girolomoni, G. Keratinocytes in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, C.; Bang, K.; Gesser, B.; Yoneyama, H.; Matsushima, K.; Larsen, C.G. A Th2 Chemokine, TARC, Produced by Keratinocytes May Recruit CLA+CCR4+ Lymphocytes into Lesional Atopic Dermatitis Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, M. Analysis of the Mechanism for the Development of Allergic Skin Inflammation and the Application for Its Treatment: Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis—Their Pathogenic Involvement. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 110, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, H.; Miyagaki, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Akatsuka, T.; Watanabe-Otobe, S.; Oka, T.; Shishido-Takahashi, N.; Suga, H.; Sugaya, M.; Sato, S. Increased IL-26 Expression Promotes T Helper Type 17- and T Helper Type 2-Associated Cytokine Production by Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 636–644.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; An, H.; Kim, J.; Gwon, M.; Gu, H.; Sung, W.J.; Han, S.M.; Pak, S.C.; Kim, M.; Park, K. Beneficial Effects of Melittin on Ovalbumin-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mouse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessler, I.; Reinheimer, T.; Kilbinger, H.; Bittinger, F.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Saloga, J.; Knop, J. Increased Acetylcholine Levels in Skin Biopsies of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.S.; Long, H.A.; Newman, C.F.; Wilson, P.A.; West, A.; McGill, P.J.; Wu, K.C.; Donaldson, M.J.; Reynolds, N.J. Proteomic Analysis of Filaggrin Deficiency Identifies Molecular Signatures Characteristic of Atopic Eczema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, S.; Pastore, S.; Fujisawa, H.; Shivji, G.M.; McKenzie, R.C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Sauder, D.N. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Suppresses Contact Hypersensitivity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 105, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Fanales-Belasio, E.; Albanesi, C.; Chinni, L.M.; Giannetti, A.; Girolomoni, G. Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Is Overproduced by Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis: Implications for Sustained Dendritic Cell Activation in the Skin. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedberg, I.M.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Komine, M.; Blumenberg, M. Keratins and the Keratinocyte Activation Cycle. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and Its Biologically Related Cytokines. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 44, 153–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröne, A. Keratinocytes and Cytokines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Scarponi, C.; Sebastiani, S.; Cavani, A.; Federici, M.; De Pità, O.; Puddu, P.; Girolomoni, G. IL-4 Enhances Keratinocyte Expression of CXCR3 Agonistic Chemokines. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Sumagin, R. ICAM-1: A Master Regulator of Cellular Responses in Inflammation, Injury Resolution, and Tumorigenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.N.W.N.; Sarma, V.; Mitra, R.S.; Dixit, V.M.; Nickoloff, B.J. Marked Synergism between Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interferon-γ in Regulation of Keratinocyte-Derived Adhesion Molecules and Chemotactic Factors. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Fujisawa, R.; Yamada, H.; Horikawa, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Hieshima, K.; Izawa, D.; Fujiie, S.; Tezuka, T.; Yoshie, O. Inducible Expression of a CC Chemokine Liver- and Activation-Regulated Chemokine (LARC)/Macrophage Inflammatory Protein (MIP)-3α/CCL20 by Epidermal Keratinocytes and Its Role in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, M.; Werfel, T. Interaction of Keratinocytes with Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Allergic Eczematous Skin Diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 6, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, F.-X.; Morel, F.; Camus, M.; Pedretti, N.; Barrault, C.; Garnier, J.; Lecron, J.-C. Keratinocytes under Fire of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Bona Fide Innate Immune Cells Involved in the Physiopathology of Chronic Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 718725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Massacrier, C.; Homey, B.; Vanbervliet, B.; Pin, J.J.; Vicari, A.; Lebecque, S.; Dezutter-Dambuyant, C.; Schmitt, D.; Zlotnik, A.; et al. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 3α Is Expressed at Inflamed Epithelial Surfaces and Is the Most Potent Chemokine Known in Attracting Langerhans Cell Precursors. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlapbach, C.; Simon, D. Update on Skin Allergy. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 69, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M. Advances in Allergic Skin Diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C. Keratinocytes in Allergic Skin Diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, T.; Breuer, K. Role of Food Allergy in Atopic Dermatitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 4, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zayadneh, E.M.; Alnawaiseh, N.A.; Altarawneh, A.H.; Aldmour, I.H.; Albataineh, E.M.; Al-Shagahin, H.; Alharazneh, A.; Alzayadneh, E. Sensitization to Inhaled Allergens in Asthmatic Children in Southern Jordan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2019, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunebaum, E.; Lavi, S. The Role of Food and Inhaled Allergens in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 1999, 3, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TUFT, L. Importance of Inhalant Allergens in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1949, 12, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Erwin, E.A.; Woodfolk, J.A.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. The Role of Inhalant Allergens in Atopic Dermatitis. In Handbook of Atopic Eczema; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet-Dahbi, S.; Renz, H. Role of Inhalant Allergens in Atopic Dermatitis. In Textbook of Atopic Dermatitis; Informa Healthcare: London, UK, 2008; pp. 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Tsai, M.H.; Tu, Y.L.; Hua, M.C.; Yao, T.C.; Yeh, K.W.; Huang, J.L. Sensitization to Food and Inhalant Allergens in Relation to Atopic Diseases in Early Childhood: A Birth Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piipponen, M.; Li, D.; Landén, N.X. The Immune Functions of Keratinocytes in Skin Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Kirsner, R. Pathophysiology of Acute Wound Healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirobe, T. Keratinocytes Regulate the Function of Melanocytes. Dermatol. Sin. 2014, 32, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivarcsi, A.; Bodai, L.; Réthi, B.; Kenderessy-Szabó, A.; Koreck, A.; Széll, M.; Beer, Z.; Bata-Csörgo, Z.; Magócsi, M.; Rajnavölgyi, E.; et al. Expression and Function of Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 in Human Keratinocytes. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.S.; Modlin, R.L. Toll-like Receptors in the Skin. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, G.; Yao, X.; Li, W. A Tryptophan Metabolite of the Skin Microbiota Attenuates Inflammation in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis through the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 2108–2119.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bogaard, E.H.; Bergboer, J.G.M.; Vonk-Bergers, M.; Van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.J.J.; Hato, S.V.; Van Der Valk, P.G.M.; Schröder, J.M.; Joosten, I.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; Schalkwijk, J. Coal Tar Induces AHR-Dependent Skin Barrier Repair in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial Peptides: Old Molecules with New Ideas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, M.D.; Gallo, R.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Jones, J.F.; Wong, C.; Streib, J.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Cytokine Milieu of Atopic Dermatitis Skin Subverts the Innate Immune Response to Vaccinia Virus. Immunity 2006, 24, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiatsurayanon, C.; Niyonsaba, F.; Smithrithee, R.; Akiyama, T.; Ushio, H.; Hara, M.; Okumura, K.; Ikeda, S.; Ogawa, H. Host Defense (Antimicrobial) Peptide, Human β-Defensin-3, Improves the Function of the Epithelial Tight-Junction Barrier in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyonsaba, F.; Ushio, H.; Nagaoka, I.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H. The Human β-Defensins (-1, -2, -3, -4) and Cathelicidin LL-37 Induce IL-18 Secretion through P38 and ERK MAPK Activation in Primary Human Keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyonsaba, F.; Ushio, H.; Nakano, N.; Ng, W.; Sayama, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Nagaoka, I.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H. Antimicrobial Peptides Human β-Defensins Stimulate Epidermal Keratinocyte Migration, Proliferation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klicznik, M.M.; Szenes-Nagy, A.B.; Campbell, D.J.; Gratz, I.K. Taking the Lead—How Keratinocytes Orchestrate Skin T Cell Immunity. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 200, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Michelle Kahlenberg, J.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The Diverse Contribution of Keratinocytes to Immune Responses in Skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, M.; Yazdi, A.S. NLRP1 Is the Key Inflammasome in Primary Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2507–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, J.; Núñez, G. Functional Expression of the Intracellular Pattern Recognition Receptor NOD1 in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dai, X.; Sayama, K.; Tohyama, M.; Shirakata, Y.; Hanakawa, Y.; Tokumaru, S.; Yang, L.; Hirakawa, S.; Hashimoto, K. Mite Allergen Is a Danger Signal for the Skin via Activation of Inflammasome in Keratinocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 806–814.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Nakashima, M.; Suzuki, Y. Nuclear DNA Damage-Triggered NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Promotes UVB-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Human Keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllisch, G.; Kalali, B.N.; Voelcker, V.; Wallich, R.; Behrendt, H.; Ring, J.; Bauer, S.; Jakob, T.; Mempel, M.; Ollert, M. Various Members of the Toll-like Receptor Family Contribute to the Innate Immune Response of Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Immunology 2005, 114, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mempel, M.; Voelcker, V.; Köllisch, G.; Plank, C.; Rad, R.; Gerhard, M.; Schnopp, C.; Fraunberger, P.; Walli, A.K.; Ring, J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Expression in Human Keratinocytes: Nuclear Factor ΚB Controlled Gene Activation by Staphylococcus Aureus Is Toll-like Receptor 2 but Not Toll-like Receptor 4 or Platelet Activating Factor Receptor Dependent. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Boyso, J.; Bravo-Patiño, A.; Baizabal-Aguirre, V.M. Collaborative Action of Toll-like and Nod-like Receptors as Modulators of the Inflammatory Response to Pathogenic Bacteria. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 432785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Shin, D.M.; Choi, D.K.; Lee, Z.W.; Kim, K.H.; Yuk, J.M.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, E.K. Innate Immune Responses to Mycobacterium Ulcerans via Toll-like Receptors and Dectin-1 in Human Keratinocytes. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, L.M.; Zijlstra-Willems, E.M.; Richters, C.D.; Ulrich, M.M.W.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. Dectin-1 Activation Induces Proliferation and Migration of Human Keratinocytes Enhancing Wound Re-Epithelialization. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 289, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, B.N.; Köllisch, G.; Mages, J.; Müller, T.; Bauer, S.; Wagner, H.; Ring, J.; Lang, R.; Mempel, M.; Ollert, M. Double-Stranded RNA Induces an Antiviral Defense Status in Epidermal Keratinocytes through TLR3-, PKR-, and MDA5/RIG-I-Mediated Differential Signaling. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The Roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in Pathogen Recognition. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.P.B.; Ardern-Jones, M.R.; Kasprowicz, V.; Bowness, P.; Jones, L.; Bailey, A.S.; Ogg, G.S. Human Keratinocyte Induction of Rapid Effector Function in Antigen-Specific Memory CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamoutounour, S.; Han, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Constantinides, M.G.; Hurabielle, C.; Harrison, O.J.; Bouladoux, N.; Linehan, J.L.; Link, V.M.; Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; et al. Keratinocyte-Intrinsic MHCII Expression Controls Microbiota-Induced Th1 Cell Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23643–23652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunimura, K.; Uruno, T.; Fukui, Y. DOCK Family Proteins: Key Players in Immune Surveillance Mechanisms. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, O.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.; Lee-Lin, S.Q.; Huang, X.; Barnabas, B.B.; Bouffard, G.G.; Brooks, S.Y.; Marfani, H.; Dekhtyar, L.; et al. Expanded Skin Virome in DOCK8-Deficient Patients. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Chung, H.; Chang, S.; Lee, S.H.; Seok, S.H.; Lee, H. Effect of Mechanical Stretch on the DNCB-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion in Human Keratinocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Komine, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Okochi, H.; Tamaki, K. Mechanical Stretching in Vitro Regulates Signal Transduction Pathways and Cellular Proliferation in Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, Q.; Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y.M. Differential in Situ Cytokine Gene Expression in Acute versus Chronic Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Implications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 40, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, S.R.V.; Wagenblast, E.; Khan, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Soto, M.; Wagner, M.; Turgeon, M.O.; Fish, L.; Erard, N.; Gable, A.L.; et al. Asparagine Bioavailability Governs Metastasis in a Model of Breast Cancer. Nature 2018, 554, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Krueger, J.G.; Lebwohl, M.G. Systemic Immune Mechanisms in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis with Implications for Treatment. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Gao, P.; Grant, A.V.; Boguniewicz, M.; DeBenedetto, A.; Schneider, L.; Beck, L.A.; Barnes, K.C.; Leung, D.Y.M. Cytokine Modulation of Atopic Dermatitis Filaggrin Skin Expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, M.D.; Fairchild, H.R.; Kim, B.E.; Bin, L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Redzic, J.S.; Hansen, K.C.; Leung, D.Y.M. Th2 Cytokines Act on S100/A11 to Downregulate Keratinocyte Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, P.Y.; Leung, D.Y.M. Immune Dysregulation in Atopic Dermatitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2006, 6, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinckier, F.; Vermylen, J. Blood Loss Following Dental Extractions in Anticoagulated Rabbits: Effects of Tranexamic Acid and Socket Packing. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1985, 59, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Mizoguchi, E.; Oettgen, H.; Bhan, A.K.; Geha, R.S. Roles of T(H)1 and T(H)2 Cytokines in a Murine Model of Allergic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennino, A.; Vocanson, M.; Toussaint, Y.; Rodet, K.; Benetière, J.; Schmitt, A.-M.; Aries, M.-F.; Bérard, F.; Rozières, A.; Nicolas, J.-F. Skin-Infiltrating CD8 + T Cells Initiate Atopic Dermatitis Lesions. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5571–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Martinez, O.; Overbergh, L.; Mathieu, C.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Chan, L.S. Early Up-Regulation of Th2 Cytokines and Late Surge of Th1 Cytokines in an Atopic Dermatitis Model. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 138, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, C.J.; Jayaratnam, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; De Waal Malefyt, R.; Meng, Q.; Kay, A.B.; Phipps, S.; Lee, T.H.; Ying, S. Early Production of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Precedes Infiltration of Dendritic Cells Expressing Its Receptor in Allergen-Induced Late Phase Cutaneous Responses in Atopic Subjects. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 64, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogiatzi, S.I.; Fernandez, I.; Bichet, J.-C.; Marloie-Provost, M.-A.; Volpe, E.; Sastre, X.; Soumelis, V. Cutting Edge: Proinflammatory and Th2 Cytokines Synergize to Induce Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Production by Human Skin Keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3373–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittler, J.K.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gulewicz, K.J.; Wang, C.Q.F.; Mitsui, H.; Cardinale, I.; De Guzman Strong, C.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Progressive Activation of TH2/TH22 Cytokines and Selective Epidermal Proteins Characterizes Acute and Chronic Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, C.; Kabashima, K.; Shiraishi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Tokura, Y. Possible Pathogenic Role of Th17 Cells for Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasraie, S.; Niebuhr, M.; Werfel, T. Interleukin (IL)-31 Induces pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Human Monocytes and Macrophages Following Stimulation with Staphylococcal Exotoxins. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 65, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; Cassidy, S.K.B.; Harrison, O.J.; Ng, W.-I.; Conlan, S.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H.; Program, N.C.S. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidisstrain diversity underlying pediatric atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M. New Insights into Atopic Dermatitis: Role of Skin Barrier and Immune Dysregulation. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.Y.; Ohtake, T.; Brandt, C.; Strickland, I.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ganz, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y.M. Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides and Skin Infections in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippke, F.; Schreiner, V.; Schwanitz, H.-J. The Acidic Milieu of the Horny Layer. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauweiler, A.M.; Goleva, E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Interferon-γ Protects from Staphylococcal Alpha Toxin-Induced Keratinocyte Death through Apolipoprotein L1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Villarreal, M.; Stewart, S.; Choi, J.; Ganguli-Indra, G.; Babineau, D.C.; Philpot, C.; David, G.; Yoshida, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; et al. Altered Composition of Epidermal Lipids Correlates with Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization Status in Atopic Dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, e125–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, M.; Boiten, W.; van Drongelen, V.; Gmelig Meijling, K.; Gooris, G.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.; Kezic, S.; van Smeden, J.; et al. Altered Expression of Epidermal Lipid Bio-Synthesis Enzymes in Atopic Dermatitis Skin Is Accompanied by Changes in Stratum Corneum Lipid Composition. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.J.; Nam, J.J.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, J.W.; Park, C.S. A Synthetic C16 Omega-Hydroxyphytoceramide Improves Skin Barrier Functions from Diversely Perturbed Epidermal Conditions. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.J.; Su, J.C.; Allen, K.J.; Abramson, M.J.; Cranswick, N.; Robertson, C.F.; Forster, D.; Varigos, G.; Hamilton, S.; Kennedy, R.; et al. A Randomized Trial of a Barrier Lipid Replacement Strategy for the Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Sensitization: The PEBBLES Pilot Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, e19–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, T. Atopic Dermatitis: An Expanding Therapeutic Pipeline for a Complex Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarmann-Stemmann, T.; Esser, C.; Krutmann, J. The Janus-Faced Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling in the Skin: Consequences for Prevention and Treatment of Skin Disorders. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.H.; Jayawickreme, C.; Rickard, D.J.; Nicodeme, E.; Bui, T.; Simmons, C.; Coquery, C.M.; Neil, J.; Pryor, W.M.; Mayhew, D.; et al. Tapinarof Is a Natural AhR Agonist That Resolves Skin Inflammation in Mice and Humans. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2110–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Stein Gold, L.; Soung, J.; Tallman, A.M.; Rubenstein, D.S.; Gooderham, M. Efficacy and Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Phase 2b, Randomized Clinical Trial of Tapinarof Cream for the Treatment of Adolescents and Adults with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Parnes, J.R.; She, D.; Crouch, S.; Rees, W.; Mo, M.; van der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab, an Anti–Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Monoclonal Antibody, in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Phase 2a Clinical Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Ponnarambil, S.; Downie, J.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Colice, G. DESTINATION: A Phase 3, Multicentre, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Trial to Evaluate the Long-Term Safety and Tolerability of Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Longhini, F.; Crimi, C.; Calabrese, C.; Gallelli, L.; Sciacqua, A.; Vatrella, A. Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Alarmins: A New Perspective for Biological Therapies of Severe Asthma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Hardman, C.S.; Westmoreland, M.; MacKenzie, T.; Cifuentes, L.; Waithe, D.; Lloyd-Lavery, A.; Marquette, A.; Londei, M.; et al. Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial of Etokimab Shows a Key Role for IL-33 in Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.K.; Jo, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, D.; Smith, B.; Ortines, R.V.; Wang, Y.; Marchitto, M.C.; Ravipati, A.; Cai, S.S.; et al. Injury, Dysbiosis, and Filaggrin Deficiency Drive Skin Inflammation through Keratinocyte IL-1α Release. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1426–1443.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzrock, R.; Hickish, T.; Wyrwicz, L.; Saunders, M.; Wu, Q.; Stecher, M.; Mohanty, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Simard, J. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Levels Predict Favorable Outcome after Bermekimab, a First-in-Class True Human Interleukin-1α Antibody, in a Phase III Randomized Study of Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1551651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Archer, N.K.; Dillen, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Ortines, R.V.; Kao, T.; Lee, S.K.; Cai, S.S.; Miller, R.J.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Epicutaneous Exposure Drives Skin Inflammation via IL-36-Mediated T Cell Responses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 653–666.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelez, H.; Choon, S.E.; Marrakchi, S.; Burden, A.D.; Tsai, T.F.; Morita, A.; Navarini, A.A.; Zheng, M.; Xu, J.; Turki, H.; et al. Trial of Spesolimab for Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zaid, N.A.; Sekar, M.; Bonam, S.R.; Gan, S.H.; Lum, P.T.; Begum, M.Y.; Mat Rani, N.N.I.; Vaijanathappa, J.; Wu, Y.S.; Subramaniyan, V.; et al. Promising Natural Products in New Drug Design, Development, and Therapy for Skin Disorders: An Overview of Scientific Evidence and Understanding Their Mechanism of Action. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 23–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Qu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, P.; et al. Mangiferin Antagonizes TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Reaction and Protects against Dermatitis in a Mice Model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 45, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, R.C.; Shah, B.J.; Jayaraaman, A.M.; Jaiswal, V. Clinical Evaluation of an Indian Polyherbal Topical Formulation in the Management of Eczema. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, G.D.; Ahn, H.J.; Cho, J.J.; Park, Y.S.; Park, C.S. The Inhibitory Effect of Naringenin on Atopic Dermatitis Induced by DNFB in NC/Nga Mice. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagula, R.L.; Wairkar, S. Cellulose Microsponges Based Gel of Naringenin for Atopic Dermatitis: Design, Optimization, in Vitro and in Vivo Investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Asadi, S.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Butcher, A. Quercetin Is More Effective than Cromolyn in Blocking Human Mast Cell Cytokine Release and Inhibits Contact Dermatitis and Photosensitivity in Humans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.K.; Hur, D.Y.; Song, S.B.; Park, Y.; Kim, T.S.; Bang, S.I.; Kim, S.; Song, H.K.; Park, H.; Cho, D.H. Tannic Acid and Quercetin Display a Therapeutic Effect in Atopic Dermatitis via Suppression of Angiogenesis and TARC Expression in Nc/Nga Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, M.-Q.; Hupe, M.; Sun, R.; Man, G.; Mauro, T.M.; Elias, P.M. Topical Apigenin Alleviates Cutaneous Inflammation in Murine Models. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 912028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Chalmers, J.R.; Hanifin, J.M.; Thomas, K.S.; Cork, M.J.; McLean, W.H.I.; Brown, S.J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Williams, H.C. Emollient Enhancement of the Skin Barrier from Birth Offers Effective Atopic Dermatitis Prevention. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horimukai, K.; Morita, K.; Narita, M.; Kondo, M.; Kitazawa, H.; Nozaki, M.; Shigematsu, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Niizeki, H.; Motomura, K.I.; et al. Application of Moisturizer to Neonates Prevents Development of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 824–830.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrett, K.P.; Peters, R.L. Emollients for Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Infancy. Lancet 2020, 395, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjerven, H.O.; Rehbinder, E.M.; Vettukattil, R.; LeBlanc, M.; Granum, B.; Haugen, G.; Hedlin, G.; Landrø, L.; Marsland, B.J.; Rudi, K.; et al. Skin Emollient and Early Complementary Feeding to Prevent Infant Atopic Dermatitis (PreventADALL): A Factorial, Multicentre, Cluster-Randomised Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, P.; Mounika, P.; Yellurkar, M.L.; Prasanna, V.S.; Sarkar, S.; Velayutham, R.; Arumugam, S. Keratinocytes: An Enigmatic Factor in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells 2022, 11, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101683
Das P, Mounika P, Yellurkar ML, Prasanna VS, Sarkar S, Velayutham R, Arumugam S. Keratinocytes: An Enigmatic Factor in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells. 2022; 11(10):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101683
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Pamelika, Pappula Mounika, Manoj Limbraj Yellurkar, Vani Sai Prasanna, Sulogna Sarkar, Ravichandiran Velayutham, and Somasundaram Arumugam. 2022. "Keratinocytes: An Enigmatic Factor in Atopic Dermatitis" Cells 11, no. 10: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101683
APA StyleDas, P., Mounika, P., Yellurkar, M. L., Prasanna, V. S., Sarkar, S., Velayutham, R., & Arumugam, S. (2022). Keratinocytes: An Enigmatic Factor in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells, 11(10), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101683





