The Anti-Tumor and Bortezomib-Sensitizing Effects of Apigenin in Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
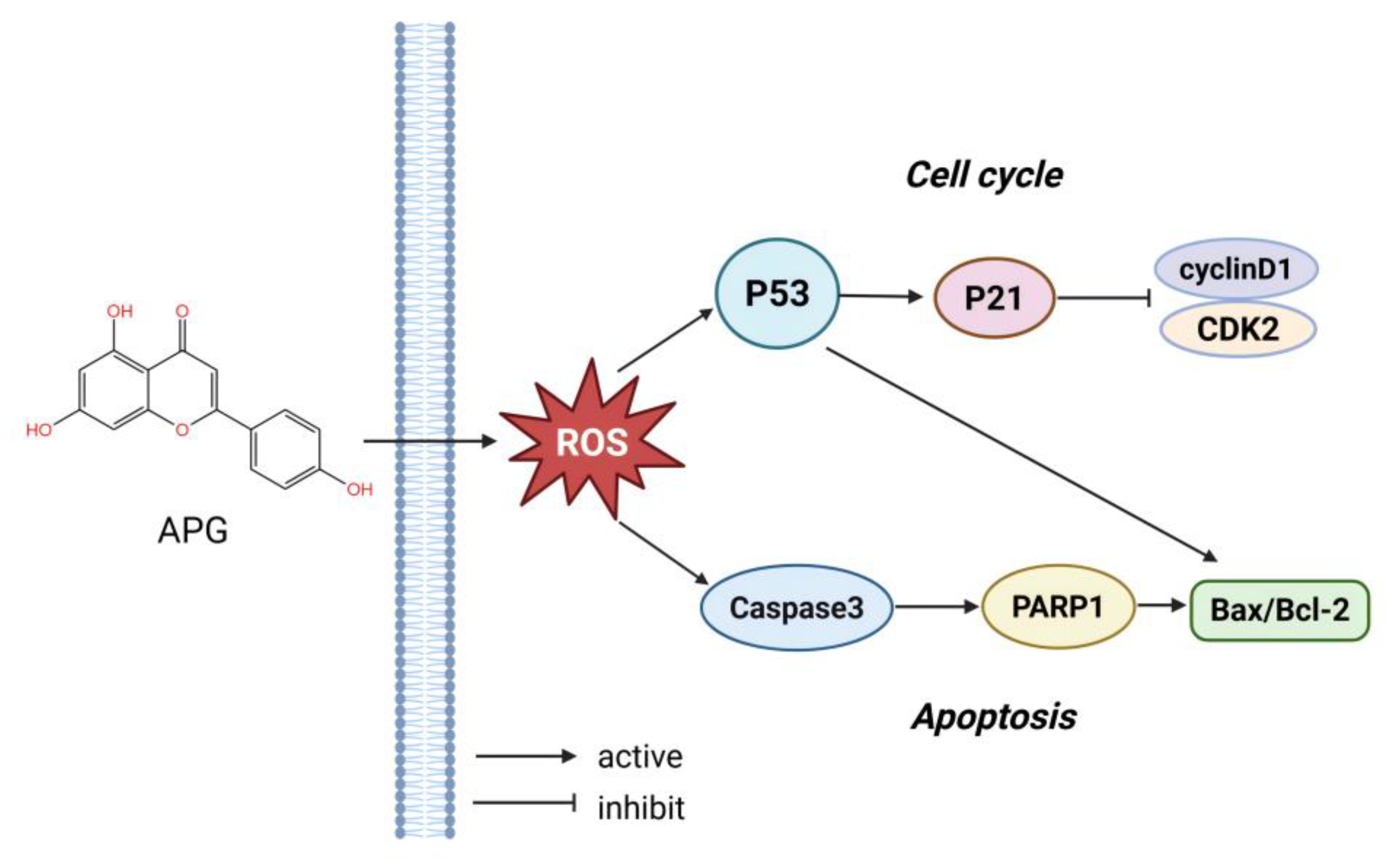
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
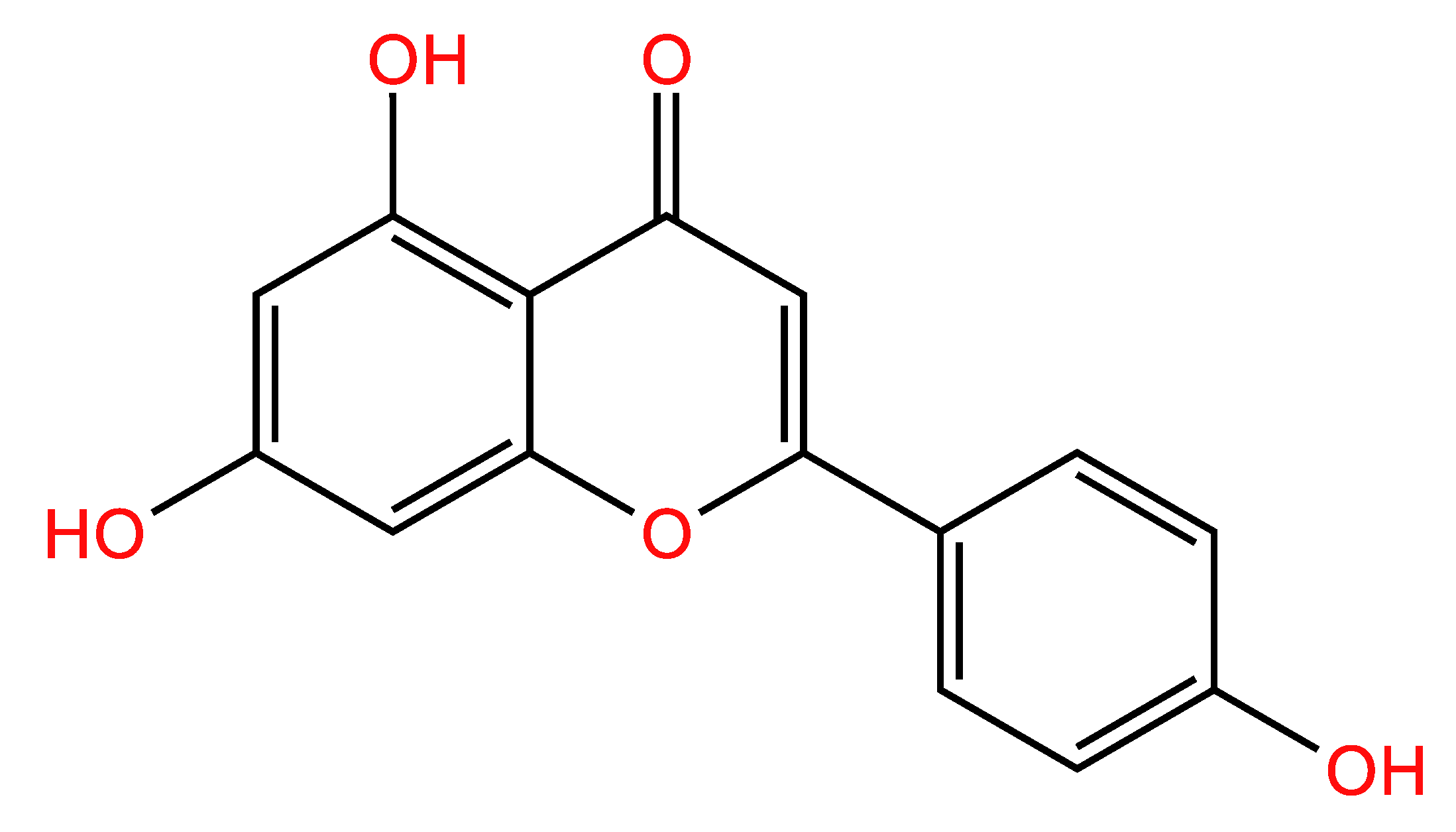
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. CCK-8 Assay
2.4. Crystal Violet Staining
2.5. Flow Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Flow Cytometer Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.7. Determination of Apoptosis
2.8. Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.9. Total RNA Preparation and RT-qPCR
2.10. Determination of Oxidative Stress-Related Indicators
3. Results
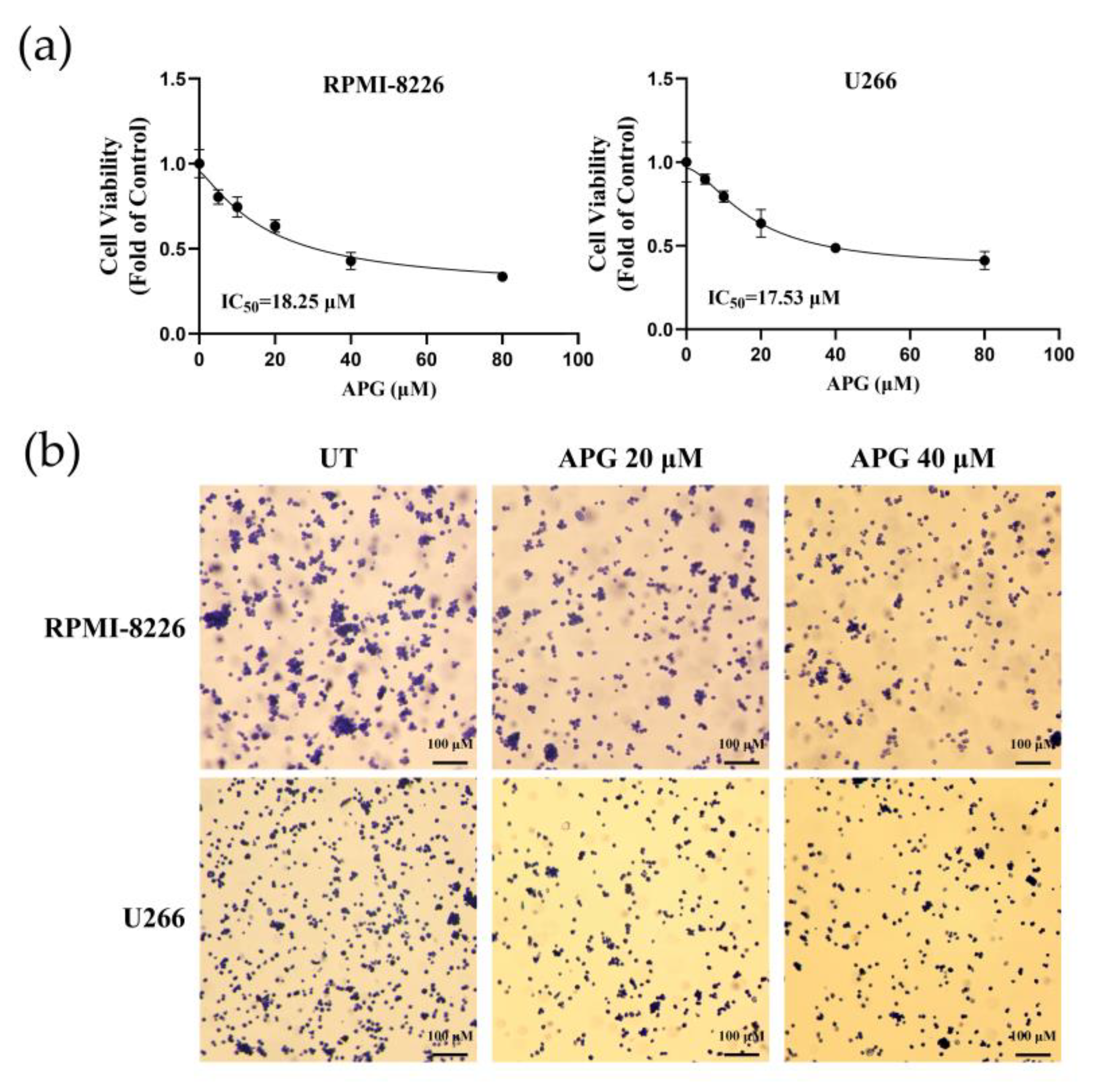
3.1. APG Inhibits MM Cell Growth
3.2. APG Induces G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest of MM Cells
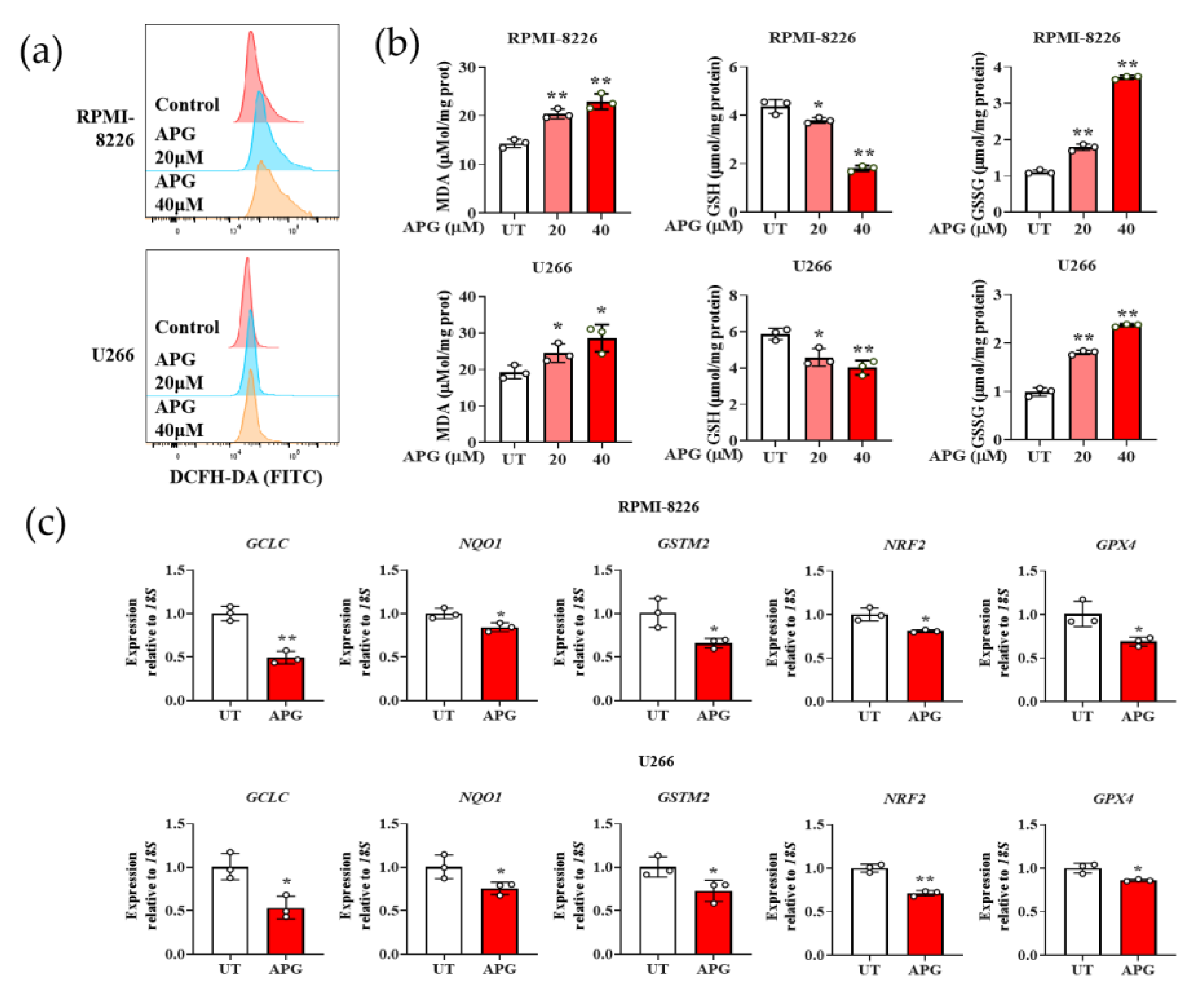
3.3. APG Induces Oxidative Stress in MM Cells
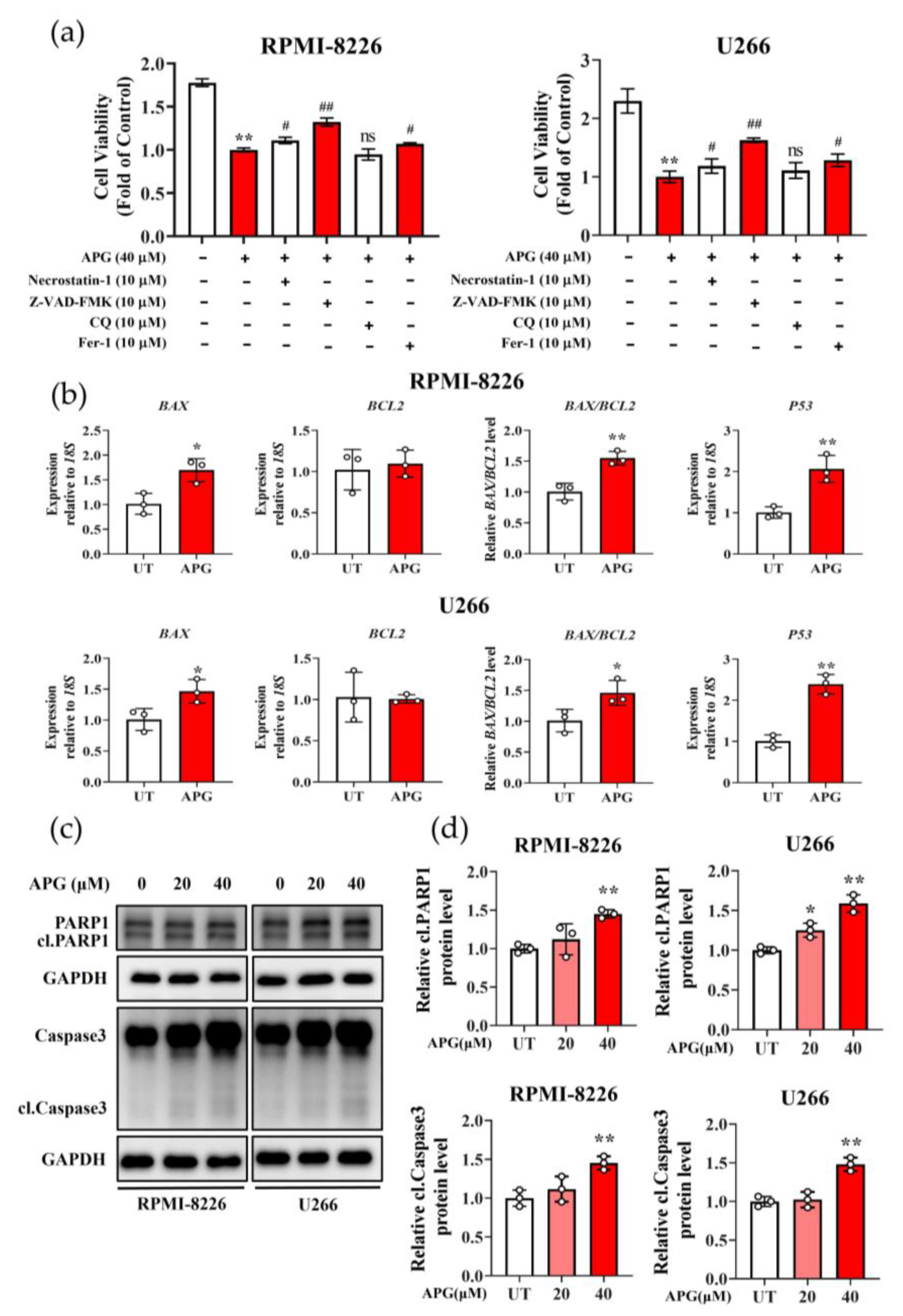
3.4. APG Promotes Apoptosis in MM Cells
3.5. APG Potentiates the Anti-Tumor Effects of Bortezomib (BTZ)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIF | Apoptosis-inducing factor |
| APG | Apigenin |
| BAX | BCL2-associated X |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BTZ | Bortezomib |
| CAK | Cdk-activating kinase |
| Caspase 3 | Cysteine protease 3 |
| CCK-8 | Cellcountingkit-8 |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
| CDKs | Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| CQ | Chloroquine |
| CyclinD1 | G1/S-Specific Cyclin-D1 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| GCLC | Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Catalytic Subunit |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GSSG | Glutathione Disulfide |
| GSTM2 | Glutathione S-Transferase Mu 2 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 |
| NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| P21 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| P53 | Tumor Protein p53 |
| PARP1 | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 |
| PCD | Programmed cell death |
| PI | Proteasome inhibitor |
| RNA18SN5 | RNA, 18S ribosomal N5 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| WB | Western blot |
References
- Palumbo, A.; Anderson, K. Multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgren, O. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and smoldering multiple myeloma: Biological insights and early treatment strategies. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2013, 2013, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, A.; Seow, H.; Pond, G.P.; Gayowsky, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Visram, A.; Kaedbey, R.; D’Souza, A.; Mohyuddin, G.R.; Wildes, T.M.; et al. Cancer-specific mortality in multiple myeloma: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Haematologica 2023, 108, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plakoula, E.; Kalampounias, G.; Alexis, S.; Verigou, E.; Kourakli, A.; Zafeiropoulou, K.; Symeonidis, A. Prognostic value of psmb5 and correlations with lc3ii and reactive oxygen species levels in the bone marrow mononuclear cells of bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma patients. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerini-Molteni, S.; Ferrarini, M.; Cozza, S.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Sitia, R. Redox homeostasis modulates the sensitivity of myeloma cells to bortezomib. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Bayir, H.; Belousov, V.; Chang, C.J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Davies, M.J.; Dick, T.P.; Finkel, T.; Forman, H.J.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.; et al. Guidelines for measuring reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in cells and in vivo. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Plou, F.J.; Perez-Lebena, E. The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ros) revisited: Outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, J.; Samali, A.; Orrenius, S. Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Kaviani, E.; Vakili, O.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Tahamtan, M.; Savardashtaki, A. Caspase-3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, M.; Onishi, M.; Uno, A.; Tanimichi, A.; Nobeyama, A.; Mori, M.; Yamada, S.; Negi, S.; Bu, X.; Kato, J.; et al. The 89-kda parp1 cleavage fragment serves as a cytoplasmic par carrier to induce aif-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ueta, E.; Kimura, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Osaki, T. Reactive oxygen species (ros) control the expression of bcl-2 family proteins by regulating their phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioni, D.; Garavello, W.; Rigolio, R.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, R.; Nicolini, G. Apigenin impairs oral squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Woo, J.K.; Jang, B.H.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.G. Induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis by apigenin by inhibiting stat3 signaling in her2-overexpressing mda-mb-453 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2869–2882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Xie, L. Apigenin promotes apoptosis, inhibits invasion and induces cell cycle arrest of t24 human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Giuliano, A.E.; Law, R.E.; Van Herle, A.J. Apigenin inhibits growth and induces g2/m arrest by modulating cyclin-cdk regulators and erk map kinase activation in breast carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M.; Negri, E.; Lagiou, P.; Talamini, R.; Maso, L.D.; Montella, M.; Franceschi, S.; La Vecchia, C. Flavonoids and ovarian cancer risk: A case-control study in Italy. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Heideman, L.; Chung, C.S.; Pelling, J.C.; Koehler, K.J.; Birt, D.F. Cell-cycle arrest at g2/m and growth inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol. Carcinog. 2000, 28, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pi, C.; Wang, G. Inhibition of pi3k/akt/mtor pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, Z.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Apigenin inhibits migration and invasion via modulation of epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, S.; Rossi, C.; Poggi, A.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Natali, P.G.; Brunetti, M.; Aiello, F.B.; Piantelli, M. Flavonoids apigenin and quercetin inhibit melanoma growth and metastatic potential. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 87, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.J.; Smith, M.R.; Nastoupil, L.J. Follicular lymphoma: The long and winding road leading to your cure? Blood Rev. 2023, 57, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Donk, N.; Pawlyn, C.; Yong, K.L. Multiple myeloma. Lancet 2021, 397, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Chen, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Mu, C. Cell-based therapeutics for the treatment of hematologic diseases inside the bone marrow. J. Control Release 2021, 339, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendowski, M. Pu-h71: An improvement on nature’s solutions to oncogenic hsp90 addiction. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Xue, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, F. Resveratrol sensitizes carfilzomib-induced apoptosis via promoting oxidative stress in multiple myeloma cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketkaew, Y.; Osathanon, T.; Pavasant, P.; Sooampon, S. Apigenin inhibited hypoxia induced stem cell marker expression in a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 74, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, T.K.; Sang, N.; Giordano, A. Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and cdk inhibitors: Implications in cell cycle control and cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1995, 5, 127–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, C.; Huijuan, W.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Q. Apigenin, a flavonoid constituent derived from p. Villosa, inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by cyclind1/cdk4 regulation via p38 mapk-p21 signaling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, A.; Ahmadi, Y.; Yousefi, B. Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair 2016, 42, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, M.; Banik, N.L.; Ray, S.K. Sequential htert knockdown and apigenin treatment inhibited invasion and proliferation and induced apoptosis in human malignant neuroblastoma sk-n-dz and sk-n-be2 cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 51, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.W.; Chiang, L.C.; Lin, C.C. Apigenin induced apoptosis through p53-dependent pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. P53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ji, P.; Liu, B.; Qiao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Deng, T.; Ba, Y. Apigenin enhances the cisplatin cytotoxic effect through p53-modulated apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.; Montenarh, M.; Wagner, P. Regulation of cak kinase activity by p53. Oncogene 1998, 17, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Rehmannioside a improves cognitive impairment and alleviates ferroptosis via activating pi3k/akt/nrf2 and slc7a11/gpx4 signaling pathway after ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 289, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Garg, V.K.; Goel, N. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis: Role in cancer development and prognosis. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 125, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.O.; Van Houten, B.; Durrant, J.D. Parp1: Structural insights and pharmacological targets for inhibition. DNA Repair 2021, 103, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldani, C.; Scovassi, A.I. Poly(adp-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update. Apoptosis 2002, 7, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldani, C.; Lazze, M.C.; Bottone, M.G.; Tognon, G.; Biggiogera, M.; Pellicciari, C.E.; Scovassi, A.I. Poly(adp-ribose) polymerase cleavage during apoptosis: When and where? Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 269, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Yao, X.C.; Liu, W.L.; Kang, F.H.; Zou, Z.X.; Xu, K.P.; Xu, P.S.; Tan, G.S. Identification of a new natural biflavonoids against breast cancer cells induced ferroptosis via the mitochondrial pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Guan, H.; Yu, H.; Sun, Z. Apigenin induces autophagic cell death in human papillary thyroid carcinoma bcpap cells. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3464–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Lattuada, D.; Morsanuto, V.; Nava, U.; Bolis, G.; Vacca, G.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Cisari, C.; Molinari, C. Vitamin d protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress through the autophagic and survival pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Accession Number | Amplicon Size | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCL2 | NM_000657 | 89 | Forward: GGTGGGGTCATGTGTGTGG Reverse: CGGTTCAGGTACTCAGTCATCC |
| BAX | NM_138763 | 155 | Forward: CCCGAGAGGTCTTTTTCCGAG Reverse: CCAGCCCATGATGGTTCTGAT |
| P53 | NM_001126118 | 125 | Forward: CAGCACATGACGGAGGTTGT Reverse: TCATCCAAATACTCCACACGC |
| GCLC | NM_001197115 | 79 | Forward: GGAGGAAACCAAGCGCCAT Reverse: CTTGACGGCGTGGTAGATGT |
| NQO1 | NM_001025433 | 196 | Forward: GAAGAGCACTGATCGTACTGGC Reverse: GGATACTGAAAGTTCGCAGGG |
| GSTM2 | NM_000848 | 99 | Forward: TGTGCGGGGAATCAGAAAAGG Reverse: CTGGGTCATAGCAGAGTTTGG |
| NRF2 | NM_001145412 | 174 | Forward: TCAGCGACGGAAAGAGTATGA Reverse: CCACTGGTTTCTGACTGGATGT |
| GPX4 | NM_001039847 | 100 | Forward: GAGGCAAGACCGAAGTAAACTAC Reverse: CCGAACTGGTTACACGGGAA |
| RNA18SN5 | NR_003286 | 158 | Forward: ACCCGTTGAACCCCATTCGTGA Reverse: GCCICACAAACCACCAATCGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; Ding, B. The Anti-Tumor and Bortezomib-Sensitizing Effects of Apigenin in Multiple Myeloma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090717
Chen Y, Wu L, Wang S, Chen H, Chen M, Huang Y, Ding B. The Anti-Tumor and Bortezomib-Sensitizing Effects of Apigenin in Multiple Myeloma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090717
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ye, Lan Wu, Siyu Wang, Huihao Chen, Miaojun Chen, Yanfen Huang, and Bin Ding. 2025. "The Anti-Tumor and Bortezomib-Sensitizing Effects of Apigenin in Multiple Myeloma" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090717
APA StyleChen, Y., Wu, L., Wang, S., Chen, H., Chen, M., Huang, Y., & Ding, B. (2025). The Anti-Tumor and Bortezomib-Sensitizing Effects of Apigenin in Multiple Myeloma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090717





