New Perspectives on the Use of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic and Estrogen-Dependent Conditions Through Hormonal Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
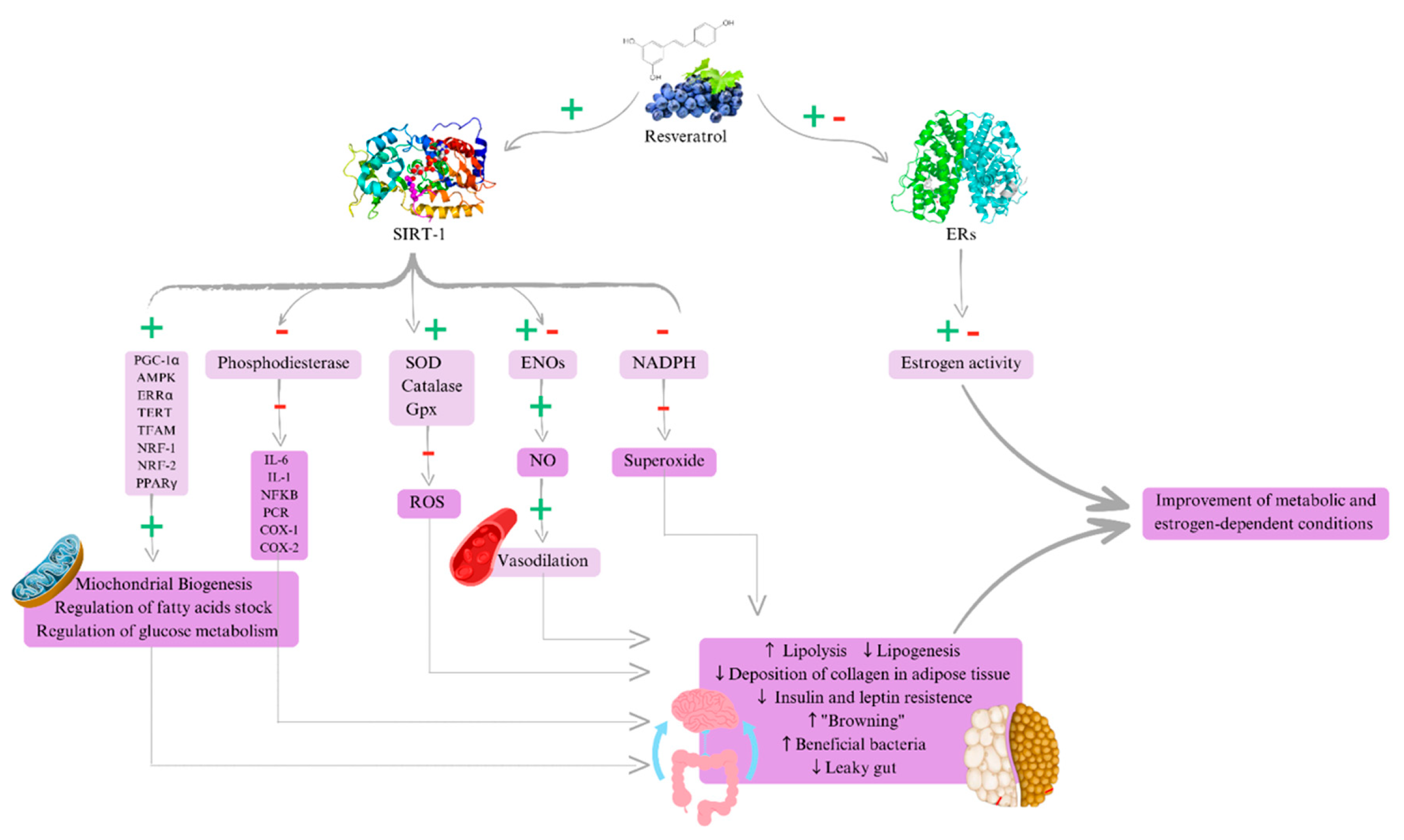
3.1. Metabolic and Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Resveratrol
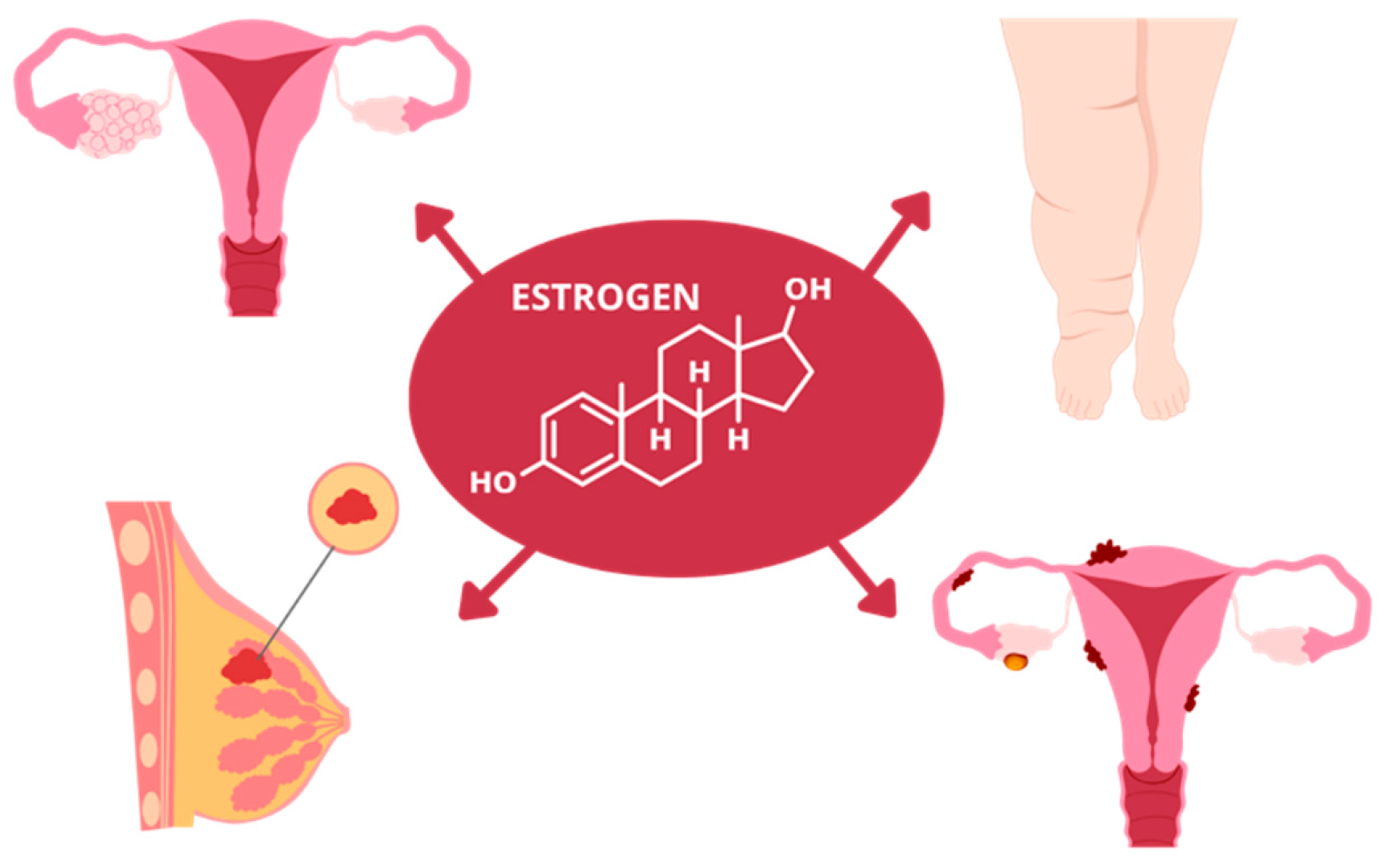
3.2. Future Perspectives of Resveratrol in Estrogen-Dependent Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petraglia, F.; Musacchio, C. Hormone-dependent gynaecological disorders: A pathophysiological perspective for appropriate treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 22, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Palasuberniam, P.; Pare, R. The Role of Estrogen across Multiple Disease Mechanisms. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8170–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rannestad, T.; Eikeland, O.J. Quality of life, pain, and psychological well-being in women suffering from gynecological disorders. J. Women’s Health Gend. Based Med. 2000, 9, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Ji, W.; Yan, M.; Zou, X.; Chen, T.; Bai, F.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Song, L. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes in women of childbearing age, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021. Front. Glob. Womens Health 2025, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martínez-Hervás, S.; Ascaso, J.F. The metabolic syndrome: Current situation and future perspective. Rev. Clínica Española (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 221, 480–488. [Google Scholar]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Estrogen and androgen receptors: Regulators of fuel homeostasis and emerging targets for diabetes and obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, L.; Ma, F.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Contributions of common foods to resveratrol intake in the Chinese diet. Foods 2024, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.P.A.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptors and the metabolic network. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhon, D.D.; Min, L. Effects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol on Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9932218. [Google Scholar]
- Thaung, Z.; Howe, P. Long-term resveratrol supplementation improves pain perception, menopausal symptoms, and overall well-being in postmenopausal women: Findings from a 24-month randomized, controlled, crossover trial. Menopause 2020, 28, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Berenguer, T.; Jakszyn, P.; Martínez, C.; Sánchez, M.J.; Navarro, C.; Chirlaque, M.D.; Tormo, M.J.; et al. Concentrations of resveratrol and derivatives in foods and estimation of dietary intake in a Spanish population: European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Spain cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koç, T.Y.; Doğan, S.; Karadayı, M. Potential Using of Resveratrol and Its Derivatives in Medicine. Eurasian J. Med. 2024, 56, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.S.; Thomas, R.G. Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of resveratrol for Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylka, P.; Kucinska, M. Resveratrol Analogues as Selective Estrogen Signaling Pathway Modulators: Structure–Activity Relationship. Molecules 2022, 27, 6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Hayes, A.W. Resveratrol and endoplasmic reticulum stress: A review of the potential protective mechanisms of the polyphenol. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 5564–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Fadlalmola, H.; Elhusein, A.M. Efficacy of resveratrol in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2023, 44, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei-Zarghani, S.; Rafraf, M. Resveratrol and Markers of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Animal and Clinical Studies. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Geng, J. Effects of Resveratrol on Metabolic Indicators in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9734738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Tang, Z. Resveratrol against Cardiac Fibrosis: Research Progress in Experimental Animal Models. Molecules 2021, 26, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Balakrishnan, A. Micelle/Hydrogel Composite as a “Natural Self-Emulsifying Reversible Hybrid Hydrogel (N’SERH)” Enhances the Oral Bioavailability of Free (Unconjugated) Resveratrol. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12835–12845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.Y.; Elguindy, N.M.; Saleh, A.M.; Balbaa, M. Biochemical and molecular evaluation of resveratrol and selenium nanoparticles in managing type 2 diabetes and its complications. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Mattson, M.P.; Calabrese, V. Resveratrol commonly displays hormesis: Occurrence and biomedical significance. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 980–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liao, W.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Theofanous, D.; Britton, R.G.; Aburido, G.; Pepper, C.; Sri Undru, S.; Howells, L. Resveratrol for the Management of Human Health: How Far Have We Come? A Systematic Review of Resveratrol Clinical Trials to Highlight Gaps and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaung Zaw, J.J.; Howe, P.R.; Wong, R.H. Long-term effects of resveratrol on cognition, cerebrovascular function and cardio-metabolic markers in postmenopausal women: A 24-month randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaito, A.; Posadino, A.M.; Younes, N.; Hasan, H.; Halabi, S.; Alhababi, D.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Eid, A.H.; Nasrallah, G.K.; et al. Potential Adverse Effects of Resveratrol: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, J.L.; Tyulmenkov, V.V.; Jernigan, S.C.; Klinge, C.M. Resveratrol Acts as a Mixed Agonist/Antagonist for Estrogen Receptors α and β. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3657–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, I.G.; Rushing, B.R. Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Acylcarnitines as Major Metabolic Targets of Resveratrol in Breast Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2025, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, F.; Guan, M.; Wu, X. Effect and mechanism of resveratrol against polycystic ovary syndrome: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1529231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, F.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Crespo, T.S.; Amaro, L.B.R.; Rocha, E.F.; Fereira, A.C.; Lelis, D.d.F.; Baldo, T.d.O.F.; Baldo, M.P.; Santos, S.H.S. Oral supplementation with resveratrol improves hormonal profile and increases expression of genes associated with thermogenesis in oophorectomy mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 591, 112268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorabi, A.M.; Aslani, S. Effect of resveratrol on C-reactive protein: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6754–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Nikpayam, O. A comprehensive insight into the potential effects of resveratrol supplementation on SIRT-1: A systematic review. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaito, A.; Al-Mansoob, M.; Ahmad, S.M.; Haider, M.Z.; Eid, A.H.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Giordo, R. Resveratrol-Mediated Regulation of Mitochondria Biogenesis-associated Pathways in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Molecular Insights and Potential Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpino, F.M.; Figueiredo, L.M. Resveratrol supplementation and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4465–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, A.D.; Malcangi, G. Benefits and Implications of Resveratrol Supplementation on Microbiota Modulations: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoca, M.; Becer, E. The role of resveratrol in diabetes and obesity associated with insulin resistance. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J. The role of metformin and resveratrol in the prevention of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α accumulation and fibrosis in hypoxic adipose tissue. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xiao, X. Deciphering the Anti-obesity Benefits of Resveratrol: The “Gut Microbiota-Adipose Tissue” Axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpino, F.M.; Figueiredo, L.M. What is the effect of resveratrol on obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 41, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. The Effect of Resveratrol Supplementation on Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, F.; Eftekhari, M.H. Effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Berberis integerrima and resveratrol extract on ovarian morphology and biochemical parameters in Letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome rat model: An experimental study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2020, 18, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Jorge, G.C.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S. Oral resveratrol supplementation improves Metabolic Syndrome features in obese patients submitted to a lifestyle-changing program. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenjian, S.; Moini, A. Resveratrol treatment in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome decreased pro-inflammatory and endoplasmic reticulum stress markers. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2020, 83, e13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ligt, M.; Bergman, M. No effect of resveratrol supplementation after 6 months on insulin sensitivity in overweight adults: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Lv, Y. Biological investigations on therapeutic effect of chitosan encapsulated nano resveratrol against gestational diabetes mellitus rats induced by streptozotocin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, A.; Namazi, G. The effects of resveratrol on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.O.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S. Effect of resveratrol on expression of genes involved thermogenesis in mice and humans. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjabeen, W.; Khan, D.A. Role of resveratrol supplementation in regulation of glucose hemostasis, inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2022, 66, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarinezhad, A.; Roozbeh, J. Resveratrol reduces albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Resveratrol reduces liver endoplasmic reticulum stress and improves insulin sensitivity in vivo and in vitro. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, T. Suppression of p66Shc prevents hyperandrogenism-induced ovarian oxidative stress and fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, J. Resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice via modulating the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Khan, D.A. δ-Tocotrienol in Combination with Resveratrol Improves the Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Biomarkers in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2023, 21, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, D.; Elshopakey, G.E. Effects of Resveratrol Against Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats: Role of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 3362005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, M.S.; Cacciapuoti, N. Hypothalamic-Ovarian axis and Adiposity Relationship in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Physiopathology and Therapeutic Options for the Management of Metabolic and Inflammatory Aspects. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.W.; Zhang, R. Pharmaceuticals targeting signaling pathways of endometriosis as potential new medical treatment: A review. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2489–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulun, S.E.; Yildiz, S.; Adli, M.; Chakravarti, D.; Parker, J.B.; Milad, M.; Yang, L.; Chaudhari, A.; Tsai, S.; Wei, J.J. Endometriosis and adenomyosis, shared pathophysiology. Fertil. Steril. 2023, 119, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Malentacchi, F. Epigenetics of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors in Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzer, K.; Hill, J.L. Lipedema and the Potential Role of Estrogen in Excessive Adipose Tissue Accumulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dull, A.M.; Moga, M.A. Therapeutic Approaches of Resveratrol on Endometriosis via Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Angiogenic Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, L.; Surico, D.; Deambrogio, F.; Scatuzzi, A.; Marzullo, P.; Tinelli, R.; Molinari, C.; Surico, N. Preliminary data on the effectiveness of resveratrol in a new formulation in treatment of hot flushes. Minerva Ginecol. 2015, 67, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Thaung, Z. Regular Supplementation With Resveratrol Improves Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Song, M. Does resveratrol improve cognition in humans? A scientometric study to an in-depth review. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 2413–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
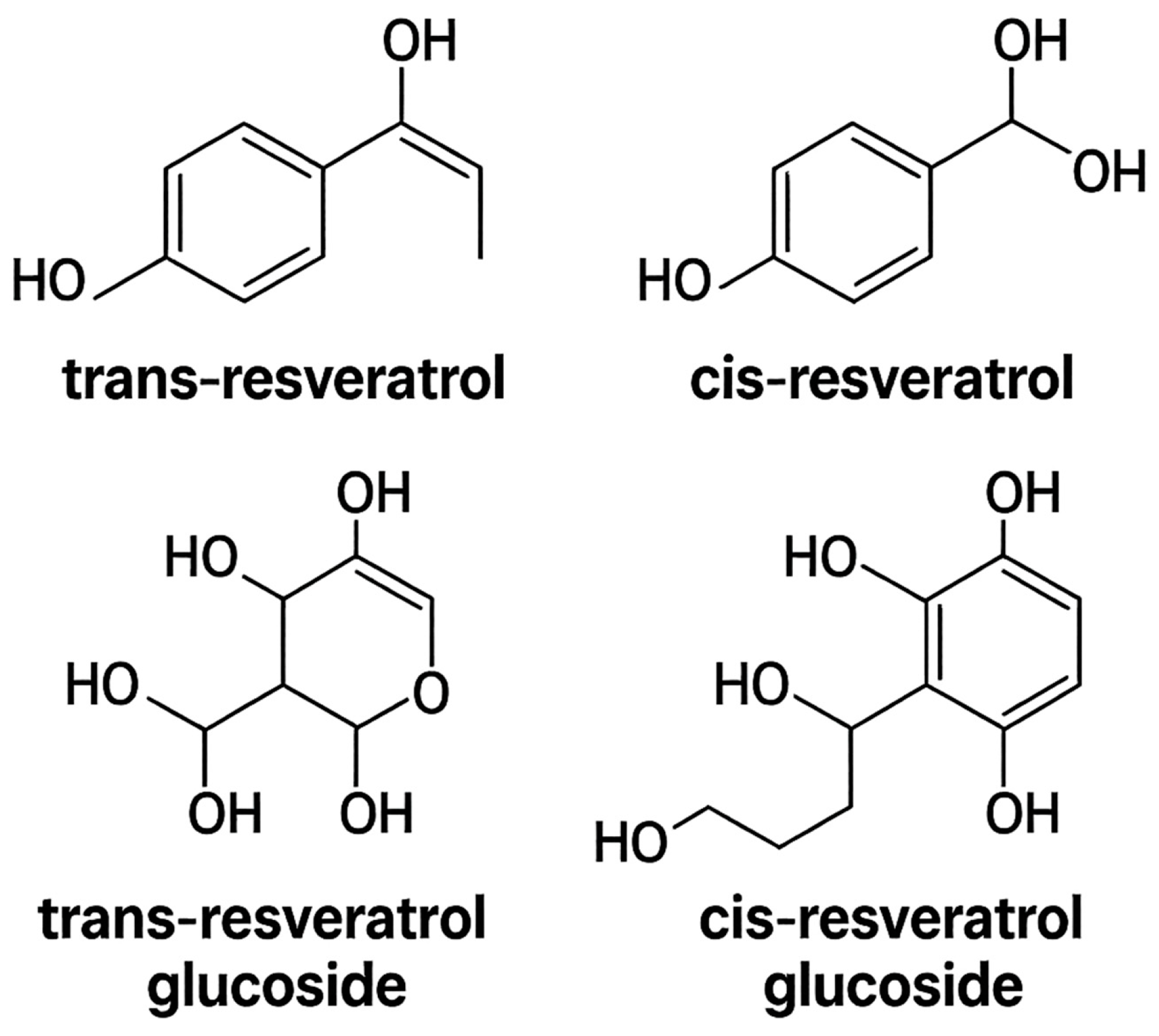
| Source | Total Resveratrol (µg/100 g or µg/L) | Predominant Form(s) | [Reference] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red grape | 50–1000 | Trans + Piceides | [7,10] |
| Red wine | 1980–7130 µg/L | Trans | [7] |
| Raw peanut | 74 | Trans + Cis | [7] |
| Germinated peanut | 1170–2570 | Trans | [7] |
| Blueberry | 50–100 | Trans | [7] |
| Peach | 461.6 | Aglycone | [7] |
| Apple | 67 | Cis + Trans | [7] |
| Pear | 34.43 | Cis + Trans | [7] |
| Grapefruit | 82 | Cis + Trans | [7] |
| Reference | Sample | Duration | Study Design | Resveratrol Doses | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdollahi et al., 2019 [40] | 71 overweight individuals with T2DM | 8 weeks | Randomized double blind | T-RSV 1 g daily or placebo | Significative reduction in fasting blood glucose in the group that ingested T-RSV |
| Ashkar et al., 2020 [41] | 10 Sprague–Dawley rats | 21 days | Preclinical | Oral administration of 20 mg/kg/day resveratrol after PCOS induction | Improvement of lipid profile, insulin resistance, MDA, and TNF-α Increase in SOD Reduction in cystic follicles and ovarian weight |
| Batista-Jorge et al., 2020 [42] | 25 obese patients with metabolic syndrome | 12 weeks | Randomized trial | 250 mg RSV or placebo capsule daily in combination with a physical activity program + diet for 3 months | RSV improved TC, HDL, VLDL, urea, creatinine, and albumin vs. placebo. Anthropometric parameters were significantly different after 3 months of physical activity for both placebo and RSV |
| Brenjian et al., 2020 [43] | Cumulus cells obtained from 40 patients with PCOS | 40 days | Clinical | T-RSV 800 mg/kg/day orally | Alterations in serum Decrease in IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB |
| De Ligt et al., 2020 [44] | 41 overweight individuals | 24 weeks | Randomized double blind | T-RSV 150 mg daily or placebo | There was no improvement in insulin sensitivity, but there was a significant reduction in Hb1Ac in the group that ingested RSV |
| Du et al., 2020 [45] | 18 male mice | 28 days | Preclinical | Chitosan-encapsulate RSV 100 mg/kg/day orally | Decrease in blood glucose Decrease in TC, TG, LDL Increase in HDL Decrease in IL-6, MCP-1 Increase in SOD and GSH activity |
| Gorabi et al., 2021 [31] | 1741 individuals | 10 weeks | Meta-analysis of 35 RCTs | Average RSV and T-RSV ≥500 mg daily | Significant reduction in CRP in inflammatory conditions |
| Hoseini et al., 2019 [46] | 56 individuals with T2DM and cardiovascular disease | 4 weeks | Randomized double blind | 500 mg daily or placebo | Significant effect on glycemic control in the intervention group |
| Andrade et al., 2019 [47] | 32 male mice | 8 weeks | Randomized clinical trial | T-RSV 500 mg daily | Increase gene expression of SIRT1 Increase in UCP-1 expression Increase in adiponectin levels Decrease in TC and TG levels |
| Mahjabeen et al., 2019 [48] | 110 subjects with T2DM | 24 weeks | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel-group trial | T-RSV 200 mg/day | Significant decrease in glucose and Hb1Ac Significant decrease in insulin and HOMA-IR |
| Sattarinezhad et al., 2019 [49] | 60 individuals with T2DM and albuminuria | 12 weeks | Randomized double blind | T-RSV 500 mg daily + losartan or placebo +losartan | Significant reduction in diabetes parameters like fasting blood glucose and insulin resistance |
| Thaung et al., 2021 [25] | 125 postmenopausal women | 24 months | Randomized double blind | 75 mg daily or placebo | Improvement in insulin resistance in the group that ingested RSV |
| Zhao et al., 2019 [50] | 30 male mice, 6 weeks old | 12 weeks | Preclinical | 60 mg/kg/day i.g. | Decrease in blood glucose Increase in insulin sensitivity Decrease in serum TC and hepatic TG |
| Wang et al., 2020 [51] | 21 Sprague–Dawley mice, 3 weeks old | 35 days | Preclinical | Daily injection of 100 mg/kg resveratrol during the PCOS induction | Reduction in body weight, ovarian interstitial fibrosis, and serum and ovarian levels of MDA Increase in ovarian weight, numbers of luteal cells and antral follicles, and serum and ovarian levels of SOD Enhancement of SIRT1 protein expression No effect on androgen receptor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renke, G.; Fuschini, A.C.; Clivati, B.; Teixeira, L.M.; Cuyabano, M.L.; Erel, C.T.; Rosado, E.L. New Perspectives on the Use of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic and Estrogen-Dependent Conditions Through Hormonal Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090692
Renke G, Fuschini AC, Clivati B, Teixeira LM, Cuyabano ML, Erel CT, Rosado EL. New Perspectives on the Use of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic and Estrogen-Dependent Conditions Through Hormonal Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090692
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenke, Guilherme, Ana Carolina Fuschini, Beatriz Clivati, Laura Mocellin Teixeira, Maria Luisa Cuyabano, C. Tamer Erel, and Eliane Lopes Rosado. 2025. "New Perspectives on the Use of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic and Estrogen-Dependent Conditions Through Hormonal Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090692
APA StyleRenke, G., Fuschini, A. C., Clivati, B., Teixeira, L. M., Cuyabano, M. L., Erel, C. T., & Rosado, E. L. (2025). New Perspectives on the Use of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic and Estrogen-Dependent Conditions Through Hormonal Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090692








