Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Shed Light on the Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in a Novel Albino Tea (Camellia sinensis) Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
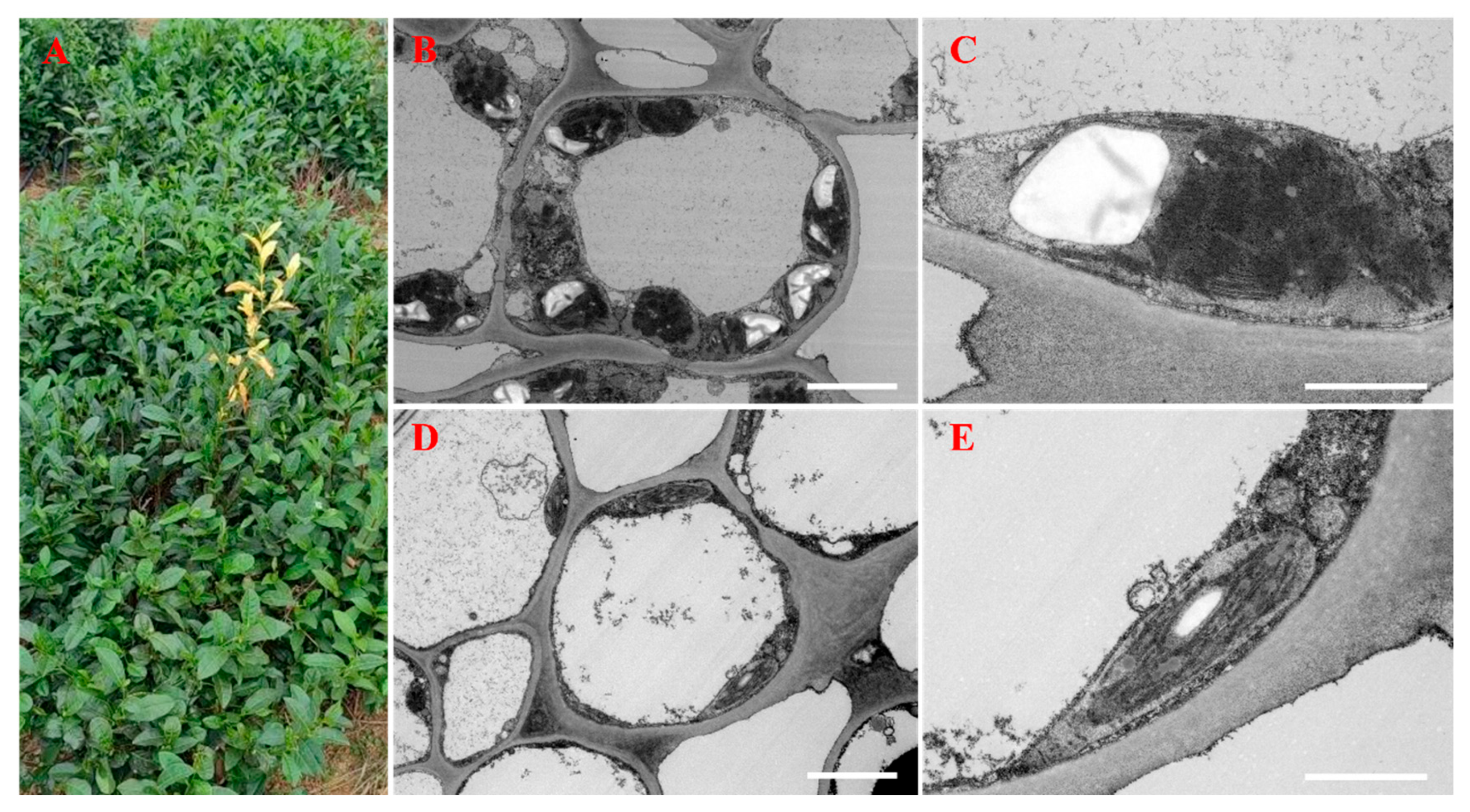
2.2. Ultrastructural Observations of Normal and Albino Leaves
2.3. Widely Targeted Metabolite Analysis
2.4. Illumina Transcriptome Sequencing and DEG Identification
2.5. ONT Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis of Alternative Splicing and lncRNAs
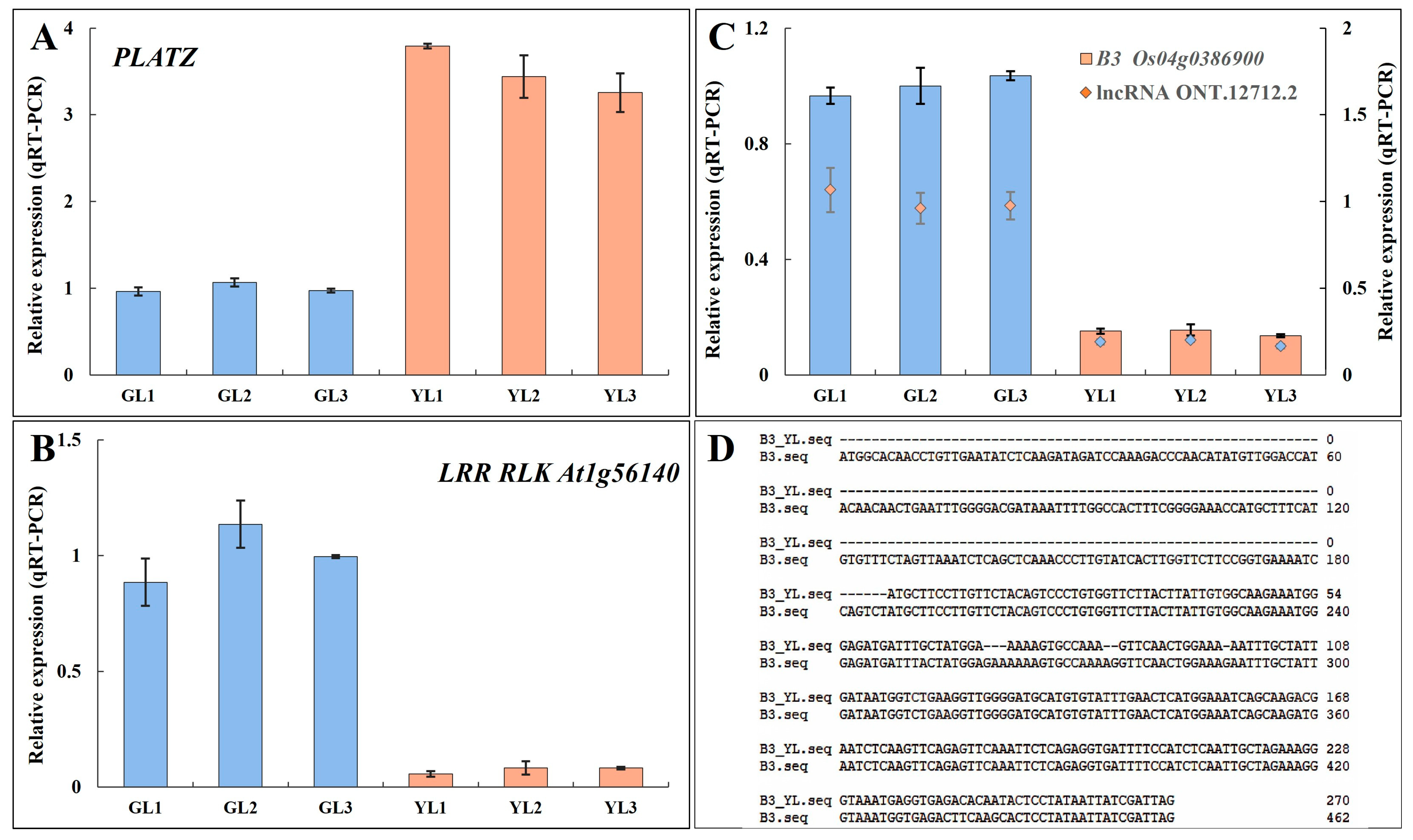
2.6. qRT–PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ultrastructural Characteristics of Normal and Albino Leaves
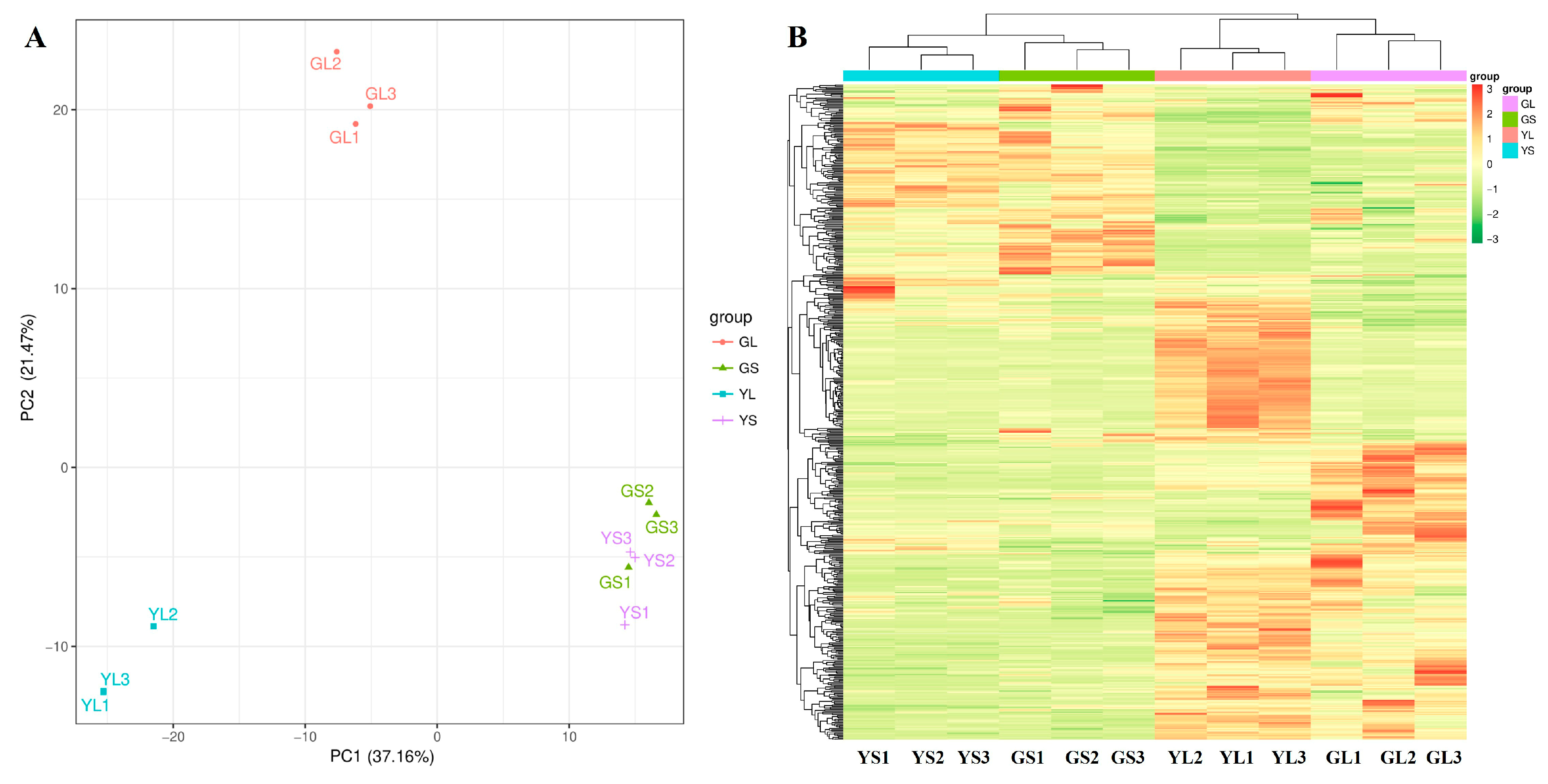
3.2. Differentially Abundant Metabolites in Normal and Albino Leaves and Stems
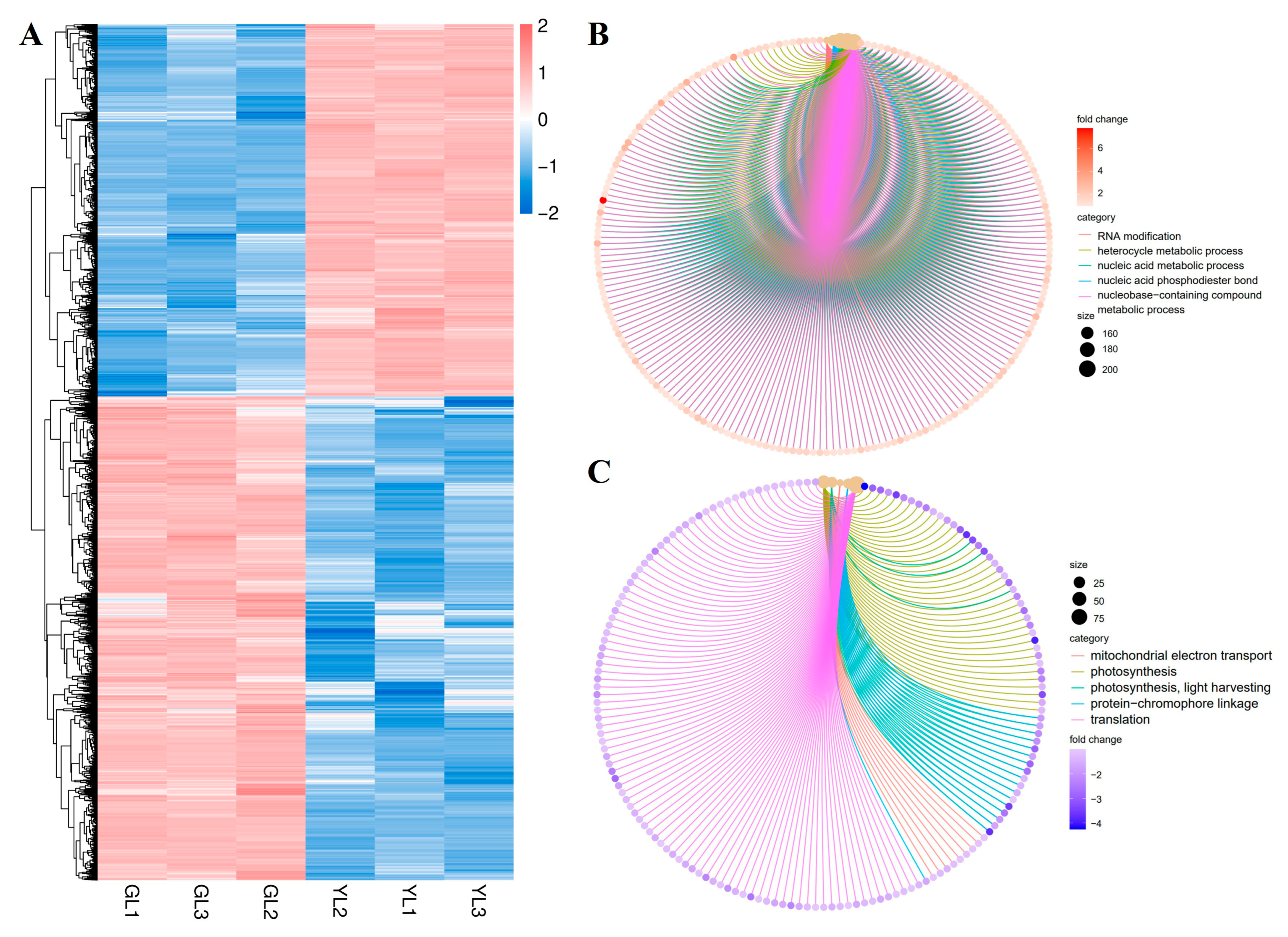
3.3. RNA Sequencing, Reference Genome Alignment, and GO Analysis of DEGs
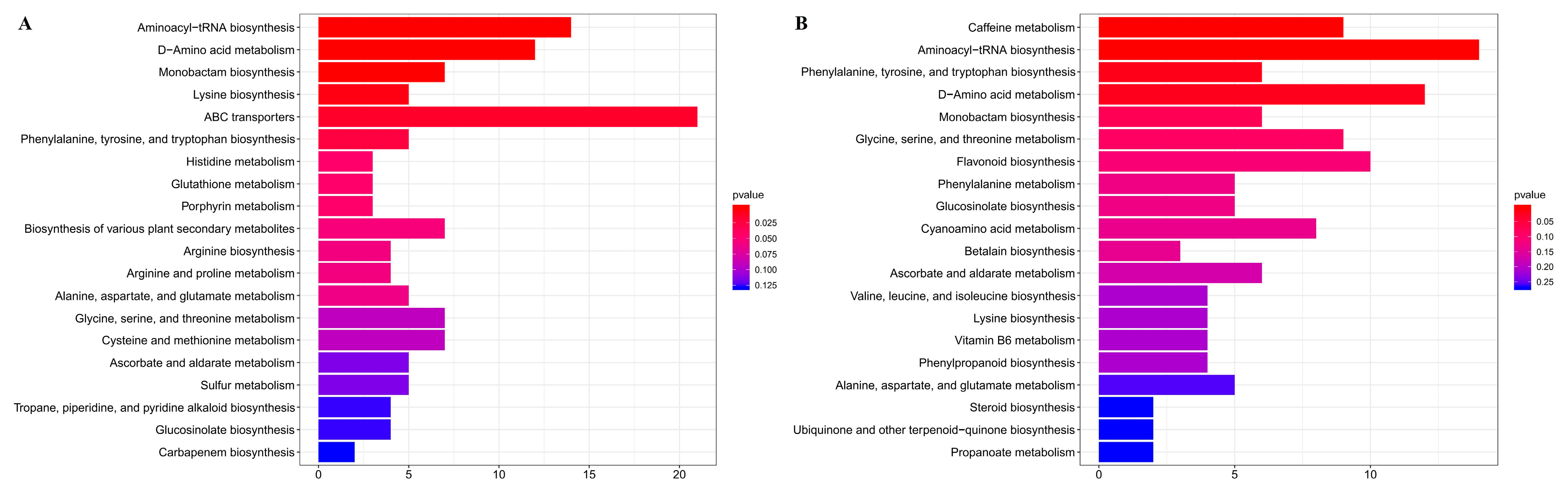
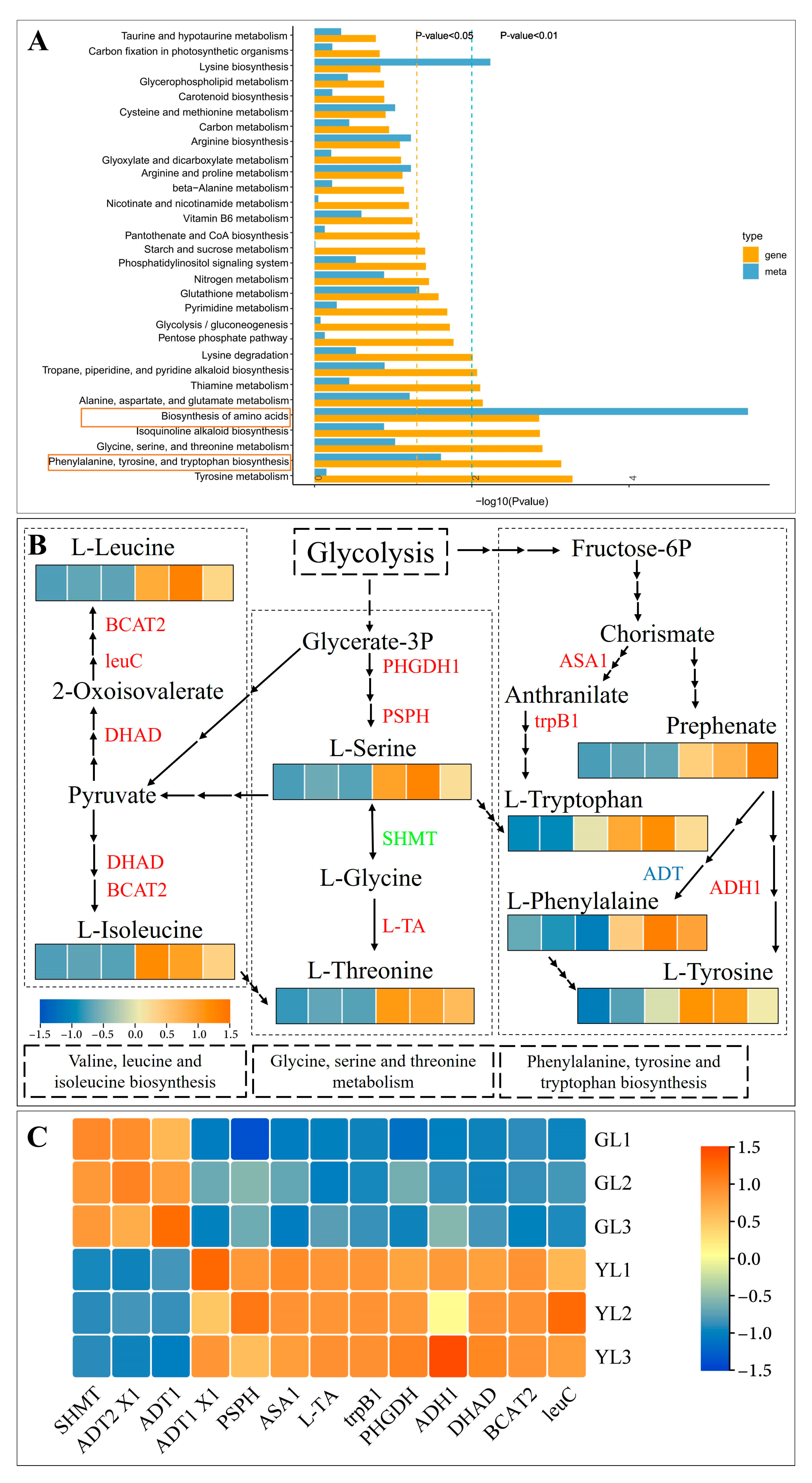
3.4. Integrated KEGG Analysis of Metabolites and DEGs in Normal and Albino Leaves
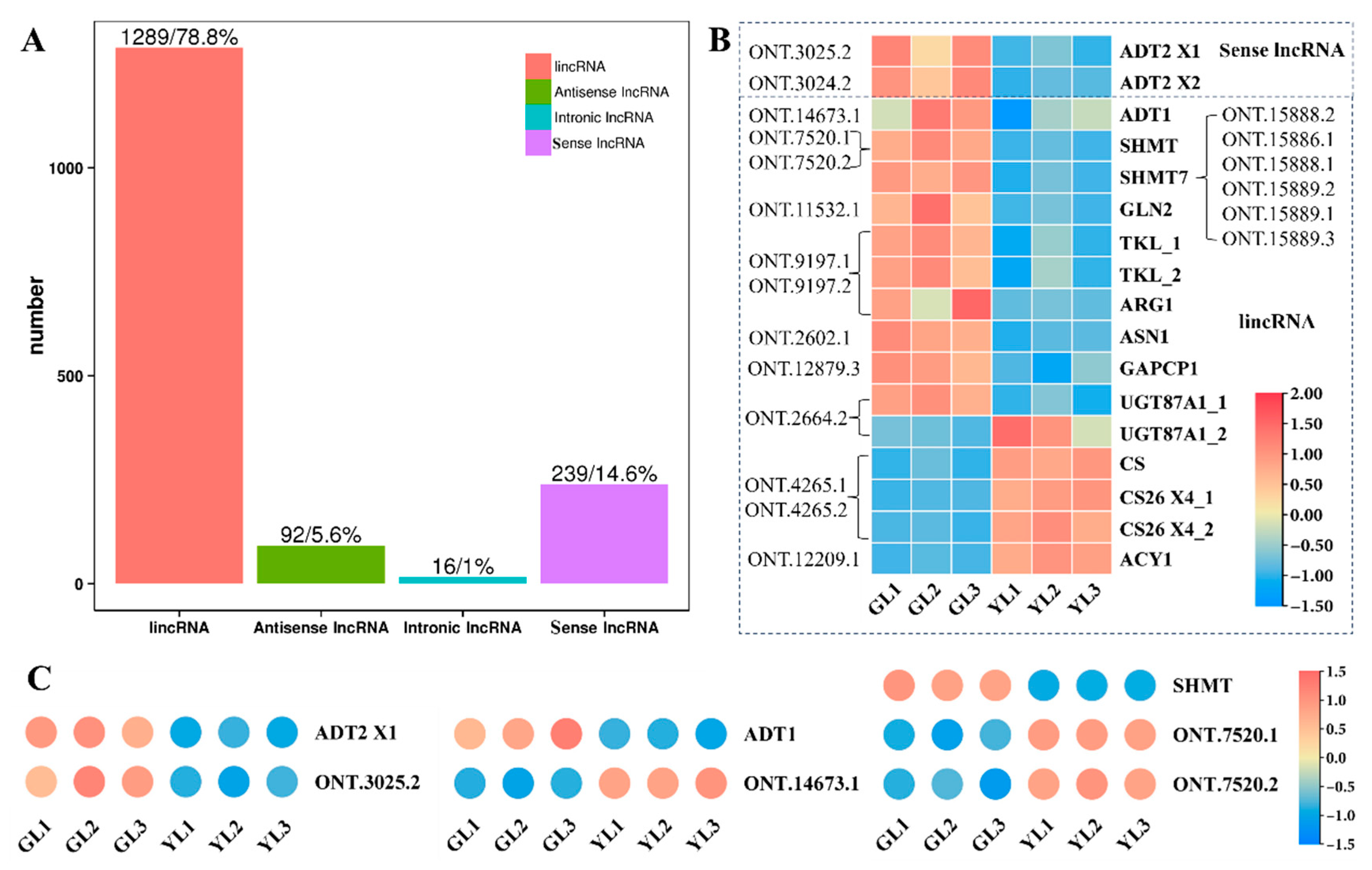
3.5. Analysis of lncRNAs and Their Targeted DEGs Involved in AAA Biosynthesis
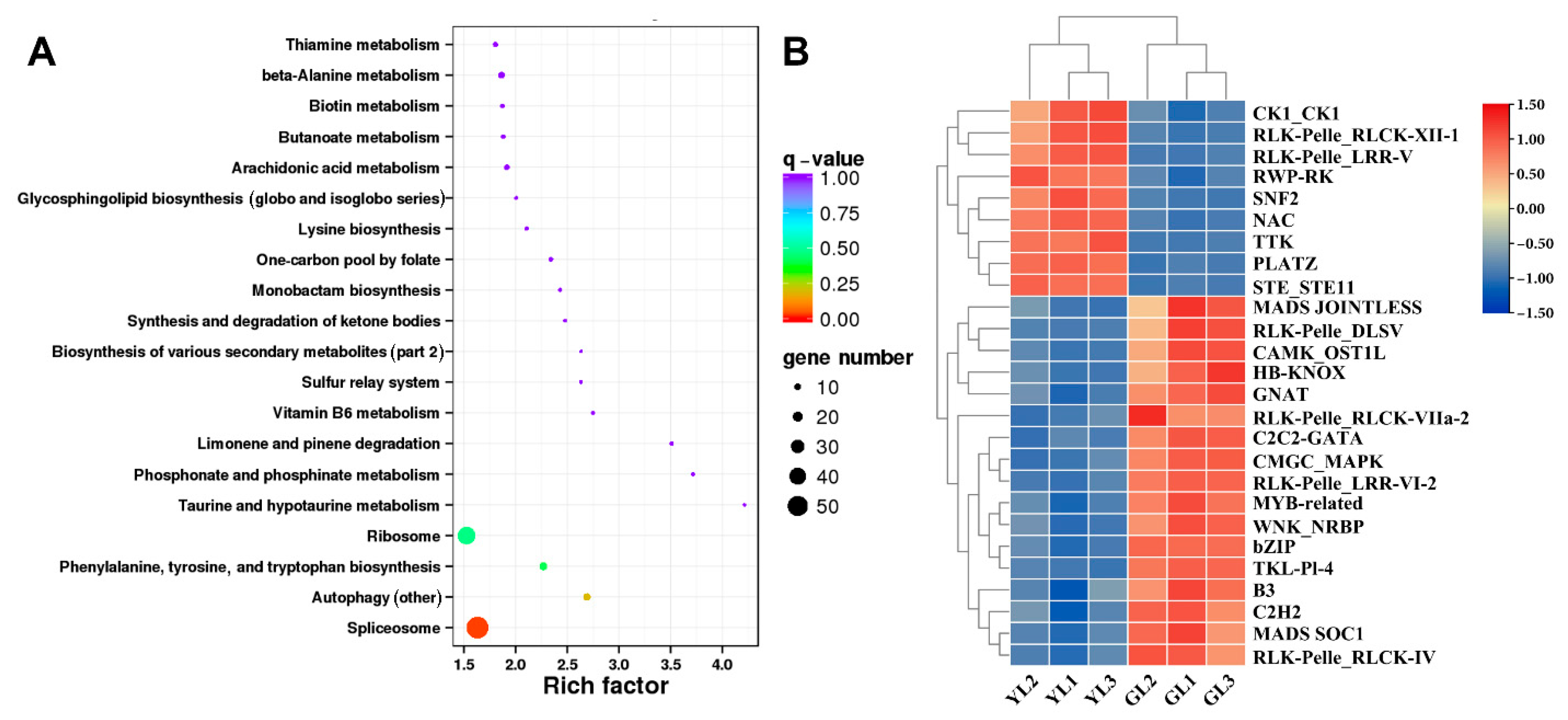
3.6. Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Transcription Factor Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J.; Li, P.; Xia, T.; Wan, X. Exploring plant metabolic genomics: Chemical diversity, metabolic complexity in the biosynthesis and transport of specialized metabolites with the tea plant as a model. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y. Regulation of biosynthesis of the main flavor-contributing metabolites in tea plant (Camellia sinensis): A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 10520–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Ma, J.Q.; Huang, D.J.; Ma, C.L.; Jin, J.Q.; Yao, M.Z.; Chen, L. Comprehensive dissection of metabolic changes in albino and green tea cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, M.; Enoki, H.; Oikawa, A.; Ohta, D.; Saito, K.; Hachiya, T.; Sakakibara, H.; Kusano, M.; Fukushima, A.; Saito, K.; et al. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome of Arabidopsis albino or pale green mutants with disrupted nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Qu, Z. Comparative studies on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of different tea extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, M. The identification and evaluation of two different color variations of tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4951–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Tong, H. Amino acids and flavonoids analysis reveals quality constituents difference among different albino tea resources. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Lu, J.L.; Li, Q.S.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Ding, C.Q.; Liang, Y.R.; Yang, Y.J. Dissection of chemical composition and associated gene expression in the pigment-deficient tea cultivar ‘Xiaoxueya’ reveals an albino phenotype and metabolite formation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Ma, Q. Widely targeted metabolomic analyses of albino tea germplasm ‘Huabai 1’ and ‘Baiye 1’. All Life 2021, 14, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.H.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liang, Y.R. High-light-induced degradation of photosystem II subunits’ involvement in the albino phenotype in tea plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Han, J.; Zhu, B.; Jia, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, R.; Deng, W.W.; Zhang, Z.Z. Significantly increased amino acid accumulation in a novel albino branch of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Planta 2019, 249, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Kambe, Y.; Ohshio, M.; Kunihiro, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Morita, A.; Ikka, T. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal etiolation-induced metabolic changes leading to high amino acid contents in a light-sensitive Japanese albino tea cultivar. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 611140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.; Yang, X. Tea aroma formation from six model manufacturing processes. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Qin, M.; Song, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Ren, Z.; Liu, H.; Duan, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. Molecular link in flavonoid and amino acid biosynthesis contributes to the flavor of Changqing tea in different seasons. Foods 2022, 11, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Zou, Z.; Arkorful, E.; Lv, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Sun, K.; Li, X. Transcriptomic analyses identify albino-associated genes of a novel albino tea germplasm ‘Huabai 1’. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Tian, S.; Lu, C.; Wang, K.; Shen, C. Transcriptomic analyses reveal variegation-induced metabolic changes leading to high L-theanine levels in albino sectors of variegated tea (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Z.; Wen, W.; Yao, M.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Ni, D.; Chen, L. Comprehensive dissection of variation and accumulation of free amino acids in tea accessions. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhad263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Yue, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ye, N. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics provide novel insight into changes in specialized metabolites in an albino tea cultivar (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntz). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hao, X.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Integrative transcriptome and whole-genome bisulfite sequencing analyses of a temperature-sensitive albino tea plant cultivar. Physiol. Plant 2023, 175, e14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, P.; Liu, G.; Wei, S. The intron retention variant CsClpP3m is involved in leaf chlorosis in some tea cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 804428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Huang, X.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Lin, J.; Yan, M.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, K. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor CsMYB42 regulates theanine biosynthesis in albino tea leaves. Plant Sci. 2023, 336, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.H.; Dudareva, N. Aromatic amino acids: A complex network ripe for future exploration. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikaya, V.; El Arbi, N.; Rojas-Murcia, N.; Nardeli, S.M.; Goretti, D.; Schmid, M. Insights into the role of alternative splicing in plant temperature response. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 7384–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J. Editorial: lncRNA in plants: Function, mechanisms and applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1238185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Shen, Y.; Li, F.; Yue, R.; Duan, J.; Ye, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. metabolite and transcriptome analysis revealed the different mechanisms of characteristic compound biosynthesis and transcriptional regulation in tea flowers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1016692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X.T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.L.; Sun, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Gong, X.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; et al. Serum metabolomics for early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by UHPLC-QTOF/MS. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; He, Q. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Li, F.D.; Tong, W.; Li, P.H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Li, R.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Tea Plant Information Archive (TPIA): A comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.L.; Chen, L.B.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Yu, J.; Li, F.D.; Li, R.P.; et al. The reference genome of tea plant and resequencing of 81 diverse accessions provide insights into genome evolution and adaptation of tea plants. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Olsen, H.E.; Paten, B.; Akeson, M. The Oxford Nanopore MinION: Delivery of nanopore sequencing to the genomics community. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 239. [Google Scholar]
- Foissac, S.; Sammeth, M. ASTALAVISTA: Dynamic and flexible analysis of alternative splicing events in custom gene datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W297–W299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, L.T.; Bu, D.C.; Zhao, G.G.; Yu, K.T.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, Y.N.; Chen, R.S.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Park, H.J.; Dasari, S.; Wang, S.; Kocher, J.P.; Li, W. CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Penelope, C.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, gkt1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, W.; Zeng, P.; Wang, J.Y.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.C.; Cui, Q.H. LncTar: A tool for predicting the RNA targets of long noncoding RNAs. Brief. Bioinform. 2015, 16, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wu, X.H.; Li, D.; Borthakur, D.; Ye, J.H.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lu, J.L. Analysis of differentially expressed genes in tissues of Camellia sinensis during dedifferentiation and root redifferentiation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H.; Fu, X.M.; Liao, Y.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zeng, L.T.; Tang, J.C.; Li, J.L.; Lai, J.H.; Yang, Z.Y. Differential accumulation of specialized metabolite L-theanine in green and albino-induced yellow tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Han, Y.X.; He, S.Q.; Cheng, Q.H.; Tong, H.R. Differential metabolic profiles of pigment constituents affecting leaf color in different albino tea resources. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, E.; Cetin, D.; Akbudak, M.A. Aromatic amino acids biosynthesis genes identification and expression analysis under salt and drought stresses in Solanum lycopersicum L. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 250, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.G.; Hu, W.Z.; Xu, Y.P.; Yang, X.Z.; Ji, Y.R.; Feng, K.; Sarengaowa. Metabolomics and physiological analyses validate previous findings on the mechanism of response to wounding stress of different intensities in broccoli. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Guy, A.; Galili, G.; Dor, E.; Schweitzer, R.; Amir, R.; Hacham, Y. Enhanced production of aromatic amino acids in tobacco plants leads to increased phenylpropanoid metabolites and tolerance to stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 604349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ruan, J. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the mechanism underlying the weakening of carbon metabolism in chlorotic tea leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhou, F.; Shen, C.; Liu, Z. Multi-omics research in albino tea plants: Past, present, and future. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bross, C.D.; Howes, T.R.; Abolhassani Rad, S.; Kljakic, O.; Kohalmi, S.E. Subcellular localization of Arabidopsis arogenate dehydratases suggests novel and non-enzymatic roles. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.C.; Kong, L.G.; Zheng, G.M.; Zhao, Y.J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, J.W.; Liu, C.; Chu, J.; Ding, X.H.; Zhang, X.S.; et al. Maize requires arogenate dehydratase 2 for resistance to Ustilago maydis and plant development. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Tellez, S.; Alcantara-Enguidanos, A.; Martinez-Seidel, F.; Casatejada-Anchel, R.; Saeheng, S.; Bailes, C.L.; Erban, A.; Barbosa-Medeiros, D.; Alepuz, P.; Matus, J.T.; et al. The serine-glycine-one-carbon metabolic network orchestrates changes in nitrogen and sulfur metabolism and shapes plant development. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 404–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Sandoval, F.J.; Santiago, K.; Roje, S. One-carbon metabolism in plants: Characterization of a plastid serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhai, G.; Shao, J.; Tao, Y. Characterization and molecular cloning of a serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (OsSHM1) in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, T.; Li, L.; Chai, M.; Feng, Z.; Yu, S. Genome-wide identification of the serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene revealed the function of GhSHMT11s involved in plant growth development and salt stress tolerance in cotton. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 222, 119687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Li, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of B3 transcription factor genes in Populus alba × Populus glandulosa. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1193065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Feng, X.X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.S. Genomic investigation of duplication, functional conservation, and divergence in the LRR-RLK Family of Saccharum. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Identification and Characterization of PLATZ Transcription Factors in Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucher, M.; Guérin, C.; El Jaziri, M.; Behr, M. Integration of the plant-specific PLATZ transcription factors into gene regulatory networks controlling developmental processes. Criti Rev. Plant Sci. 2024, 43, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Jun, S.E.; Park, S.; Timilsina, R.; Kwon, D.S.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nam, H.G.; et al. ORESARA15, a PLATZ transcription factor, mediates leaf growth and senescence in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, C.; An, Y.; Chen, N.; Huang, L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, J. Comparative analysis of PLATZ transcription factors in six poplar species and analysis of the role of PtrPLATZ14 in leaf development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Song, L. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Shed Light on the Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in a Novel Albino Tea (Camellia sinensis) Mutation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080644
Gao Y, Li S, Zhang X, Yu S, Liu X, Yuan C, Yao Y, Zhang F, Song L. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Shed Light on the Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in a Novel Albino Tea (Camellia sinensis) Mutation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080644
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ying, Suimei Li, Xiaojia Zhang, Shuwei Yu, Xinyu Liu, Changbo Yuan, Yuantao Yao, Fan’an Zhang, and Lubin Song. 2025. "Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Shed Light on the Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in a Novel Albino Tea (Camellia sinensis) Mutation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080644
APA StyleGao, Y., Li, S., Zhang, X., Yu, S., Liu, X., Yuan, C., Yao, Y., Zhang, F., & Song, L. (2025). Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Shed Light on the Regulation of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in a Novel Albino Tea (Camellia sinensis) Mutation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080644





