Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Key Points
- •
- Aerobic exercise offers modest benefits for sleep quality and symptoms of insomnia.
- •
- The limited number of published controlled clinical trials makes it difficult to analyze the effects of aerobic exercise on inflammation markers.
- •
- Well-controlled studies are necessary to support the potential of aerobic exercise as a treatment for improving sleep quality and regulating immune–metabolic functions
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focused Question
- (i)
- Population: human subjects;
- (ii)
- Intervention or exposure: exercise protocol and sleep disorders;
- (iii)
- Comparison: no exercise;
- (iV)
- Outcome: subjective sleep quality/insomnia and circulating inflammatory markers;
- (V)
- Study: randomized controlled trials.
2.2. Identification of Manuscripts
2.3. Screening for Relevance
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
- •
- Randomized controlled trials in humans.
- •
- Peer-reviewed articles.
- •
- Studies that include at least one inflammatory marker.
- •
- Studies evaluating the effects of exercise on inflammatory markers.
- •
- Studies evaluating the effect of exercise on sleep disorders (insomnia and sleep quality).
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
- •
- The exercise intervention period was less than eight weeks.
- •
- The article does not present data disaggregated by sex.
- •
- The article does not include a clearly structured exercise intervention
- •
- The article is a case study or a systematic review.
- •
- The article does not report inflammatory markers or lacks data for analysis.
- •
- The study involves animals, cell cultures, or in vitro models.
- •
- The article is not in English or Spanish.
2.6. Retrieval of Full-Text Articles and Evaluation
2.7. Data Extraction
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
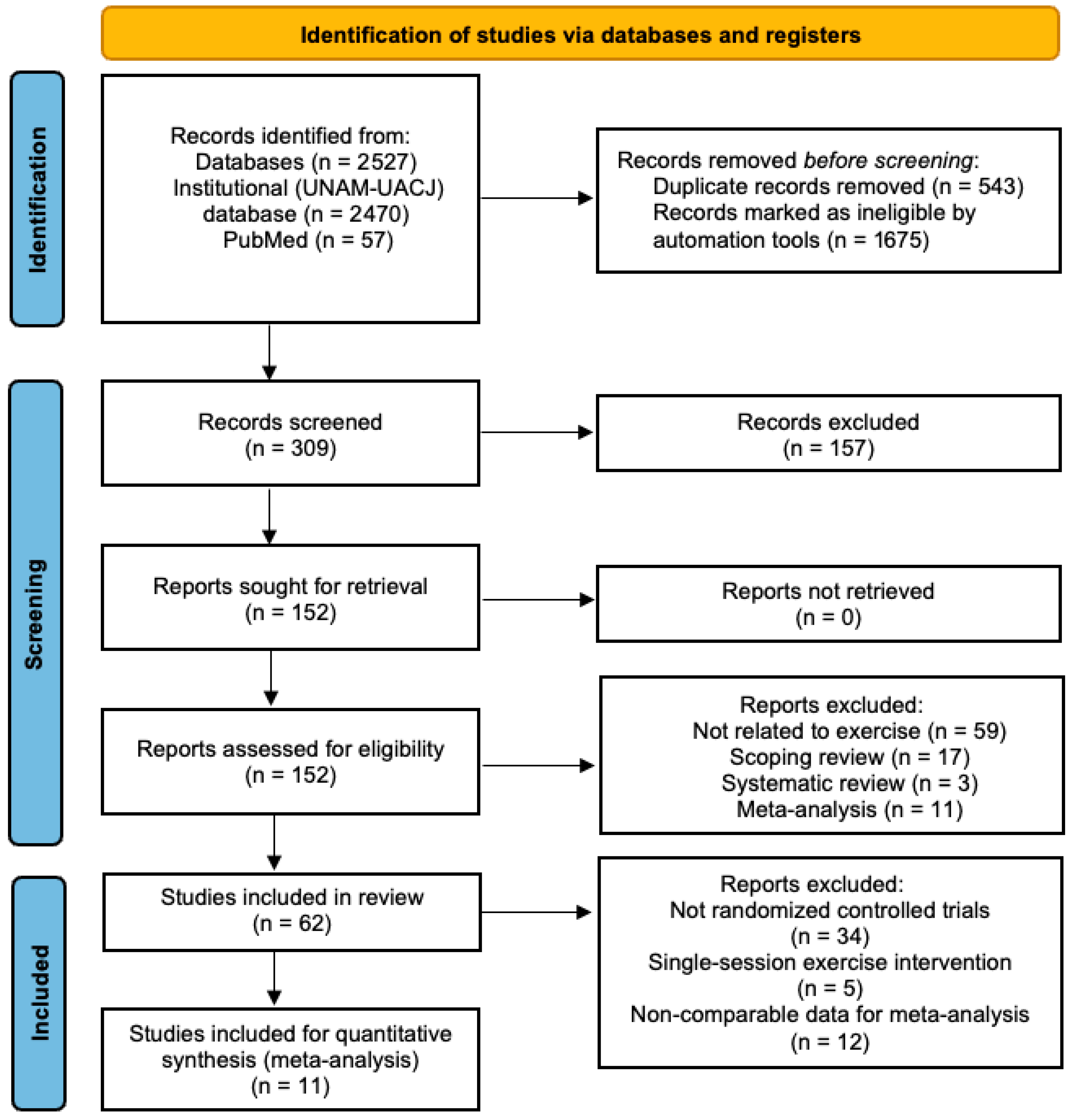
3.1. Characteristics of the Search
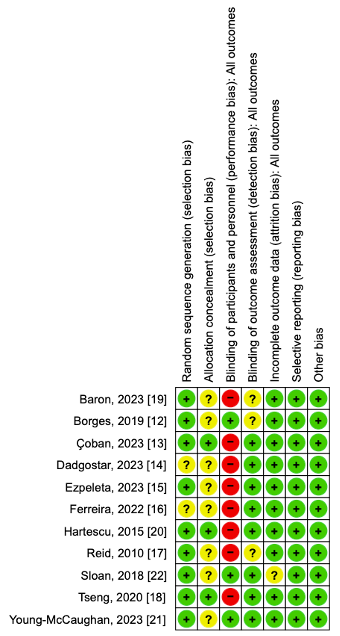
3.2. Risk of Bias
3.3. Subject Characteristics
3.4. Study Design
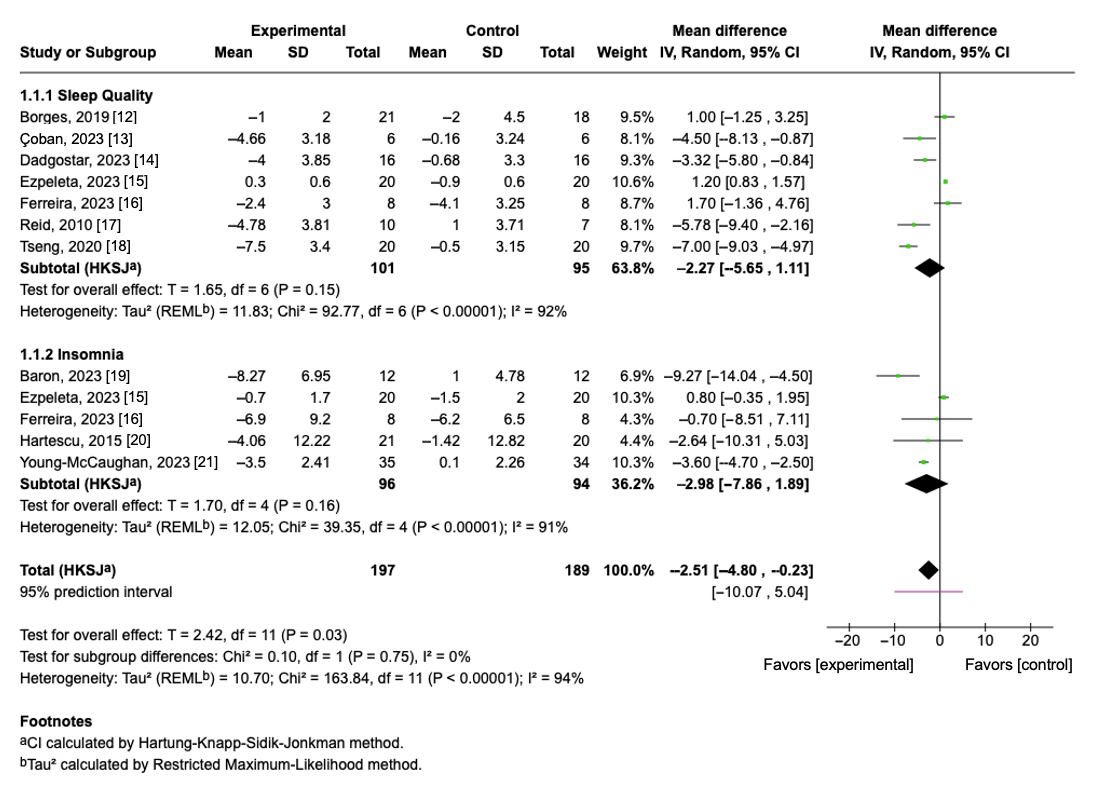
3.5. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality
3.6. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Insomnia Severity
3.7. Overall Pooled Effect of Sleep Quality and Insomnia
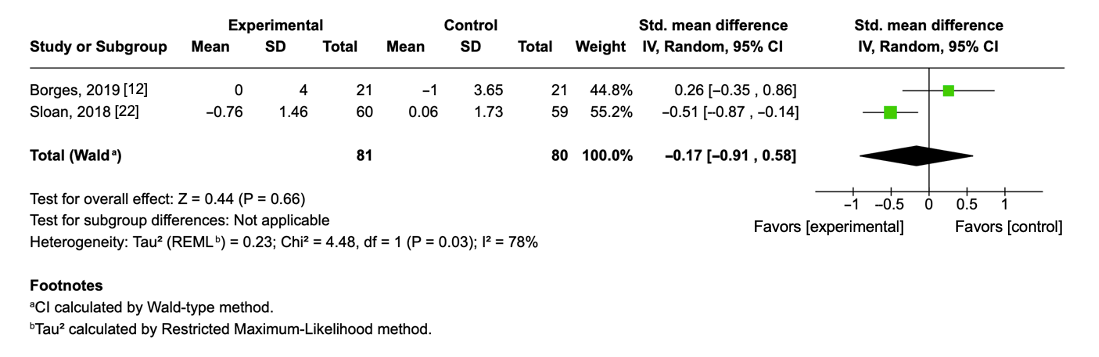
3.8. Effect of Aerobic Physical Exercise on Interleukin-6 Levels
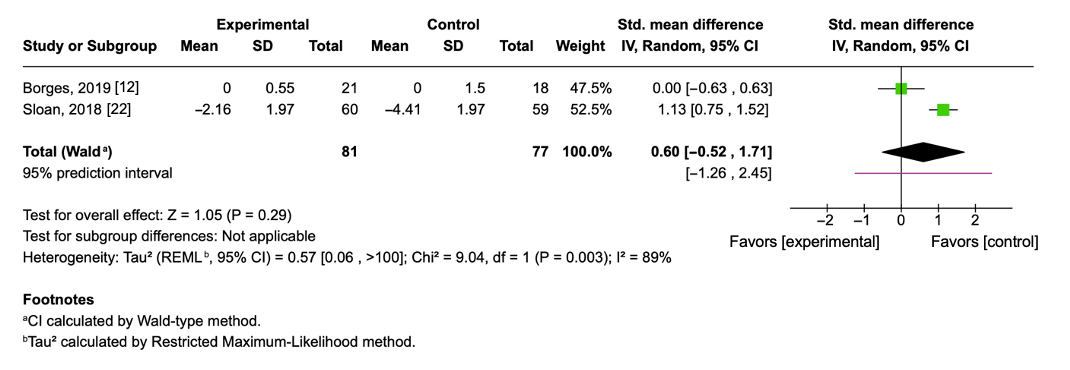
3.9. Effect of Aerobic Physical Exercise on Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha
4. Discussion
4.1. Aerobic Exercise and Subjective Sleep Quality: PSQI
4.2. Variability in Insomnia Outcomes Following Aerobic Exercise Interventions
4.3. Pooled Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality and Insomnia Symptoms
4.4. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on IL-6
4.5. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on TNF-α
4.6. Strengths
4.7. Limitations
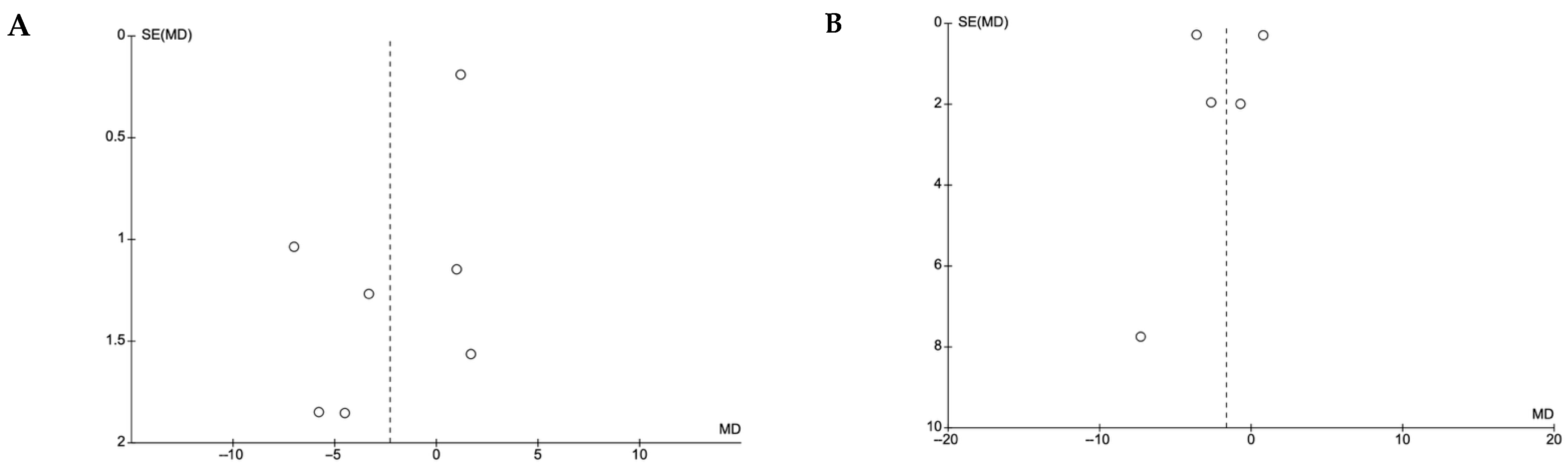
4.8. Publication of Bias
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Yin, J.; Gong, R.; Zhang, M.; Ding, L.; Shen, T.; Cai, Y.; He, S.; Peng, D. Associations between sleep disturbance, inflammatory markers and depressive symptoms: Mediation analyses in a large NHANES community sample. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 126, 110786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, R.; Goyal, A.; Jialal, I. Chronic inflammation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Coppack, S.W. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbarino, S.; Lanteri, P.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Magnavita, N.; Scoditti, E. Role of sleep deprivation in immune-related disease risk and outcomes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kianian, T.; Navidia, A.; Aghamohamadi, F.; Saber, S. Comparing the effects of aerobic and anaerobic exercise on sleep quality among male nonathlete students. Nurs. Midwifery Stud. 2017, 6, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá Souza, H.; de Melo, C.M.; Piovezan, R.D.; Miranda, R.E.E.P.C.; Carneiro-Junior, M.A.; Silva, B.M.; Thomatieli-Santos, R.V.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D.; D’Almeida, V. Resistance training improves sleep and anti-inflammatory parameters in sarcopenic older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, M.A.; Leggate, M.; Viana, J.L.; King, J.A. The effect of physical activity on mediators of inflammation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program], Version 5.4; The Cochrane Collaboration: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020.
- Mollayeva, T.; Thurairajah, P.; Burton, K.; Mollayeva, S.; Shapiro, C.M.; Colantonio, A. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index as a screening tool for sleep dysfunction in clinical and non-clinical samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 25, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerri, L.Q.; Justo, M.C.; Clemente, V.; Gomes, A.A.; Pereira, A.S.; Marques, D.R. Insomnia Severity Index: A reliability generalisation meta-analysis. J. Sleep Res. 2023, 32, e13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, Y.G.; Cipriano, L.H.C.; Aires, R.; Zovico, P.V.C.; Campos, F.V.; de Araújo, M.T.M.; Gouvea, S.A. Oxidative stress and inflammatory profiles in obstructive sleep apnea: Are short-term CPAP or aerobic exercise therapies effective? Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çoban, Ö.; Ün Yıldırım, N.; Yaşa, M.E.; Sonkaya, A.R. Effects of different exercise programs on symptoms, sleep, and quality of life in patients with primary restless legs syndrome. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgostar, H.; Basharkhah, A.; Ghalehbandi, M.F.; Kashaninasab, F. An investigation on the effect of exercise on insomnia symptoms. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Kalam, F.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Varady, K.A. Alternate-day fasting combined with exercise: Effect on sleep in adults with obesity and NAFLD. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, W.S.; Santana, M.G.; Youngstedt, S.D.; de Assis, D.E.; de Assis, B.P.; de Cerqueira, D.P.; Mazzaro, M.C.; Passos, G.S. Effects of exercise training and exercise plus acupuncture on chronic insomnia: A feasibility study. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, K.J.; Baron, K.G.; Lu, B.; Naylor, E.; Wolfe, L.; Zee, P.C. Aerobic exercise improves self-reported sleep and quality of life in older adults with insomnia. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.H.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Chien, M.Y. Effects of exercise training on sleep quality and heart rate variability in middle-aged and older adults with poor sleep quality: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, P.; Hermand, É.; Bourlois, V.; Pezé, T.; Aron, C.; Lombard, R.; Hurdiel, R. Effect of aerobic exercise training on sleep and core temperature in middle-aged women with chronic insomnia: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartescu, I.; Morgan, K.; Stevinson, C.D. Increased physical activity improves sleep and mood outcomes in inactive people with insomnia: A randomized controlled trial. J. Sleep Res. 2015, 24, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young-McCaughan, S.; Straud, C.L.; Bumstead, S.; Pruiksma, K.E.; Taylor, D.J.; Jacoby, V.M.; Yarvis, J.S.; Peterson, A.L. Aerobic exercise improves sleep in US active duty service members following brief treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1249543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, R.P.; Shapiro, P.A.; McKinley, P.S.; Bartels, M.; Shimbo, D.; Lauriola, V.; Karmally, W.; Pavlicova, M.; Choi, C.J.; Choo, T.H.; et al. Aerobic exercise training and inducible inflammation: Results of a randomized controlled trial in healthy, young adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds III, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Guy, C.D.; Piercy, D.; Pan, Y.; Diehl, A.M.; Suzuki, A. 929 Associations of Sleep Duration and Sleep Quality With Clinical and Histologic Features of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Gastroenterology 2014, 146, S-931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, M.; Harada, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Tobita, R.; Tsujimoto, H.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Kataoka, Y.; Noda, A. Exercise can improve sleep quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.J.; Yu, H.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W. Effects of exercise on sleep quality and insomnia in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 664499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Arias, J.Á.; Marín-Cascales, E.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Hernandez, A.V.; Pérez-López, F.R. Effect of exercise on sleep quality and insomnia in middle-aged women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Maturitas 2017, 100, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Kong, Y.; Yu, B.; Shi, S.; He, H. Effects of exercise on sleep quality in general population: Meta-analysis and systematic review. Sleep Med. 2024, 125, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.C.B.; Mina, T.; Xie, W.; Low, Y.D.; Yew, Y.W.; Wang, X.; Riboli, E.; Elliott, P.; Lee, J.; Ngeow, J.; et al. The relationships between sleep and adiposity amongst multi-ethnic Asian populations: A cross-sectional analysis of the Health for Life in Singapore (HELIOS) study. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 49, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid-Valero, J.J.; Martínez-Selva, J.M.; Ordoñana, J.R. Sleep quality and body mass index: A co-twin study. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweatt, S.K.; Gower, B.A.; Chieh, A.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Sleep quality is differentially related to adiposity in adults. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, E.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y. TNF-α downregulates CIDEC via MEK/ERK pathway in human adipocytes. Obesity 2016, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, D.D.; Chen, R.; Li, S.; Wu, J. The gap between statistical and clinical significance: Time to pay attention to clinical relevance in pa-tient-reported outcome measures of insomnia. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Targeting interleukin-6 signaling in clinic. Immunity 2019, 50, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, B.J.; Hsu, F.C.; Brinkley, T.J.; Church, T.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Pahor, M. Exercise training and plasma C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in elderly people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, L.K.; Flynn, M.G.; Campbell, W.W.; Craig, B.A.; Robinson, J.P.; Timmerman, K.L.; McFarlin, B.K.; Coen, P.M.; Talbert, E. The influence of exercise training on inflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, A.L.; Steinberg, G.R.; Macaulay, S.L.; Thomas, W.G.; Holmes, A.G.; Ramm, G.; Prelovsek, O.; Hohnen-Behrens, C.; Watt, M.J.; James, D.E.; et al. Interleukin-6 increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenius, V.; Wallenius, K.; Ahrén, B.; Rudling, M.; Carlsten, H.; Dickson, S.L.; Ohlsson, C.; Jansson, J.O. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedell-Neergaard, A.S.; Lehrskov, L.L.; Christensen, R.H.; Legaard, G.E.; Dorph, E.; Larsen, M.K.; Launbo, N.; Fagerlind, S.R.; Seide, S.K.; Nymand, S.; et al. Exercise-induced changes in visceral adipose tissue mass are regulated by IL-6 signaling: A randomized controlled trial. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawari, B.Y.; Merawati, D.; Pranoto, A. Acute Aerobic Exercise Decreased Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) Levels in Obese Adolescent Females. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2021, 15, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, K.I.; Middelbeek, R.J.; Goodyear, L.J. Exercise effects on white adipose tissue: Beiging and metabolic adaptations. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.M.; Puri, V. Mechanism of TNF-[alpha]-Induced Lipolysis in Human Adipocytes Uncovered. Obesity 2016, 24, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Korkutata, A.; Korkutata, M.; Lazarus, M. The impact of exercise on sleep and sleep disorders. npj Biol. Timing Sleep 2025, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, X. The association between sedentary behavior, exercise, and sleep disturbance: A mediation analysis of inflammatory biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1080782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Participants, Age (years) | Exercise Protocol | Δ Sleep Quality (PSQI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borges, 2019 [12] | 22 males/17 females (50 ± 11.3) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill walking); 3 times/week; ~50 min/session; 8 weeks | C: −0.44 ± 0.11 E: −0.5 ± 0.1 |
| Çoban, 2023 [13] | 6 males/6 females (44 ± 11.6) | Aerobic exercise on a treadmill; 3 times/week; 40 min/session; 8 weeks | C: −0.05 ± 0.33 E: −1.47 ± 0.42 |
| Dadgostar, 2023 [14] | 12 males/20 females (43.7 ± 0) | Combined exercise (aerobic and strength); 6 days/week (3 aerobic + 3 strength); 30–60 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −0.21 ± 0.13 E: −1.04± 0.14 |
| Ezpeleta, 2023 [15] | 8 males/32 females (44 ± 3) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill, bike, or elliptical); 5 times/week; 60 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −1.5 ± 0.16 E: 0.5 ± 0.11 |
| Ferreira, 2022 [16] | 3 males/13 females (44.9 ± 9.58) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill); 3 times/week; 50 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −1.26 ± 0.35 E: −0.8 ± 0.29 |
| Reid, 2010 [17] | 1 male/16 females (62.6 ± 4.35) | Moderate aerobic exercise (walking, bike, or treadmill); 4 times/week; 10–40 min/session; progressive intensity (55–75% HRmax); 16 weeks | C: 0.27 ± 0.29 E: −1.25 ± 0.28 |
| Tseng, 2020 [18] | 7 males/33 females (61.65 ± 7.10) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill); 3 times/week; 50 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −0.16 ± 0.10 E: −2.21 ± 0.22 |
| Study | Participants, Age (years) | Exercise Protocol | Δ Insomnia (ISI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baron, 2023 [19] | 24 females (45.7 ± 6.8) | Moderate–vigorous aerobic exercise (active walking outdoors or on a treadmill); 3 sessions/week; 75 min/session; 12 weeks | C: 0.21 ± 0.17 E: −1.19 ± 0.23 |
| Ezpeleta, 2023 [15] | 8 males/32 females (44 ± 3) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill, bike, or elliptical); 5 times/week; 60 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −0.75 ± 0.11 E: −0.41 ± 0.10 |
| Ferreira, 2022 [16] | 3 males/13 females (44.9 ± 9.58) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill); 3 times/week; 50 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −0.95 ± 0.31 E: −0.75 ± 0.29 |
| Hartescu, 2015 [20] | 10 males/30 females (59.8 ± 9.49) | Moderate-intensity brisk walking; ≥5 days/week; ≥30 min/day; 6 months | C: −0.11 ± 0.10 E: −0.33 ± 0.10 |
| Young-McCaughan, 2023 [21] | 63 males/5 females (35.5 ± 7.21) | Moderate aerobic exercise; 5 times/week; 20–25 min/session; 8 weeks | C: 0.04 ± 0.06 E: −1.45 ± 0.09 |
| Study | Participants, Age (years) | Exercise Protocol | Δ IL-6 (pg∙mL −1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borges, 2020 [12] | 22 males/17 females (50 ± 11.3) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill walking); 3 times/week; ~50 min/session; 8 weeks | C: −0.27 ± 0.11 E: 0.0 ± 0.10 |
| Sloan, 2018 [22] | 56 males/63 females (31.3 ± 5.96) | Progressive aerobic exercise (cycling, treadmill, StairMaster); 4 times/week; 40–55 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −0.03 ± 0.03 E: −0.55 ± 0.04 |
| Study | Participants, Age (years) | Exercise Protocol | Δ TNF-α (pg∙mL −1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borges, 2020 [12] | 22 males/17 females (50 ± 11.3) | Moderate aerobic exercise (treadmill walking); 3 times/week; ~50 min/session; 8 weeks | C: 0.0 ± 0.1 E: 0.0 ± 0.1 |
| Sloan, 2018 [22] | 56 males/63 females (31.3 ± 5.96) | Progressive aerobic exercise (cycling, treadmill, StairMaster); 4 times/week; 40–55 min/session; 12 weeks | C: −2.22 ± 0.05 E: −0.62 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubio-Valles, M.; Ramos-Jimenez, A. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070572
Rubio-Valles M, Ramos-Jimenez A. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070572
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubio-Valles, Mariazel, and Arnulfo Ramos-Jimenez. 2025. "Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070572
APA StyleRubio-Valles, M., & Ramos-Jimenez, A. (2025). Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070572






