Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Pathogenic and Protective Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
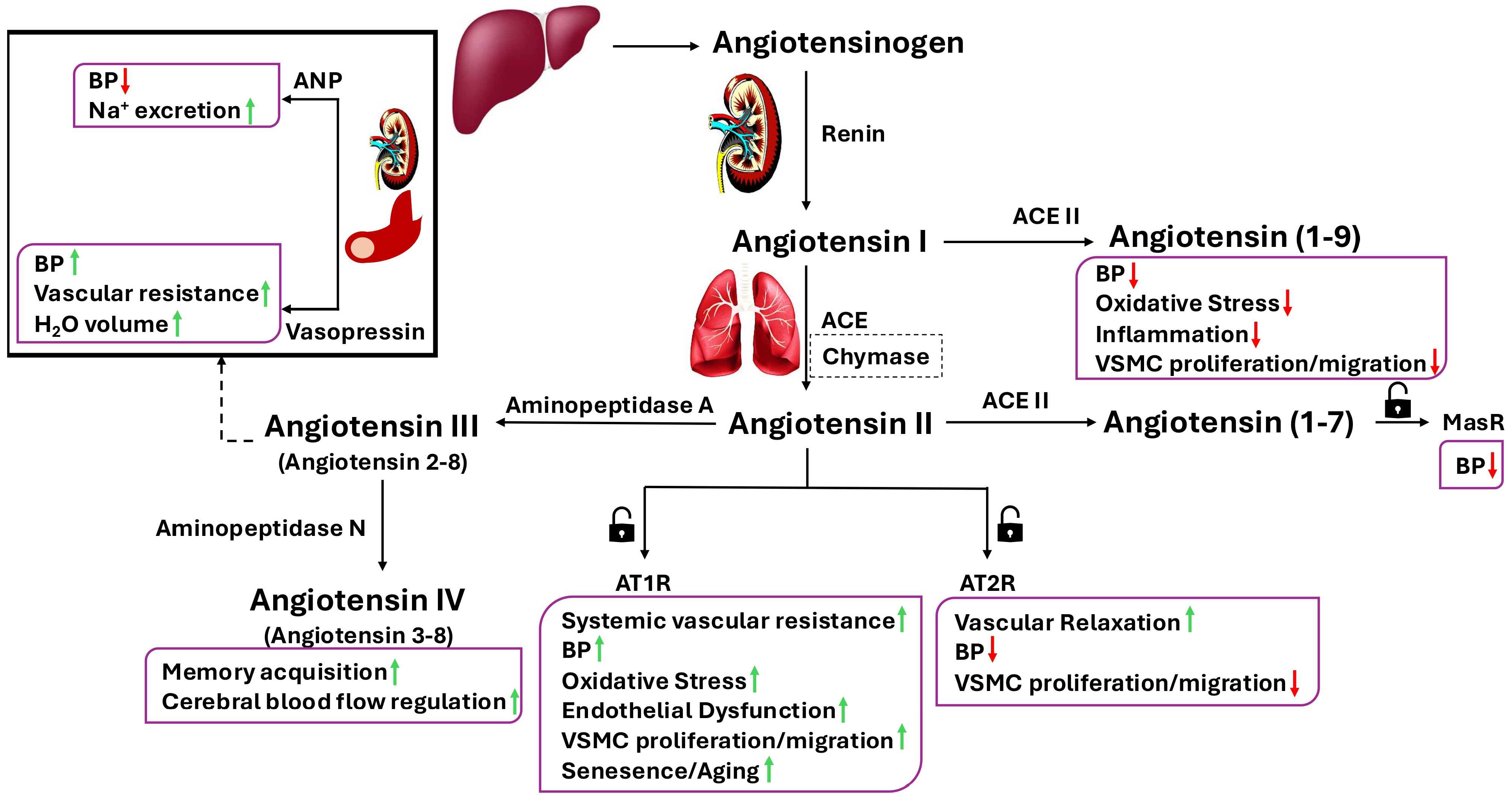
2. A Brief Overview of the Renin–Angiotensin Aldosterone System
3. A Brief Overview of the Renin–Angiotensin Aldosterone System Receptors
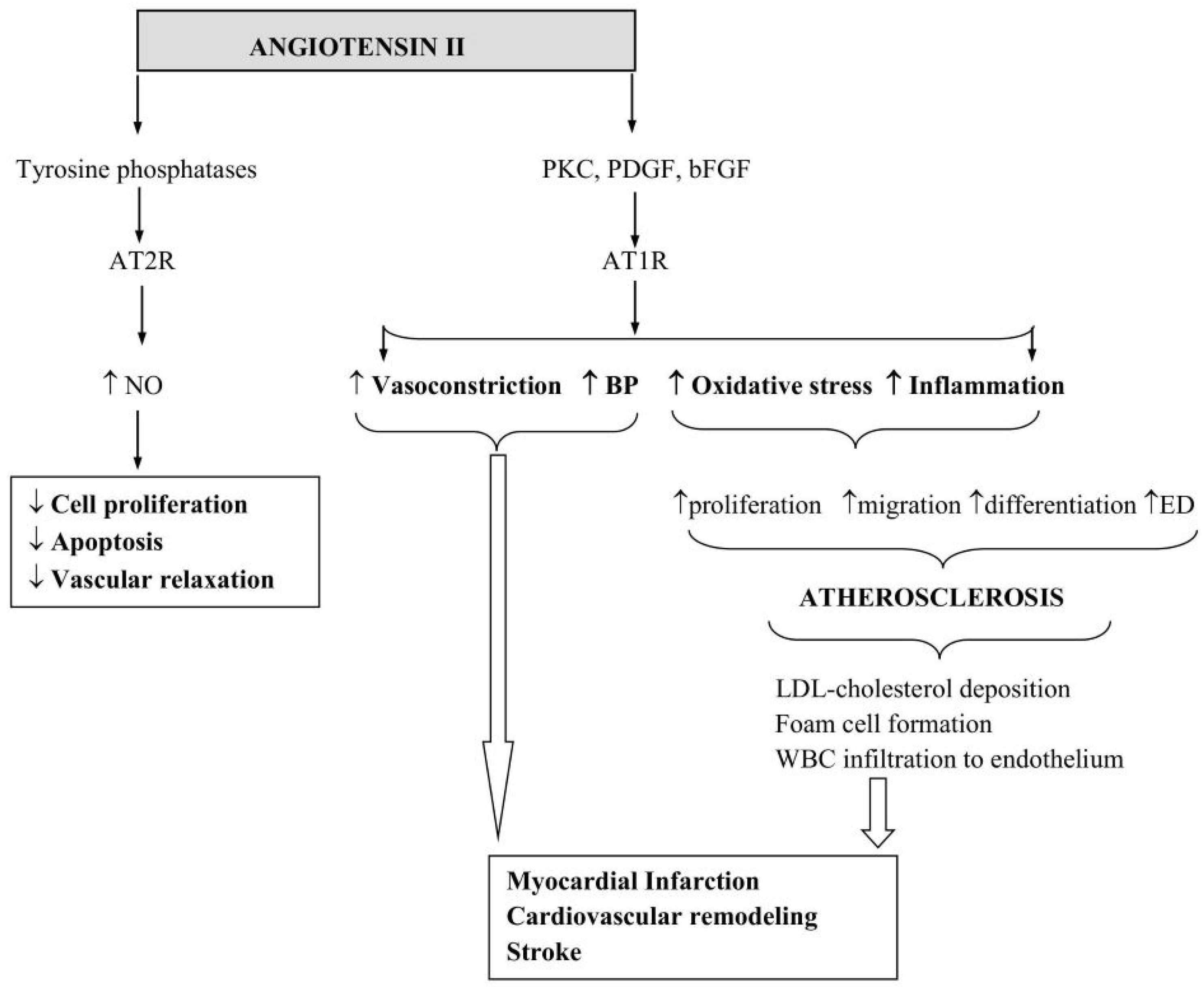
4. Angiotensin II and Its Mechanism of Action
5. Ang II in Cell Senescence and Organismal Ageing
6. Angiotensin II in Cardiovascular Disease
7. Impact of RAAS Modulation on Disease Outcome
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinoshita, J.; Fushida, S.; Harada, S.; Yagi, Y.; Fujita, H.; Kinami, S.; Ninomiya, I.; Fujimura, T.; Kayahara, M.; Yashiro, M.; et al. Local angiotensin II-generation in human gastric cancer: Correlation with tumor progression through the activation of ERK1/2, NF-kappaB and survivin. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Valenzuela, R.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. The intracellular renin-angiotensin system: Friend or foe. Some light from the dopaminergic neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, M.; Nabel, E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2–a new cardiac regulator. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1795–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisham, N.F.; Bayraktutan, U. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Treatment of Hypertension in Ischaemic Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, e4–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Tang, P.; Yuan, M.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Cai, Z. Role of angiotensin II in aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1002138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossena, S.; Marino, A. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Aging. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaux, A.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Angiotensin III: A central regulator of vasopressin release and blood pressure. Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 2001, 12, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Ong, F.S.; Blackwell, W.L.; Shah, K.H.; Giani, J.F.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Shen, X.Z.; Fuchs, S.; Touyz, R.M. A modern understanding of the traditional and nontraditional biological functions of Angiotensin-converting enzyme. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Huang, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Qin, S.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; et al. A comprehensive investigation of the mRNA and protein level of ACE2, the putative receptor of SARS-CoV-2, in human tissues and blood cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froogh, G.; Pinto, J.T.; Le, Y.; Kandhi, S.; Aleligne, Y.; Huang, A.; Sun, D. Chymase-dependent production of angiotensin II: An old enzyme in old hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H223–H231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhushan, S.; Bratti, M.; Montero-Hernández, J.E.; El Ghoneimi, A.; Benhamou, M.; Charles, N.; Daugas, E.; Blank, U. Mast Cell Chymase and Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Daugas, E.; Blank, U. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; San Hipólito-Luengo, Á.; Villalobos, L.A.; Vallejo, S.; Valencia, I.; Michalska, P.; Pajueleo-Lozano, N.; Sanchez-Perez, I.; Leon, R.; Bartha, J.L.; et al. The angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis protects from endothelial cell senescence via klotho and Nrf2 activation. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Besada, M.A.; Valenzuela, R.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Parga, J.A.; Lanciego, J.L.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Paracrine and Intracrine Angiotensin 1-7/Mas Receptor Axis in the Substantia Nigra of Rodents, Monkeys, and Humans. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5847–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaranza, M.P.; Jalil, J.E. Protective Role of the ACE2/Ang-(1-9) Axis in Cardiovascular Remodeling. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 594361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A. Aminopeptidases: Structure and function. FASEB J. 1993, 2, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugandhar, V.G.; Clark, M.A. Angiotensin III: A physiological relevant peptide of the renin angiotensin system. Peptides 2013, 46, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q. Atrial natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular biology and disease (NPPA). Gene 2015, 569, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Nolan, P.L.; Johnston, C.I. Role of Vasopressin in Blood Pressure Regulation Through its Modulatory Effect on Baroreceptor Reflex. In Fundamental Fault in Hypertension. Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine; Sambhi, M.P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, A.K.; Gulati, A. Controls of Central and Peripheral Blood Pressure and Hemorrhagic/Hypovolemic Shock. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroth, U.; Unger, T. The renin-angiotensin system and its receptors. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 33, S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padia, S.H.; Howell, N.L.; Siragy, H.M.; Carey, R.M. Renal Angiotensin Type 2 Receptors Mediate Natriuresis via Angiotensin III in the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor-Blocked Rat. Hypertension 2006, 47, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.T.; Haspula, D.; Alanazi, A.Z.; Clark, M.A. Roles of Angiotensin III in the brain and periphery. Peptides 2022, 153, 170802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, R.S. Aminopeptidase N in arterial hypertension. Heart Fail. Rev. 2008, 13, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.Y.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O.; Lee, J.; Mustafa, T.; McDowall, S.G.; Albiston, A.L. Angiotensin AT4 Receptor. In Angiotensin Vol. I. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Unger, T., Schölkens, B.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 163/1. [Google Scholar]
- De Bundel, D.; Smolders, I.; Vanderheyden, P.; Michotte, Y. Ang II and Ang IV: Unraveling the mechanism of action on synaptic plasticity, memory, and epilepsy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.L.; Li, X.C. New insights and perspectives on intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: Focus on intracrine/intracellular angiotensin II. Peptides 2011, 32, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhuo, J.J. Intratubular and intracellular renin-angiotensin system in the kidney: A unifying perspective in blood pressure control. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, F.; Camins, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Bicker, J.; Falcão, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Fortuna, A. Targeting brain Renin-Angiotensin System for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Past, present and future. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, A.; Zouein, F.A.; Zayeri, Z.D.; Zibara, K. An Update on the Tissue Renin Angiotensin System and Its Role in Physiology and Pathology. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Haber, E. The renin-angiotensin system. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 291, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, P.; Wong, P.C.; Chiu, A.T.; Herblin, W.F.; Benfield, P.; Carini, D.J.; Lee, R.J.; Wexler, R.R.; Saye, J.A.; Smith, R.D. Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 205–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davisson, R.L.; Oliverio, M.I.; Coffman, T.M.; Sigmund, C.D. Divergent functions of angiotensin II receptor isoforms in the brain. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, J.; Chiarello, R.; Villar, D.; Kandalam, U.; Castejon, A.M.; Clark, M.A. Regulation of c-fos, c-jun and c-myc gene expression by angiotensin II in primary cultured rat astrocytes: Role of ERK1/2 MAP kinases. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, K.; Ji, H.; Clark, A.J.; Shapira, H.; Catt, K.J. Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9455–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griendling, K.K.; Lassegue, B.; Alexander, R.W. Angiotensin receptors and their therapeutic implications. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, S.S.; Sellers, J.C.; Devor, D.C.; Musgrove, L.C.; Neill, J.D. Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs: Differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 183, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasc, J.M.; Shanmugam, S.; Sibony, M.; Corvol, P. Tissue-specific expression of type 1 angiotensin II receptor subtypes. An in situ hybridization study. Hypertension 1994, 24, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.F.; Uno, S.; Ishihata, A.; Nakamura, N.; Inagamiet, T. Identification of a cis-acting glucocorticoid responsive element in the rat angiotensin II type 1A promoter. Circ. Res. 1995, 77, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparo, M.D.; Catt, K.J.; Inagami, T.; Wright, J.W.; Unger, T. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The Angiotensin II Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 415–472. [Google Scholar]
- Sumners, C.; de Kloet, A.D.; Krause, E.G.; Unger, T.; Steckelings, U.M. Angiotensin type 2 receptors: Blood pressure regulation and end organ damage. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 21, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Sovic, W.; Gill, J.; Ragula, N.; Salem, M.; Hughes, G.J.; Colbert, G.B.; Mooney, J.L. Angiotensin II: A Review of Current Literature. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.S.; Vinh, A.; McCarthy, C.A.; Gaspari, T.A.; Widdop, R.E. AT2 receptors: Functional relevance in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 120, 292–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crackower, M.; Sarao, R.; Oudit, G.; Yagil, C.; Kozieradzki, I.; Scanga, S.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; da Costa, J.; Zhang, L.; Pei, Y.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 2002, 417, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etelvino, G.M.; Peluso, A.A.; Santos, R.A. New components of the renin-angiotensin system: Alamandine and the MAS-related G protein-coupled receptor D. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; Soares, E.; et al. Discovery and characterization of alamandine: A novel component of the renin-angiotensin system. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M. Newly discovered components and actions of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 2013, 62, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenak, J.; Paulis, L.; Simko, F. Angiotensin A/Alamandine/MrgD Axis: Another Clue to Understanding Cardiovascular Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Smolders, I.; Vanderheyden, P.; Demaegdt, H.; van Eeckhaut, A.; Vauquelin, G.; Lukaszuk, A.; Tourwe, D.; Chai, S.; Albiston, A.; et al. Pressor and renal hemodynamic effects of the novel angiotensin A peptide are angiotensin II type 1A receptor dependent. Hypertension 2011, 57, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiyakare, B.; Alsaadon, H.; Mathai, M.L.; Hayes, A.; Zulli, A. Reduction of angiotensin A and alamandine vasoactivity in the rabbit model of atherogenesis: Differential effects of alamandine and Ang (1-7). Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 95, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, V.; Vanholder, R.; van der Giet, M.; Tölle, M.; Karadogan, S.; Gobom, J.; Furkert, J.; Oksche, A.; Krause, E.; Tran, T.N.A.; et al. Mass-spectrometric identification of a novel angiotensin peptide in human plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, Z.T.; Ribiczey, P.; Kató, E.; Tóth, Z.E.; Varga, Z.V.; Giricz, Z.; Hanuska, A.; Al-Khrasani, M.; Zsembery, A.; Telles, T.; et al. Angiotensin IV Receptors in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex: Neuronal Expression and NMDA Inhibition. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.; Delarue, F.; Burcklé, C.; Bouzhir, L.; Giller, T.; Sraer, J.D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nádasy, G.L.; Balla, A.; Dörnyei, G.; Hunyady, L.; Szekeres, M. Direct Vascular Effects of Angiotensin II (A Systematic Short Review). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C.; Zheng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhuo, J.l. Genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanska-Sadowska, E.; Czarzasta, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A. Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System and the Vasopressinergic System Interactions in Cardiovascular Disorders. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Zaballos, S.; Martínez-Sellés, M. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Heart Failure. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, A.; Zibara, K. Efficiency and specificity of RAAS inhibitors in cardiovascular diseases: How to achieve better end-organ protection? Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Differential mechanisms of angiotensin II and PDGF-BB on migration and proliferation of coronary artery smooth muscle cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 45, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McBean, G.J. Cysteine, Glutathione, and Thiol Redox Balance in Astrocytes. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.A.; Bayraktutan, U.; Young, I.S.; Soong, C.V. N-acetylcysteine does not improve the endothelial and smooth muscle function in the human saphenous vein. Vasc. Endovasc. Sur. 2007, 41, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktutan, U. Free radicals, diabetes and endothelial dysfunction. Diabet. Obes. Metabol. 2002, 4, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmesser, U.; Dikalov, S.; Price, S.R.; McCann, L.; Fukai, T.; Holland, S.M.; Mitch, W.E.; Harrison, D.G. Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to uncoupling of endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase in hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktutan, U. Reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide and hypertensive endothelial dysfunction. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2005, 1, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Change of telomere length in angiotensin II-induced human glomerular mesangial cell senescence and the protective role of losartan. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, K.; Cicalese, S.; Elliott, K.J.; Kawai, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Eguchi, S. Targeting molecular mechanism of vascular smooth muscle senescence induced by angiotensin II, a potential therapy via senolytics and senomorphics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. The oxidative damage theory of aging. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liu, J.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Yang, P.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin/RAS signaling mediates age-related renal fibrosis and is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.M.; Griendling, K.K. NADPH oxidases and angiotensin II receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, N.; Paglia, N.; Stella, I.; de Cavanagh, E.M.; Ferder, L.; del Rosario, A.M.; Inserra, F. Protective effect of the inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system on aging. Regul. Pept. 2005, 128, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, R.R.; Alwjwaj, M.; Othman, A.O.; Rakkar, K.; Sprigg, N.; Bath, P.M.; Bayraktutan, U. Inhibition of oxidative stress delays senescence and augments functional capacity of endothelial progenitor cells. Brain Res. 2022, 1787, 147925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ya, J.; Kadir, R.R.; Bayraktutan, U. Delay of endothelial cell senescence protects cerebral barrier against age-related dysfunction: Role of senolytics and senomorphics. Tissue Barriers 2023, 11, 2103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ya, J.; Bayraktutan, U. Senolytics and Senomorphics Targeting p38MAPK/NF-κB Pathway Protect Endothelial Cells from Oxidative Stress-Mediated Premature Senescence. Cells 2024, 13, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.M.; Bartholomew, J.; Campisi, J.; Acosta, M.; Reagan, J.D.; Ames, B.N. Molecular analysis of H2O2-induced senescent-like growth arrest in normal human fibroblasts: p53 and Rb control G1 arrest but not cell replication. Biochem. J. 1998, 332, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Ge, W. Kaempferol prevents against Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling through attenuating Ang II-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 74, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feresin, R.G.; Huang, J.; Klarich, D.S.; Zhao, Y.; Pourafshar, S.; Arjmandi, B.H.; Salazar, G. Blackberry, raspberry and black raspberry polyphenol extracts attenuate angiotensin II-induced senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4175–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, N.; Imai, E.; Karber, A.; Welch, W.J.; Wilcox, C.S. A Mouse Model of Angiotensin II Slow Pressor Response: Role of Oxidative Stress. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Schmidt, M.O.; Kallakury, B.; Jain, S.; Mehdikhani, S.; Levi, M.; Mendonca, M.; Welch, W.; Riegel, A.T.; Wilcox, C.S.; et al. Low Dose Chronic Angiotensin II Induces Selective Senescence of Kidney Endothelial Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 782841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cavanagh, E.M.; Inserra, F.; Ferder, L. Angiotensin II blockade: A strategy to slow ageing by protecting mitochondria? Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, B.; Guan, Y.; Chien, S.; Wang, N. Klotho is a target gene of PPARgamma. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.J.; Mogi, M.; Tamura, K.; Iwanami, J.; Sakata, A.; Fujita, T.; Tsukuda, K.; Jing, F.; Iwai, M.; Horiuchi, M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein prevents vascular smooth muscle cell senescence via inactivation of calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2009, 47, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benigni, A.; Corna, D.; Zoja, C.; Sonzogni, A.; Latini, R.; Salio, M.; Conti, S.; Rottoli, D.; Longaretti, L.; Cassis, P.; et al. Disruption of the Ang II type 1 receptor promotes longevity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, B.J.; Sinclair, D.A. The intersection between aging and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, P.E.; Ferrario, C.M.; Tallant, E.A. Regulation of ACE2 in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H2373–H2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.W.; von Eckardstein, A. Androgens and coronary artery disease. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 183–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, M.E.; Karas, R.H. Molecular and cellular basis of cardiovascular gender differences. Science 2005, 308, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Bharadwaj, D.; Prasad, G.; Grechko, A.V.; Sazonova, M.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Renin-Angiotensin System in Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis and Treatment of CVD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, K.; Hernandez, W.; Ansari, R.A.; Ferder, L. Inflammation, oxidative stress and renin angiotensin system in atherosclerosis. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; El Mabrouk, M.; He, G.; Wu, X.H.; Schiffrin, E.L. Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition attenuates Ang II-mediated signaling and contraction in SHR vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Lehtonen, J.Y.; Daviet, L. Signaling mechanism of the AT2 receptor: Crosstalk between AT1 and AT2 receptors in cell growth. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 10, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifune, M.; Sasamura, H.; Shimuzu-Hirota, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Saruta, T. Angiotensin II type 2 receptors stimulate collagen synthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 2000, 36, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschina, E.; Lauer, D.; Lange, C.; Unger, T. Angiotensin AT2 receptors reduce inflammation and fibrosis in cardiovascular remodelling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktutan, U. Effects of angiotensin II on nitric oxide generation in growing and resting rat aortic endothelial cells. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktutan, U.; Ulker, S. Effects of angiotensin II on nitric oxide generation in proliferating and quiescent rat coronary microvascular endothelial cells. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, B.; McKeown, P.P.; Bayraktutan, U. Blockade of angiotensin II provides additional benefits in hypertension- and ageing-related cardiac and vascular dysfunctions beyond its blood pressure-lowering effects. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktutan, U.; Yang, Z.K.; Shah, A.M. Selective dysregulation of nitric oxide synthase type 3 in cardiac myocytes but not coronary microvascular endothelial cells of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searles, C.D.; Miwa, Y.; Harrison, D.G.; Ramasamy, S. Posttranscriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase during cell growth. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, N. Endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by angiotensin II and histamine in isolated arteries of dog. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 81, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Lazos, S.A.; Tong, K. Ang II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siragy, H.M.; Gasparo, M.; Carey, R.M. Angiotensin type 2 receptor mediates valsartan-induced hypotension in conscious rats. Hypertension 2000, 35, 1074–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohlke, P.; Pees, C.; Unger, T. AT2 receptor stimulation increases aortic cyclic GMP in SHRSP by a kinin-dependent mechanism. Hypertension 1998, 31, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, V.S.; Campbell, M.; McKeown, P.P.; Bayraktutan, U. Internal mammary artery smooth muscle cells resist migration and possess high antioxidant capacity. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 72, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holvoet, P.; Collen, D. Thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1997, 8, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzau, V.J.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Sedding, D.G. Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: New perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulker, S.; McMaster, D.; McKeown, P.P.; Bayraktutan, U. Impaired activities of antioxidant enzymes elicit endothelial dysfunction in spontaneous hypertensive rats despite enhanced vascular nitric oxide generation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Antioxidants attenuate hyperglycaemia-mediated brain endothelial cell dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability. Diabet. Obes. Metabol. 2009, 11, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 1998, 279, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktutan, U.; Blayney, L.; Shah, A.M. Molecular Characterization and Localization of the NAD(P)H Oxidase Components gp91-phox and p22-phox in Endothelial Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktutan, U.; Draper, N.; Lang, D.; Shah, A.M. Expression of a functional neutrophil-type NADPH oxidase in cultured rat coronary microvascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktutan, U. Nitric oxide synthase and NAD(P)H oxidase modulate coronary endothelial cell growth. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 36, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, A.; Cassis, P.; Remuzzi, G. Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catt, K.J.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cain, M.D.; Cran, E.; Best, J.B.; Coghlan, J.P. Angiotensin II Blood-levels in Human Hypertension. Lancet 1971, 297, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papademetriou, V. The potential role of AT1-receptor blockade in the prevention and reversal of atherosclerosis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, S34–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, J.T.; Sauer, W.H.; Berlin, J.A.; Kimmel, S.E. Comparison of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in the primary prevention of myocardial infarction in hypertensive patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, F.; Li, X.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on All-Cause Mortality, Cardiovascular Deaths, and Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todor, S.; Bîrluțiu, V.; Topîrcean, D.; Mihăilă, R. Role of biological markers and CT severity score in predicting mortality in patients with COVID-19: An observational retrospective study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Michel, T.; MvMurray, J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Solomon, S.D. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.D.; Coffman, T.M. Recent advances involving the renin-angiotensin system. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayraktutan, U. Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Pathogenic and Protective Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070501
Bayraktutan U. Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Pathogenic and Protective Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070501
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayraktutan, Ulvi. 2025. "Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Pathogenic and Protective Pathways" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070501
APA StyleBayraktutan, U. (2025). Angiotensin II and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Pathogenic and Protective Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070501





