Leech Extract Enhances the Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
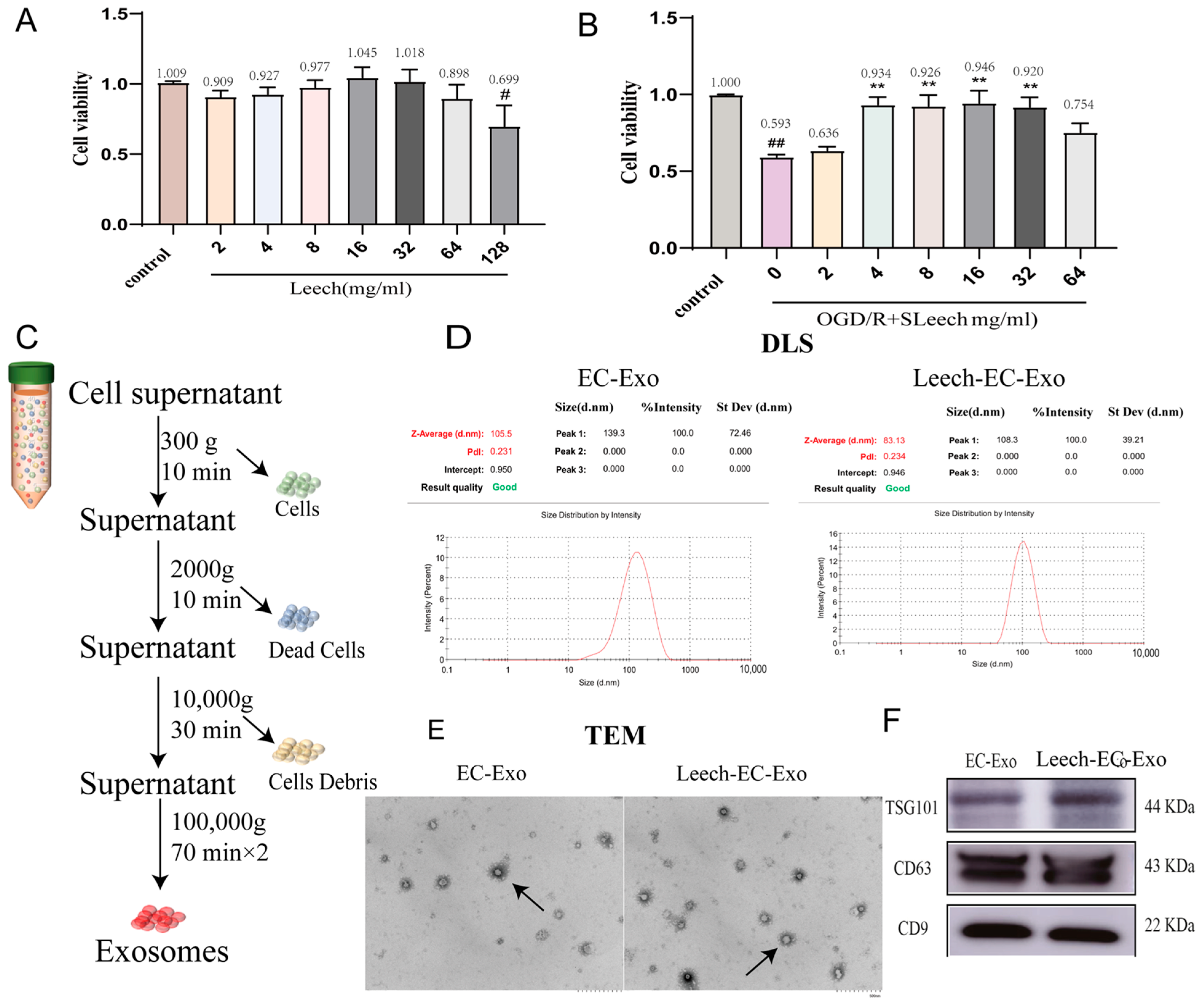
2.1. Extraction and Identification of EC-Exo
2.1.1. Extraction of EC-Exo
2.1.2. Identification of EC-Exo
2.2. In Vitro Experiments
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Cell Grouping and Drug Administration
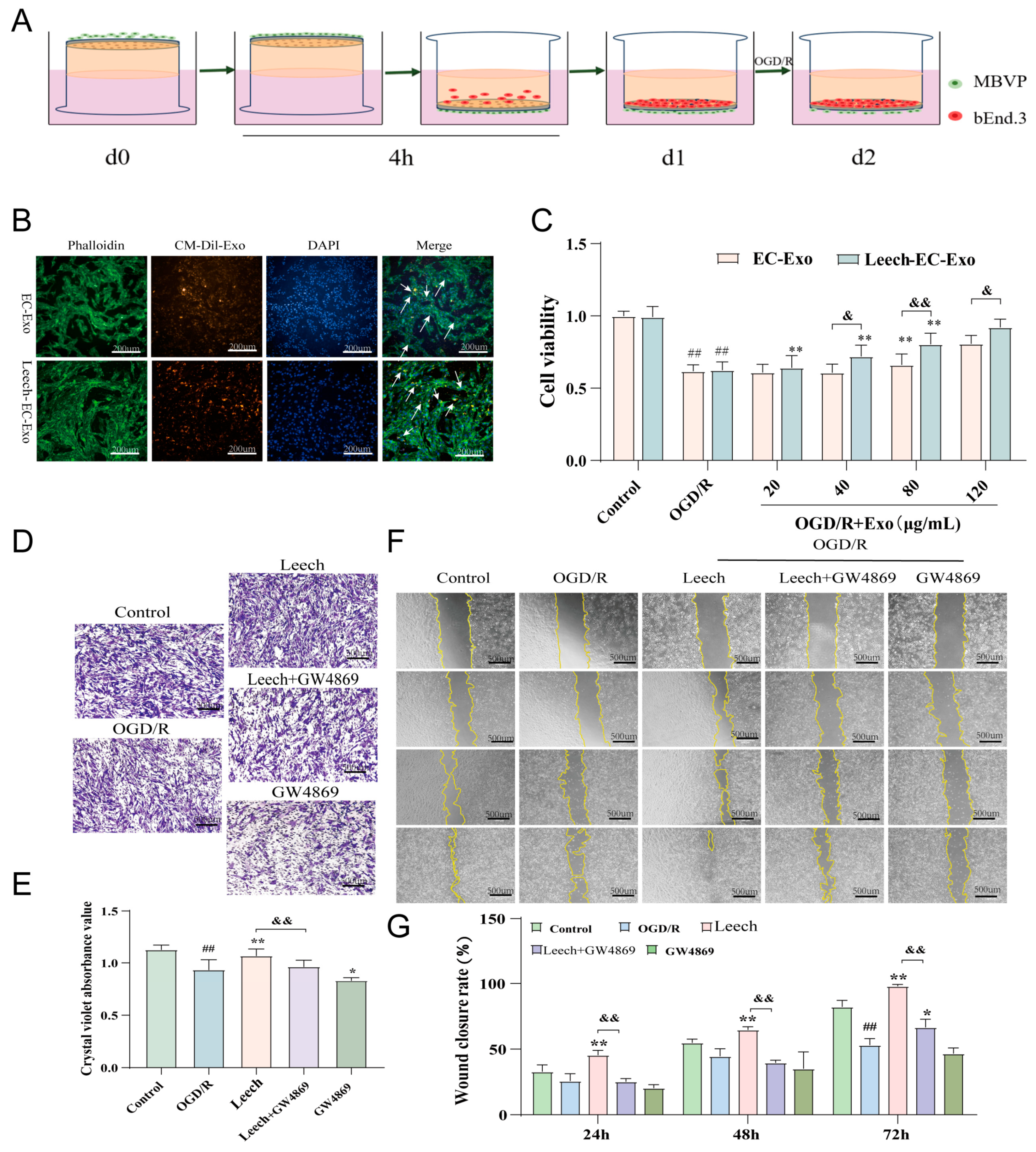
2.2.3. Cells Viability Assays
2.2.4. Assessment of Uptake Capacity of MBVP Uptake to EC-Exo
2.2.5. Transwell Experiments
2.2.6. Cell Scratch Assays
2.3. In Vivo Experiments
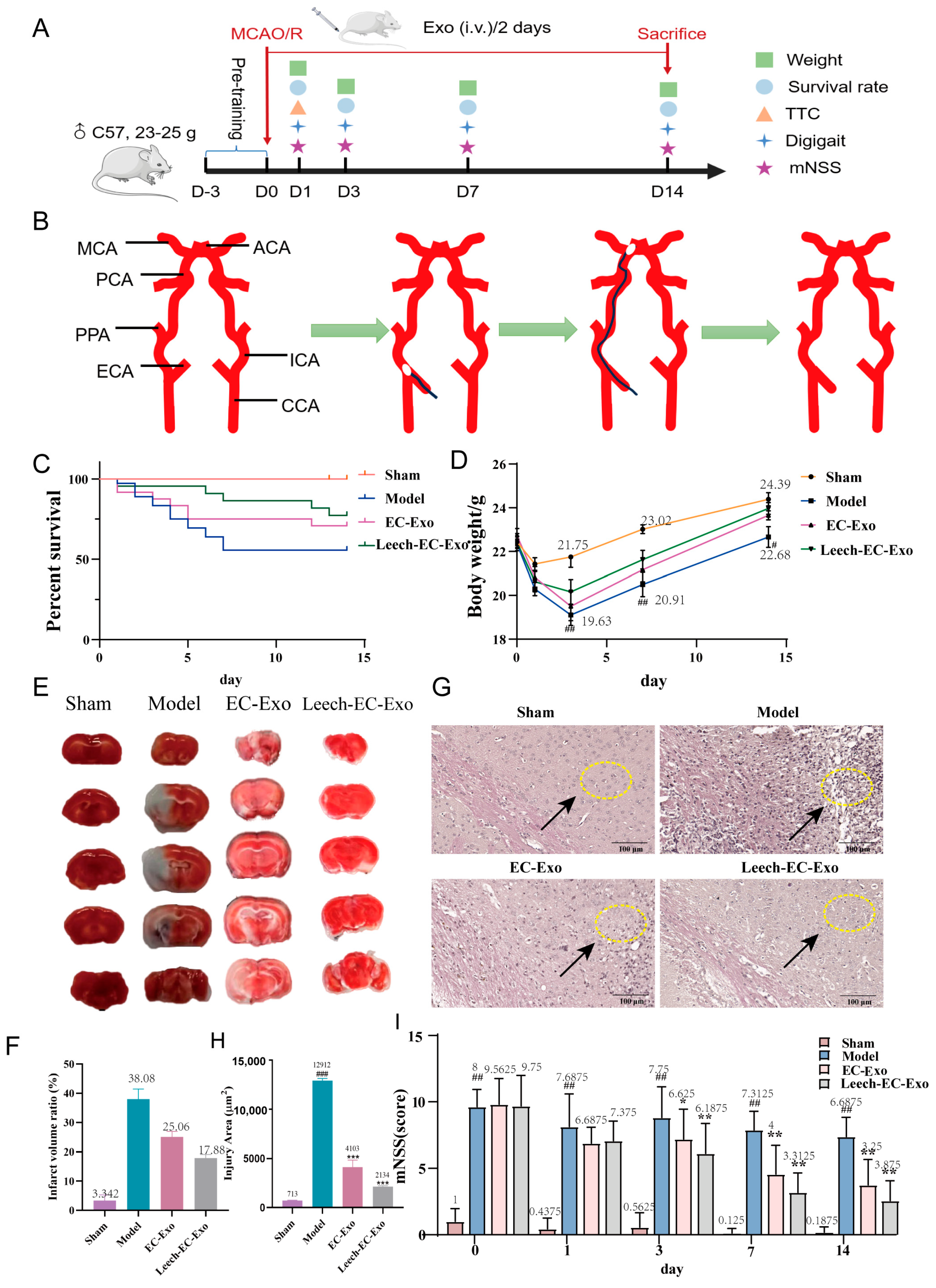
2.3.1. Animals
2.3.2. Establishment of Mouse MCAO/R Model and Leech Treatment
2.3.3. Animal Euthanasia and Organ Collection
2.3.4. Modified Neurological Severity Score (mNSS)
- (1)
- Motion test
- ①
- Tail suspension test:
- 0 points for balancing;
- 1 point for the flexion of a contralateral forelimb;
- 2 points for the flexion of a contralateral hind limb;
- 3 points for head turns away from the vertical axis by more than 10° within 30 s.
- ②
- Walking test:
- 0 points for going straight normally;
- 1 point for not being able to go straight normally;
- 2 points for turning to the same side;
- 3 points for falling on the same side as the paraplegia.
- (2)
- Sensation test:
- ①
- Placement test—mouse placed on the edge of the table:
- 0 points for forelimbs on the table;
- 1 point for no forelimbs on the table.
- ②
- Proprioception test—mouse pushed to the edge of the table:
- 0 points for resisting with the opposite forelimb;
- 1 point for no resistance.
- (3)
- Balance test—mouse placed on wooden strips with a width of 0.6 cm, height of 1.2 cm, and length of 120 cm:
- 0 points for keeping static balance for greater than 60 s;
- 1 point for grasping the edge of the balance beam tightly;
- 2 points for holding the balance beam tightly and one limb sliding off the balance beam;
- 3 points for holding the balance beam and two limbs sliding down or trying to keep balance for more than 60 s;
- 4 points for holding the balance beam and two limbs sliding down or trying to keep balance for 40 ~ 59 s and then falling down;
- 5 points for holding the balance beam and two limbs sliding down or trying to keep balance for 20 ~ 39 s and then falling down;
- 6 points for falling off the balance beam in less than 20 s or not trying to keep balance.
- (4)
- Reflection test
- ①
- Auricular reflex—touch the external auditory canal of mouse with a cotton swab:
- 0 points for shaking head;
- 1 point for not shaking.
- ②
- Corneal reflex—touch the cornea with cotton:
- 0 points for blinking;
- 1 point for not blinking.
- ③
- Panic reflex—make a noise using fast-elastic cardboard:
- 0 points for jumping;
- 1 point for not jumping.
- (5)
- Abnormal movement: 1 point for dystonia after epilepsy and myoclonia.
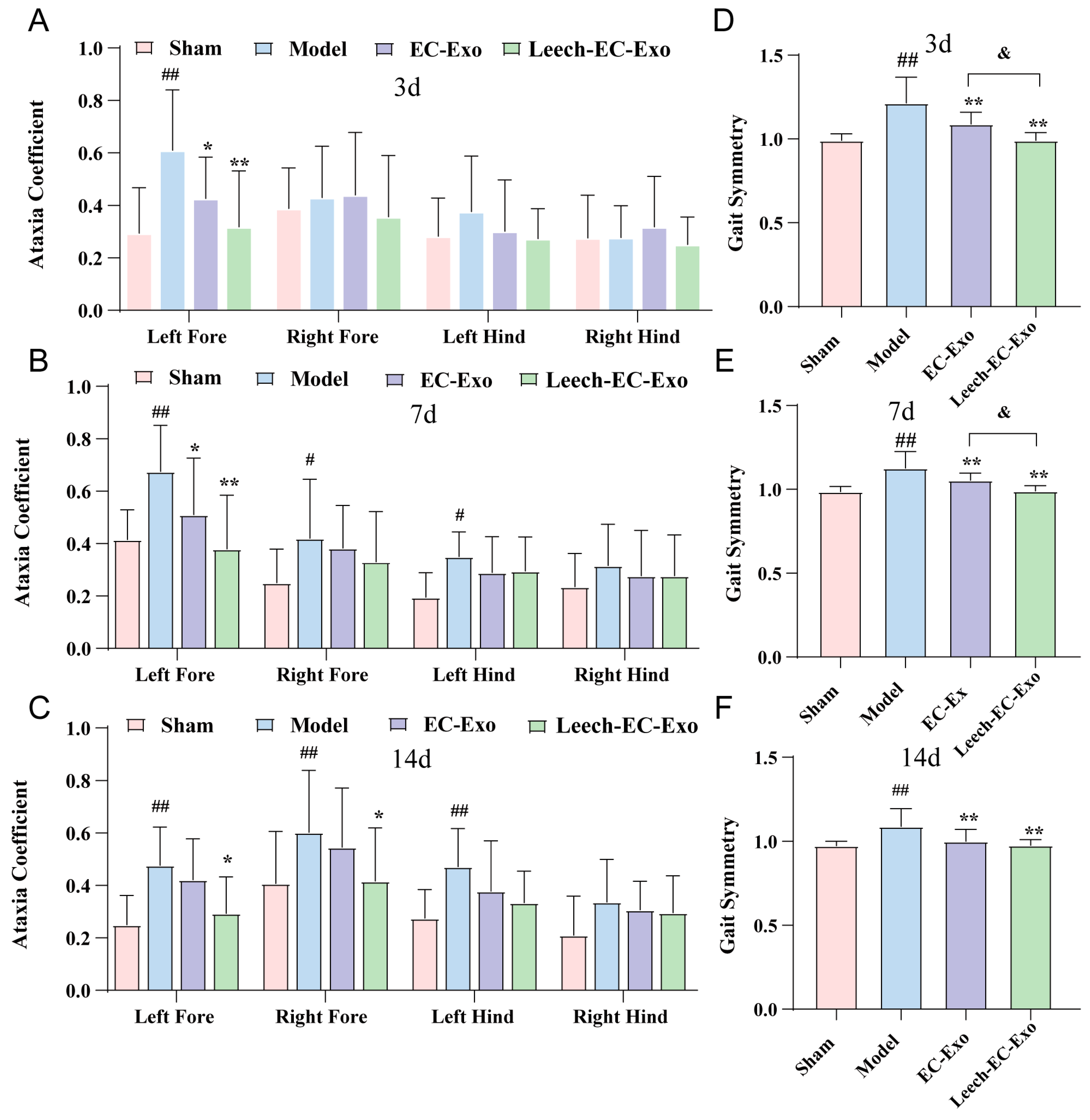
2.3.5. Gait Analysis
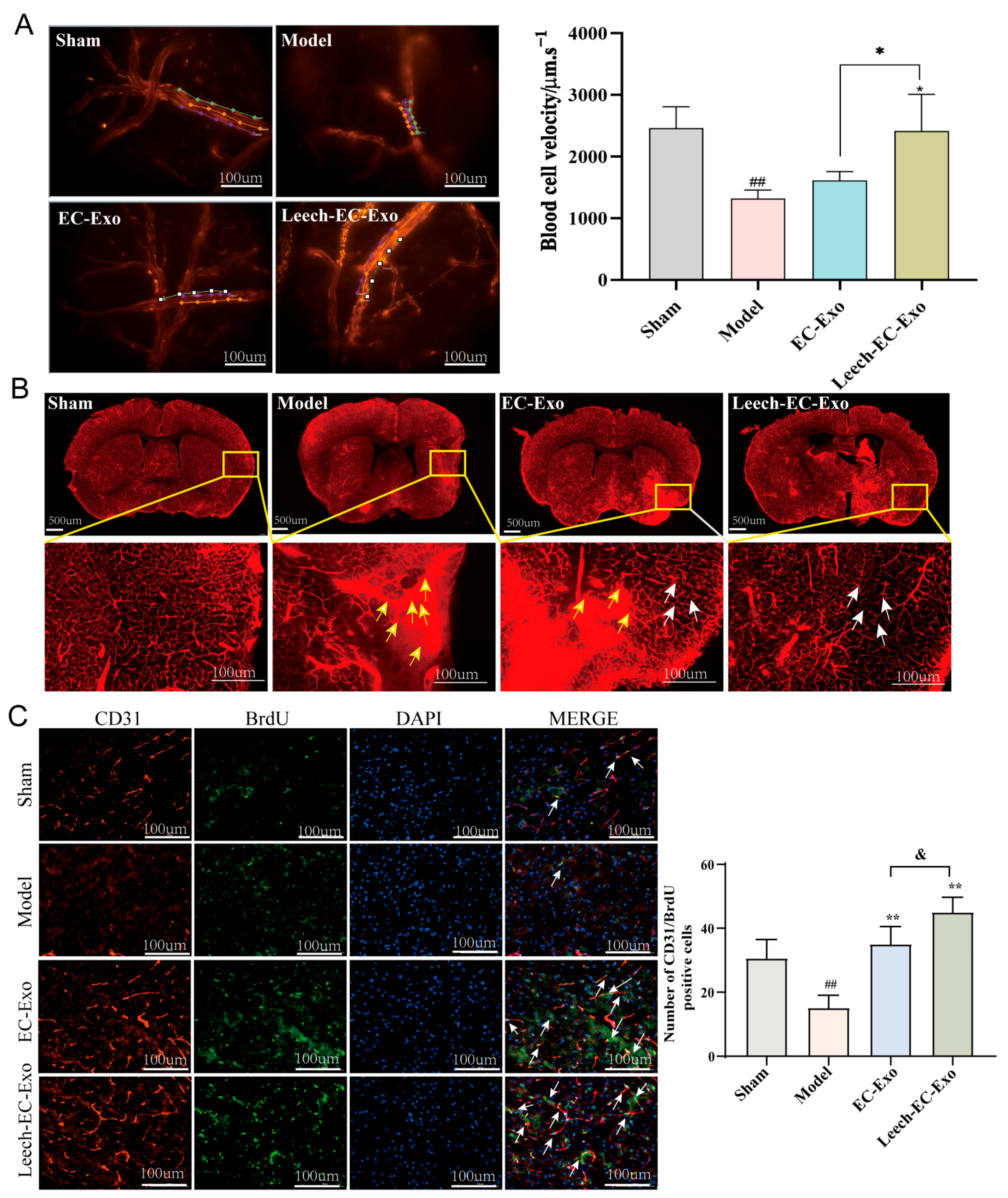
2.3.6. Observation of Velocity of Erythrocytes in Microvessels
2.3.7. TTC Staining
2.3.8. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.3.9. Observation of Capillary Density
2.3.10. Immunofluorescence Staining
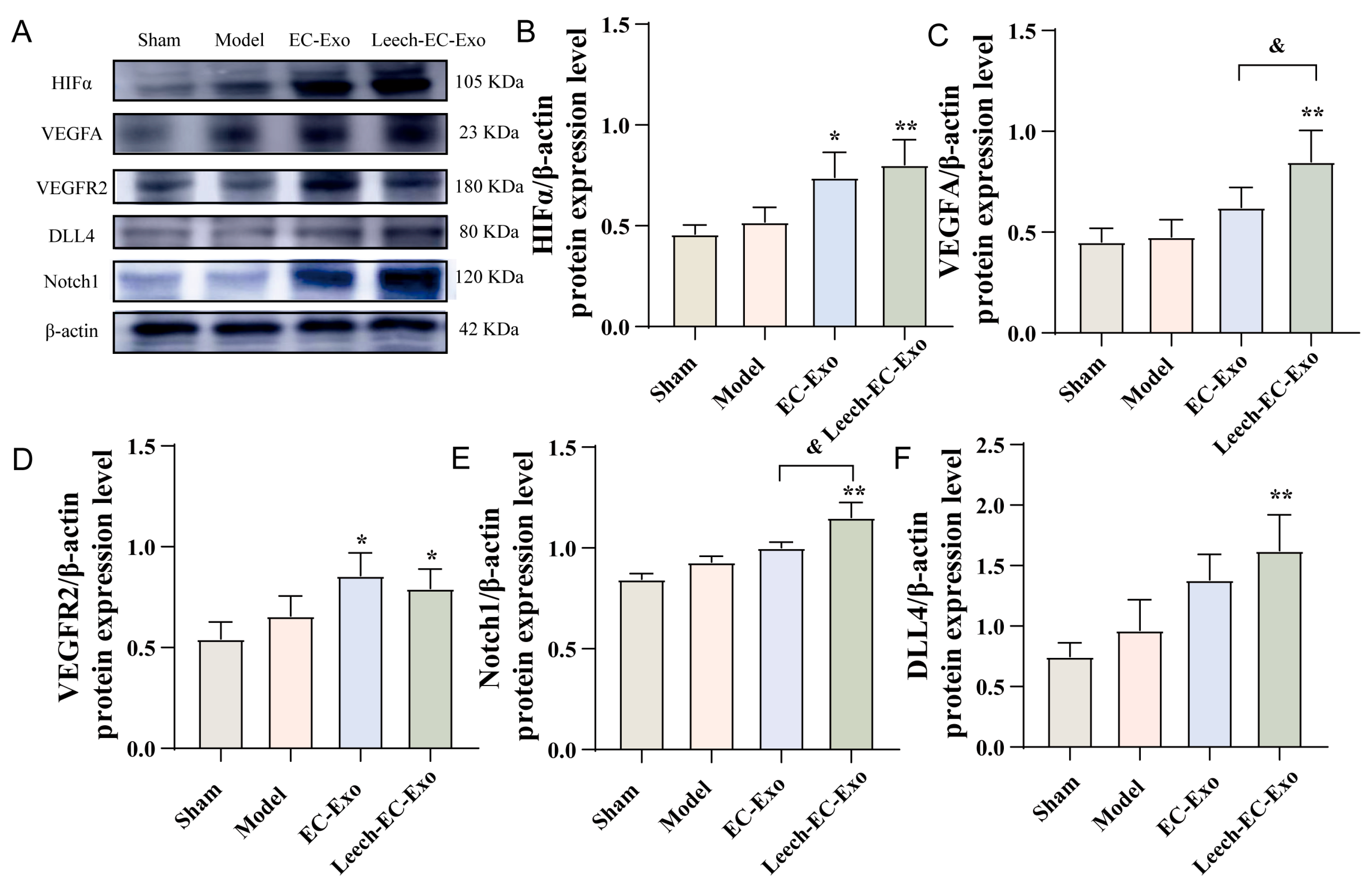
2.3.11. Western Blotting Analysis
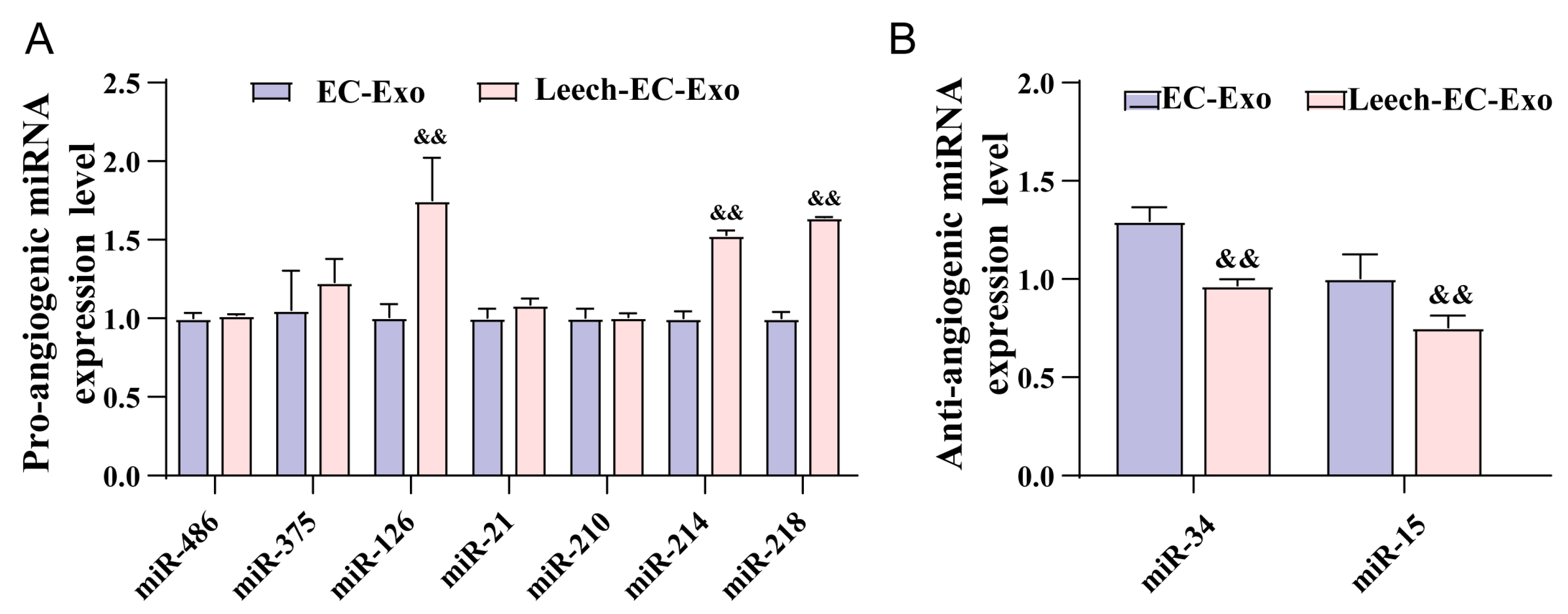
2.3.12. Real-Time PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Exosomes
3.2. Leech Enhances the Efficacy of EC-Exo in Facilitating the Proliferation and Migration of Pericytes
3.3. Leech Enhances the Efficacy of EC-Exo in Improving Pathology in MCAO/R Mice
3.4. Leech Enhances the Efficacy of EC-Exo in Improving Motor Function in MCAO/R Mice
3.5. Leech Enhances the Efficacy of EC-Exo in Promoting Collateral Circulation Establishment in MCAO/R Mice
3.6. Leech Modulates the Impact of EC-Exo on the HIFα-VEGF-DLL4-Notch1 Signaling Pathway in MCAO/R Mice
3.7. Leech Regulates the Species and Quantity of Angiogenesis-Related miRNA in EC-Exo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Exo | Exosome |
| EC | Endothelial cell |
| IS | Ischemic stroke |
| MBVP | Mouse brain microvascular pericyte |
| MCAO/R | Middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion |
| tPA | Tissue plasminogen activator |
| OGD/R | Oxygen–glucose deprivation/reoxygenation |
| mNSS | Modified neurological severity score |
| WB | Western blotting |
| MWCO | Molecular weight cut-off |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light-scattering particle |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| CCA | Carotid artery |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| ECA | External carotid artery |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| H&E | Hematoxylin–eosin staining |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
References
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Khatri, P. Stroke. Lancet 2020, 396, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1767–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ni, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B. Application of Nanozymes and its Progress in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2024, 15, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Su, P.W.; Ma, L.Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Fei, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Ma, K.; Han, B.B.; et al. Progress on traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of ischemic stroke via the gut-brain axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthels, D.; Das, H. Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, T.; Asai, T.; Yanagida, Y.; Namba, M.; Koide, H.; Shimizu, K.; Oku, N. Combination therapy with liposomal neuroprotectants and tissue plasminogen activator for treatment of ischemic stroke. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1879–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmeier, L.; Kniep, H.; Thomalla, G.; Bendszus, M.; Subtil, F.; Bonekamp, S.; Aamodt, A.H.; Fuentes, B.; Gizewski, E.R.; Hill, M.D.; et al. Arterial Collaterals and Endovascular Treatment Effect in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Infarct: A Secondary Analysis of the TENSION Trial. Radiology 2025, 314, e242401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, J.W.; Jeon, Y.S.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, T.J.; Jung, Y.J.; et al. Multiphase MR Angiography Collateral Map: Functional Outcome after Acute Anterior Circulation Ischemic Stroke. Radiology 2020, 295, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, S.; et al. Predicting Futile Recanalization by Cerebral Collateral Recycle Status in Patients with Endovascular Stroke Treatment: The CHANOA Score. Acad. Radiol. 2025, 32, 2876–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kweon, J.Y.; Choi, S.; Jeon, H.; Sung, M.; Gao, R.; Liu, C.; Kim, C.; Ahn, Y.J. Non-Invasive Photoacoustic Cerebrovascular Monitoring of Early-Stage Ischemic Strokes In Vivo. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2409361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguida, G.; Shuaib, A. Collateral Circulation in Ischemic Stroke: An Updated Review. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Miao, C.-Y. Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, R.; Tan, J.L.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.F.; Ma, L.; Shi, S. Mechanism of disturbed endothelial cell function on angiogenesis following ischemic brain stroke (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2025, 29, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Liao, W.; Qiu, W.; Luo, G.; Wang, J. Large vessel occlusion identification network with vessel guidance and asymmetry learning on CT angiography of acute ischemic stroke patients. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 101, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrullo, V.; Matos, R.S.; McVey, J.H.; Gupta, P.; Madeddu, P.; Johnston, J.D.; Van Der Veen, D.R.; Velliou, E.G.; Campagnolo, P. The vascular clock: A new insight into endothelial cells and pericytes crosstalk. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, J.; Ding, P.; Gao, Y. The role of endothelial cell-pericyte interactions in vascularization and diseases. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 67, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, Z.; Peshkova, M.; Gonen, Z.B.; Coretchi, I.; Eken, A.; Yay, A.H.; Dogan, M.E.; Gokce, N.; Akalin, H.; Kosheleva, N.; et al. EVs vs. EVs: MSCs and Tregs as a source of invisible possibilities. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 101, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardpour, S.; Hassani, S.N.; Mardpour, S.; Sayahpour, F.; Vosough, M.; Ai, J.; Aghdami, N.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Baharvand, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from human embryonic stem cell-MSCs ameliorate cirrhosis in thioacetamide-induced chronic liver injury. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 9330–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Tian, L.; Guo, B.; Dai, T.; Lv, Q.; Xie, J.; Liu, F.; Bao, H.; Cao, F.; et al. Exosome-capturing scaffold promotes endogenous bone regeneration through neutrophil-derived exosomes by enhancing fast vascularization. Biomaterials 2025, 319, 123215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, H.; Mohit, E.; Namazi, I.; Rajabi, S.; Samadian, A.; Hajizadeh-Saffar, E.; Aghdami, N.; Baharvand, H. Exosomes secreted by hypoxic cardiosphere-derived cells enhance tube formation and increase pro-angiogenic miRNA. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 4150–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zou, W.; Yu, X.; Liang, H. Research Progress of Leech Anticoagulant Components in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 41, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, J.E.; Zhang, H.; Lassance-Soares, R.M.; Prabhakar, P.; Najafi, A.H.; Burnett, M.S.; Epstein, S.E. Aging causes collateral rarefaction and increased severity of ischemic injury in multiple tissues. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Pharmacological Action of Shuizhi (Leech) and Its Application in Encephalopathy. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 42, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, D.; Lu, J.; Cui, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Z.; Lv, Z.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Mechanism of Hirudo in Treatment of Stroke: A Review. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2023, 29, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, S. Research progress on the mechanism of leech in treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. China Med. Herald. 2021, 18, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, Q.; Guo, L.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, T.; Liang, B.; Yao, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, L. Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes Protect Neurons from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Pu, J.; Chen, Y.; Mao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, B.; Zhang, B. Plasma Exosomes Spread and Cluster Around β-Amyloid Plaques in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; You, S.; Ding, X.; Luan, P.; Xu, J.; Cui, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Protective effect and underlying mechanism of muscone on acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 308, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, L.; Dygert, L.; Toborek, M. Induction of Ischemic Stroke and Ischemia-reperfusion in Mice Using the Middle Artery Occlusion Technique and Visualization of Infarct Area. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, e54805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayev, L.; Alonso, O.F.; Busto, R.; Zhao, W.; Ginsberg, M.D. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke 1996, 27, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.Y. Therapeutic application of exosomes in ischaemic stroke. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, B.; Sun, C.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, D. Vascular Endothelial Cell-derived Exosomes Protect Neural Stem Cells Against Ischemia/reperfusion Injury. Neuroscience 2020, 441, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jung, J.H.; Arvola, O.; Santoso, M.R.; Giffard, R.G.; Yang, P.C.; Stary, C.M. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Protect Astrocyte Cultures From in vitro Ischemia and Decrease Injury as Post-stroke Intravenous Therapy. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Smith, E.E.; Reeves, M.J.; Grau-Sepulveda, M.V.; Pan, W.; Olson, D.M.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Schwamm, L.H. Time to treatment with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator and outcome from acute ischemic stroke. JAMA 2013, 309, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, M. Combining Human Umbilical Cord Blood Cells With Erythropoietin Enhances Angiogenesis/Neurogenesis and Behavioral Recovery After Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, M.; Willing, A.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, J.; Chopp, M. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, M.; Cromie, M.; Chacon, R.; Blonigan, J.; Garcia, V.; Akimenko, I.; Hamer, M.; Paine, P.; Stok, M.; Shrager, J.B.; et al. Bioengineered constructs combined with exercise enhance stem cell-mediated treatment of volumetric muscle loss. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, P.; Cui, C.; Chopp, M.; Zacharek, A.; Wang, F.; Landschoot-Ward, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, J. MiR-126 Mediates Brain Endothelial Cell Exosome Treatment-Induced Neurorestorative Effects After Stroke in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice. Stroke 2019, 50, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Xi, X.; Tan, N.; Zhang, L. SNHG12 Promotes Angiogenesis Following Ischemic Stroke via Regulating miR-150/VEGF Pathway. Neuroscience 2018, 390, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.; Jeong, H.U.; Choi, J.G.; Jeon, S.G.; Song, E.J.; Hong, S.P.; Oh, M.S. Memory-enhancing effects of Cuscuta japonica Choisy via enhancement of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 311, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, X. Chrysophanol protects PC12 cells against oxygen glucose deprivation-evoked injury by up-regulating miR-216a. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayajiki, K.; Kobuchi, S.; Tawa, M.; Okamura, T. Nitrergic nerves derived from the pterygopalatine ganglion innervate arteries irrigating the cerebrum but not the cerebellum and brain stem in monkeys. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, J.E.; Santoro, M.M.; Morton, S.U.; Yu, S.; Yeh, R.F.; Wythe, J.D.; Ivey, K.N.; Bruneau, B.G.; Stainier, D.Y.; Srivastava, D. miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Moderate exercise has beneficial effects on mouse ischemic stroke by enhancing the functions of circulating endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 330, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanaro, P.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Di Stefano, V.; Melchionna, R.; Romani, S.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15878–15883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wen, H.; Huang, J.; Liao, P.; Liao, H.; Tu, J.; Zeng, Y. Extracellular vesicle-enclosed miR-486-5p mediates wound healing with adipose-derived stem cells by promoting angiogenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9590–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.C.; Tien, Y.J.; Wen, C.J.; Yeh, T.S.; Yu, M.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yen, T.C.; Hsieh, S.Y. MicroRNA-214 downregulation contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Cui, H.; Li, Q.; Zhong, H.; Yu, J.; Li, P.; He, X. Upregulation of microRNA-218 reduces cardiac microvascular endothelial cells injury induced by coronary artery disease through the inhibition of HMGB1. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 3079–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Lin, Y.W.; Huang, P.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Tseng, S.Y.; Chao, T.H.; Chen, Z.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Hong, C.S. Deletion of MicroRNA-21 Impairs Neovascularization Following Limb Ischemia: From Bedside to Bench. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 826478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Qu, P.; Wu, H.; Liu, P.; Luo, J.; Chi, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, C. Circulating exosomal miR-21 mediates HUVEC proliferation and migration through PTEN/PI3K/AKT in Crohn’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.G.; Jamaiyar, A.; Sausen, G.; Cheng, H.S.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Zhuang, R.; Chen, J.; Goodney, P.P.; Creager, M.A.; Sabatine, M.S.; et al. MicroRNA-375 repression of Kruppel-like factor 5 improves angiogenesis in diabetic critical limb ischemia. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Balkom, B.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Smits, M.; Brummelman, J.; den Ouden, K.; de Bree, P.M.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Pegtel, D.M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Würdinger, T.; et al. Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3997–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Xiao, H.; Bai, X.; Zou, Y.; Hu, W.; Lin, X.; Zhu, C.; Liang, Y.; Xiong, W. Astragaloside IV drug-loaded exosomes (AS-IV EXOs) derived from endothelial progenitor cells improve the viability and tube formation in high-glucose impaired human endothelial cells by promoting miR-214 expression. Endokrynol. Pol. 2022, 73, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xie, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhang, A. MicroRNA-214 targets COX-2 to antagonize indoxyl sulfate (IS)-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y. miR-214 Protects Against Uric Acid-Induced Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, J.; Chen, A.F. MicroRNA-34a induces endothelial progenitor cell senescence and impedes its angiogenesis via suppressing silent information regulator 1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E110–E116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhan, T.; Tao, J.; Xu, B.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, G.; Lin, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-34a induces transdifferentiation of glioma stem cells into vascular endothelial cells by targeting Notch pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Jin, Y.; Song, H.; Chen, X. MicroRNA-34a attenuates VEGF-mediated retinal angiogenesis via targeting Notch1. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, T.; Tao, W.; Xu, F.; Yang, H.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; et al. MicroRNA-15b Targets VEGF and Inhibits Angiogenesis in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 3404–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bennett, S.; Kuek, V.; Xiang, C.; Xu, H.; Rosen, V.; Xu, J. Endothelial cells produce angiocrine factors to regulate bone and cartilage via versatile mechanisms. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ahmad, A.; Taboada, C.B.; Gassmann, M.; Ogunshola, O.O. Astrocytes and pericytes differentially modulate blood-brain barrier characteristics during development and hypoxic insult. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2011, 31, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.D.; Winkler, E.A.; Sagare, A.P.; Singh, I.; LaRue, B.; Deane, R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes Control Key Neurovascular Functions and Neuronal Phenotype in the Adult Brain and during Brain Aging. Neuron 2023, 111, 3131–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Betsholtz, C. Pericytes: Developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Mäe, M.; Nisancioglu, M.H.; Wallgard, E.; Niaudet, C.; He, L.; Norlin, J.; Lindblom, P.; Strittmatter, K.; et al. Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature 2010, 468, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Kebede, A.A.; Barres, B.A. Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 2010, 468, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; Goyal, M.; Liebeskind, D.S. Collateral Circulation in Ischemic Stroke: Assessment Tools and Therapeutic Strategies. Stroke 2015, 46, 3302–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Pruthviraja, D.; Gupta, A.; Mathew, J.; Kannath, S.K.; Prakash, A.; Rajan, J. Multilevel Multimodal Framework for Automatic Collateral Scoring in Brain Stroke. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 33730–33748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruani, A.; Obadia, M.; Fontaine, L.; Savatovsky, J.; Albucher, J.F.; Calviere, L.; Raposo, N.; Cognard, C.; Viguier, A.; Albers, G.W.; et al. Hypoperfusion intensity ratio to differentiate between stroke etiologies in patients with a large vessel occlusion. Eur. Stroke J. 2024, 23969873241306264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; et al. Impact of cerebral collateral recycle status on clinical outcomes in elderly patients with endovascular stroke treatment. J. Neuroradiol. 2025, 52, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Torbey, M.T. Angiogenesis and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Vascular Remodeling after Stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walshe, T.E.; Connell, P.; Cryan, L.; Ferguson, G.; Gardiner, T.; Morrow, D.; Redmond, E.M.; O’Brien, C.; Cahill, P.A. Microvascular retinal endothelial and pericyte cell apoptosis in vitro: Role of hedgehog and Notch signaling. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4472–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, F.; Cao, W.; Li, X.; et al. Kaempferol promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1α/VEGF-A/Notch1 pathway in ischemic stroke rats. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 185, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Yin, Q.; Li, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L. The Circadian System Is Essential for the Crosstalk of VEGF-Notch-mediated Endothelial Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mao, W.; Niu, L.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.; et al. NSC-derived exosomes enhance therapeutic effects of NSC transplantation on cerebral ischemia in mice. Elife 2023, 12, e84493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Shahzad, K.; Zheng, J. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of miRNA | miRNA | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-angiogenic | miR-126 | VEGF | Stimulate VEGF-dependent AKT and ERK signal transduction to inhibit P85 | [43] |
| PI3K | Inhibit endothelial cell damage and promote angiogenesis | [44] | ||
| Pcdh7 | Promote cell proliferation and angiogenesis | |||
| miR-210 | Ephrin-A3 | Effects of VEGF on capillary-like formation and endothelial cell chemotaxis | [45] | |
| VEGF | ||||
| miR-486 | TLR4 | Inhibit TLR4/NF-κB axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis; promote cell proliferation and angiogenesis | [46,47] | |
| miR-218 | HMGB1 | Promote endothelial cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis; reduce inflammatory damage | [48] | |
| miR-21 | PTEN | Inhibit PTEN/PI3K/AKT and apoptosis of endothelial cells, promote angiogenesis | [49,50] | |
| miR-375 | KLF5 | Endothelial cell migration, proliferation, germination, and vascular network formation; promote angiogenesis and arteriography | [51] | |
| miR-214 | ATM | Stimulate angiogenesis by silencing neighboring mutant cells with cerebellar ataxia and vascular expansion through microvascular dilation | [52] | |
| PI3K | Improve viability and tube formation of human endothelial cells damaged by high glucose levels | [53] | ||
| COX-2 | Downregulate COX-2/PGE2 axis and target COX-2 antagonized indoxyl sulfate (IS)-induced endothelial cell apoptosis | [54,55] | ||
| Anti-angiogenic | miR-34 | SirT1 | Inhibit Sirt1 to induce aging and impair EPC-mediated angiogenesis | [56] |
| Notch1 | Inhibit angiogenesis induced by VEGF | [57,58] | ||
| miR-15 | CCNB1 | Inhibit angiogenesis | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, M.; Su, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Chai, L.; Yuan, Q.; Hu, L. Leech Extract Enhances the Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070499
Cao Y, Sun J, Guo L, Wang M, Su L, Zhang T, Wang S, Chai L, Yuan Q, Hu L. Leech Extract Enhances the Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070499
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yushuang, Jin Sun, Lichen Guo, Meng Wang, Linlin Su, Tong Zhang, Shaoxia Wang, Lijuan Chai, Qing Yuan, and Limin Hu. 2025. "Leech Extract Enhances the Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070499
APA StyleCao, Y., Sun, J., Guo, L., Wang, M., Su, L., Zhang, T., Wang, S., Chai, L., Yuan, Q., & Hu, L. (2025). Leech Extract Enhances the Pro-Angiogenic Effects of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070499






