Investigating the Mechanism of Emodin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway and Mitochondrial Autophagy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Experimental Cells
2.1.2. Experimental Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. CCK-8 Assay to Detect Cell Viability
2.2.3. ELISA Assay for Detecting HIF-1α, IL-1β, IL-18 Levels in Cells
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy to Observe Cell Pyroptosis
2.2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy for Detecting Cell Autophagosomes
2.2.6. Western Blot Method to Detect Protein Expression of HIF-1α, NLRP3, BNIP3 in MH7A Cells
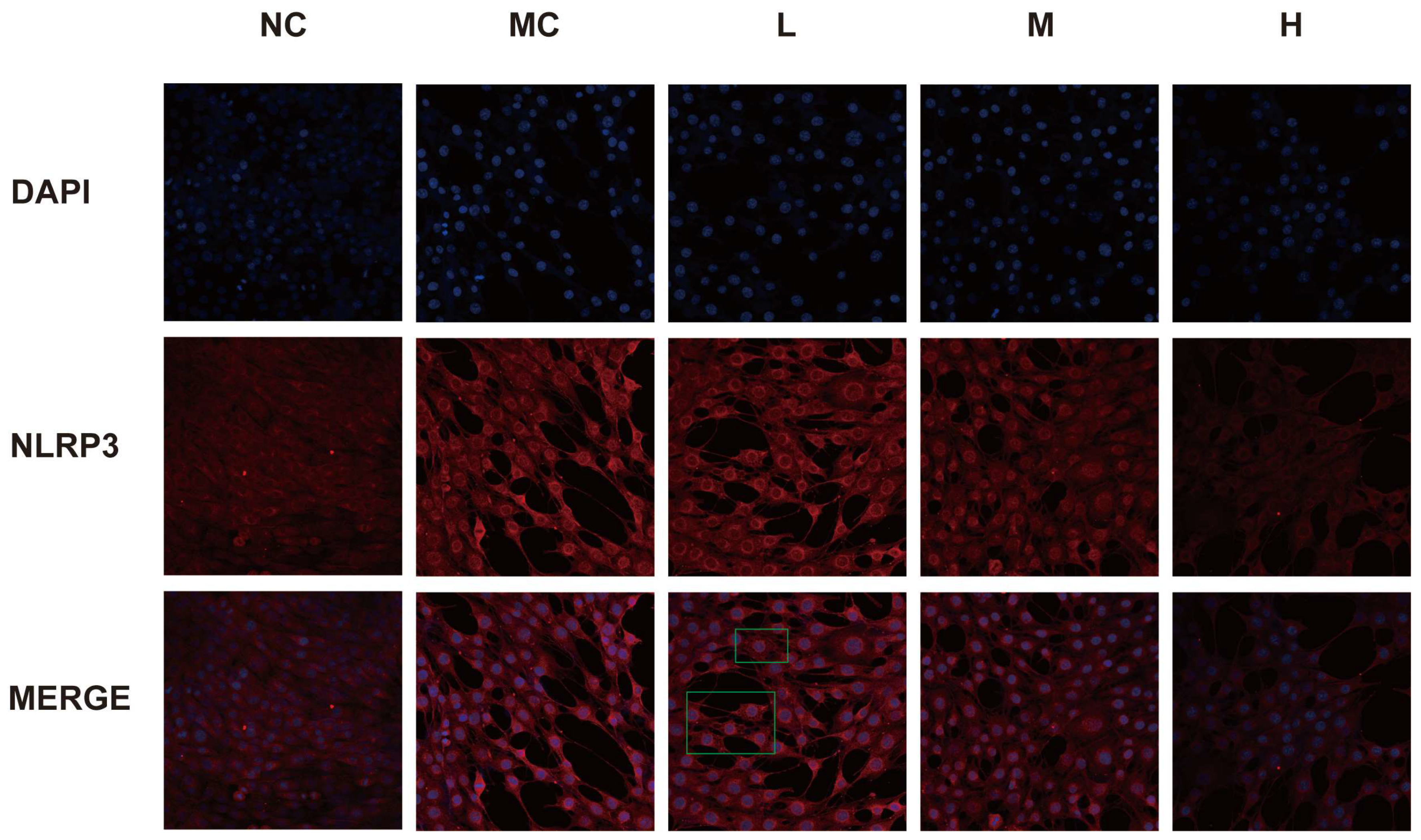
2.2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining Method to Detect NLRP3 Expression
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
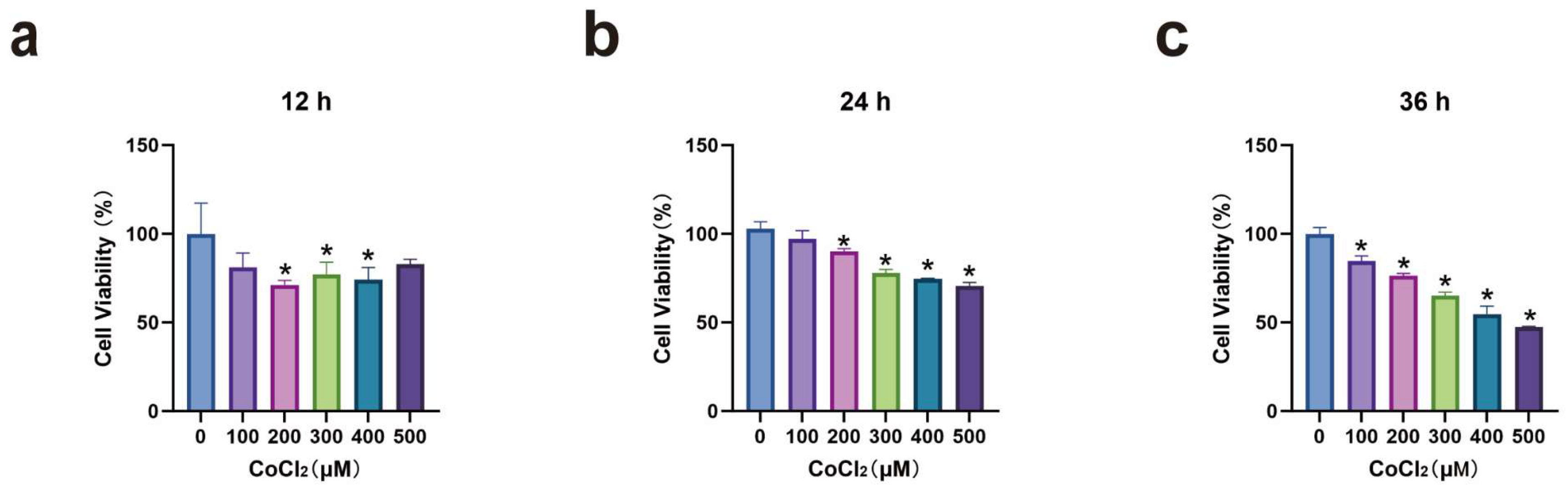
3.1. MH7A Cell Viability After CoCl2 Induction
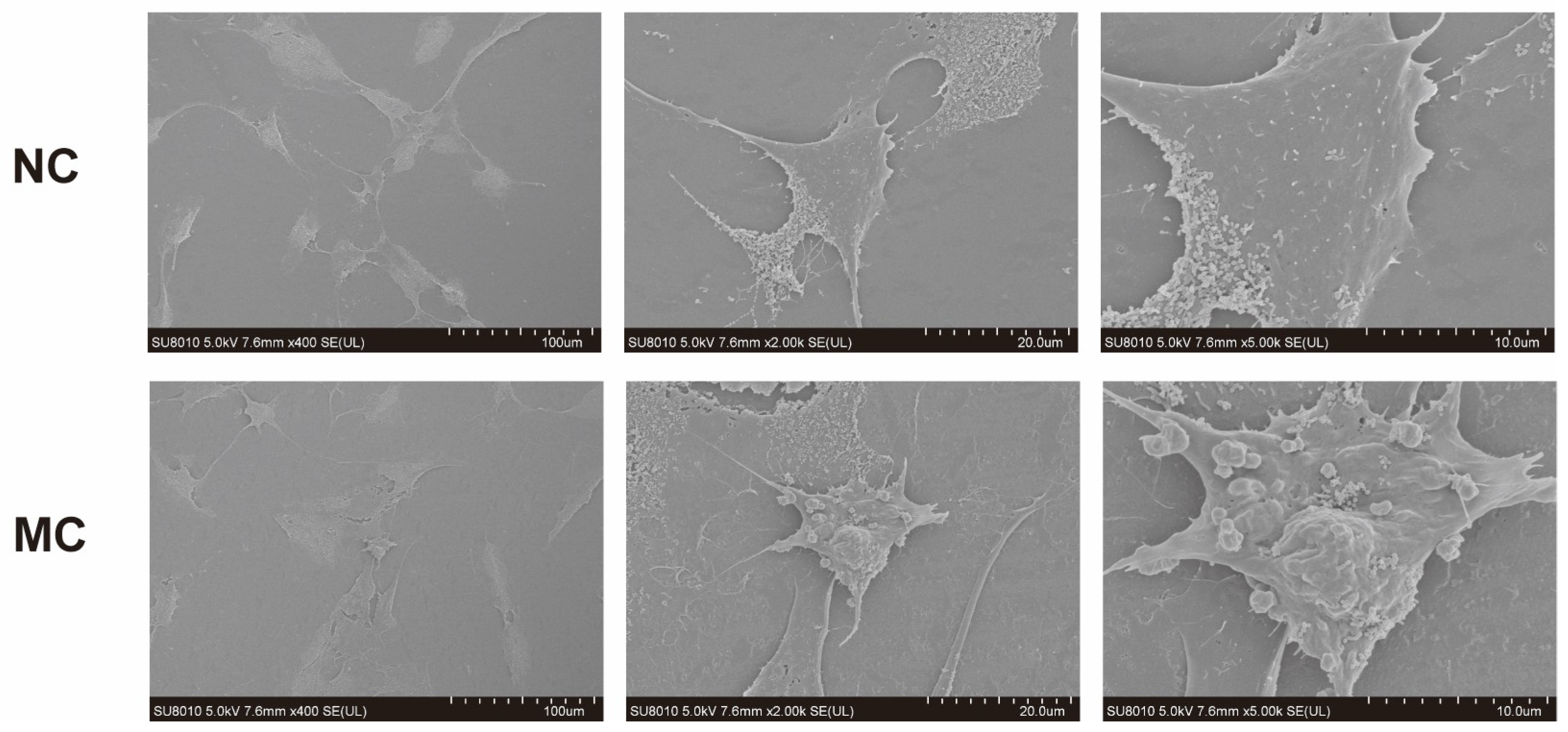
3.2. Morphological Changes of MH7A Cells After CoCl2 Induction
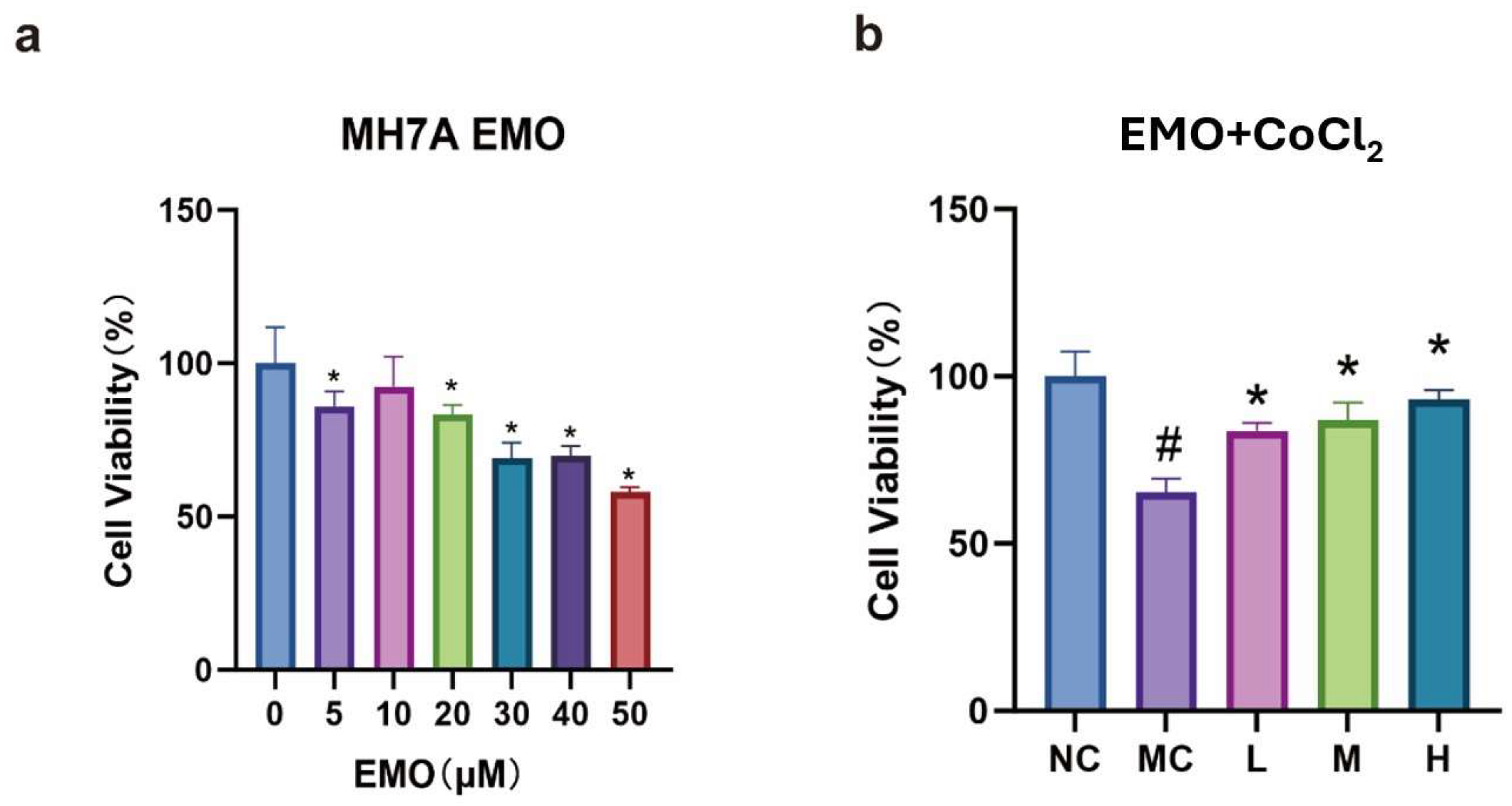
3.3. CCK-8 Detection of Cell Viability in Each Group
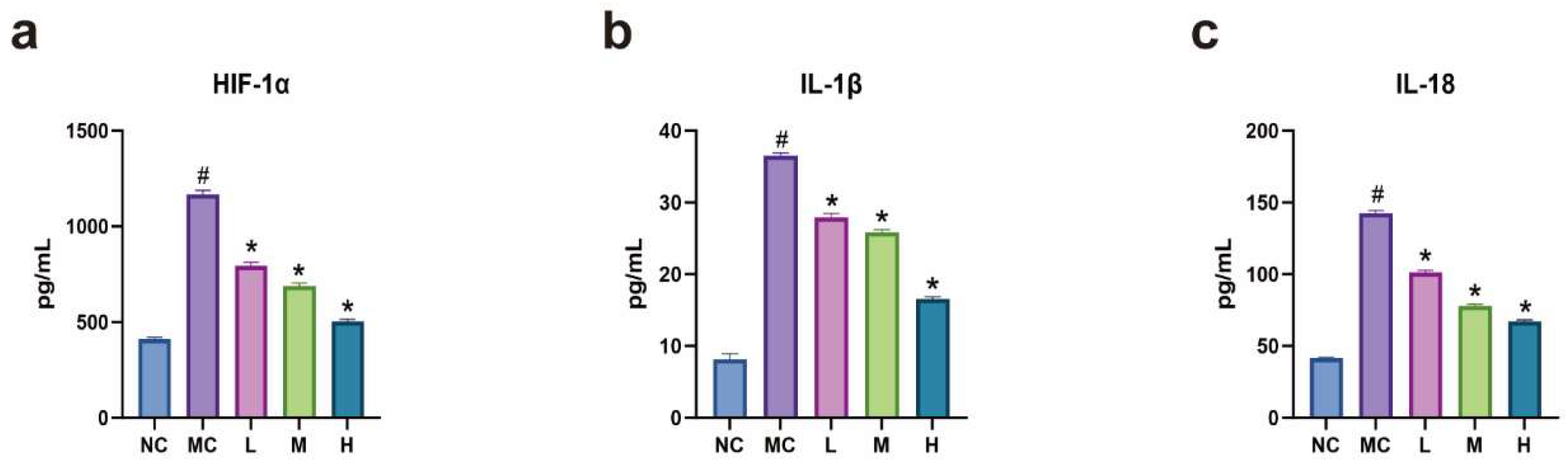
3.4. Expression Levels of HIF-1α, IL-1β, and IL-18 in Each Group of Cells
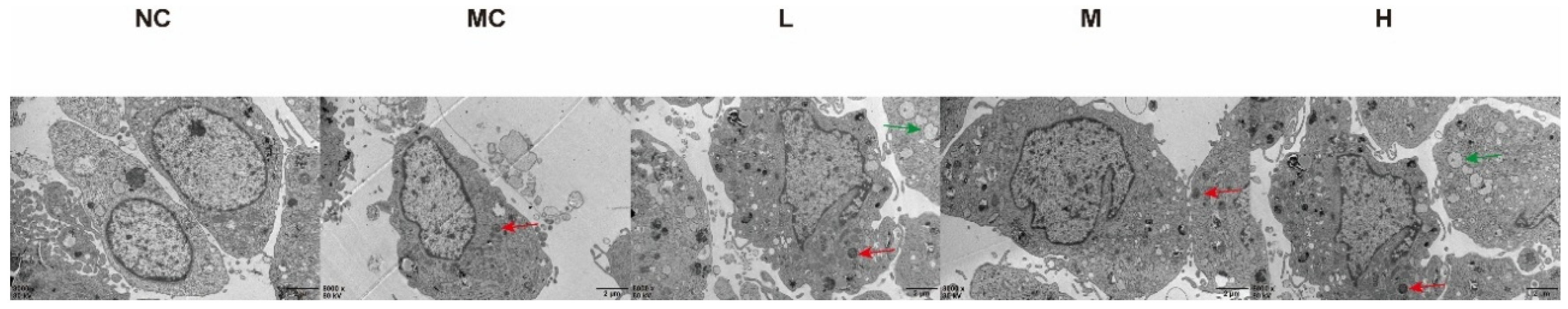
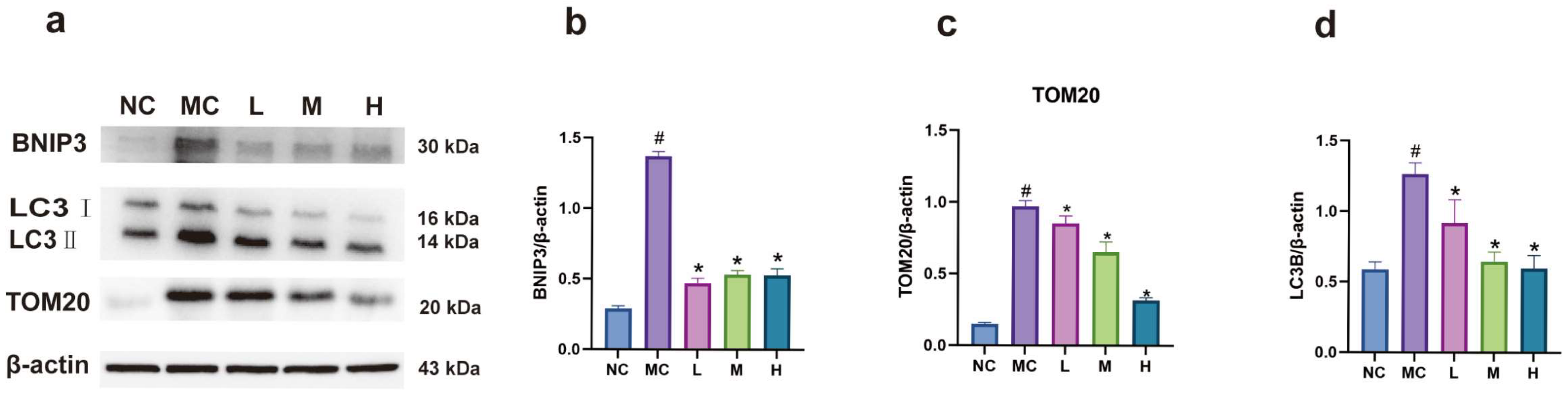
3.5. Observation of Mitochondrial Autophagy in MH7A Cells Using Electron Microscopy
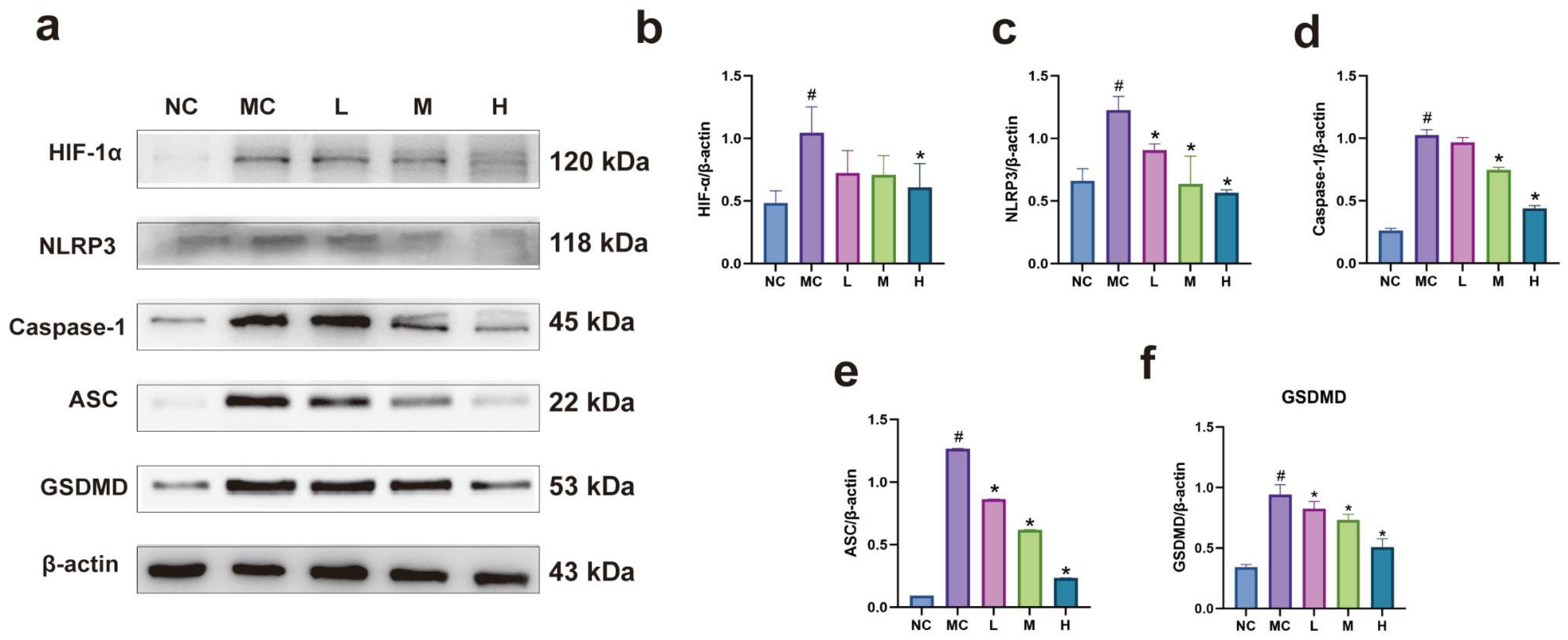
3.6. Expression of Pyroptosis-Related Proteins in Each Group of Cells
3.7. Expression of NLRP3 in Each Group of Cells
3.8. Expression of BNIP3 and LC3B Proteins in Each Group of Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.B.; Wang, F.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z. Update on the role of extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2022, 24, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Tie, Q.; Zhang, L. Targeted inhibition of the GRK2/HIF-1α pathway is an effective strategy to alleviate synovial hypoxia and inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113, 109271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Y.S.; Sargis, T.; Reichert, E.C.; Rudasi, E.; Fuja, D.; Jonasch, E.; Koh, M.Y. Hypoxia-associated factor (HAF) mediates neurofibromin ubiquitination and degradation leading to Ras-ERK pathway activation in hypoxia. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L. The HIF-1/BNIP3 pathway mediates mitophagy to inhibit the pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sánchez, J.; Chánez-Cárdenas, M.E. The use of cobalt chloride as a chemical hypoxia model. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 39, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachami, G.; Simos, G.; Hatziefthimiou, A.; Bonanou, S.; Molyvdas, P.A.; Paraskeva, E. Cobalt Induces Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells by a Reactive Oxygen Species– and PI3K-Dependent Mechanism. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Liakos, P.; Tsakalof, A.; Georgatsou, E.; Simos, G.; Bonanou, S. Cobalt induces Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in HeLa cells by an iron-independent, but ROS-, PI-3K- and MAPK-dependent Mechanism. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salnikow, K.; Donald, S.P.; Bruick, R.K.; Zhitkovich, A.; Phang, J.M.; Kasprzak, K.S. Depletion of Intracellular Ascorbate by the Carcinogenic Metals Nickel and Cobalt Results in the Induction of Hypoxic Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40337–40344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Hu, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q.; Mei, D.; Xue, Z.; et al. The ROS/GRK2/HIF-1α/NLRP3 pathway mediates pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and the regulation of monomer derivatives of paeoniflorin. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4566851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.L.; Rong, X.F. Effects of Compound Rhubarb Powder on NF-κB receptor activator ligand and osteoprotegerin in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2019, 28, 6–9+14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.C.; Yang, W.; Zeng, L.; Cao, C.H.; Yuan, S.; Rong, X.F. Bone protective effect of emodin in collagen-induced arthritis rats: Based on inhibition of ferroptosis and degradation of matrix metalloproteinases. J. South. Med. Univ. 2023, 43, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Rong, X. Emodin promotes the recovery of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the crosstalk between macrophage subsets and synovial fibroblast subsets. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2024, 8, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Rong, X.F.; Peng, F.F. Effects of emodin on ERK1/2 and p38MAPK in TNF-α-induced fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. J. Immunol. 2017, 33, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Cai, X.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Dai, S.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xing, J.; et al. Emodin suppresses NLRP3/GSDMD-induced inflammation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanner, S.; Poggetti, A. Swan-neck and boutonniere deformity in rheumatoid hand. Hand Clin. 2025, 41, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xin, W.; Li, Y.; He, S.; Ma, C.; Zheng, X.; et al. Circular RNA Calm4 regulates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells pyroptosis via the circ-Calm4/miR-124-3p/PDCD6 axis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1675–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghlali, G.; Lawlor, K.E.; Tate, M.D. Die another way: Interplay between influenza A virus, inflammation and cell death. Viruses 2020, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariathasan, S.; Weiss, D.S.; Newton, K.; McBride, J.; O’Rourke, K.; Roose-Girma, M.; Lee, W.P.; Weinrauch, Y.; Monack, D.M.; Dixit, V.M. Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP. Nature 2006, 440, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Kuffa, P.; Martínez-Colón, G.; Smith, B.L.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Núñez, G. K+ efflux is the common trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by bacterial toxins and particulate matter. Immunity 2013, 38, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaney, A.J.; Leppla, S.H.; Moayeri, M. Bacterial exotoxins and the inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, P.I.; Lee, B.; Hoyle, C.; Yu, S.; Lopez-Castejon, G.; Lowe, M.; Brough, D. The NLRP3-inflammasome as a sensor of organelle dysfunction. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202006194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Chen, M.J.; Wei, J. Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1/Parkin-mediated autophagy in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy in C57BL/6 mice. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 48, 030006051985559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, D.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, F. MICU1 alleviates hypobaric hypoxia-induced myocardial injury through regulating Ca2+ uptake to inhibit mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Cell. Signal. 2025, 125, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Liu, X.; Meng, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.M.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.X.; Cui, H.; Tang, X.Q.; Li, X.H.; et al. Kanglexin delays heart aging by promoting mitophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 43, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, D.; Zhou, L.; Tian, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Rong, X. Investigating the Mechanism of Emodin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway and Mitochondrial Autophagy. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070486
Du D, Zhou L, Tian J, Cheng L, Zhang H, Tang Y, Qiu Z, Zhang T, Rong X. Investigating the Mechanism of Emodin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway and Mitochondrial Autophagy. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070486
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Dehao, Linlan Zhou, Jiayu Tian, Lianying Cheng, Han Zhang, Yifu Tang, Zexuan Qiu, Tingdan Zhang, and Xiaofeng Rong. 2025. "Investigating the Mechanism of Emodin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway and Mitochondrial Autophagy" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070486
APA StyleDu, D., Zhou, L., Tian, J., Cheng, L., Zhang, H., Tang, Y., Qiu, Z., Zhang, T., & Rong, X. (2025). Investigating the Mechanism of Emodin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway and Mitochondrial Autophagy. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070486






