Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Cacao: Insights from an In Vitro Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants Information
2.2. Preparation of Cacao Products and In Vitro Fecal Incubation
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Gut Microbiota Data Analysis
2.5. Metabolite Profiling of Cacao Powder
3. Results and Discussion
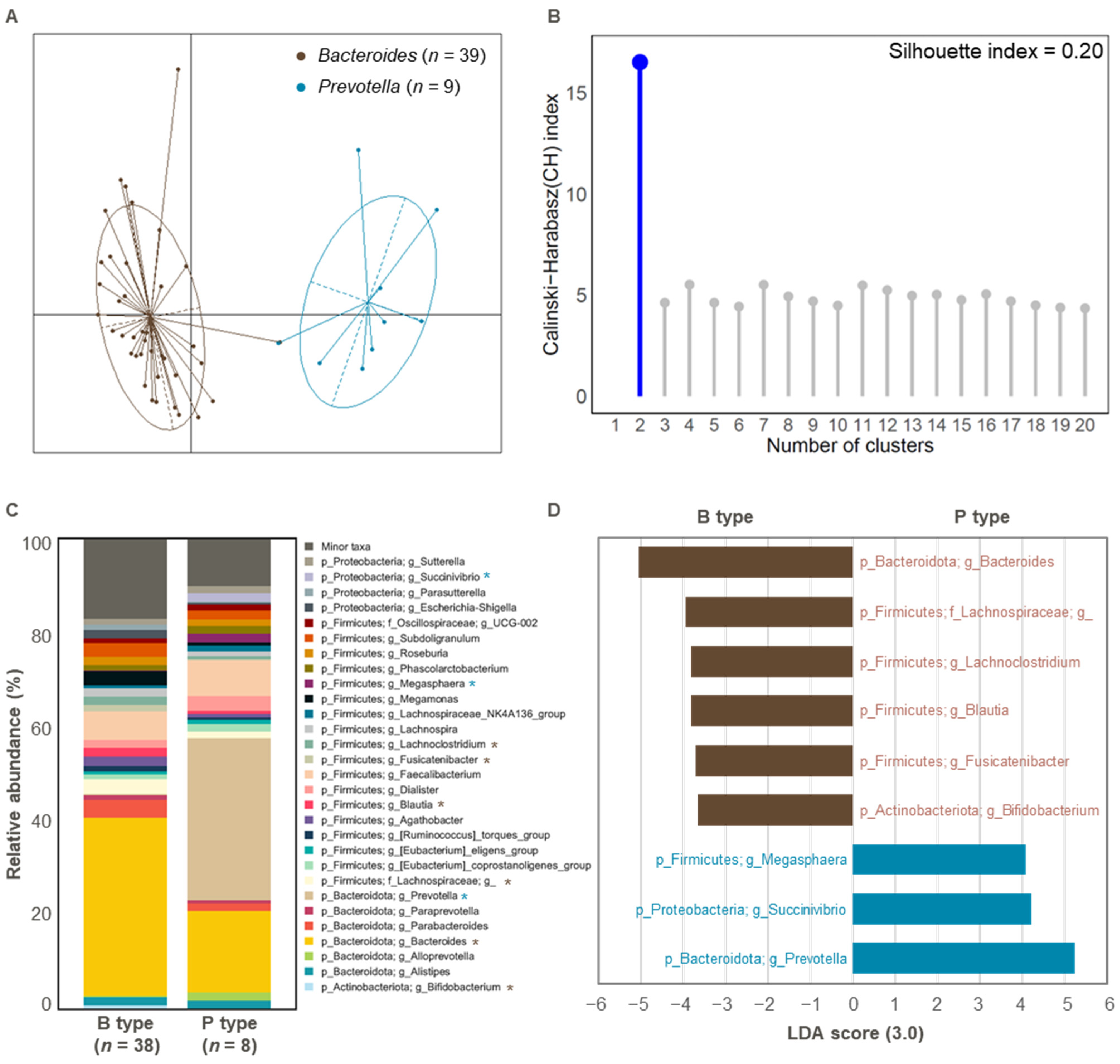
3.1. Comparison of Gut Microbial Composition Between the Two Enterotypes
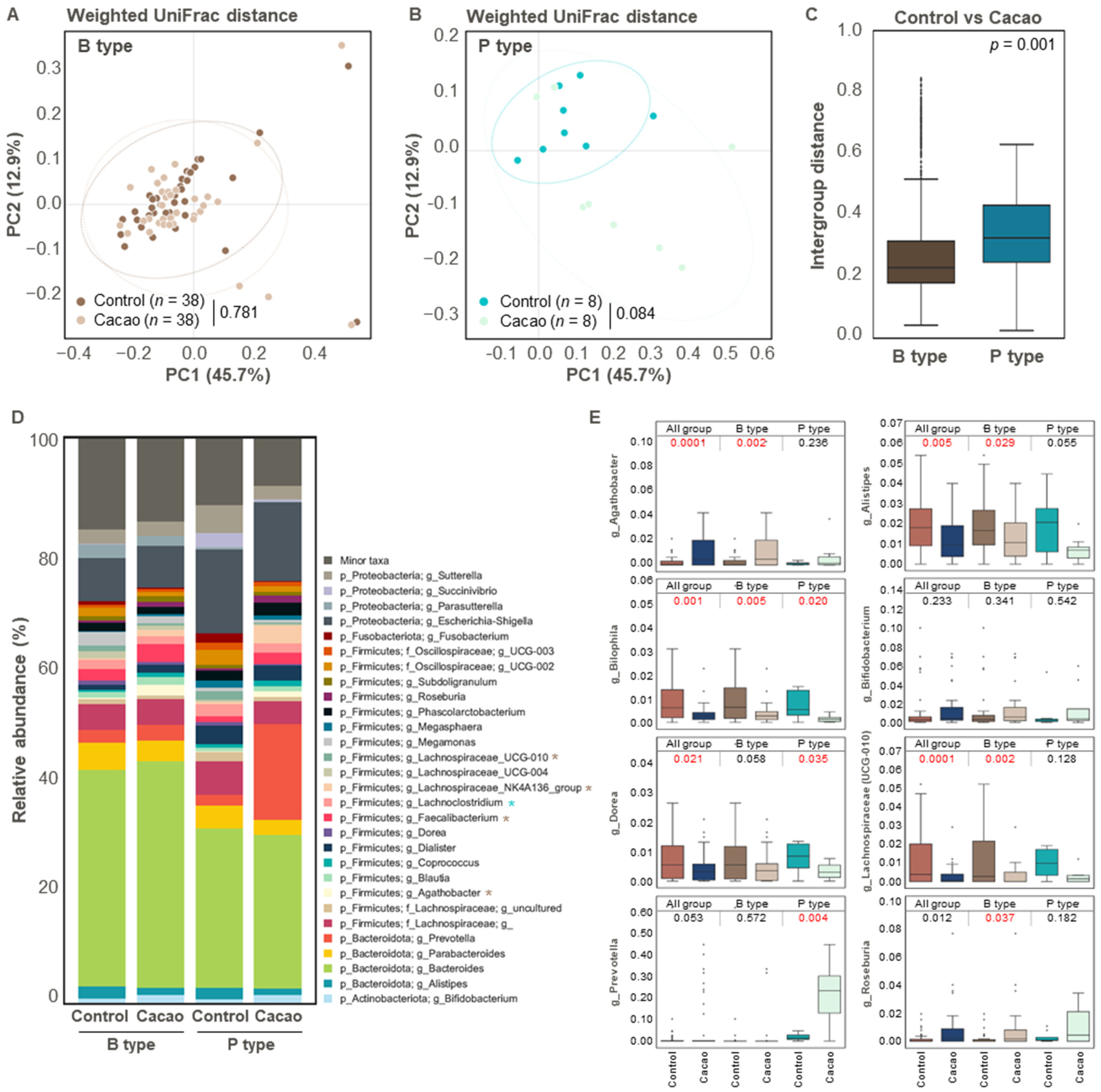
3.2. Differences in Gut Microbiota According to Cacao Treatment
3.3. Effect of Cacao on Gut Microbiota Diversity and Structure According to Enterotype
3.4. Predictive KEGG Functional Profiling According to Cacao Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andújar, I.; Recio, M.C.; Giner, R.M.; Ríos, J. Cocoa polyphenols and their potential benefits for human health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 906252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Bossacoma, M.; Massot-Cladera, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Castell, M. Influence of a Cocoa-Enriched Diet on the Intestinal Immune System and Microbiota; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Di Mattia, C.D.; Sacchetti, G.; Mastrocola, D.; Serafini, M. From cocoa to chocolate: The impact of processing on in vitro antioxidant activity and the effects of chocolate on antioxidant markers in vivo. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massot-Cladera, M.; Pérez-Berezo, T.; Franch, A.; Castell, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J. Cocoa modulatory effect on rat faecal microbiota and colonic crosstalk. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Bossacoma, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Franch, À.; Castell, M. Gut microbiota in a rat oral sensitization model: Effect of a cocoa-enriched diet. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7417505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massot-Cladera, M.; Abril-Gil, M.; Torres, S.; Franch, A.; Castell, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J. Impact of cocoa polyphenol extracts on the immune system and microbiota in two strains of young rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounis, X.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Vulevic, J.; Gibson, G.R.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Spencer, J.P. Prebiotic evaluation of cocoa-derived flavanols in healthy humans by using a randomized, controlled, double-blind, crossover intervention study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.-M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorvitovskaia, A.; Holmes, S.P.; Huse, S.M. Interpreting Prevotella and Bacteroides as biomarkers of diet and lifestyle. Microbiome 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Rho, M.; Song, Y.-M.; Lee, K.; Sung, J.; Ko, G. Stability of gut enterotypes in Korean monozygotic twins and their association with biomarkers and diet. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, A.C.; Fernandes, G.R.; Da Silva, I.T.; Almeida-Pititto, B.; Gomes, E.P.; Pereira, A.d.C.; Ferreira, S.R. Enterotype may drive the dietary-associated cardiometabolic risk factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, L.; Roager, H.M.; Astrup, A.; Hjorth, M.F. Microbial enterotypes in personalized nutrition and obesity management. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayar, S.; Jannink, J.-L.; White, P.J. Digestion residues of typical and high-β-glucan oat flours provide substrates for in vitro fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5306–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food–an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylkas, A.M.; Juneja, L.R.; Slavin, J.L. Comparison of different fibers for in vitro production of short chain fatty acids by intestinal microflora. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, H.K.; Tetu, S.G.; Chong, R.W.; Ashton, J.; Packer, N.H.; Paulsen, I.T. Cereal products derived from wheat, sorghum, rice and oats alter the infant gut microbiota in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Abou-Samra, E.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mayne, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, K.; Walker, K.; Stintzi, A.; Figeys, D. An in vitro model maintaining taxon-specific functional activities of the gut microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.; Kang, S.; Park, G.; Shin, H. The impact of makgeolli consumption on gut microbiota: An enterotype-based preliminary study. J. Microbiol. 2024, 62, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Shin, H. The impact of coffee on gut microbial structure based on in vitro fecal incubation system. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.; Beiko, R.G. 16S rRNA Gene Analysis with QIIME2; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calinski, T.; Harabasz, J. A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun. Stat. 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venema, K.; Van den Abbeele, P. Experimental models of the gut microbiome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, C.; Wen, C.; Dong, X.; Sun, X.; Cao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, B.; Song, S. Gut microbiota response to sulfated sea cucumber polysaccharides in a differential manner using an in vitro fermentation model. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Bushmanc, F.D.; Lewis, J.D. Diet, the human gut microbiota, and IBD. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Unno, T.; Kang, S.; Park, S. A Korean-style balanced diet has a potential connection with Ruminococcaceae enterotype and reduction of metabolic syndrome incidence in Korean adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ezeji, J.C.; Sarikonda, D.K.; Hopperton, A.; Erkkila, H.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Martinez, S.P.; Cominelli, F.; Kuwahara, T.; Dichosa, A.E.; Good, C.E. Parabacteroides distasonis: Intriguing aerotolerant gut anaerobe with emerging antimicrobial resistance and pathogenic and probiotic roles in human health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1922241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, S.K.; Freedman, S.N.; Mangalam, A.K. Gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis: The players involved and the roles they play. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Das, C.; Mande, S.S. In silico analysis of putrefaction pathways in bacteria and its implication in colorectal cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, K.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Hu, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, M.; Hu, R.; Liu, Y.; Chi, H.; Wang, H. Disordered gut microbiota and alterations in metabolic patterns are associated with atrial fibrillation. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsgaard Bendtsen, K.M.; Krych, L.; Sørensen, D.B.; Pang, W.; Nielsen, D.S.; Josefsen, K.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, A.K. Gut microbiota composition is correlated to grid floor induced stress and behavior in the BALB/c mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, A.; Van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and their role as members of the human gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Cantabrana, C.; Delgado, S.; Ruiz, L.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A. Bifidobacteria and their health-promoting effects. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, BAD-0010-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliano, V.; Corollaro, M.L.; Vitaglione, P.; Napolitano, A.; Ferracane, R.; Travaglia, F.; Arlorio, M.; Costabile, A.; Klinder, A.; Gibson, G. In vitro bioaccessibility and gut biotransformation of polyphenols present in the water-insoluble cocoa fraction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, S44–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounis, X.; Vulevic, J.; Kuhnle, G.G.; George, T.; Leonczak, J.; Gibson, G.R.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Spencer, J.P. Flavanol monomer-induced changes to the human faecal microflora. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialonska, D.; Ramnani, P.; Kasimsetty, S.G.; Muntha, K.R.; Gibson, G.R.; Ferreira, D. The influence of pomegranate by-product and punicalagins on selected groups of human intestinal microbiota. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 140, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolara, P.; Luceri, C.; De Filippo, C.; Femia, A.P.; Giovannelli, L.; Caderni, G.; Cecchini, C.; Silvi, S.; Orpianesi, C.; Cresci, A. Red wine polyphenols influence carcinogenesis, intestinal microflora, oxidative damage and gene expression profiles of colonic mucosa in F344 rats. Mutat. Res.-Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2005, 591, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Halder, C.V.; de Sousa Faria, A.V.; Andrade, S.S. Action and function of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; Van Der Veeken, J.; Deroos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, A.; Huang, K.D.; Asnicar, F.; Fehlner-Peach, H.; Pasolli, E.; Karcher, N.; Armanini, F.; Manghi, P.; Bonham, K.; Zolfo, M. The Prevotella copri complex comprises four distinct clades underrepresented in westernized populations. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 666–679.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Hosomi, K.; Sawane, K.; Kunisawa, J. Metabolism of dietary and microbial vitamin B family in the regulation of host immunity. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Ussery, D.W.; Nielsen, J.; Nookaew, I. A closer look at bacteroides: Phylogenetic relationship and genomic implications of a life in the human gut. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LEVEL2 | LEVEL3 | All Group (n = 46) | B Type (n = 38) | P Type (n = 8) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | p Value | Cacao | Control | p Value | Cacao | Control | p Value | Cacao | ||
| Amino acid metabolism | Glycine serine and threonine metabolism | 2.14 | 0.001 | - | 2.12 | 0.001 | - | - | - | - |
| Tryptophan metabolism | 2.12 | 0.044 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Valine leucine and isoleucine degradation | 2.27 | 0.006 | - | 2.19 | 0.018 | - | - | - | - | |
| Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites | Tropane, piperidine, and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis | 2.58 | 0.006 | - | 2.59 | 0.003 | - | - | - | - |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Starch and sucrose metabolism | - | 0.000 | 2.43 | - | 0.000 | 2.38 | - | - | - |
| Galactose metabolism | - | 0.043 | 2.50 | - | 0.042 | 2.47 | - | - | - | |
| Propanoate metabolism | 2.31 | 0.009 | - | 2.27 | 0.027 | - | - | - | - | |
| Citrate cycle (TCAcycle) | 2.32 | 0.020 | - | 2.32 | 0.038 | - | - | - | - | |
| Butanoate metabolism | 2.26 | 0.002 | - | 2.26 | 0.005 | - | - | - | - | |
| Energy metabolism | Nitrogen metabolism | 2.15 | 0.033 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Carbon-fixation pathways in prokaryotes | 2.49 | 0.019 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Methane metabolism | 2.13 | 0.000 | - | - | - | - | 2.66 | 0.019 | - | |
| Lipid metabolism | Secondary bile acid biosynthesis | - | - | - | - | 0.044 | 2.94 | - | - | - |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | - | - | - | - | 0.044 | 2.33 | - | - | - | |
| Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Thiamine metabolism | - | 0.004 | 2.53 | - | 0.004 | 2.54 | - | - | - |
| Riboflavin metabolism | - | 0.037 | 2.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Lipoic acid metabolism | 2.73 | 0.012 | - | 2.62 | 0.032 | - | - | - | - | |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.031 | 2.74 | |
| Metabolism of other amino acids | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 2.45 | 0.014 | - | 2.46 | 0.037 | - | - | - | - |
| Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Aminobenzoate degradation | 2.10 | 0.002 | - | 2.06 | 0.007 | - | - | - | - |
| Nitrotoluene degradation | 2.31 | 0.044 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.; Son, B.; Shin, H. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Cacao: Insights from an In Vitro Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060414
Kim J, Jung S, Kim G, Kim J, Son B, Shin H. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Cacao: Insights from an In Vitro Model. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(6):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060414
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jinshil, Sunil Jung, Gyungcheon Kim, Jinwoo Kim, Bokyung Son, and Hakdong Shin. 2025. "Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Cacao: Insights from an In Vitro Model" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 6: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060414
APA StyleKim, J., Jung, S., Kim, G., Kim, J., Son, B., & Shin, H. (2025). Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Cacao: Insights from an In Vitro Model. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(6), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060414





