Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Reagents and Cell Culture
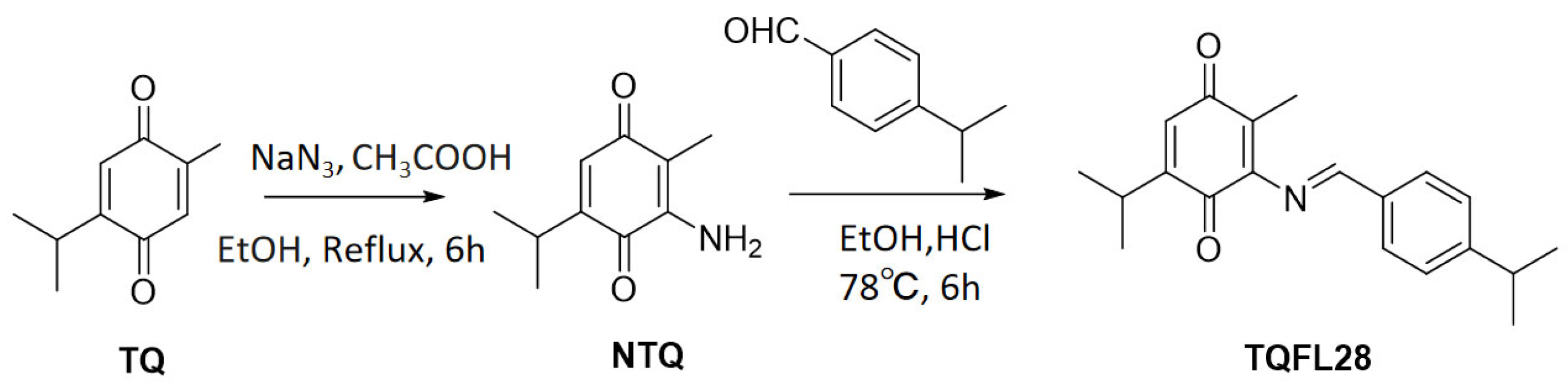
2.3. Chemical Synthesis
2.4. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) Assays
2.5. Assays for Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion
2.6. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Assays
2.7. Mouse Allograft Assays
2.8. Histopathological Assessment
2.9. Mouse Toxicity Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of a New TQ Derivative TQFL28
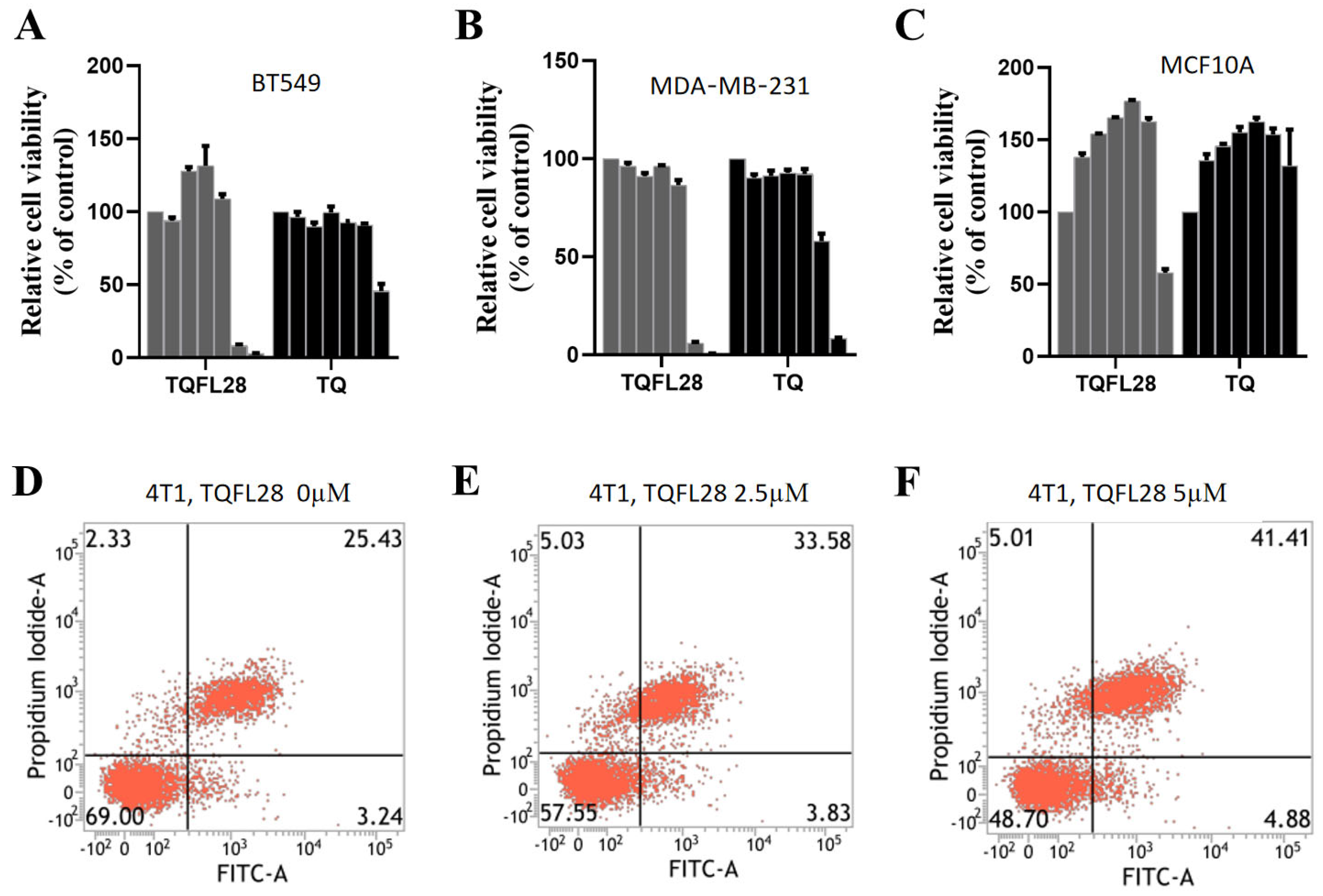
3.2. TQFL28 Shows Higher Cytotoxic Sensitivity than TQ in Breast Cancer Cells
3.3. Effect on Cell Apoptosis by TQFL28
3.4. TQFL28 Suppresses the Growth, Migration, and Invasiveness of Breast Cancer Cells
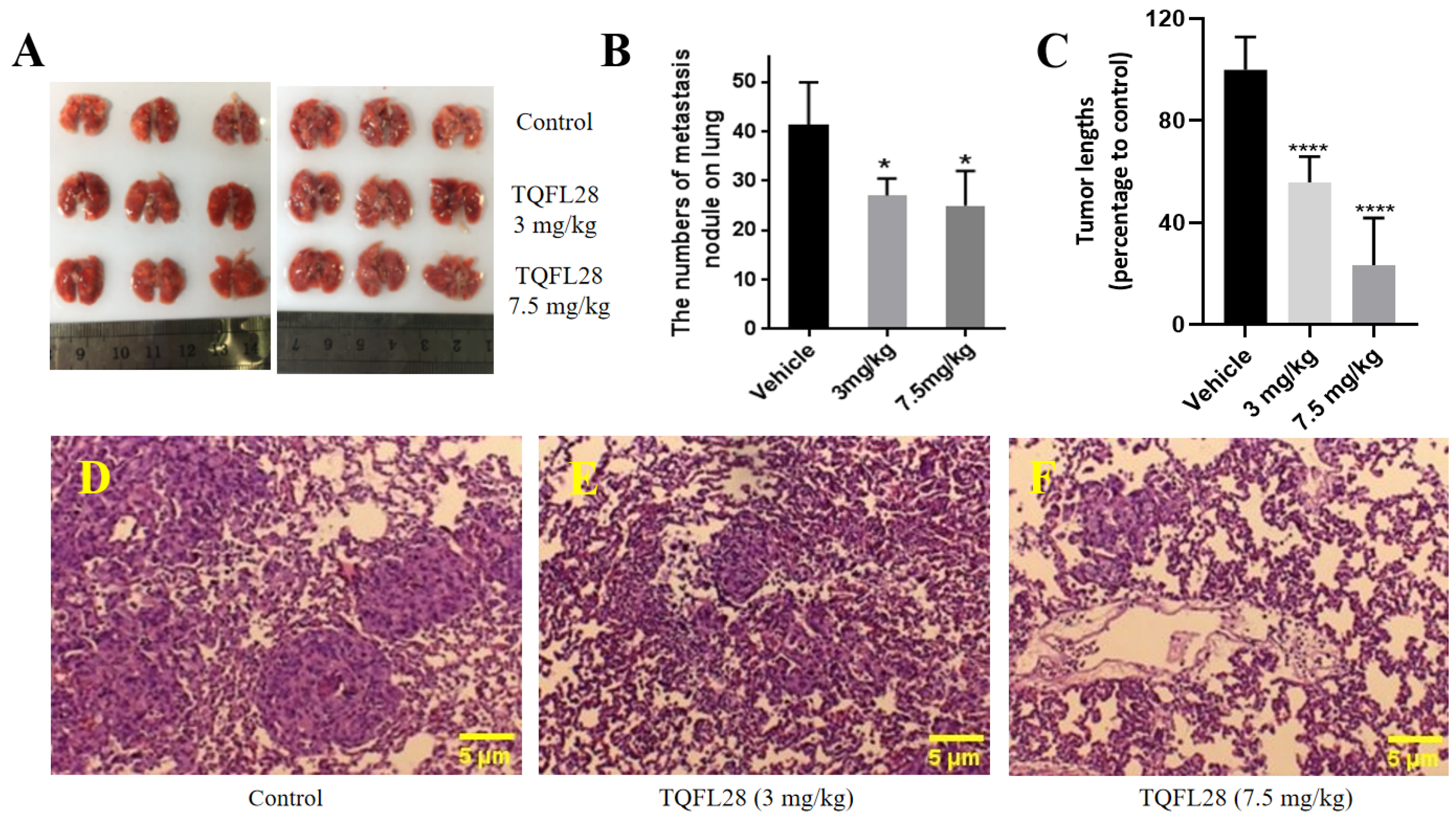
3.5. TQFL28 Inhibits Tumor Growth in Mice
3.6. TQFL28 Inhibits Migration to the Lungs of Breast Cancer Cells In Vivo
3.7. TQFL28 Shows Less Toxicity in Mice than TQ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TQ | Thymoquinone |
| TQFL28 | (E)-5-isopropyl-3-((4-isopropylbenzylidene)amino)-2-methylcyclo hexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HRMS | High-resolution mass spectrum |
| LD50 | Half-lethal dose |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| RTCA | Real-time cell analyzer |
References
- DeSantis, C.E.; Ma, J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Newman, L.A.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Song, B.; Wei, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Tima, S.; Chiampanichayakul, S.; Xiao, X.; Anuchapreeda, S.; et al. Exploring breast cancer associated-gene panel for next-generation sequencing and identifying new, pathogenic variants in breast cancer from western China. J. Cancer 2025, 16, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, S.G. Breast Cancer: An Overview of Current Therapeutic Strategies, Challenge, and Perspectives. Breast Cancer 2023, 15, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, M.S.; Awada, A. Primary chemotherapy for breast cancer: The evidence and the future. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwas, K.M.; Meyer, M.; Goncalves, M.; Moldenhauer, G.; Bulbuc, N.; Knabe, S.; Luckner-Minden, C.; Ziegelmeier, C.; Heussel, C.P.; Zornig, I.; et al. Co-Stimulatory Bispecific Antibodies Induce Enhanced T Cell Activation and Tumor Cell Killing in Breast Cancer Models. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.A.; Fearon, D.T. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science 2015, 348, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazieh, K.; Bell, R.; Agarwal, N.; Abraham, J. Novel targeted therapies for metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jia, Q.; Wu, M.S.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Zou, C.Y.; Tang, Q.; Lu, J.; Huang, G.; et al. Degalactotigonin, a Natural Compound from Solanum nigrum L., Inhibits Growth and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma through GSK3beta Inactivation-Mediated Repression of the Hedgehog/Gli1 Pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. An. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Vyawahare, A.; Kumar, A.; Rehman, M.U.; Qamar, W.; Khan, A.Q.; Khan, R. Thymoquinone (2-Isoprpyl-5-methyl-1, 4-benzoquinone) as a chemopreventive/anticancer agent: Chemistry and biological effects. Saudi Pharm. J. SPJ Off. Publ. Saudi Pharm. Soc. 2019, 27, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.S.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Hamid, S.B.S. Formulation, Characterization and Cytotoxicity Effects of Novel Thymoquinone-PLGA-PF68 Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Tania, M.; Wei, C.; Mei, Z.; Fu, S.; Cheng, J.; Xu, J.; Fu, J. Thymoquinone inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating TWIST1 expression to reduce epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19580–19591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, T.D.; Hamurcu, Z.; Delibasi, N.; Cinar, V.; Guler, A.; Gokce, S.; Nurdinov, N.; Ozpolat, B. Thymoquinone Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing Autophagy, Beclin-1 and LC3. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseb, A.O.; Chinnakannu, K.; Chen, D.; Sivanandam, A.; Tejwani, S.; Menon, M.; Dou, Q.P.; Reddy, G.P. Androgen receptor and E2F-1 targeted thymoquinone therapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7782–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Du, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Zeng, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, G.; et al. Thymoquinone induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cell via endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Farkhondeh, T. Thymoquinone-induced antitumor and apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10421–10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Boltze, C.; Al-Hmaira, J.; Hartig, R.; Roessner, A.; Schneider-Stock, R. Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent mechanism. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 25, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durga, B.B.; Ramachandran, V.; Senthil, B.; Soloman, V.G.; Elshikh, M.S.; Almutairi, S.M.; Wen, Z.H.; Lo, Y.H. Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20221000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfatama, M.; Choukaife, H.; Al Rahal, O.; Zin, N.Z.M. Thymoquinone Pectin Beads Produced via Electrospray: Enhancing Oral Targeted Delivery for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvejeh, P.M.; Chermahini, F.A.; Soltani, A.; Lorigooini, Z.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Mobini, G.R.; Khosravian, P. Improved Therapeutic Efficacy: Liposome-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Delivering Thymoquinone to MCF-7 Cells. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, M.M.; Sarieddine, R.; Alwattar, J.K.; Chouaib, R.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Anticancer Activity of Thymoquinone Cubic Phase Nanoparticles Against Human Breast Cancer: Formulation, Cytotoxicity and Subcellular Localization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9557–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.S.; Hamid, S.B.S. Thymoquinone-PLGA-PF68 Nanoparticles Induce S Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis, Leading to the Inhibition of Migration and Colony Formation in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Curr. Mol. Med. 2025, 25, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhader, M.M. Thymoquinone in the clinical treatment of cancer: Fact or fiction? Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, M.A.; Harshita; Ahmad, J.; Khan, M.A.; Beg, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Insights into the Targeting Potential of Thymoquinone for Therapeutic Intervention Against Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Tania, M.; Fu, S.; Fu, J. Thymoquinone, as an anticancer molecule: From basic research to clinical investigation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51907–51919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Gupta, M.; Devhare, L.D.; Tiwari, R. Therapeutic and Phytochemical Properties of Thymoquinone Derived from Nigella sativa. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2024, 16, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmail, H.A.; Alamoudi, A.A.; Noorwali, A.; Hegazy, G.A.; Ajabnoor, G.M.; Al-Abd, A.M. Thymoquinone Enhances Paclitaxel Anti-Breast Cancer Activity via Inhibiting Tumor-Associated Stem Cells Despite Apparent Mathematical Antagonism. Molecules 2020, 25, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, A.; Alkhawajah, A.A.; Randhawa, M.A.; Shaikh, N.A. Oral and intraperitoneal LD50 of thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa, in mice and rats. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2008, 20, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Zou, H.; Xiao, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Fu, S.; Peng, J.; Xie, X.; Fu, J. TQFL12, a novel synthetic derivative of TQ, inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis and invasion through activating AMPK/ACC pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10101–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Yao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Fan, X.; Xie, C.; Cheng, J.; Fu, J.; et al. Cordycepin Inhibits Drug-resistance Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Activating AMPK Signaling Pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Qin, L.; He, T.; Qin, J.; Hong, J.; Wong, J.; Liao, L.; Xu, J. The TWIST/Mi2/NuRD protein complex and its essential role in cancer metastasis. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, S.; Effenberger, K.; Schobert, R. Effects of thymoquinone-fatty acid conjugates on cancer cells. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, E.; Imenshahidi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 5439–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Natarajan, P.; Reddy, U.K.; Du, W.; Sirbu, C.; Sissoko, M.; Hankins, G.R. Deciphering the dose-dependent effects of thymoquinone on cellular proliferation and transcriptomic changes in A172 glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.B.; Zhao, S.T.; Xu, Z.Q.; Hu, L.J.; Zeng, R.Y.; Qiu, Z.C.; Peng, H.Z.; Zhou, L.F.; Cao, Y.P.; Wan, L. Thymoquinone mitigates cardiac hypertrophy by activating adaptive autophagy via the PPAR-gamma/14-3-3gamma pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrief, A.I.; Elshenawy, D.S.; Elsukary, A.E.; Elekhtiar, S.A.; Yahia, O.A. Behavioral and histological study on the neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone on the cerebellum in AlCl3-induced neurotoxicity in rats through modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy. J. Mol. Histol. 2025, 56, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbilek, M.; Deniz, C.D.; Eroglu Gunes, C.; Kurar, E.; Reisli, I.; Kursunel, M.A.; Topcu, C.; Koc, M. Anticancer activity of thymoquinone in non-small cell lung cancer and possible involvement of PPAR-gamma pathway. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2025, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.A.; Ginawi, O.T.; El-Hadiyah, T.; El-Khatib, A.S.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Al-Sawaf, H.A. Effects of volatile oil constituents of Nigella sativa on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice: Evidence for antioxidant effects of thymoquinone. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2001, 110, 239–251. [Google Scholar]


| IC50 Values at 24 h (μM) | IC50 Values at 48 h (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell lines | TQFL28 | TQ | TQFL28 | TQ |
| BT549 | 38.78 ± 1.589 | 63.67 ± 1.804 | 27.32 ± 1.436 | 64.15 ± 1.807 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 39.63 ± 1.598 | 57.17 ± 1.757 | 27.53 ± 1.440 | 40.85 ± 1.611 |
| MCF-10A | 74.20 ± 1.870 | >100 | 43.30 ± 1.636 | >100 |
| D\H | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 120 | 144 | 168 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TQ | 120 | 8 | 8 | / | / | / | / | / |
| (mg/kg) | 80 | 7 | 8 | / | / | / | / | / |
| 50 | 7 | 8 | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 25 | 2 | 8 | / | / | / | / | / | |
| LD50 | 33.75 | |||||||
| 95% IC | 17.5–46.5 | |||||||
| TQFL28 | 120 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| (mg/kg) | 80 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 50 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| 25 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| LD50 | 59.43 | |||||||
| 95% IC | 41.6–83.6 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Zou, H.; Wei, C.; Du, J.; Xiao, T.; Li, T.; El-Far, A.; Cheng, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, X. Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060412
He J, Zou H, Wei C, Du J, Xiao T, Li T, El-Far A, Cheng J, Fu J, Liu X. Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(6):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060412
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiayue, Hui Zou, Chunli Wei, Jun Du, Ting Xiao, Ting Li, Ali El-Far, Jingliang Cheng, Junjiang Fu, and Xiaoyan Liu. 2025. "Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 6: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060412
APA StyleHe, J., Zou, H., Wei, C., Du, J., Xiao, T., Li, T., El-Far, A., Cheng, J., Fu, J., & Liu, X. (2025). Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(6), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060412





