Effect of 14-Week Supplementation of Highly Purified Policosanol (Raydel®) and a Sugar Cane Extract Powder (SCEP) on Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Variables in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: Insight into Liver, Kidney, and Brain Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
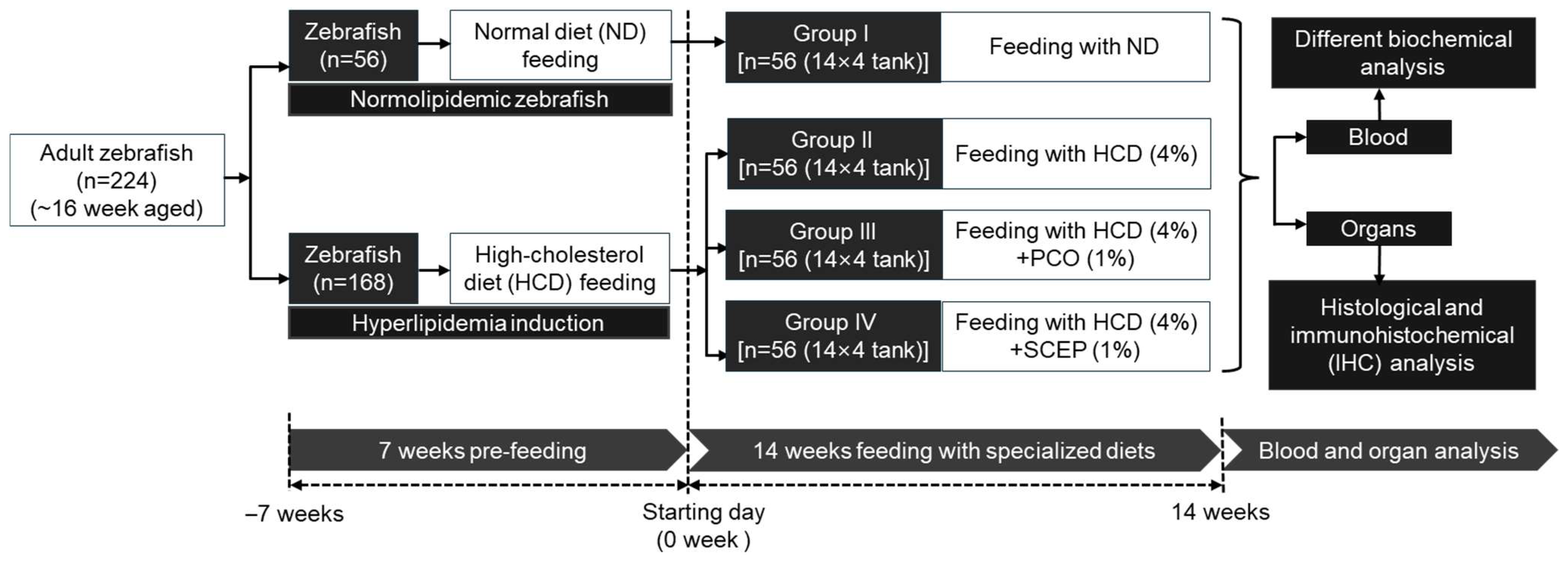
2.2. Zebrafish Husbandry
2.3. Preparation of Different Dietary Formulations
2.4. Supplementation of Different Dietary Formulations
2.5. Collection of Blood and Organs
2.6. Analysis of Blood Lipid Profile, Hepatic Function Biomarkers, Glucose, and Antioxidant Variables
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Cellular Senescence, Dihydroethidium (DHE), and Acridine Orange (AO) Fluorescent Staining
2.9. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zebrafish Survivability and Body Weight
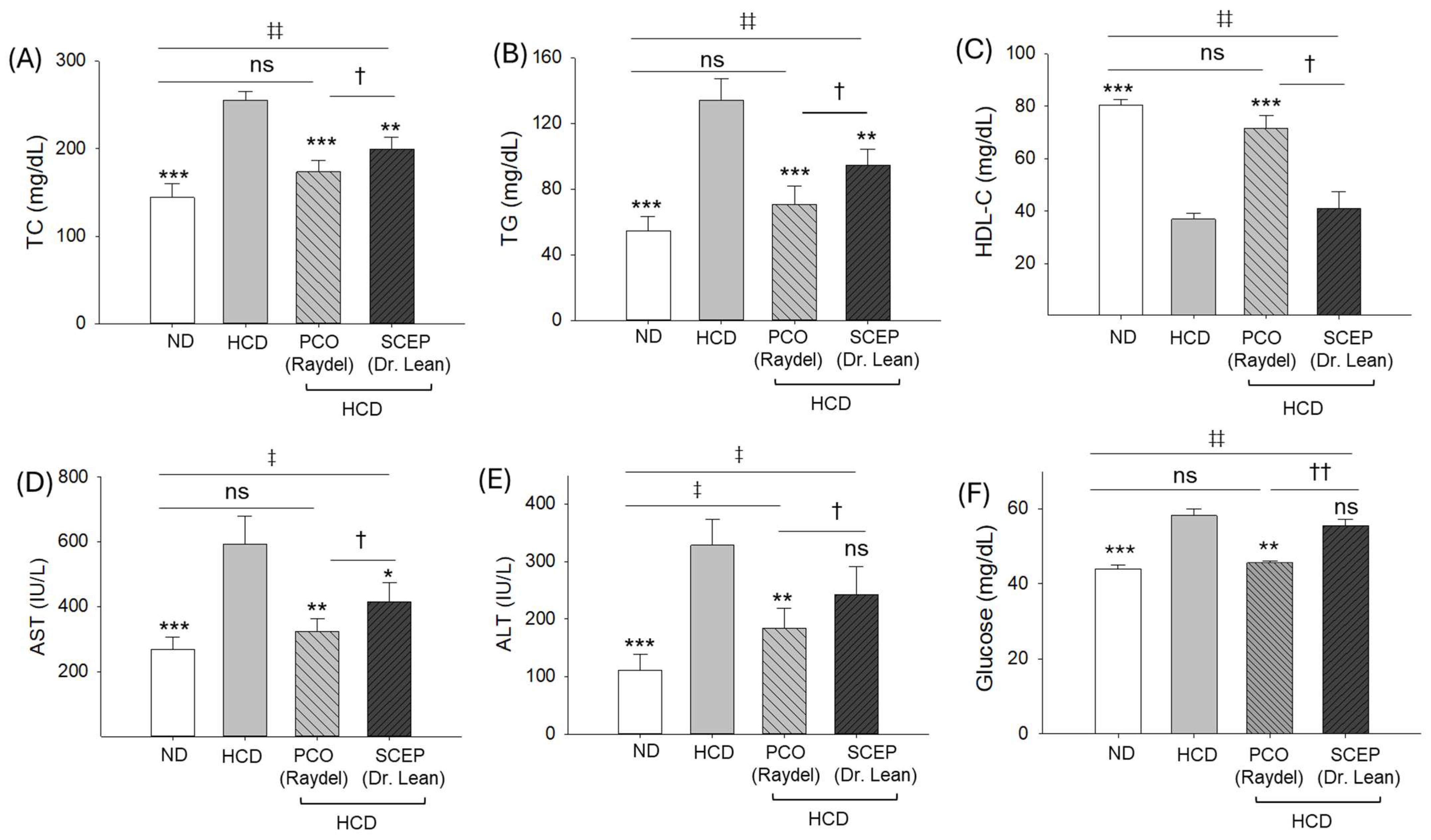
3.2. Blood Lipid Profile, Hepatic Function Biomarkers, and Glucose Level
3.3. Blood Oxidative and Antioxidant Variables
3.4. Morphology and Organ/Body Weight Analysis
3.5. Liver Histology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
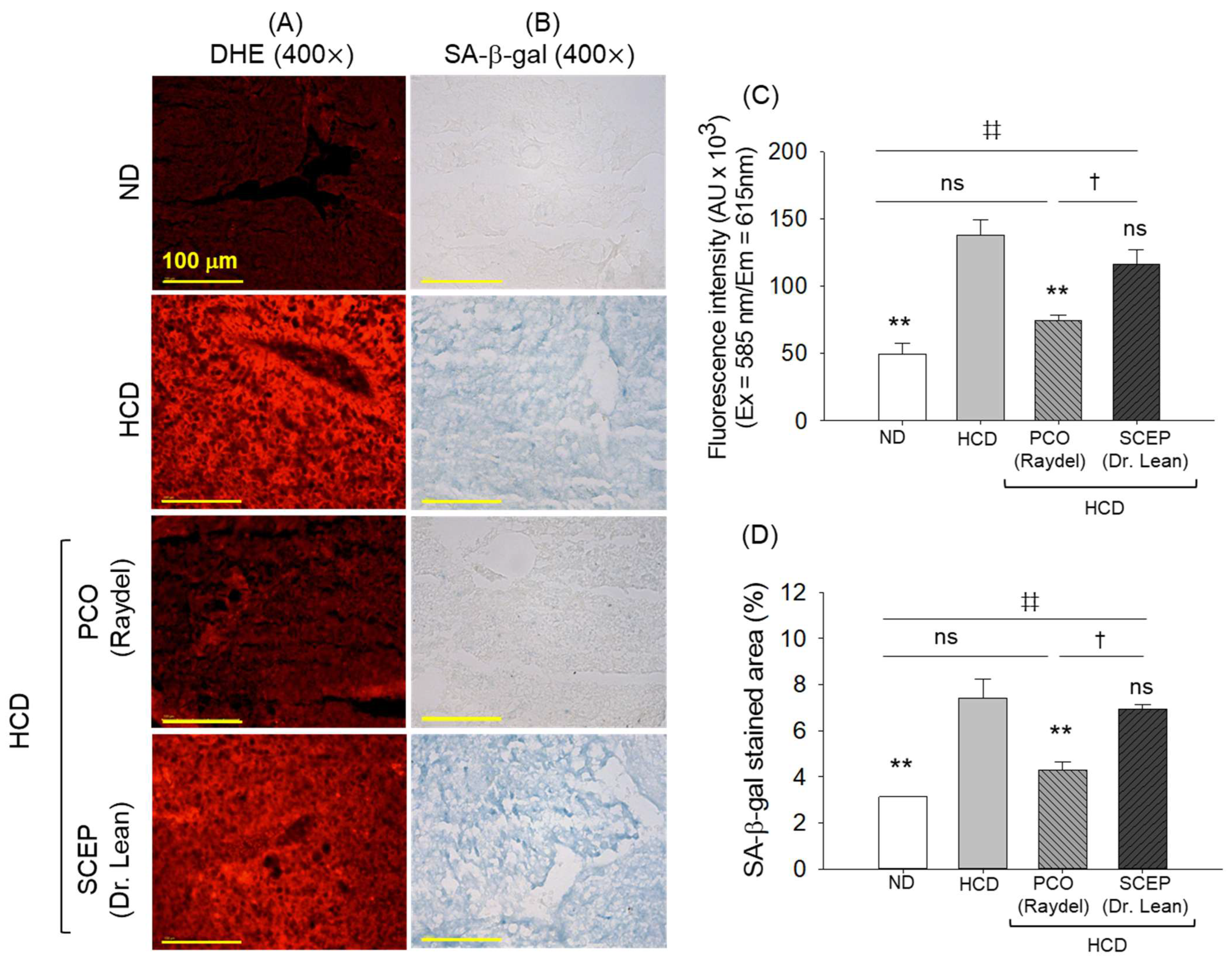
3.6. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Senescence in the Hepatic Tissue
3.7. Kidney Histology
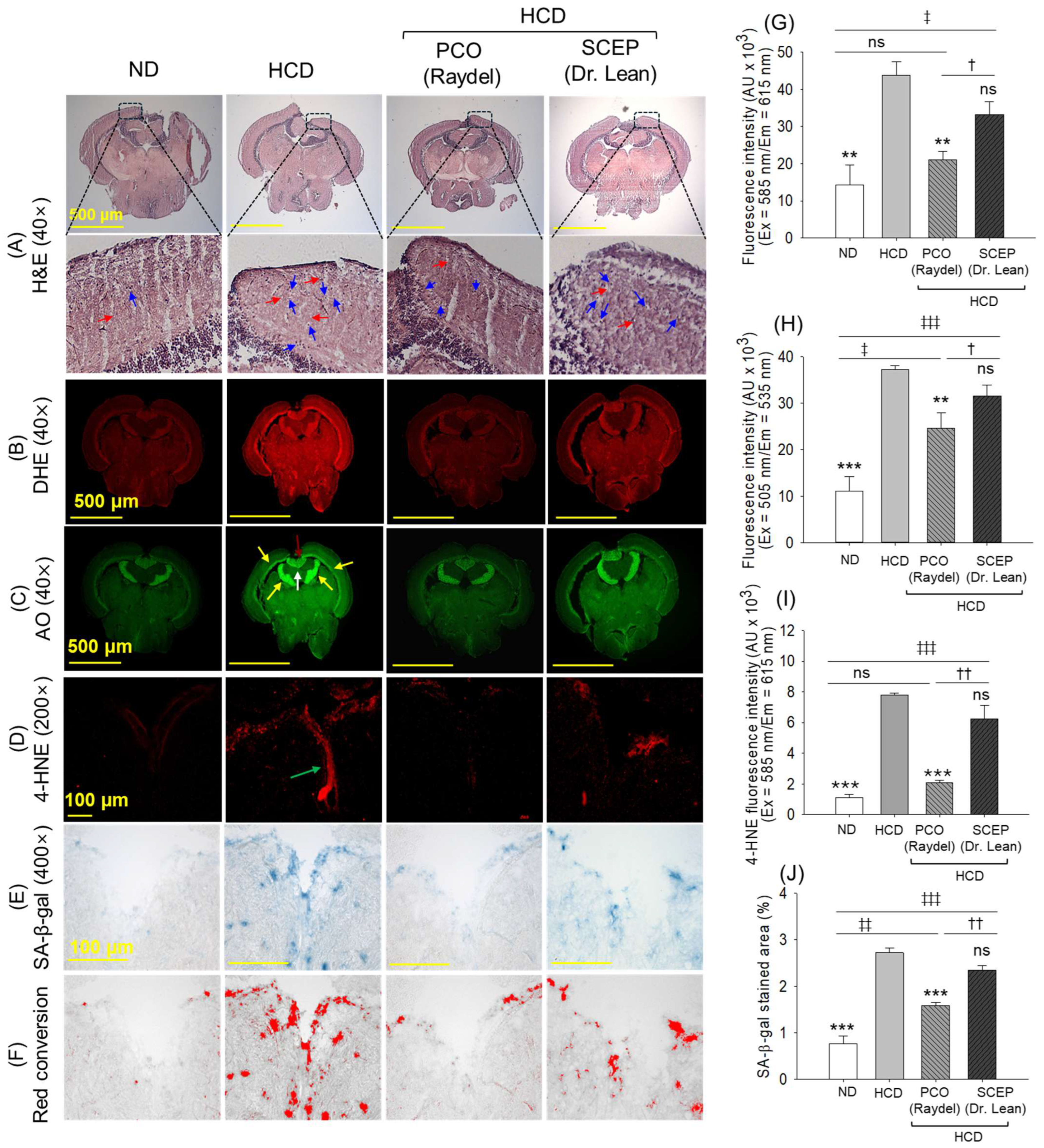
3.8. Brain Histology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kargar, S.; Ansari, H. Prevalence of dyslipidemias in the Middle East region: A systematic review & meta-analysis study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102870. [Google Scholar]
- Hedayatnia, M.; Asadi, Z.; Zare-Feyzabadi, R.; Yaghooti-Khorasani, M.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Ghaffarian-Zirak, R.; Nosrati-Tirkani, A.; Mohammadi-Bajgiran, M.; Rohban, M.; Sadabadi, F.; et al. Dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease risk among the MASHAD study population. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, S.; Gan, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, D.; Addo-Yobo, E.; Trofimovitch, D.; Yue, W.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Prevalence and risk factors for dyslipidemia among adults in rural and urban China: Findings from the China national stroke screening and prevention project (CNSSPP). BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shi, S.; Liu, B.; Shan, M.; Tang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, C. Bioactive compounds from herbal medicines to manage dyslipidemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcântara Neto, O.D.; Silva, R.C.; Assis, A.M.; Pinto Ede, J.F. Factors associated with dyslipidemia in children and adolescents enrolled in public schools of Salvador, Bahia. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2012, 15, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Obesity and Dyslipidemia. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.R.; Anjana, R.M.; Deepa, M.; Pradeepa, R.; Bhansali, A.; Dhandania, V.K. Prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban and rural India: The ICMR-INDIAB study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, O.; Mulec, H.; Knight-Gibson, C.; Attman, P.O.; Kron, B.; Larsson, R.; Weiss, L.; Wedel, H.; Alaupovic, P. Lipoprotein abnormalities are associated with increased rate of progression of human chronic renal insufficiency. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahdkaran, M.; Sistanizad, M. From Lipids to Glucose: Investigating the role of dyslipidemia in the risk of insulin resistance. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 250, 106744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, N.; Korol, L.; Burdeyna, O.; Snisar, L. Impact of dyslipidemia on oxidative stress in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: A cross-sectional study. Atherosclerosis 2024, 395, 118106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.B.; Barbosa, D.S.; Hsin, C.Y.; Maranhao, R.C.; Abdalla, D.S. Evaluation of oxidative stress in patients with hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 1995, 117, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.; Reith, C.; Emberson, J.; Armitage, J.; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Blumenthal, R.; Danesh, J.; Smith, G.D.; DeMets, D.; et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet 2016, 388, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, J.; Matou-Nasri, S.; Alghamdi, F.; Alghamdi, S.; Alfadhel, M.; Padmanabhan, S. Risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects of lipid-lowering drugs: A mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Colletti, A.; Bajraktari, G.; Descamps, O.; Djuric, D.M.; Ezhov, M.; Fras, Z.; Katsiki, N.; Langlois, M.; Latkovskis, G.; et al. Lipid lowering nutraceuticals in clinical practice: Position paper from an International Lipid Expert Panel. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 965–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach, M.; Patti, A.M.; Giglio, R.V.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bajraktari, G.; Bruckert, E.; Descamps, O.; Djuric, D.M.; Ezhov, M.; et al. The role of nutraceuticals in statin intolerant patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Jiao, R.; Ma, K.Y. Cholesterol-lowering nutraceuticals and functional foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8761–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, L.K.; Jimoh, A.O.; Tukur, U.M.; Imam, M.U. A review of the effects of policosanol on metabolic syndrome. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R.; Kazeminejad, S.; Jalalzadeh, M.; Majd, S.S.; Kavyani, Z.; Askari, G.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of policosanol supplementation on blood glucose: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 212, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, S.H. Efficacy assessment of five policosanol brands and damage to vital organs in hyperlipidemic zebrafish by six-week supplementation: Highlighting the toxicity of red yeast rice and safety of Cuban policosanol (Raydel®). Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.K.; Pandey, S.; Tomar, R.; Sahoo, J.; Kumar, D.; Jangra, A. Therapeutic potential of policosanol in the concurrent management of dyslipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.-E.; Yun, J.-M.; Kim, D.; Kim, O.-K. Policosanol attenuates cholesterol synthesis via AMPK activation in hypercholesterolemic rats. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrabi, S.; Ferchichi, A.; Bacheli, A.; Fellah, H. Policosanol composition, antioxidant and anti-arthritic activities of milk thistle (Silybium marianum L.) oil at different seed maturity stages. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canavaciolo, V.L.G.; Gómez, C.V. “Copycat-policosanols” versus genuine policosanol. Rev. CENIC Cienc. Químicas 2007, 38, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, D.; Han, E.; Jung, J. Physiological activities of policosanol extracted from sugarcane wax. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Korean FDA Database for the Product Specification. Available online: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/portal/specialinfo/searchInfoProduct.do?menu_grp=MENU_NEW04&menu_no=2815#page2 (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, C. A comparative effect of 12-week dietary intervention of policosanol (Raydel®) and red yeast rice (RYR, Kobayashi) in managing dyslipidemia and organ damage in hyperlipidemic zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, C.-E.; Kim, J.-E.; Kwon, H.-S. The Consumption of beeswax alcohol (BWA, Raydel®) improved zebrafish motion and swimming endurance by protecting the brain and liver from oxidative stress induced by 24 Weeks of supplementation with high-cholesterol and D-galactose diets: A comparative analysis between BWA and Coenzyme Q10. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, M.-S.; Bahuguna, A. Oral supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil augments plasma antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory abilities with enhancement of high-density lipoproteins functionality in rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb-prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J.; Kim, J.-E. Prolonged supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil bestows an antiaging effect, improves blood lipid profile and spinal deformities, and protects vital organs of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against age-related degeneration: Two-years consumption study. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J. Long-term supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil improves dyslipidemia and hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic zebrafish: Suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation against carboxymethyllysine toxicity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, L.C.; Sen, R.; Menzel, J.; Goyama, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Artinger, K.B. The conserved and divergent roles of Prdm3 and Prdm16 in zebrafish and mouse craniofacial development. Dev. Biol. 2020, 461, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Seo, W.D.; Jia, Y.; Wu, C.; Jun, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Barley sprout extract containing policosanols and polyphenols regulate AMPK, SREBP2 and ACAT2 activity and cholesterol and glucose metabolism in vitro and in vivo. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, N.-Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Kang, D.-J. Combination therapy of Cuban policosanol (Raydel®, 20 mg) and Intensive exercise for 12 weeks resulted in improvements in obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia without a decrease in serum coenzyme Q10: Enhancement of lipoproteins quality and antioxidant functionality in obese participants. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Yadav, D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-R. Consumption of Cuban policosanol improves blood pressure and lipid profile via enhancement of HDL functionality in healthy women subjects: Randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled study. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4809525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, H.-Y.; Kang, Y.-R.; Chang, H.-B.; Chun, H.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Kwon, Y.-I. Effects of long-term supplementation of policosanol on blood cholesterol/glucose levels and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase activity in a rat model fed high cholesterol diets. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Matsuzaka, T.; Kaushik, M.K.; Sugasawa, T.; Ohno, H.; Wang, Y.; Motomura, K.; Shimura, T.; Okajima, Y.; Mizunoe, Y. Octacosanol and policosanol prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders by activating brown adipose tissue and improving liver metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puska, L.G.; Nagy, Z.B.; Giricz, Z.; Onody, A.; Csonka, C.; Kitajka, K.; Hackler, L., Jr.; Zvara, A.; Ferdinandy, P. Cholesterol diet- induced hyperlipidemia influences gene expression pattern of rat hearts: A DNA microarray study. FEBS Lett. 2004, 562, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kozan, D.; Anderson, J.L.; Hensley, M.; Shen, M.C.; Wen, J.; Moll, T.; Kozan, H.; Rawls, J.F.; Farber, S.A. A high-cholesterol zebrafish diet promotes hypercholesterolemia and fasting-associated liver triglycerides accumulation. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodgie, F.D.; Katocs, A.S., Jr.; Largis, E.E.; Wrenn, S.M.; Cornhill, J.F.; Herderick, E.E.; Lee, S.J.; Virmani, R. Hypercholesterolemia in the rabbit induced by feeding graded amounts of low-level cholesterol. Methodological considerations regarding individual variability in response to dietary cholesterol and development of lesion type. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jia, Y.; Thach, T.T.; Han, Y.; Kim, B.; Wu, C.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, S.J. Hexacosanol reduces plasma and hepatic cholesterol by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and suppression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in HepG2 and C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Li, L.; Porter, T.D. Policosanol inhibits cholesterol synthesis in hepatoma cells by activation of AMP-kinase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Rapport, L.; Lockwood, G.B. Octacosanol in human health. Nutrition 2003, 19, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Sasaki, K.; Abe, S.; Nakashima, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kim, J.-E.; Cho, K.-H. Cuban policosanol improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux capacity in healthy Japanese subjects. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1297008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.H.; Leung, K.Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Policosanol has no antioxidant activity in human low-density lipoprotein but increases excretion of bile acids in hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6289–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne Research. Policosanol Monograph. Altern. Med. Rev. 2004, 9, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Tricò, D.; Trifirò, S.; Mengozzi, A.; Morgantini, C.; Baldi, S.; Mari, A.; Natali, A. Reducing cholesterol and fat intake improves glucose tolerance by enhancing β Cell function in nondiabetic subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordiano, R.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Mangifesta, R.; Panzera, C.; Gangemi, S.; Minciullo, P.L. Malondialdehyde as a potential oxidative stress marker for allergy-oriented diseases: An update. Molecules 2023, 28, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Binnenmars, S.H.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; la Bastide-van Gemert, S.; Kieneker, L.M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Serum free sulfhydryl status associates with new-onset chronic kidney disease in the general population. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Post, A.; Gemert, S.L.B.-V.; Kieneker, L.M.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Gordijn, S.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.; Mulder, D.J.; et al. Systemic oxidative stress associates with new-onset hypertension in the general population. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L. Measurement of protein thiol groups and glutathione in plasma. Methods Enzym. 1994, 233, 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Teratani, T.; Tomita, K.; Suzuki, T.; Oshikawa, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Shimamura, K.; Tominaga, S.; Hiroi, S.; Irie, R.; Okada, Y. A high-cholesterol diet exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice via accumulation of free cholesterol in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 152–164.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noa, M.; Mendoza, S.; Mas, R.; Mendoza, N. Effect of policosanol on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in Sprague-Dawley rats. Drugs R D 2003, 4, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, P.; Sacco, J.; Adeli, K. Autophagy: Emerging roles in lipid homeostasis and metabolic control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubser, L.; Weider, K.I.; Drake, S.M. Acute liver injury induced by red yeast rice supplement. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2019, 12, e227961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, S.; Farr, J.N.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. The role of cellular senescence in ageing and endocrine disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flensted-Jensen, M.; Oró, D.; Rørbeck, E.A.; Zhang, C.; Madsen, M.R.; Madsen, A.N.; Norlin, J.; Feigh, M.; Larsen, S.; Hansen, H.H. Dietary intervention reverses molecular markers of hepatocellular senescence in the GAN diet-induced obese and biopsy-confirmed mouse model of NASH. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honzumi, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Kurihara, M.; Fujiyoshi, M.; Uchida, M.; Watanabe, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishii, I. The effect of cholesterol overload on mouse kidney and kidney-derived cells. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterslund, P.; Christensen, H.D.; Urbahnke, J.; Cappeln, A. Red yeast rice as the presumed cause of acute kidney and liver failure. Ugeskr. Laeger 2019, 181, V02190107. [Google Scholar]
- Gyurászová, M.; Gurecká, R.; Bábíčková, J.; Tóthová, Ľ. Oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of kidney disease: Implications for noninvasive monitoring and identification of biomarkers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5478708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R.; Lovell, M.A. Four-hydroxynonenal, a product of lipid peroxidation, is increased in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1998, 19, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, X.-L.; Yang, L.; Shi, F.; Gao, L.-B.; Zhong, Y.-J.; Sun, H.; He, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis contributes to chemosensitization effect of saikosaponins on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, N.; Yassin, F.; Makled, S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Albogami, S.M.; Mostafa-Hedeab, G.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Elewa, Y.H.A. Oral supplementation of policosanol alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, M.; Huang, Q.; Xie, L.; Huang, Z. Monacolin K Induces apoptosis of human glioma U251 cells by triggering ROS-mediated oxidative damage and regulating MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.S.; Cordeiro, T.M.; Dos Santos Lacerda Soares, T.M.; Ferreira, R.N.; Simões e Silva, A.C. Kidney-brain axis inflammatory crosstalk: From bench to bedside. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, E. A troubled mind troubles the kidney: A brain-to-kidney axis? Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Does the Liver Affect Brain Health? Available online: https://www.alzdiscovery.org/cognitive-vitality/blog/how-doesthe-liver-affect-brain-health#ref-4 (accessed on 11 November 2024).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, C. Effect of 14-Week Supplementation of Highly Purified Policosanol (Raydel®) and a Sugar Cane Extract Powder (SCEP) on Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Variables in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: Insight into Liver, Kidney, and Brain Health. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050354
Cho K-H, Bahuguna A, Lee SH, Kim J-E, Lee Y, Jeon C. Effect of 14-Week Supplementation of Highly Purified Policosanol (Raydel®) and a Sugar Cane Extract Powder (SCEP) on Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Variables in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: Insight into Liver, Kidney, and Brain Health. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050354
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyung-Hyun, Ashutosh Bahuguna, Sang Hyuk Lee, Ji-Eun Kim, Yunki Lee, and Cheolmin Jeon. 2025. "Effect of 14-Week Supplementation of Highly Purified Policosanol (Raydel®) and a Sugar Cane Extract Powder (SCEP) on Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Variables in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: Insight into Liver, Kidney, and Brain Health" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050354
APA StyleCho, K.-H., Bahuguna, A., Lee, S. H., Kim, J.-E., Lee, Y., & Jeon, C. (2025). Effect of 14-Week Supplementation of Highly Purified Policosanol (Raydel®) and a Sugar Cane Extract Powder (SCEP) on Dyslipidemia and Oxidative Variables in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: Insight into Liver, Kidney, and Brain Health. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050354


_Kim.png)




