Construction and Evaluation of a HCoV-OC43 S2 Subunit Vaccine Fused with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence Against Coronavirus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
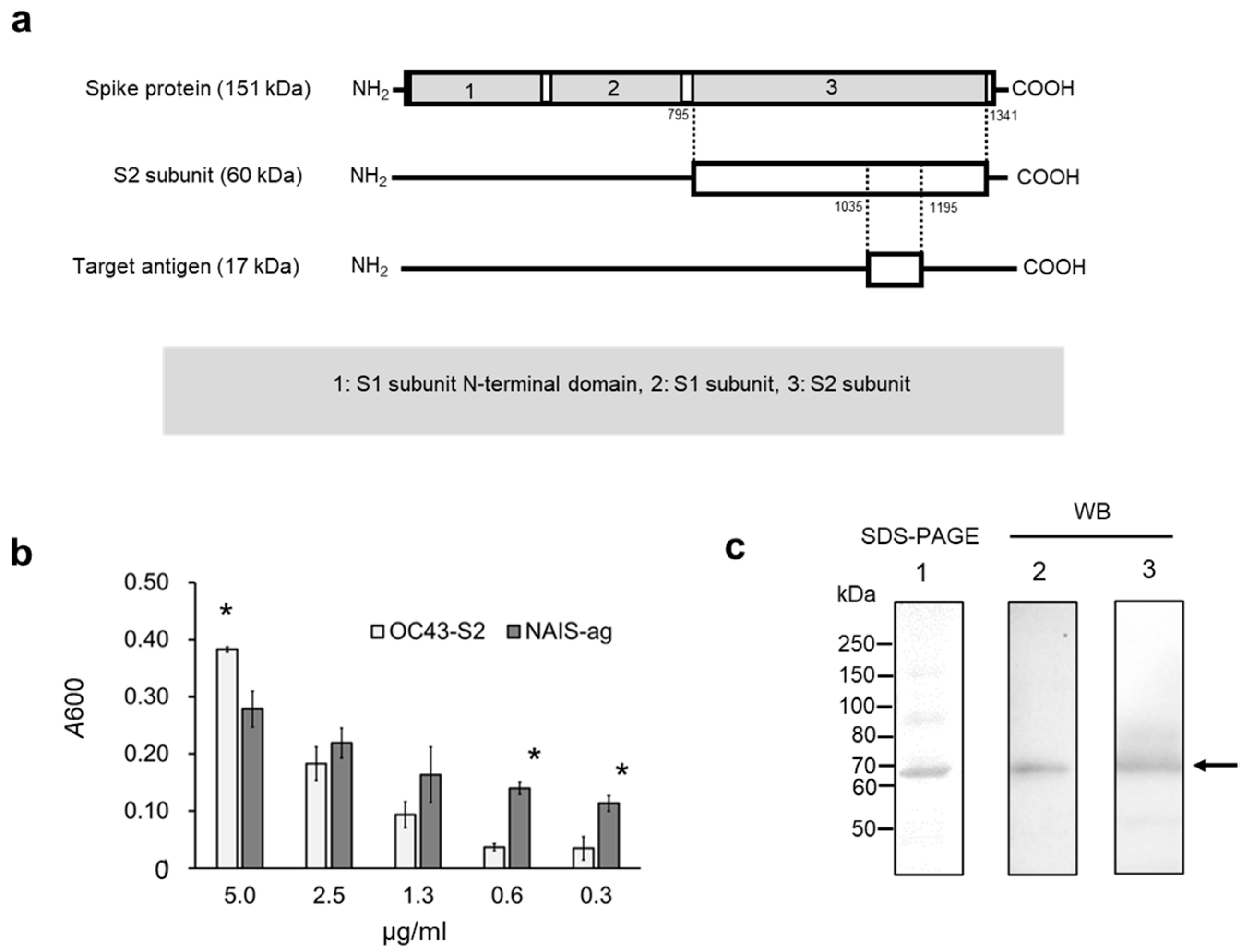
2.1. Vaccine Design for Intranasal Immunization
2.2. Intranasal Immunization
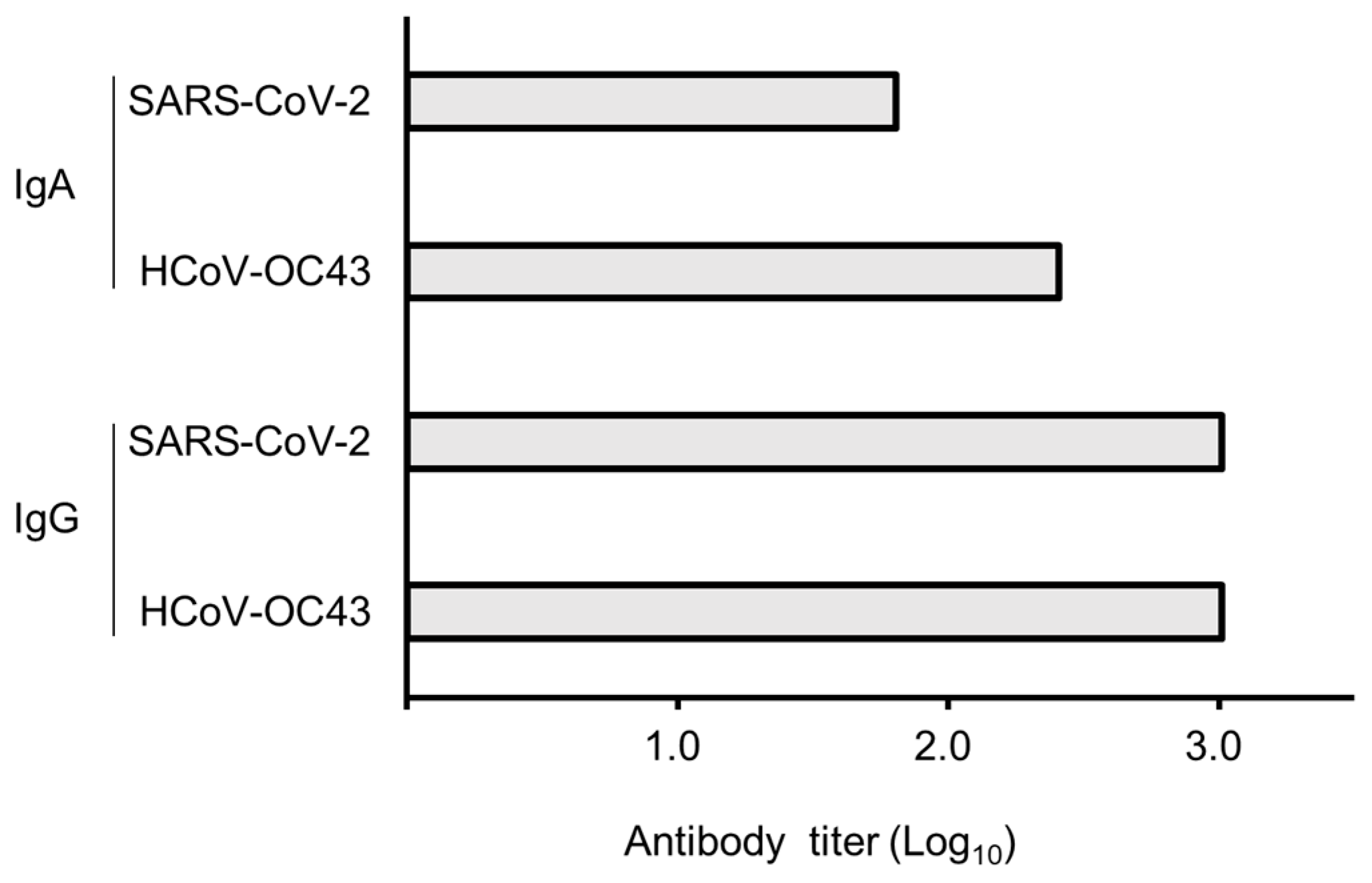
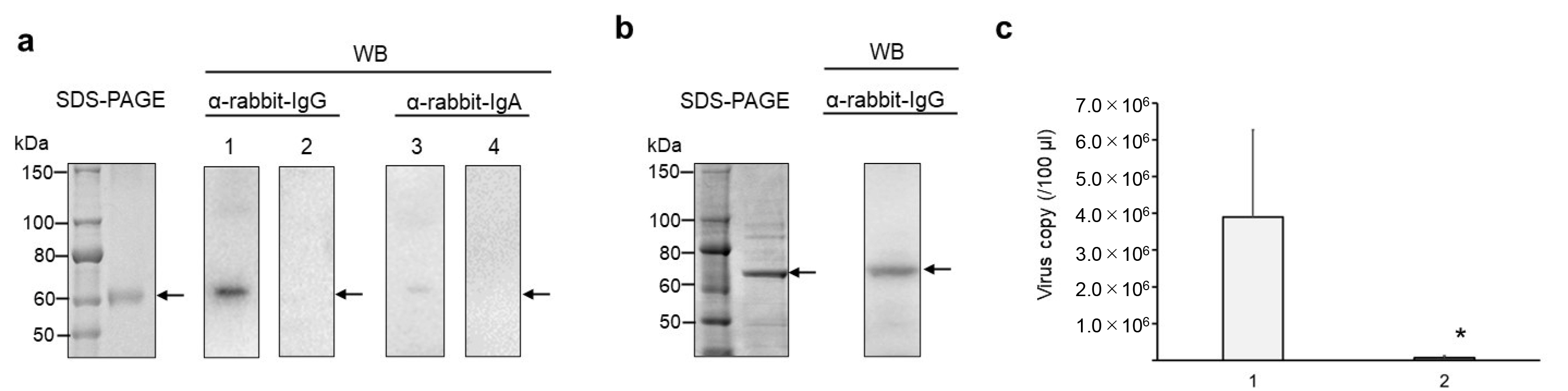
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and Western Blotting (WB)
2.4. Neutralization Assay of HCoV–OC43 Virus
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sano, K.; Ainai, A.; Suzuki, T.; Hasegawa, H. Intranasal inactivated influenza vaccines for the prevention of seasonal influenza epidemics. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2018, 17, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Kojima, K.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Itoh, T.; Hosomi, O.; Kawamoto, E. Intranasal immunization with a non-adjuvanted adhesive protein descended from Pasteurella pneumotropica and its preventive efficacy against opportunistic infection in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5729–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Takeda, K.; Uchida, K.; Iyoda, M.; Ishikawa, H. Intranasal Immunization with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence-Fused Antigens Elicits Antigen-Specific Antibody Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Dai, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, F. A systematic review of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Hillyer, C.; Du, L. Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Coronaviruses. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Mahajan, S.; Overton, J.A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Martini, S.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D339–D343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Moës, E.; Maes, P.; Duson, G.; Van Ranst, M. Development of One-Step, Real-Time, Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assays for Absolute Quantitation of Human Coronaviruses OC43 and 229E. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5452–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavinder, J.J.; Hoi, K.H.; Reddy, S.T.; Wine, Y.; Georgiou, G. Systematic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of the Rabbit Immunoglobulin Repertoire. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Bidon, M.; Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R.; Daniel, S. Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, W.J.; Longo, D.L. A Possible Role for Anti-idiotype Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trougakos, I.P.; Terpos, E.; Alexopoulos, H.; Politou, M.; Paraskevis, D.; Scorilas, A.; Kastritis, E.; Andreakos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Adverse effects of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: The spike hypothesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzou, P.L.; Tao, K.; Pond, S.L.K.; Shafer, R.W. Coronavirus Resistance Database (CoV-RDB): SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, and plasma from vaccinated persons. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, S.; Coyle, E.M.; Klenow, L.; Tang, J.; Grubbs, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Golding, H.; Khurana, S. Antibody signature induced by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein immunogens in rabbits. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wec, A.Z.; Wrapp, D.; Herbert, A.S.; Maurer, D.P.; Haslwanter, D.; Sakharkar, M.; Jangra, R.K.; Dieterle, M.E.; Lilov, A.; Huang, D.; et al. Broad neutralization of SARS-related viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. Science 2020, 369, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycke, N.; Lebrero-Fernández, C. ADP-ribosylating enterotoxins as vaccine adjuvants. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 41, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y. Recent advances in nontoxic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and its derivative adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sasaki, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Shigenaga, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Iyoda, M. Construction and Evaluation of a HCoV-OC43 S2 Subunit Vaccine Fused with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence Against Coronavirus Infection. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050355
Sasaki H, Ishikawa H, Shigenaga A, Suzuki Y, Iyoda M. Construction and Evaluation of a HCoV-OC43 S2 Subunit Vaccine Fused with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence Against Coronavirus Infection. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050355
Chicago/Turabian StyleSasaki, Hiraku, Hiroki Ishikawa, Ayako Shigenaga, Yoshio Suzuki, and Masayuki Iyoda. 2025. "Construction and Evaluation of a HCoV-OC43 S2 Subunit Vaccine Fused with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence Against Coronavirus Infection" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050355
APA StyleSasaki, H., Ishikawa, H., Shigenaga, A., Suzuki, Y., & Iyoda, M. (2025). Construction and Evaluation of a HCoV-OC43 S2 Subunit Vaccine Fused with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence Against Coronavirus Infection. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050355







