A Clinical Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Group A β-Hemolytic Streptococcus Coinfection and Venous Thrombosis in a Child with Congenital Thrombophilia
Abstract
1. Introduction
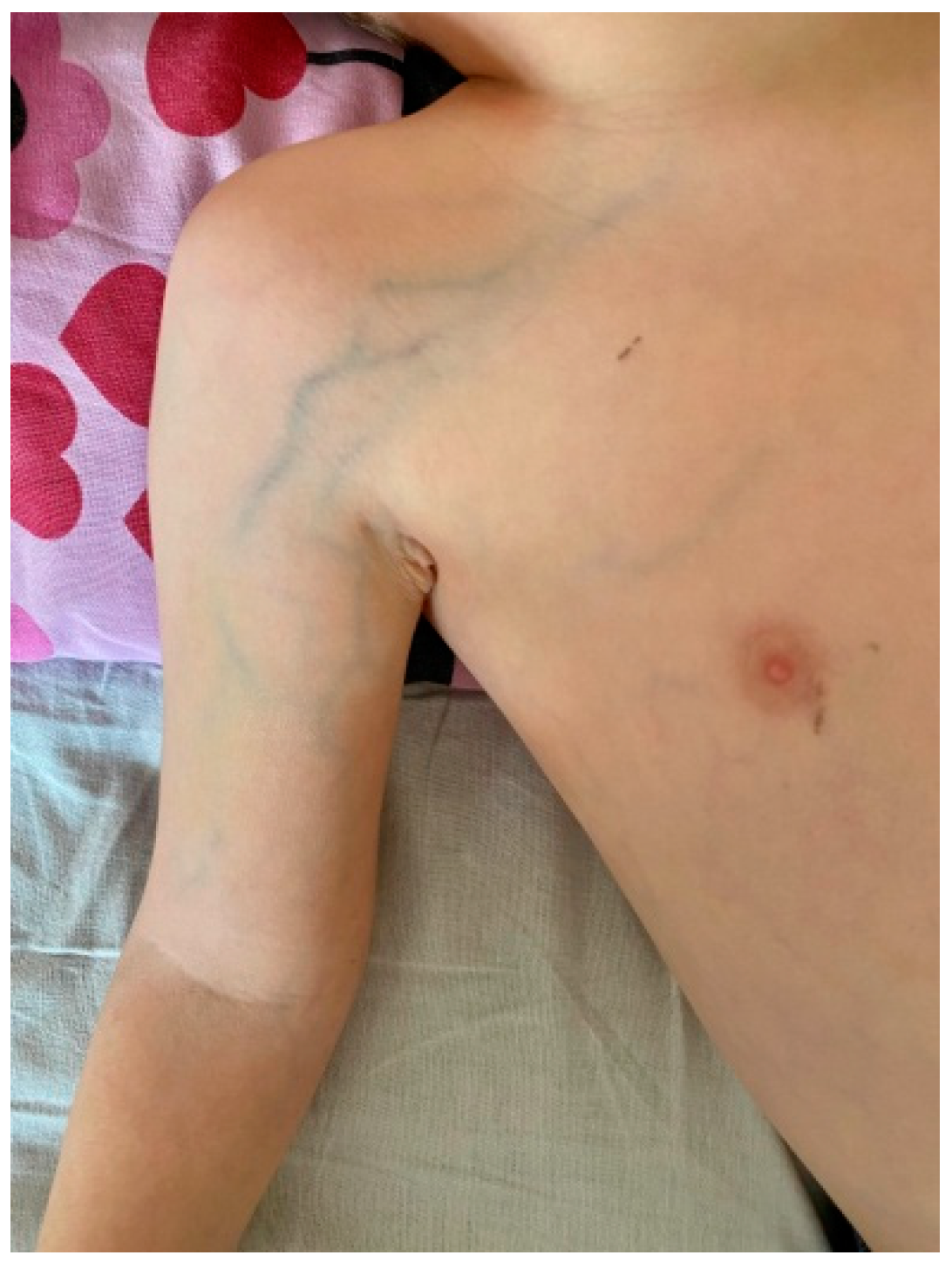
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with COVID-19 Scientific Brief 15 May 2020 Background [Internet]. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents-with-covid-19 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Porritt, R.A.; Binek, A.; Paschold, L.; Rivas, M.N.; McArdle, A.; Yonker, L.M.; Alter, G.; Chandnani, H.K.; Lopez, M.; Fasano, A.; et al. The autoimmune signature of hyperinflammatory multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e151520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ganeva, M.; Teltcharova, A.; Dimirova, A.; Hristova, D.; Temelkova, K.; Vasilev, T.; Kostova, V.; Stefanov, S. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A year and a half of experience of University Children’s Hospital, Sofia, Bulgaria, PReS2022-ABS-1262. In Proceedings of the 28th European Paediatric Rheumatology Congress (PReS 2022), Prague, Czech Republic, 20–23 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- CDC COVID Data Tracker: Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pediatric-data (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Caorsi, R.; Consolaro, A.; Speziani, C.; Sozeri, B.; Ulu, K.; Faugier-Fuentes, E.; Menchaca-Aguayo, H.; Ozen, S.; Sener, S.; Rahman, S.A.; et al. The HyperPed-COVID international registry: Impact of age of onset, disease presentation and geographical distribution on the final outcome of MIS-C. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 147, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassandro, G.; Palmieri, V.V.; Palladino, V.; Amoruso, A.; Faienza, M.F.; Giordano, P. Venous Thromboembolism in Children: From Diagnosis to Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghafry, M.; Vagrecha, A.; Malik, M.; Levine, C.; Uster, E.; Aygun, B.; Appiah-Kubi, A.; Vlachos, A.; Capone, C.A.; Rajan, S.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) and the Prothrombotic State: Coagulation Profiles and Rotational Thromboelastometry in a MIS-C Cohort. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, S.; Rubino, C.; Lasagni, D.; Pegoraro, F.; Resti, M.; Simonini, G.; Indolfi, G. Thromboembolic complications in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C: A narrative review. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 944743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, W.S. Preventing Thrombosis in Children with MIS-C. J. Pediatr. 2023, 262, 113766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, V.; Niccolai, R.; Marrani, E.; Maccora, I.; Bertini, F.; Pagnini, I.; Simonini, G.; Lasagni, D.; Trapani, S.; Mastrolia, M.V. Thrombotic Events in MIS-C Patients: A Single Case Report and Literature Review. Children 2023, 10, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, H.B.; Sartain, S.E.; Kumar, R.; Armstrong, K.; Ballester, L.; Betensky, M.; Cohen, C.T.; Diaz, R.; Diorio, C.; Goldenberg, N.A.; et al. Rate of thrombosis in children and adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19 or MIS-C. Blood 2021, 138, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdle, A.J.; Vito, O.; Patel, H.; Seaby, E.G.; Shah, P.; Wilson, C.; Broderick, C.; Nijman, R.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Munblit, D.; et al. Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Channon-Wells, S.; Vito, O.; McArdle, A.J.; Seaby, E.G.; Patel, H.; Shah, P.; Pazukhina, E.; Wilson, C.; Broderick, C.; D’Souza, G.; et al. Immunoglobulin, glucocorticoid, or combination therapy for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A propensity-weighted cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e184–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Gorelik, M.; Lapidus, S.K.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.M.; Kernan, K.F.; Schulert, G.S.; Seo, P.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Clinical Guidance for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With SARS-CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in Pediatric COVID-19: Version 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, E1–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, P.; Marin, G.; Filleron, A.; Michon, A.-L.; Marchandin, H.; Godreuil, S.; Rodière, M.; Sarrabay, G.; Touitou, I.; Meslin, P.; et al. Evaluation of post-infectious inflammatory reactions in a retrospective study of 3 common invasive bacterial infections in pediatrics. Medicine 2022, 101, e30506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.H.; Zhang, S.; Porritt, R.A.; Rivas, M.N.; Paschold, L.; Willscher, E.; Binder, M.; Arditi, M.; Bahar, I. Superantigenic character of an insert unique to SARS-CoV-2 spike supported by skewed TCR repertoire in patients with hyperinflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25254–25262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Riitano, F.; Valentini, P. Pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally related with SARS-CoV-2: Immunological similarities with acute rheumatic fever and toxic shock syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Torre, F.; Calabrese, G.; Signorile, K.; Bizzoco, F.; Mastrorilli, C.; Strippoli, A.; Amato, D.; Carella, F.; Vairo, U.; Giordano, P.; et al. Efficacy of sildenafil and high-dose anakinra in an MIS-C patient with pulmonary vasculitis: A case report. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 10, 1015617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Vázquez, E.; Aguilera-Alonso, D.; Carrasco-Colom, J.; Calvo, C.; Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Mellado, I.; Grandioso, D.; Rincón, E.; Jové, A.; Cercenado, E.; et al. Increasing incidence and severity of invasive Group A streptococcal disease in Spanish children in 2019–2022. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2023, 27, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Vázquez, E.; Aguilera-Alonso, D.; Carbayo, T.; Figueroa-Ospina, L.M.; Sanz-Santaeufemia, F.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Vázquez-Ordoñez, C.; Carrasco-Colom, J.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Jiménez-Montero, B.; et al. Epidemiology and clinical features of Streptococcus pyogenes bloodstream infections in children in Madrio, Spain. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.; Giroir, B.; Randolph, A. International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: Definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmcke, S.; Mörgelin, M.; Malmström, J.; Linder, A.; Chew, M.; Thorlacius, H.; Herwald, H. Stimulation of blood mononuclear cells with bacterial virulence factors leads to the release of pro-coagulant and pro-inflammatory microparticles. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmcke, S.; Mörgelin, M.; Herwald, H. Activation of the human contact system on neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D., Jr.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diorio, C.; McNerney, K.O.; Lambert, M.; Paessler, M.; Anderson, E.M.; Henrickson, S.E.; Chase, J.; Liebling, E.J.; Burudpakdee, C.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Evidence of thrombotic microangiopathy in children with SARS-CoV-2 across the spectrum of clinical presentations. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6051–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, L.; Shekhar, S.; Bansal, A.; Kumar, S. COVID-19 associated arterial ischaemic stroke and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A case report. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasic, S.; Popovic, S.; Kravljanac, R.; Prijic, S.; Vukomanovic, V. Intracardiac Thrombosis in the Three-Year-Old Boy with Normal Left Ventricle Systolic Function in MIS-C Associated with COVID-19. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, e2022028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ozyurek, E.; Balta, G.; Degerliyurt, A.; Parlak, H.; Aysun, S.; Gürgey, A. Significance of factor V, prothrombin, MTHFR, and PAI-1 genotypes in childhood cerebral thrombosis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2007, 13, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfirevic, Z.; Simundic, A.-M.; Nikolac, N.; Sobocan, N.; Alfirevic, I.; Stefanovic, M.; Vucicevic, Z.; Topic, E. Frequency of Factor II G20210A, Factor V Leiden, MTHFR C677T and PAI-1 5G/4G Polymorphism in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism: Croatian Case Control Study. Biochem. Medica 2010, 20, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagle, P.; Cuello, C.A.; Augustine, C.; Bonduel, M.; Brandão, L.R.; Capman, T.; Chan, A.K.C.; Hanson, S.; Male, C.; Meerpohl, J.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3292–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
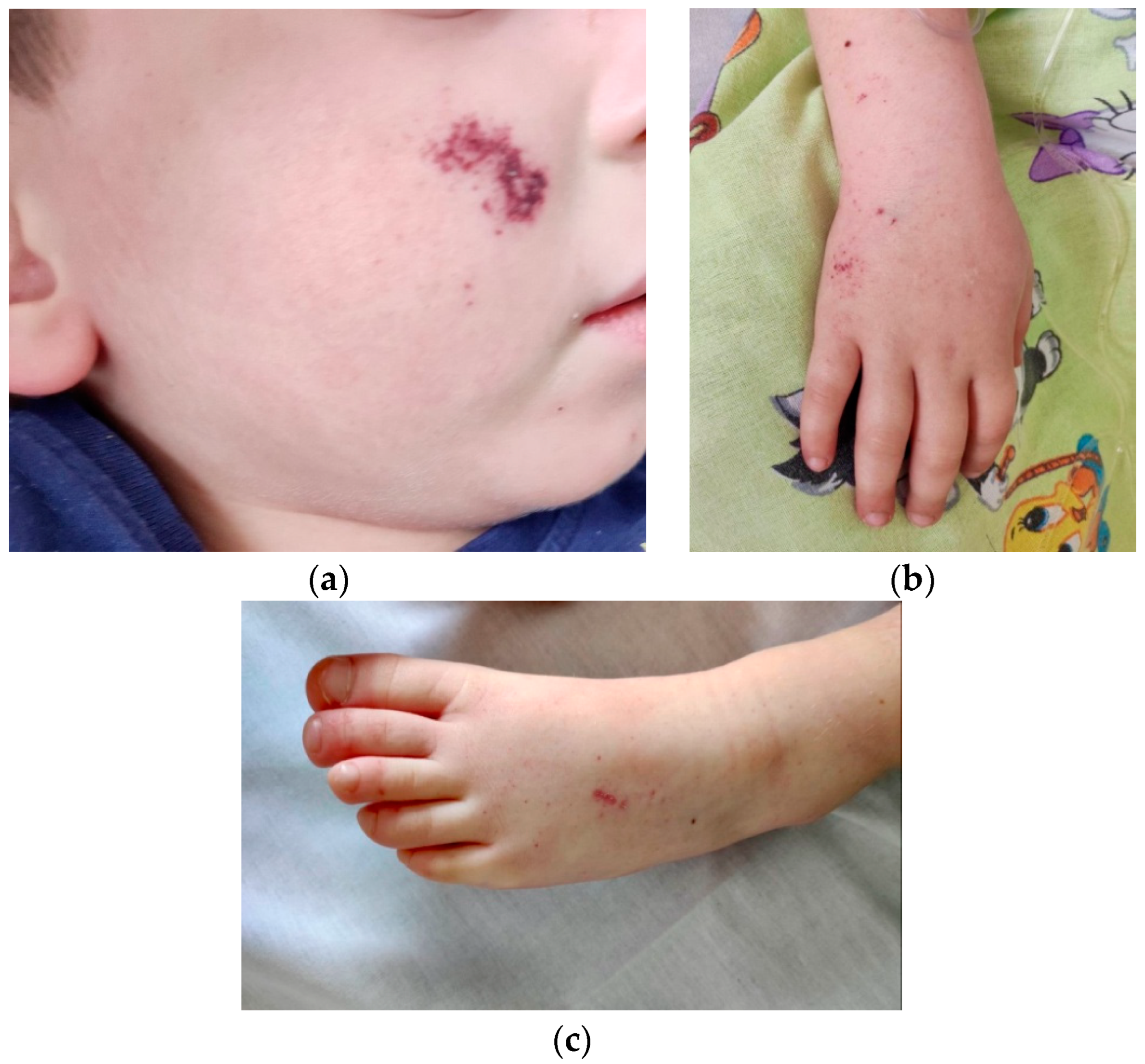
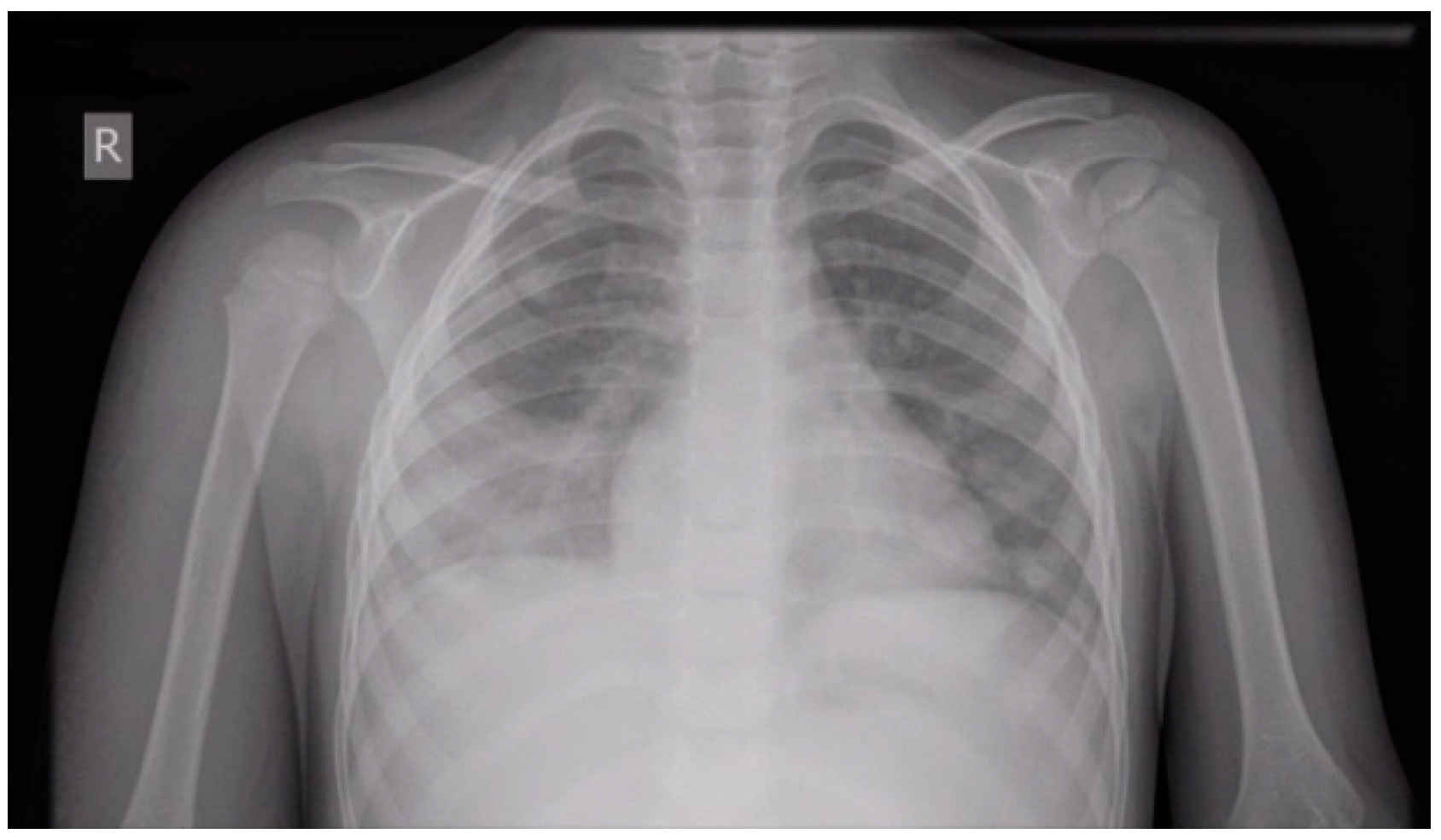
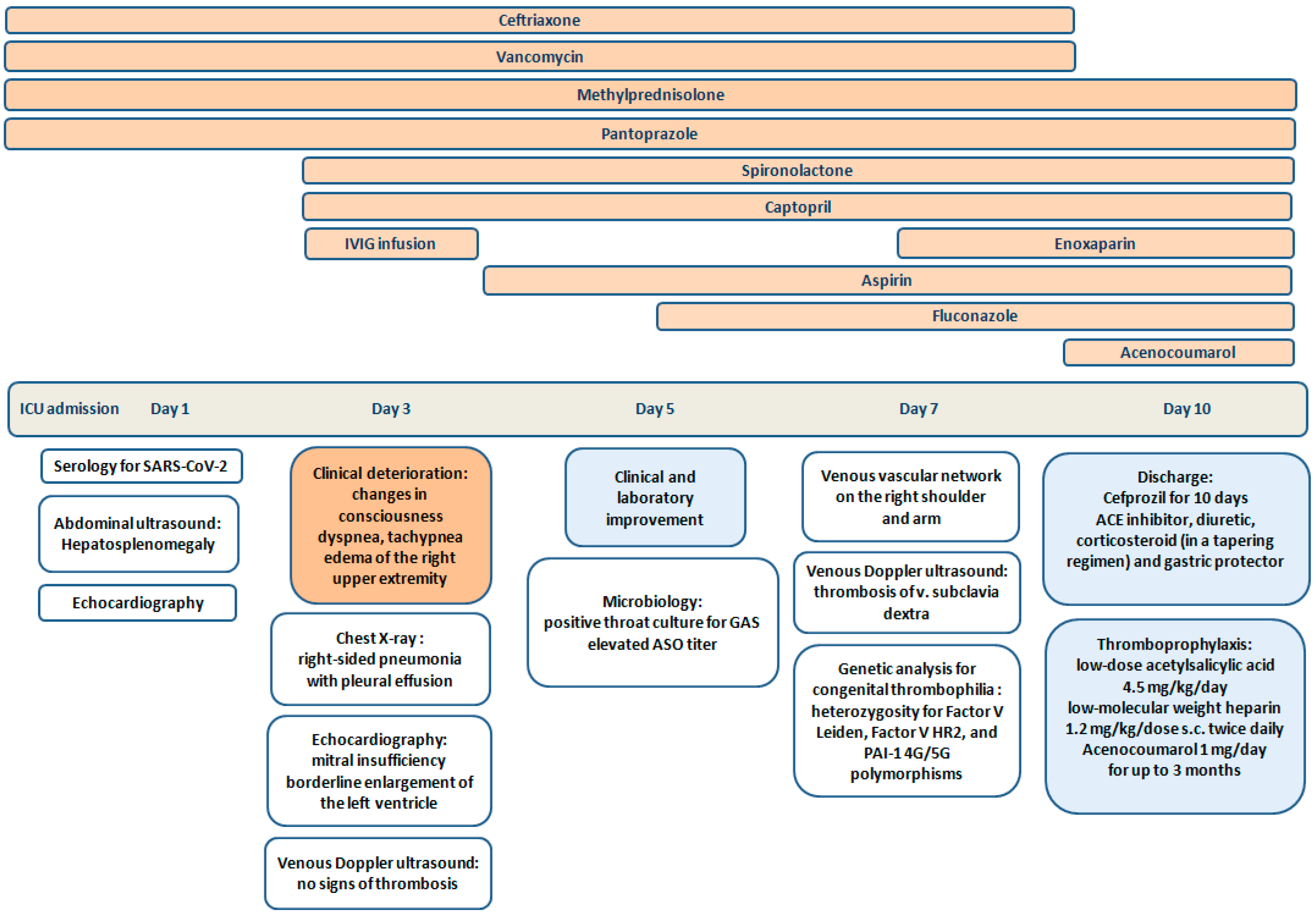
| Normal Ranges | Day 1 * | Day 3 | Day 5 ** | Day 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White blood count | 5.5–15.5 × 109/L | 37.43 | 19.26 | 24.99 | 25.79 |
| Lymphocytes | 29–65% | 3.4 | 17.1 | 15.5 | 17.7 |
| Neutrophils | 30–60% | 94.5 | 76.4 | 82.1 | 79.9 |
| Red blood count | 3.9–5.1 × 1012/L | 4.51 | 3.06 | 3.57 | 3.76 |
| Hemoglobin | 111–143 g/L | 114 | 75 | 87 | 93 |
| Platelets | 286–509 × 109/L | 82 | 74 | 430 | 633 |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 1–18 mm/h | 35 | – | – | 30 |
| C-reactive protein | 0–5 mg/L | 503.27 | >200 | 20.4 | 20.5 |
| Procalcitonin | <0.1 ng/mL | 42.29 | – | 14.58 | 0.3 |
| Ferritin | 4.4–64 ng/mL | 8494.2 | 667 | – | 509 |
| Uric acid | 0–420 µmol/L | 610 | 289 | – | 256 |
| Albumin | 38–54 g/L | 31.99 | – | – | 35.77 |
| Troponin I | 0–1 ng/mL | <0.01 | 0.011 | 0.003 | <0.01 |
| NT-pro BNP | <300 pg/mL | 9105 | 1357 | 420 | 302 |
| ASAT | <50 U/L | 159 | – | – | 15 |
| ALAT | <36 U/L | 64 | – | – | 12 |
| LDH | 120–300 U/L | 975 | 284 | – | 324 |
| Antistreptolysin O titer | 0–150 IU/mL | 6.16 | – | – | 178.52 |
| Fibrinogen | 200–400 mg/dL | 354 | 274 | – | 314 |
| D-dimer | <500 ng/mL | >3000 | 2878 | 1895 | 936.5 |
| aPTT | 28–34 s | 47.4 | 24.3 | 24.7 | 25.9 |
| INR | 0.9–1.2 | 2.06 | 1.37 | 1.28 | 1.07 |
| Prothrombin time | 11–14 s | 27 | 18.7 | 17 | 12.7 |
| SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgA | >0.6 BAU/mL | 1.78 | – | – | – |
| SARS-CoV-2 IgG | >1.6 BAU/mL | 8.4 | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoyanova, Z.; Temelkova, K.; Ganeva, M.; Vasilev, T.; Dasheva-Dimitrova, A.; Kibarova-Hristova, D.; Stefanov, S. A Clinical Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Group A β-Hemolytic Streptococcus Coinfection and Venous Thrombosis in a Child with Congenital Thrombophilia. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050334
Stoyanova Z, Temelkova K, Ganeva M, Vasilev T, Dasheva-Dimitrova A, Kibarova-Hristova D, Stefanov S. A Clinical Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Group A β-Hemolytic Streptococcus Coinfection and Venous Thrombosis in a Child with Congenital Thrombophilia. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050334
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoyanova, Zdravka, Katya Temelkova, Margarita Ganeva, Teodor Vasilev, Anna Dasheva-Dimitrova, Desislava Kibarova-Hristova, and Stefan Stefanov. 2025. "A Clinical Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Group A β-Hemolytic Streptococcus Coinfection and Venous Thrombosis in a Child with Congenital Thrombophilia" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050334
APA StyleStoyanova, Z., Temelkova, K., Ganeva, M., Vasilev, T., Dasheva-Dimitrova, A., Kibarova-Hristova, D., & Stefanov, S. (2025). A Clinical Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Group A β-Hemolytic Streptococcus Coinfection and Venous Thrombosis in a Child with Congenital Thrombophilia. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050334









