Conformational Flexibility of a Lipocalin Allergen (Mus m 1): Implications for Molecular Allergy Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structure Preparation
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.3. Intramolecular HINT Force-Field
2.4. Computational Resources
3. Results
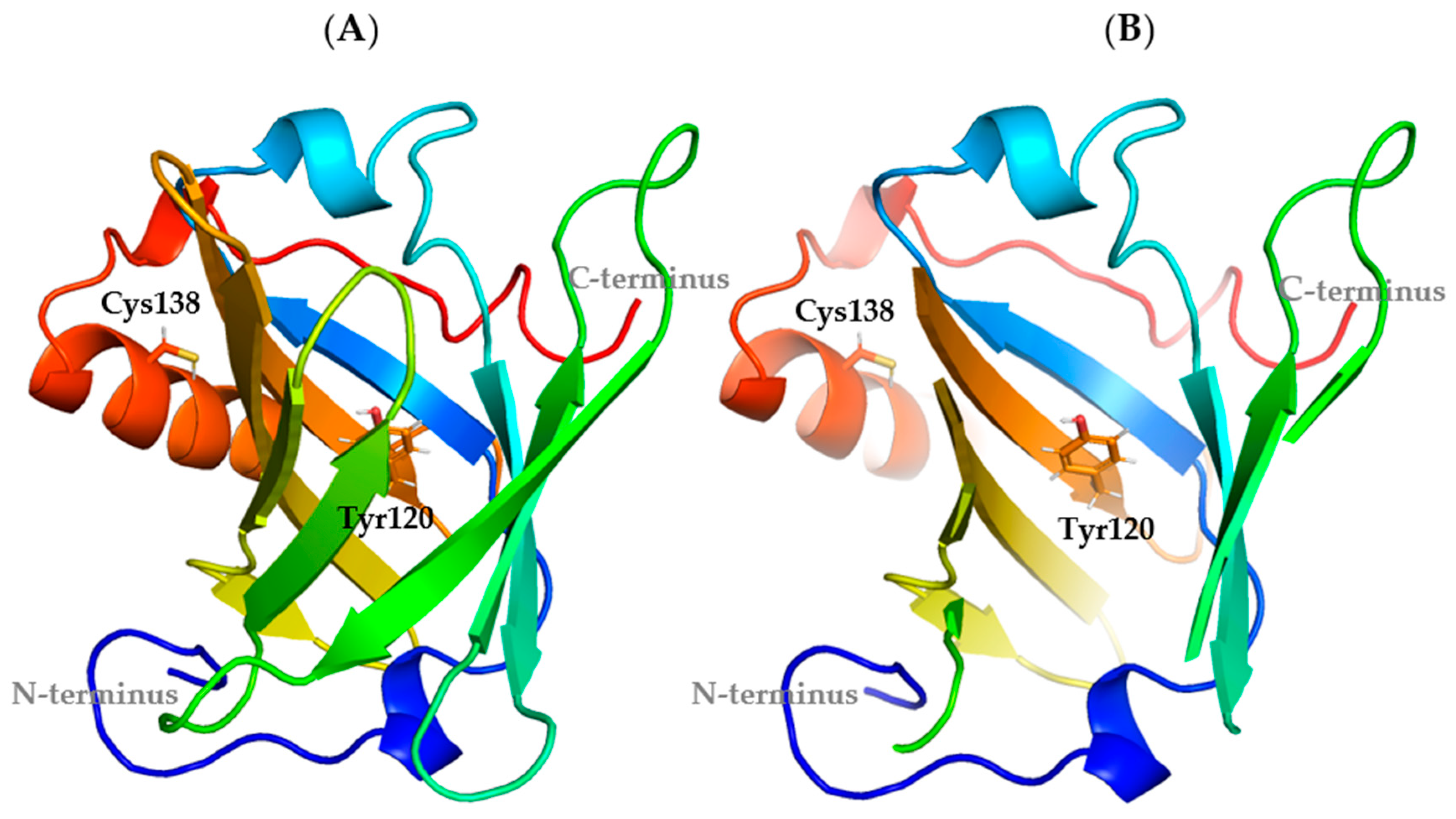
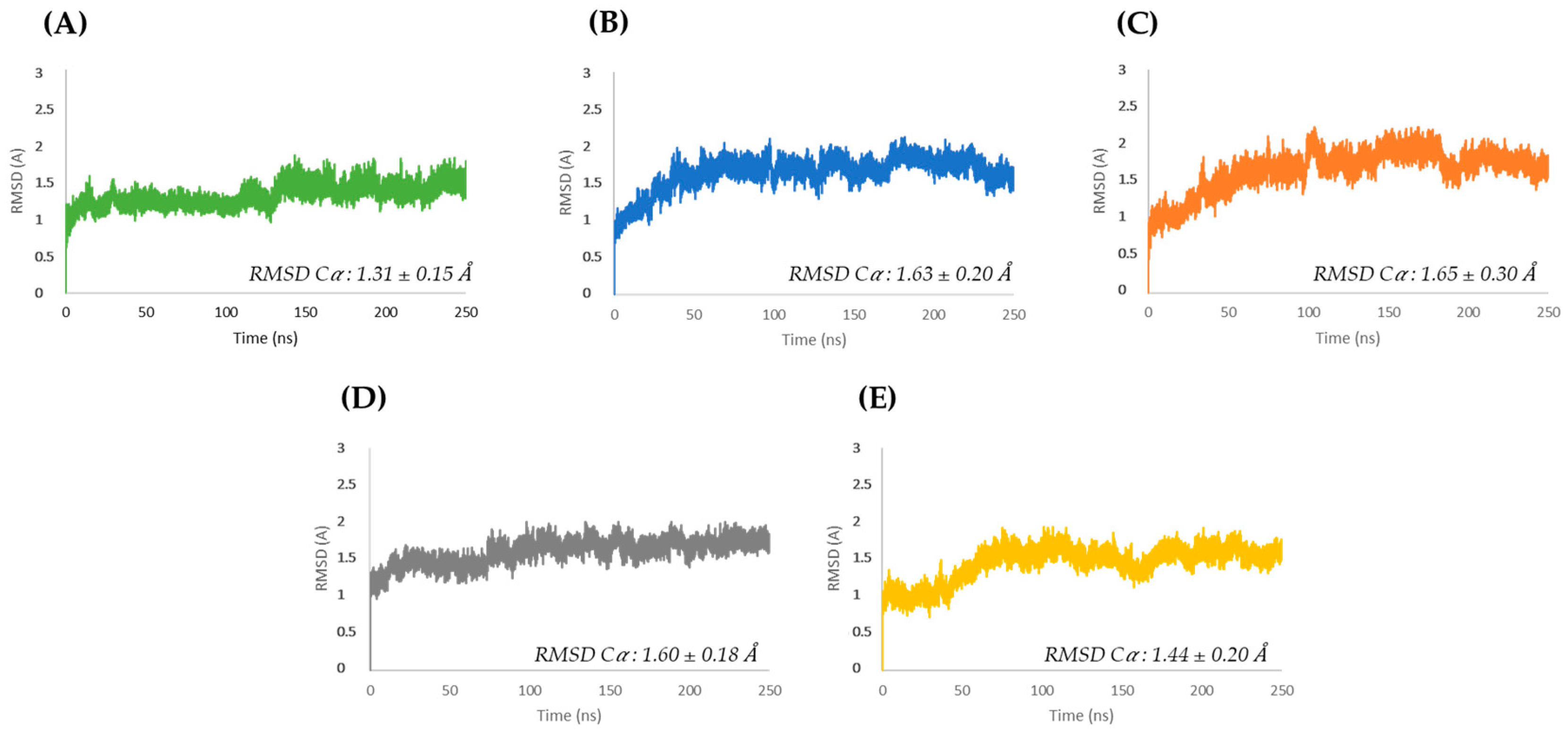
3.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
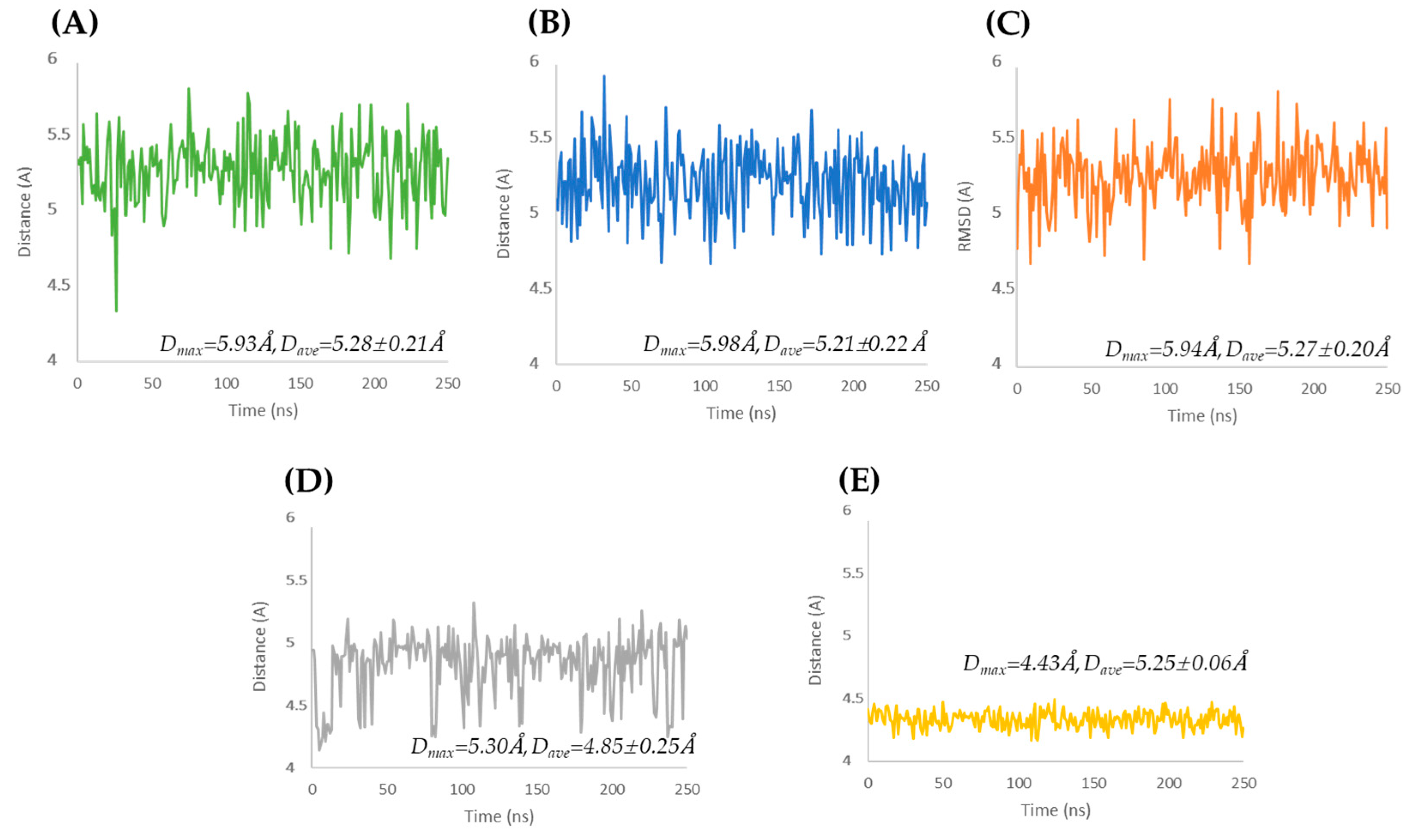
The Oscillatory Motion of the α-Helix Motif
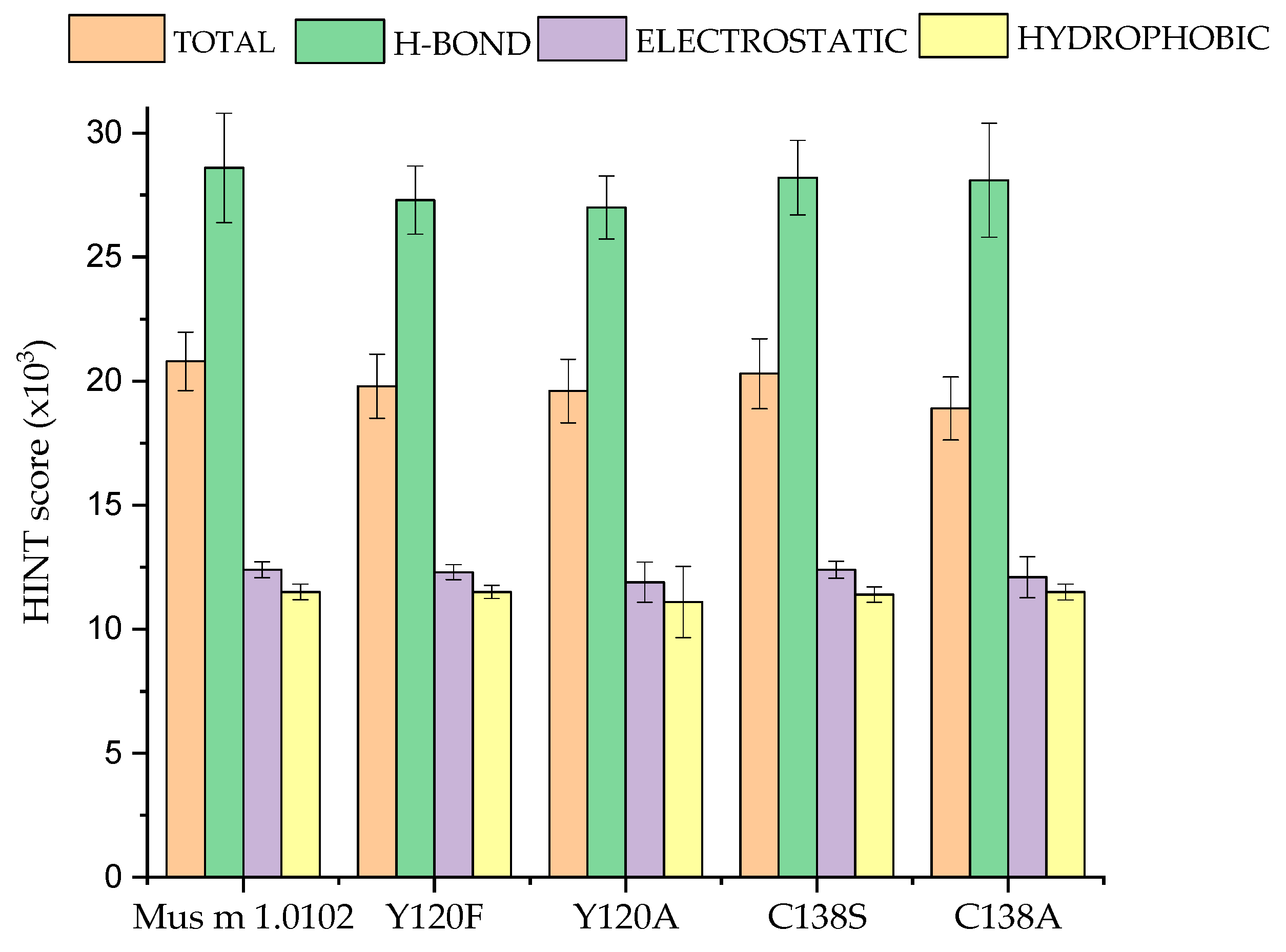
3.2. HINT-Based Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virtanen, T. Lipocalin allergens. Allergy 2001, 56 (Suppl. 67), 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, C.; Kuehn, A.; Hentges, F. Animal lipocalin allergens. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruszcz, M.; Chew, F.T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Hurlburt, B.K.; Mueller, G.A.; Pomés, A.; Rouvinen, J.; Villalba, M.; Wöhrl, B.M.; Breiteneder, H. Allergens and their associated small molecule ligands-their dual role in sensitization. Allergy 2021, 76, 2367–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, T. Inhalant mammal-derived lipocalin allergens and the innate immunity. Front. Allergy 2022, 2, 824736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahradnik, E.; Raulf, M. Respiratory allergens from furred mammals: Environmental and occupational exposure. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, T.; Kinnunen, T.; Rytkönen-Nissinen, M. Mammalian lipocalin allergens—Insights into their enigmatic allergenicity. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindaye, S.T.; Sun, C.; Esfahani, S.A.Z.; Matsui, E.C.; Sheehan, M.J.; Rabin, R.L.; Slater, J.E. Diversity and complexity of mouse allergens in urine; house dust; and allergen extracts assessed with an immuno-allergomic approach. Allergy 2021, 76, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücke, C.; Franzoni, L.; Abbate, F.; Löhr, F.; Ferrari, E.; Sorbi, R.T.; Rüterjans, H.; Spisni, A. Solution structure of a recombinant mouse major urinary protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuser, P.R.; Franzoni, L.; Ferrari, E.; Spisni, A.; Polikarpov, I. The X-ray structure of a recombinant major urinary protein at 1.75 Å resolution. A comparative study of X-ray and NMR-derived structures. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E.; Corsini, R.; Burastero, S.E.; Tanfani, F.; Spisni, A. The allergen Mus m 1.0102: Cysteine residues and molecular allergology. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 120, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertinhez, T.A.; Ferrari, E.; Casali, E.; Patel, J.A.; Spisni, A.; Smith, L.J. The binding cavity of mouse major urinary protein is optimised for a variety of ligand binding modes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Breda, D.; Longhi, R.; Vangelista, L.; Nakaie, C.R.; Elviri, L.; Casali, E.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Spisni, A.; Burastero, S.E. In search of a vaccine for mouse allergy: Significant reduction of Mus m 1 allergenicity by structure-guided single-point mutations. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E.; Casali, E.; Burastero, S.E.; Spisni, A.; Pertinhez, T.A. The allergen Mus m 1.0102: Dissecting the relationship between molecular conformation and allergenic potency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Corsini, R.; Burastero, S.E.; Tanfani, F.; Spisni, A. Thermal stability, ligand binding and allergenicity data of Mus m 1.0102 allergen and its cysteine mutants. Data Brief. 2020, 29, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, G.E.; Semus, S.F.; Abraham, D.J. HINT: A new method of empirical hydrophobic field calculation for CoMFA. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1991, 5, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, G.E.; Abraham, D.J. Hydrophobicity: Is LogP(o/w) more than the sum of its parts? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 35, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Kellogg, G. Hydrophobicity—Shake flasks, protein folding and drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Kellogg, G.E.; Cozzini, P. From oncoproteins to spike proteins: The evaluation of intramolecular stability using hydropathic force field. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2022, 36, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.; Brozell, S.; Cerutti, D.; Cheatham, T.; Cruzeiro, V.; Darden, T.; Duke, R.; et al. Amber 2021; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncharich, R.J.; Brooks, B.R.; Pastor, R.W. Langevin dynamics of peptides: The frictional dependence of isomerization rates of N-acetylalanyl-N′-methylamide. Biopolymers 1992, 32, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åqvist, J.; Wennerström, P.; Nervall, M.; Bjelic, S.; Brandsdal, B.O. Molecular dynamics simulations of water and biomolecules with a Monte Carlo constant pressure algorithm. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 384, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräutler, V.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hünenberger, P.H. A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Cozzini, P. A combined molecular dynamics and hydropathic INTeraction (HINT) approach to investigate protein flexibility: The PPARγ case study. Molecules 2024, 29, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Cozzini, P. Hint approach on Transthyretin folding/unfolding mechanism comprehension. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzini, P.; Agosta, F.; Dolcetti, G.; Dal Palù, A. A computational workflow to predict biological target mutations: The spike glycoprotein case study. Molecules 2023, 28, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Breda, D.; Spisni, A.; Burastero, S.E. Component-Resolved Diagnosis Based on a Recombinant Variant of Mus m 1 Lipocalin Allergen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kringelum, J.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Reliable B cell epitope predictions: Impacts of method development and improved benchmarking. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.J.; Leo, A.J. Extension of the fragment method to calculate amino acid zwitterion and side chain partition coefficients. Proteins 1987, 2, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, G.E.; Marabotti, A.; Spyrakis, F.; Mozzarelli, A. HINT, a code for understanding the interaction between biomolecules: A tribute to Donald J. Abraham. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1194962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodig, S.; Čepelak, I. The potential of component-resolved diagnosis in laboratory diagnostics of allergy. Biochem. Med. 2018, 28, 020501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel-Rodríguez, A.; Armentia, A.; Martín-Armentia, B.; Corell, A.; Lozano-Estevan, M.C.; Iglesias Peinado, I. Component-resolved diagnosis in allergic disease: Utility and limitations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 489, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callery, E.L.; Keymer, C.; Barnes, N.A.; Rowbottom, A.W. Component-resolved diagnostics in the clinical and laboratory investigation of allergy. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 57, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, J.; Bridgewater, J.; Ferreira, F.; van Ree, R.; Rabin, R.L.; Vieths, S. The history, present and future of allergen standardization in the United States and Europe. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 725831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.K.; Pike, D.H.; Khan, I.J.; Nanda, V. Structural and dynamic properties of allergen and non-allergen forms of Tropomyosin. Structure 2018, 26, 997–1006.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, C.A.; Zeindl, R.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Tollinger, M.; Liedl, K.R. Allergenicity and conformational diversity of allergens. Allergies 2024, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Arandia, M.; Gómez-Casado, C.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Pacios, L.F. Molecular dynamics of major allergens from Alternaria, Birch pollen and Peach. Mol. Inform. 2014, 33, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Dong, X.; Raghavan, V. An overview of molecular dynamics simulation for food products and processes. Processes 2022, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, R.; Xu, Y.; Chi, L.; Li, Y.; Mu, G.; Zhu, X. Investigation of the structure and allergic potential of whey protein by both heating sterilization and simulation with Molecular Dynamics. Foods 2022, 11, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazorda-Ccahuana, H.L.; Theiss-De-Rosso, V.; Valencia, D.E.; Gómez, B. Heat-stable hazelnut profilin: Molecular dynamics simulations and immunoinformatics analysis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanga, S.K.; Singh, A.; Raghavan, V. Effect of thermal and electric field treatment on the conformation of Ara h 6 peanut protein allergen. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 30, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Loeffler, J.R.; Waibl, F.; Kamenik, A.S.; Hofer, F.; Liedl, K.R. Conformational selection of allergen-antibody complexes-surface plasticity of paratopes and epitopes. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2019, 32, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Führer, S.; Kamenik, A.S.; Zeindl, R.; Nothegger, B.; Hofer, F.; Reider, N.; Liedl, K.R.; Tollinger, M. Inverse relation between structural flexibility and IgE reactivity of Cor a 1 hazelnut allergens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H. Epitopes of protein binders are related to the structural flexibility of a target protein surface. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Far-UV CD Spectroscopy | Near-UV CD Spectroscopy | Fluorescence Spectroscopy (Intensity) | NPN Ligand Binding Kd (±SE, nM) | Thermal Stability a Tm, Tonset (°C) | Unfolding Reversibility b | IgE Reactivity c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mus m 1.0102 | 25.0 ± 1.5 | 75.2, 62.5 | No | ||||
| Y120F mutant | N/C | ≠ d | ↑ e | 84.0 ± 24.0 | - | - | ↓ e |
| Y120A mutant | N/C | ≠≠ | ↑↑ | - | - | - | ↓↓ |
| C138S mutant | N/C | N/C | N/C | - | 71.9, 57.5 | Yes | ↑ |
| C138A mutant | N/C | ≠ | N/C | 33.8 ± 6.4 | 78.9, 70.0 | Yes | N/C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agosta, F.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Cozzini, P.; Spisni, A.; Ferrari, E. Conformational Flexibility of a Lipocalin Allergen (Mus m 1): Implications for Molecular Allergy Diagnostics. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040234
Agosta F, Pertinhez TA, Cozzini P, Spisni A, Ferrari E. Conformational Flexibility of a Lipocalin Allergen (Mus m 1): Implications for Molecular Allergy Diagnostics. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgosta, Federica, Thelma A. Pertinhez, Pietro Cozzini, Alberto Spisni, and Elena Ferrari. 2025. "Conformational Flexibility of a Lipocalin Allergen (Mus m 1): Implications for Molecular Allergy Diagnostics" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040234
APA StyleAgosta, F., Pertinhez, T. A., Cozzini, P., Spisni, A., & Ferrari, E. (2025). Conformational Flexibility of a Lipocalin Allergen (Mus m 1): Implications for Molecular Allergy Diagnostics. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040234


_Kim.png)







