ALK-Targeted Therapy: Resistance Mechanisms and Emerging Precision Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular and Functional Basis of ALK
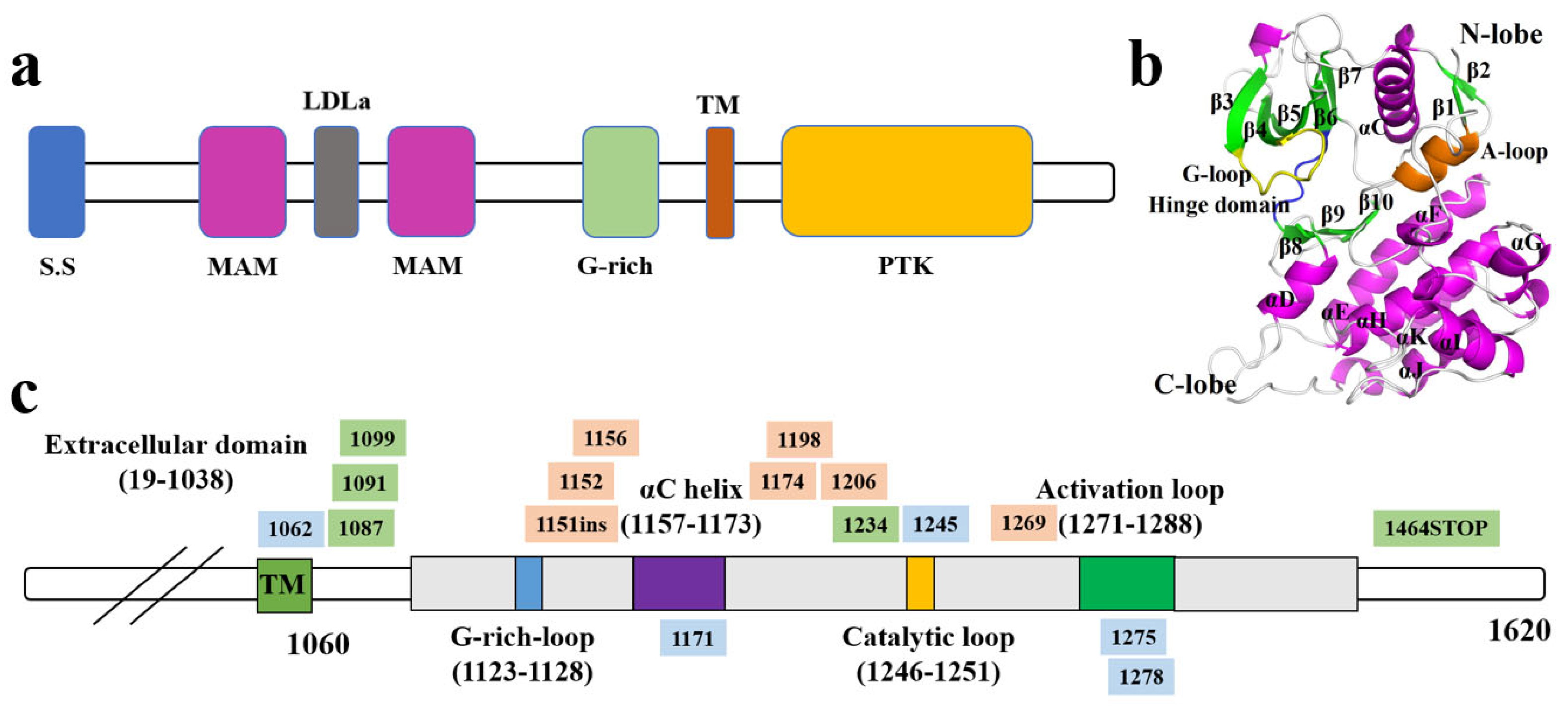
2.1. Genomic and Structural Characteristics of ALK
2.2. Physiological Function and Expression Profile of ALK
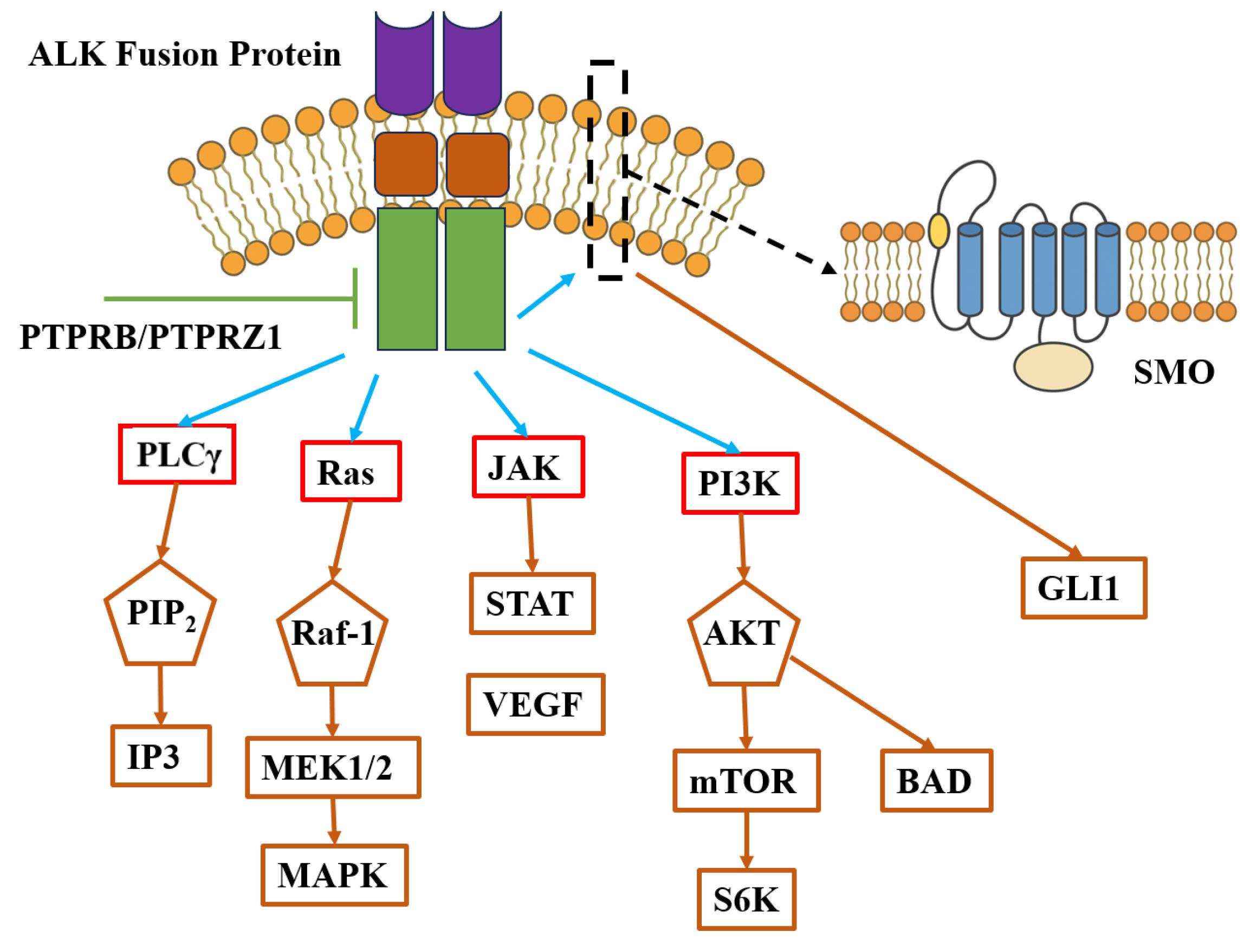
2.3. Mechanisms of Activation and Oncogenic Signaling
2.4. Associated Signaling Pathways
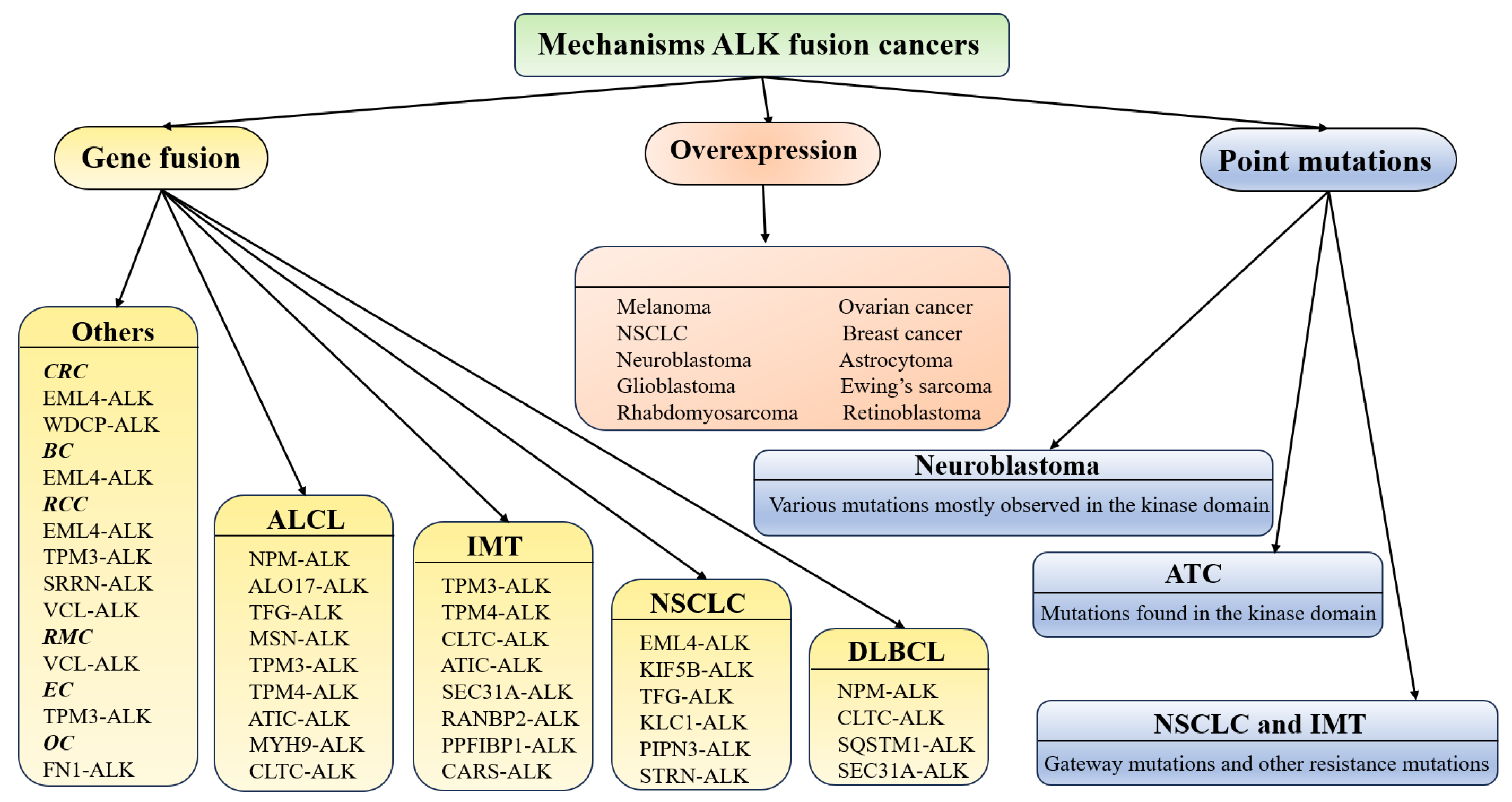
3. Role of Aberrant ALK in Diverse Malignancies
3.1. NSCLC
3.2. ALCL
3.3. Others
4. Evolution of ALK Inhibitors
4.1. First-Generation ALK Inhibitor: Crizotinib
4.2. Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors: Ceritinib, Alectinib, and Brigatinib
4.3. Third-Generation ALK Inhibitor: Lorlatinib
4.4. Next-Generation ALK Candidates and Therapeutic Strategies
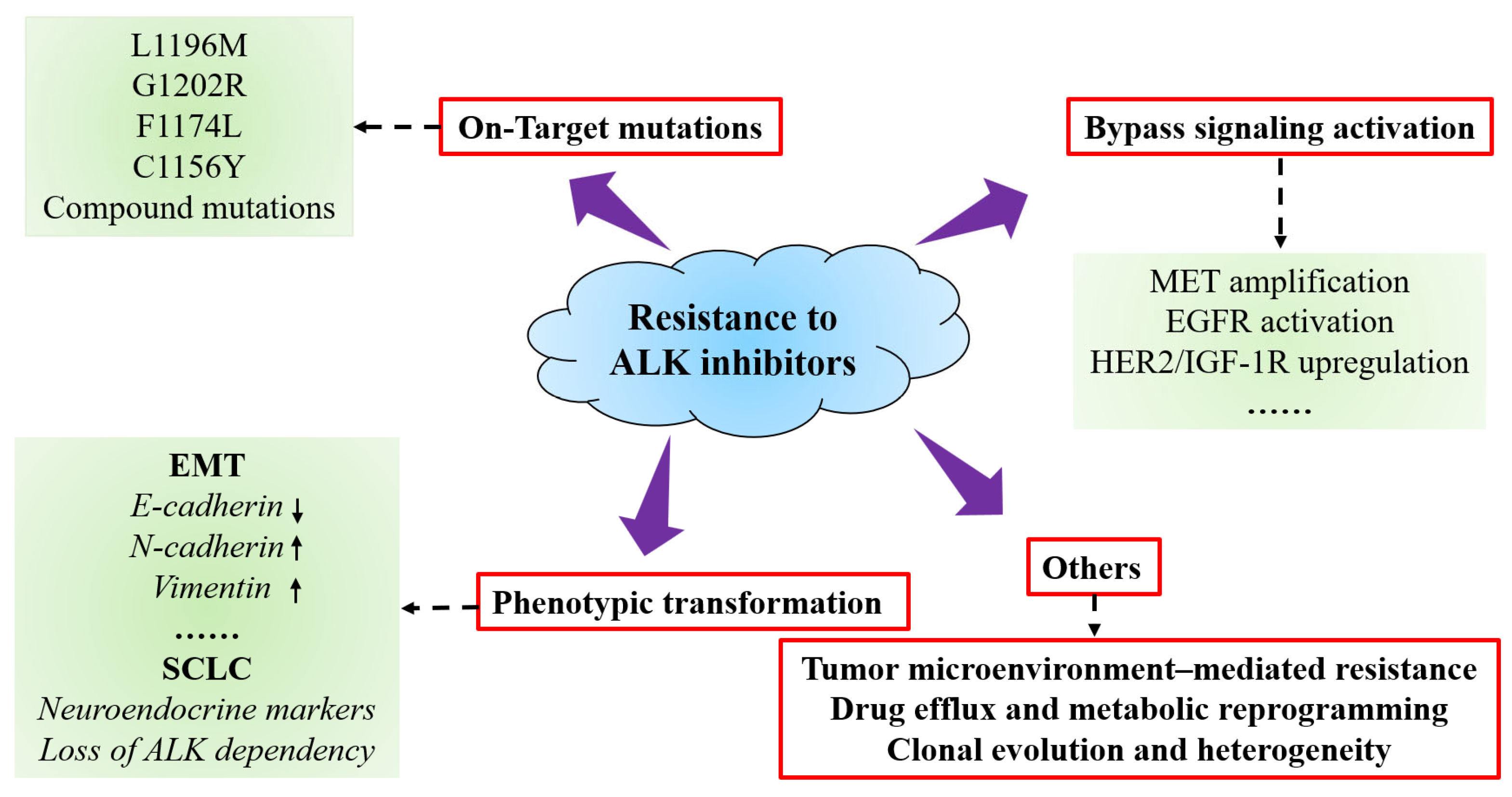
5. Resistance Mechanisms to ALK Inhibitors
5.1. On-Target Mutations
5.2. Bypass Signaling Activation
5.3. Phenotypic Transformation
5.4. Other Mechanisms
6. Strategies to Overcome Resistance
6.1. Resistance Mutation-Guided ALK Inhibitor Optimization
6.2. Combination Therapeutic Strategies
6.3. Intervention Strategies Targeting Phenotypic Transformation
6.4. Precision Medicine Guided Approaches
7. Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| PTK | Protein tyrosine kinase |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| ALCL | Anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| IMTs | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| ORR | Objective response rate |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
References
- Zhang, Y.K.; Tong, J.B.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.L.; Hou, Q. Design and molecular mechanism investigation of ALK inhibitors based on virtual screening and structural descriptor modeling. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2025, 45, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Pan, P.; Sun, H.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, T. Drug Discovery Targeting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10927–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, J.C.; Shih, J.Y. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Kinase Domain Mutation Following ALK Inhibitor(s) Failure in Advanced ALK Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis and Literature Review. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, e77–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.H.; Vernersson, E.; Grabbe, C.; Hallberg, B. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: Signalling in development and disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Ou, W.B. Genomic landscaping of receptor tyrosine kinase ALK with highly frequent rearrangements in cancers. IUBMB Life 2025, 77, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Viscardi, G.; Di Liello, R.; Fasano, M.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Role and targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Petrus, M.N.; Xiao, W.; Nicolae, A.; Raffeld, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Bamford, R.N.; Nakagawa, M.; Ouyang, S.T.; et al. Cytokine receptor signaling is required for the survival of ALK- anaplastic large cell lymphoma, even in the presence of JAK1/STAT3 mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3975–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenstein, J.M.; Chooback, N. ALK inhibitors, resistance development, clinical trials. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S59–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yasothan, U.; Kirkpatrick, P. Crizotinib. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Savooji, J.; Liu, D. Second- and third-generation ALK inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erp, A.E.M.; Hillebrandt-Roeffen, M.H.S.; van Houdt, L.; Fleuren, E.D.G.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.M.H. Targeting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) with the Second-Generation ALK Inhibitor Ceritinib. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Dhillon, S. Alectinib: A Review in Advanced, ALK-Positive NSCLC. Drugs 2018, 78, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Xia, Z.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Sun, D.; Ai, J.; Song, Z.; Geng, M.; Zhang, A. Discovery of 2,4-diarylaminopyrimidines bearing a resorcinol motif as novel ALK inhibitors to overcome the G1202R resistant mutation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzo, R.; Inghirami, G. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zito Marino, F.; Rocco, G.; Morabito, A.; Mignogna, C.; Intartaglia, M.; Liguori, G.; Botti, G.; Franco, R. A new look at the ALK gene in cancer: Copy number gain and amplification. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2016, 16, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, A.; Lasorsa, E.; Riera, L.; Machiorlatti, R.; Piva, R.; Ponzoni, M.; Kwee, I.; Bertoni, F.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Pileri, S.A.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase in human cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, R11–R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): Structure, oncogenic activation, and pharmacological inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 68, 68–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-K.; Tong, J.-B.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Y.-R. Multiscale Computational and Pharmacophore-Based Screening of ALK Inhibitors with Experimental Validation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, A. Novel Molecular Challenges in Targeting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in ALK-Expressing Human Cancers. Cancers 2017, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Tsukahara, T. Integrated analysis of the clinical consequence and associated gene expression of ALK in ALK-positive human cancers. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartari, C.J.; Scapozza, L.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. The ALK Gene, An Attractive Target for Inhibitor Development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, K.; Lamant, L.; Espinos, E.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, L.; Turturro, F.; Delsol, G.; Morris, S.W. The emerging normal and disease-related roles of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2939–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R. Therapeutic strategies and mechanisms of drug resistance in anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged lung cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 177, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R. Drug resistance in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors in the treatment of ALK-driven lung cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, D.N.; Bhatnagar, N.; Sharma, B.; Luther, W.; Moore, N.F.; Cheung, N.K.; Gray, N.S.; George, R.E. ALK inhibitor resistance in ALK(F1174L)-driven neuroblastoma is associated with AXL activation and induction of EMT. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3681–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, M.; Du, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zuo, D.; Wu, Y. EML4-ALK G1202R mutation induces EMT and confers resistance to ceritinib in NSCLC cells via activation of STAT3/Slug signaling. Cell Signal 2022, 92, 110264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W. Mutation L1196M-induced conformational changes and the drug resistant mechanism of anaplastic lymphoma kinase studied by free energy perturbation and umbrella sampling. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 30239–30248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Gao, Q.; Fu, M.; Ni, N.; Pei, Y.; Ou, W.B. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusions: Roles in cancer and therapeutic perspectives. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrustanovic, G.; Olivas, V.; Pazarentzos, E.; Tulpule, A.; Asthana, S.; Blakely, C.M.; Okimoto, R.A.; Lin, L.; Neel, D.S.; Sabnis, A.; et al. RAS-MAPK dependence underlies a rational polytherapy strategy in EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskova Kafkova, L.; Mierzwicka, J.M.; Chakraborty, P.; Jakubec, P.; Fischer, O.; Skarda, J.; Maly, P.; Raska, M. NSCLC: From tumorigenesis, immune checkpoint misuse to current and future targeted therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.L.; Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. ALK-positive lung cancer: A moving target. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.G.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, B.B.; Du, Y.F.; Niu, J.B.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.Y. ALK-based dual inhibitors: Focus on recent development for non-small cell lung cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 291, 117646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Levchenko, E.V.; Kuligina, E.S.; Orlov, S.V. Treating non-small cell lung cancer with selumetinib: An up-to-date drug evaluation. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S. An Exploration into the Origins and Pathogenesis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Positive. Cancers 2017, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosse, Y.P. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase as a Cancer Target in Pediatric Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, P.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Lin, Y. Recent progress in targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1125547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Jayalakshmi, P.; Rhodes, A.; Liam, C.K.; Tan, J.L.; Yousoof, S.; Rajadurai, P. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-K.; Tong, J.-B.; Luo, M.-X.; Xing, X.-Y.; Yang, Y.-L.; Qing, Z.-P.; Chang, Z.-L.; Zeng, Y.-R. Design and evaluation of piperidine carboxamide derivatives as potent ALK inhibitors through 3D-QSAR modeling, artificial neural network and computational analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, S.A.; Shanshal, M.; Leventakos, K.; Parikh, K. Emerging Targeted Therapies in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Cancers 2025, 17, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; Galiacy, S.; Allouche, M. Targeting ALK in Cancer: Therapeutic Potential of Proapoptotic Peptides. Cancers 2019, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioureas, D.; Beck, J.; Baltatzis, G.; Vardaki, I.; Fonseca, P.; Tsesmetzis, N.; Vega, F.; Leventaki, V.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Drakos, E.; et al. ALK+ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)-Derived Exosomes Carry ALK Signaling Proteins and Interact with Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Govi, S.; Pileri, S.A.; Savage, K.J. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 83, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaud, C.; Knörr, F.; Brugières, L.; Woessmann, W. Diagnosis and Management of ALK-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2023, 36, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A.K.; Gunnes, M.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Neuroblastoma—A Comprehensive Update. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, E.R.; Tall, J.R.; Danielson, L.S.; Gowan, S.; Jamin, Y.; Robinson, S.P.; Banerji, U.; Chesler, L. Immunoassays for the quantification of ALK and phosphorylated ALK support the evaluation of on-target ALK inhibitors in neuroblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilen, T.M.; Soerensen, J.; Bochennek, K.; Becker, M.; Schwabe, D.; Rolle, U.; Klingebiel, T.; Lehrnbecher, T. Crizotinib in ALK(+) inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors-Current experience and future perspectives. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friboulet, L.; Li, N.; Katayama, R.; Lee, C.C.; Gainor, J.F.; Crystal, A.S.; Michellys, P.-Y.; Awad, M.M.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.; et al. The ALK Inhibitor Ceritinib Overcomes Crizotinib Resistance in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.L.; Dinh, D.; et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo [4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zuo, D.; Zhang, J.; Xing, L.; Gou, W.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, X. Dual potent ALK and ROS1 inhibitors combating drug-resistant mutants: Synthesis and biological evaluation of aminopyridine-containing diarylaminopyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ban, Y.; Qin, H.; Tai, Y. CMTR1-ALK: An ALK fusion in a patient with no response to ALK inhibitor crizotinib. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Li, E.; Wang, S. Elucidation of Resistance Mechanisms to Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors Alectinib and Ceritinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratake, N.; Toyokawa, G.; Seto, T.; Tagawa, T.; Okamoto, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Takeo, S.; Mori, M. The mechanisms of resistance to second- and third-generation ALK inhibitors and strategies to overcome such resistance. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2021, 21, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Song, L.T.; Liu, R.R.; Zhai, H.L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y. Molecular inhibitory mechanism study on the potent inhibitor brigatinib against four crizotinib-resistant ALK mutations. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.S.; Liu, S.; Zou, D.; Thomas, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Romero, J.; Kohlmann, A.; Li, F.; Qi, J.; et al. Discovery of Brigatinib (AP26113), a Phosphine Oxide-Containing, Potent, Orally Active Inhibitor of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4948–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H. Second-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Revolutionary or evolutionary? J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuta, H.; Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Adachi, J.; Takemoto, A.; Kutkowska, J.; Maruyama, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Oh-Hara, T.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Gilteritinib overcomes lorlatinib resistance in ALK-rearranged cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Hou, T.; Pan, P. Dissecting the role of ALK double mutations in drug resistance to lorlatinib with in-depth theoretical modeling and analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 169, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, D.; Battiloro, C.; Della Gravara, L.; Gridelli, C. Safety and Tolerability of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Lin, J.J. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: Mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, T.; Shiraishi, H.; Fujiwara, Y. Brigatinib and lorlatinib: Their effect on ALK inhibitors in NSCLC focusing on resistant mutations and central nervous system metastases. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielbowski, K.; Zychowska, J.; Becht, R. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors-a review of anticancer properties, clinical efficacy, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1285374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Gu, S.; Xu, L.; Hou, T.; Pan, P. In-depth theoretical modeling to explore the mechanism of TPX-0131 overcoming lorlatinib resistance to ALK(L1196M/G1202R) mutation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 183, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.W.; Zhai, D.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Ung, J.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, H.; Barrera, M.; Parra, A.; Cowell, J.; et al. TPX-0131, a Potent CNS-penetrant, Next-generation Inhibitor of Wild-type ALK and ALK-resistant Mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J. Mechanisms of Resistance to ALK Inhibitors and Corresponding Treatment Strategies in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2025, 18, 2151–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognigni, V.; Pecci, F.; Lupi, A.; Pinterpe, G.; De Filippis, C.; Felicetti, C.; Cantini, L.; Berardi, R. The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolle, E.; Taucher, V.; Lindenmann, J.; Jost, P.J.; Pichler, M. Current Knowledge about Mechanisms of Drug Resistance against ALK Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Schuuring, E.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Timens, W.; den Dunnen, W.F.A.; van den Berg, A.; Ter Elst, A.; van Kruchten, M.; Kluiver, J.L.; et al. Actionability of on-target ALK Resistance Mutations in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Local Experience and Review of the Literature. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e104–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sun, K.; Gao, T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, D. SIRT1 silencing promotes EMT and Crizotinib resistance by regulating autophagy through AMPK/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway in EML4-ALK L1196M and EML4-ALK G1202R mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2024, 63, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dar, A.C. Targeting drug-resistant mutations in ALK. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, T.; Tachihara, M.; Nagano, T.; Kobayashi, K. Review of Therapeutic Strategies for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Chen, H. Optimal Care for Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review on the Role and Utility of ALK Inhibitors. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6615–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The role of the ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 3), iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingling, X.; Maoxi, C.; Wei, Y.; Jieting, Z.; Yuanyuan, Y.; Ning, X. Transformation of NSCLC to SCLC harboring EML4-ALK fusion with V1180L mutation after alectinib resistance and response to lorlatinib: A case report and literature review. Lung Cancer 2023, 186, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, R.; Borea, R.; Drago, F.; Russo, A.; Nigita, G.; Rolfo, C. Genetic drivers of tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: The role of KEAP1, SMARCA4, and PTEN mutations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e012288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. New strategies of clinical precision medicine. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N. Responder of Gefitinib Plus Crizotinib in Osimertinib Failure EGFR-mutant NSCLC-Resistant with Newly Identified STRN-ALK by Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e143–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Heist, R.S.; Lin, J.J.; Meador, C.B.; Krueger, E.A.; Do, A.; Peterson, J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of ALK/MET Combinations in Patients With ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer with Acquired MET Amplification: A Retrospective Analysis. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Arai, S.; Katayama, R.; Nanjo, S.; Tanimoto, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Is a Mechanism of ALK Inhibitor Resistance in Lung Cancer Independent of ALK Mutation Status. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Guo, S.J.; He, B.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, W.J.; Yuan, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Peng, C.; Xiong, W.; Shi, J.Y. Advances of dual inhibitors based on ALK for the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Chem. 2025, 159, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.M.; Waliany, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Peterson, J.L.; Liu, A.; Do, A.; Liang, J.; Lin, J.J. Adverse events associated with sequential immune checkpoint inhibitor and alectinib in patients with ALK-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2025, 10, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzeb, M.; Lin, H.M.; Pan, X.; Yin, Y.; Baumann, P.; Langer, C.J. Immunotherapy Treatment Patterns and Outcomes Among ALK-Positive Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, T.; Furugaki, K.; Mizuta, H.; Muraoka, S.; Nishio, M.; Adachi, J.; Uchibori, K.; Miyauchi, E.; Hayashi, H.; Katayama, R.; et al. Targeting ErbB and tankyrase1/2 prevent the emergence of drug-tolerant persister cells in ALK-positive lung cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, J.G.; Li, H.; Lv, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Increasing cisplatin exposure promotes small-cell lung cancer transformation after a shift from glucose metabolism to fatty acid metabolism. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 151, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knelson, E.H.; Patel, S.A.; Sands, J.M. PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses. Cancers 2021, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Samaddar, S. Recent Advances in the Clinical Translation of Small-Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2025, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Ku, B.M.; Olsen, S.; Park, S.; Lefterova, M.; Odegaard, J.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Longitudinal monitoring by next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in ALK rearranged NSCLC patients treated with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2944–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamodu, O.A.; Chung, C.C.; Pisanic, T.R., 2nd. Harnessing liquid biopsies: Exosomes and ctDNA as minimally invasive biomarkers for precision cancer medicine. J. Liq. Biopsy 2023, 2, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D.P.; Lee, D.J.; Kao, A.S. Liquid biopsy in non-small cell lung cancer: Is it ready for prime time yet? Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 19, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Riely, G.J.; Shaw, A.T. Targeting ALK: Precision Medicine Takes on Drug Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-K.; Tong, J.-B.; Luo, M.-X.; Qin, Z.-P.; Wang, R. ALK-Targeted Therapy: Resistance Mechanisms and Emerging Precision Strategies. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120996
Zhang Y-K, Tong J-B, Luo M-X, Qin Z-P, Wang R. ALK-Targeted Therapy: Resistance Mechanisms and Emerging Precision Strategies. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(12):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120996
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ya-Kun, Jian-Bo Tong, Mu-Xuan Luo, Zhi-Peng Qin, and Rong Wang. 2025. "ALK-Targeted Therapy: Resistance Mechanisms and Emerging Precision Strategies" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 12: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120996
APA StyleZhang, Y.-K., Tong, J.-B., Luo, M.-X., Qin, Z.-P., & Wang, R. (2025). ALK-Targeted Therapy: Resistance Mechanisms and Emerging Precision Strategies. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(12), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120996




