Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis Alters Neurotrophin-3 and -4 Expression: Impact of Metabolic and Behavioral Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort, Pain Assessment, and Surgical Protocol
2.2. Control Group Composition
2.3. Sample Collection and Molecular Analysis
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.5. NT-3 and NT-4 mRNA Expression Analysis Using Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Technique Preceded by Reverse Transcription (RTqPCR)
2.6. NT-3 and NT-4 Protein Concentration Analysis via Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis of NT-3 and NT-4 Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differential Expression of NT-3 and NT-4 in LF: mRNA and Protein Analysis
3.2. Relationship Between NT-3 and NT-4 Expression and Pain Severity
3.3. Influence of Demographic, Metabolic, and Lifestyle Factors on NT-3 and NT-4 Expression
3.4. Predictors of NT-3 and NT-4 Expression: Regression Modeling
3.4.1. Exploratory Regression: Univariate and Multivariate Models for NT-3 and NT-4 Expression
3.4.2. Comparative Multivariate Regression: Control vs. Patient Cohorts
3.4.3. Neurotrophin Expression and Pain: Integrative Regression with Lifestyle and Clinical Covariates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGE | Advanced Glycation End-product |
| Akt | Protein Kinase B |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| COL1A1 | Collagen Type I Alpha 1 Chain |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| DAB | 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine |
| DLSS | Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DRG | Dorsal Root Ganglion |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FoxO1 | Forkhead Box Protein O1 |
| GDNF | Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| LF | Ligamentum Flavum |
| L/S | Lumbosacral |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MAPK–NF-κB | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase–Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (crosstalk pathway) |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| mRNA | Messenger Ribonucleic Acid |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NGF | Nerve Growth Factor |
| NT-3 | Neurotrophin-3 |
| NT-4 | Neurotrophin-4 |
| p75NTR | p75 Neurotrophin Receptor (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily Member 16) |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| pg/mL | Picograms per Milliliter |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/Forkhead Box Protein O1 signaling axis |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| TrkA | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A |
| TrkB | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B |
| TrkC | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase C |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| µL | Microliter |
| µm | Micrometer |
References
- Kahere, M.; Hlongwa, M.; Ginindza, T.G. A Scoping Review on the Epidemiology of Chronic Low Back Pain among Adults in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, N.N.; Candido, K.D.; Vlaeyen, J.W.; Zundert, J.V.; Cohen, S.P. Low Back Pain: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Treatment. In Proceedings of the Lancet-Seminar Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Covaro, A.; Vilà-Canet, G.; De Frutos, A.G.; Ubierna, M.T.; Ciccolo, F.; Caceres, E. Management of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: An Evidence-Based Review. EFORT Open Rev. 2016, 1, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, T.; Sayed, D.; Michels, J.; Josephson, Y.; Li, S.; Calodney, A.K. A Review of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis with Intermittent Neurogenic Claudication: Disease and Diagnosis. Pain Med. 2019, 20, S32–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgstaller, J.M.; Porchet, F.; Steurer, J.; Wertli, M.M. Arguments for the Choice of Surgical Treatments in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis—A Systematic Appraisal of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Moon, S.-H.; Suk, K.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Yang, J.-H.; Lee, H.-M. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Principle: A Narrative Review. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byvaltsev, V.A.; Kalinin, A.A.; Hernandez, P.A.; Shepelev, V.V.; Pestryakov, Y.Y.; Aliyev, M.A.; Giers, M.B. Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Spinal Stenosis Formation: Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, P.A.; Mantyh, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Viktrup, L.; Tive, L. Nerve Growth Factor Signaling and Its Contribution to Pain. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Domingues, O.; Zimmer, J.; Michel, T. Revisiting the Role of Neurotrophic Factors in Inflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D. Neurotrophic Factors: An Overview. In Neurotrophic Factors: Methods and Protocols; Skaper, S.D., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-1-4939-7571-6. [Google Scholar]
- Skup, M. Neurotrophins: Evolution of Concepts on Rational Therapeutic Approaches. Postep. Biochem. 2018, 64, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobańska, M.; Sobański, D.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Gogol, P.; Strojny, D.; Pawłaszek, T.; Dammerman, W.; Grabarek, B.O. Modulation of Neurturin Expression by Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis, Lifestyle Factors, and Glycemic Dysregulation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobański, D.; Sobańska, M.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Strojny, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Changes in the Expression Profile of Growth-Associated Protein 43 in Degenerative Lumbosacral Stenosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobański, D.; Bogdał, P.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Sobańska, M.; Filipowicz, M.; Czepko, R.A.; Strojny, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Evaluation of Differences in Expression Pattern of Three Isoforms of the Transforming Growth Factor Beta in Patients with Lumbosacral Stenosis. Cell Cycle 2024, 23, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.-Y.; Hendrix, J.; Schabrun, S.; Wyns, A.; Campenhout, J.V.; Nijs, J.; Polli, A. The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurotrophin Family. Handbook of Hormones; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 471–473. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolahi, S.; Zare-Chahoki, A.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Gorji, A. A Review of Molecular Interplay between Neurotrophins and miRNAs in Neuropsychological Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6260–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateaque, S.; Merkouris, S.; Barde, Y.-A. Neurotrophin Signalling in the Human Nervous System. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1225373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Abondio, P.; Montesanto, A.; Luiselli, D.; Bruni, A.C.; Maletta, R. The Nerve Growth Factor Receptor (NGFR/p75NTR): A Major Player in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.-H.; Lu, X.-M.; Wei, J.-X.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.-T. Update on the Role of p75NTR in Neurological Disorders: A Novel Therapeutic Target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 76, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghanlou, A.E.; Yazdanian, M.; Roshani, S.; Demirli, A.; Seydyousefi, M.; Metz, G.A.S.; Faghfoori, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Pre-Ischemic Exercise Are Linked to Expression of NT-3/NT-4 and TrkB/TrkC in Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 194, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.R.; Dhawale, A.A.; Brown, M.D. Association between Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Cigarette Smoking: Clinical and Experimental Findings. JBJS Rev. 2015, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, S.; Asfour, S.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Travascio, F. Effects of Tobacco Smoking on the Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disc: A Finite Element Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, F.; Wu, D.; Li, H. A Retrospective Study: Does Cigarette Smoking Induce Cervical Disc Degeneration? Int. J. Surg. 2018, 53, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, M.; Demir, E. Relationship of Lumbar Disc Degeneration with Hemoglobin Value and Smoking. Neurochirurgie 2020, 66, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Gładysz, D.; Gralewski, M.; Garczarek, M.; Gadzieliński, M.; Grabarek, B.O. Pathomechanism of the IVDs Degeneration and the Role of Neurotrophic Factors and Concentration of Selected Elements in Genesis of Low Back Pain. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Fan, G. Effects of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on Neuronal Activity, Pain, and Related Cytokines in Rats with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2023, 27, 4120. [Google Scholar]
- Sobański, D.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Sobańska, M.; Strojny, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Effects of Pain in Lumbosacral Stenosis and Lifestyle-Related Factors on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression Profiles. Mol. Pain 2025, 21, 17448069241309001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Lin, R.; Wang, D.; Zheng, C.; Xu, W. Effects of Circulating Inflammatory Proteins on Spinal Degenerative Diseases: Evidence from Genetic Correlations and Mendelian Randomization Study. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.-L.; Yan, B.; Bao, Y.-N.; Fan, J.-F.; Liu, J.-H. Suppression of Peripheral NGF Attenuates Neuropathic Pain Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury through the TAK1-MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Ro, L.-S.; Wang, H.-L.; Chen, J.-C. Up-Regulation of Dorsal Root Ganglia BDNF and trkB Receptor in Inflammatory Pain: An in Vivo and in Vitrostudy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Gładysz, D.; Sobański, D.; Bolechała, F.; Golec, E.; Dammermann, W.; Grabarek, B.O. The Impacts of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration of the Spine, Alcohol Consumption, Smoking Tobacco Products, and Glycemic Disorders on the Expression Profiles of Neurotrophins-3 and -4. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.; Bukhari, A.B.; Malhotra, R.; De, A. IHC Profiler: An Open Source Plugin for the Quantitative Evaluation and Automated Scoring of Immunohistochemistry Images of Human Tissue Samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.B.; Dobson, E.T.A.; Rueden, C.T.; Tomancak, P.; Jug, F.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ Ecosystem: Open-source Software for Image Visualization, Processing, and Analysis. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Smith, M.T. Neurotrophins and Neuropathic Pain: Role in Pathobiology. Molecules 2015, 20, 10657–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayanti, I.A.S.; Adnyana, I.M.O.; Widyadharma, I.P.E.; Wiratnaya, I.G.E.; Mahadewa, T.G.B.; Astawa, I.N.M. Neuroinflammation Mechanism Underlying Neuropathic Pain: The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell in Neuroglia. AIMS Neurosci. 2024, 11, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; E, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y. Neuroplasticity in the Transition from Acute to Chronic Pain. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Sánchez, C.M.; Montoro, C.I.; Duschek, S.; Reyes del Paso, G.A. Depression and Trait-Anxiety Mediate the Influence of Clinical Pain on Health-Related Quality of Life in Fibromyalgia. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelides, A.; Zis, P. Depression, Anxiety and Acute Pain: Links and Management Challenges. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.; Yasin, B.; Bekker, A.; Hu, H.; Tao, Y.-X. NT-3 Contributes to Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain through TrkC-Mediated CCL2 Elevation in DRG Neurons. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonyan, S.; Pospelova, M.; Krasnikova, V.; Fionik, O.; Alekseeva, T.; Samochernykh, K.; Ivanova, N.; Vavilova, T.; Vasilieva, E.; Makhanova, A.; et al. Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) as a Potential Biomarker of the Peripheral Nervous System Damage Following Breast Cancer Treatment. Pathophysiology 2023, 30, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, F.; Favero, G.; Castrezzati, S.; Borsani, E. Role of Neurotrophins in Orofacial Pain Modulation: A Review of the Latest Discoveries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ni, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zou, D. Exogenous NT-3 Promotes Phenotype Switch of Resident Macrophages and Improves Sciatic Nerve Injury through AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 2600–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Huang, M.; Huang, L.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Q.; Lai, B.; Ma, Y. An NT-3-Releasing Bioscaffold Supports the Formation of TrkC-Modified Neural Stem Cell-Derived Neural Network Tissue with Efficacy in Repairing Spinal Cord Injury. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3766–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.A.; Kumar, J.; Teoh, S.L. Neurotrophin-3 and Neurotrophin-4: The Unsung Heroes That Lies behind the Meninges. Neuropeptides 2022, 92, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Ge, X.; Ma, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, C. Neurotrophins and Neural Stem Cells in Posttraumatic Brain Injury Repair. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2024, 7, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Turkiewicz, S.; Ditmer, M.; Sochal, M. Neurotrophins in the Neuropathophysiology, Course, and Complications of Obstructive Sleep Apnea—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Sobański, D.; Bryś, K.; Och, W.; Garczarek, M.; Ulasavets, U.; Stasiowski, M.; Dammermann, W.; Strojny, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Effect of Glycemic Disorders and Habits on the Concentration of Selected Neurotrophic Factors in Patients with Lumbosacral Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliri, A.W.; Tommasi, S.; Besaratinia, A. Relationships among Smoking, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Macromolecular Damage, and Cancer. Mutat. Res. 2021, 787, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, B.; Li, R.; Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Liang, W. Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factors, Neurotrophin-3, and Neurotrophin-4 in the Nucleus Accumbens during Heroin Dependency and Withdrawal. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimbar, L.; Moleta, Y. Naloxone Effectiveness: A Systematic Review. J. Addict. Nurs. 2018, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.W.; Mooney, S.M. Chronic Exposure to Ethanol Alters Neurotrophin Content in the Basal Forebrain-Cortex System in the Mature Rat: Effects on Autocrine-Paracrine Mechanisms. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 60, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena-Ocaña, N.; Araos, P.; Flores, M.; García-Marchena, N.; Silva-Peña, D.; Aranda, J.; Rivera, P.; Ruiz, J.J.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.J.; et al. Evaluation of Neurotrophic Factors and Education Level as Predictors of Cognitive Decline in Alcohol Use Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Peña, D.; García-Marchena, N.; Alén, F.; Araos, P.; Rivera, P.; Vargas, A.; García-Fernández, M.I.; Martín-Velasco, A.I.; Villanúa, M.Á.; Castilla-Ortega, E.; et al. Alcohol-Induced Cognitive Deficits Are Associated with Decreased Circulating Levels of the Neurotrophin BDNF in Humans and Rats. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-T.; Chang, C.-N.; Wu, J.H.; Chung, C.-Y.; Weng, H.-H.; Cheng, W.-C.; Lee, T.-H. Cigarette Smoking Decreases Neurotrophin-3 Expression in Rat Hippocampus after Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 60, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, H. Passive Smoking Elevates Neurotrophin Levels in Tears. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, N.J.; Phan, T.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.P.; Park, J.M. Modulating Neuroplasticity for Chronic Pain Relief: Noninvasive Neuromodulation as a Promising Approach. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, C. Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Death in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaogang, M.; Quanshan, H.; Liping, Z.; Kaken, H. The Expression of Cytokine and Its Significance for the Intervertebral Disks of Kazakhs. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 31, e22087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, K.R.; Walter, B.A.; Laudier, D.M.; Krishnamoorthy, D.; Mosley, G.E.; Spiller, K.L.; Iatridis, J.C. Accumulation and Localization of Macrophage Phenotypes with Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine J. 2018, 18, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielewicz, J.; Daniluk, B.; Kamieniak, P. VAS and NRS, Same or Different? Are Visual Analog Scale Values and Numerical Rating Scale Equally Viable Tools for Assessing Patients after Microdiscectomy? Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 5337483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
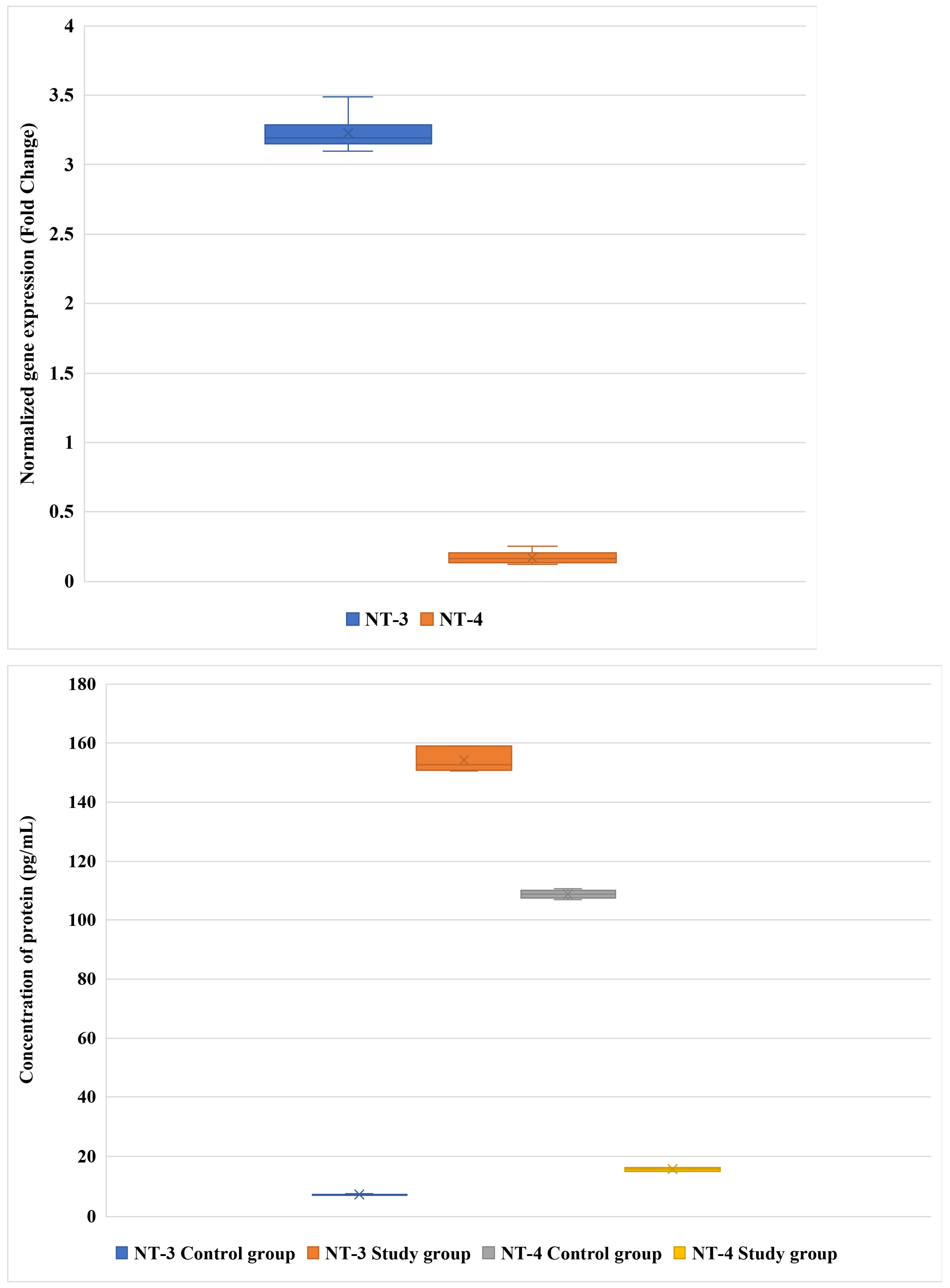
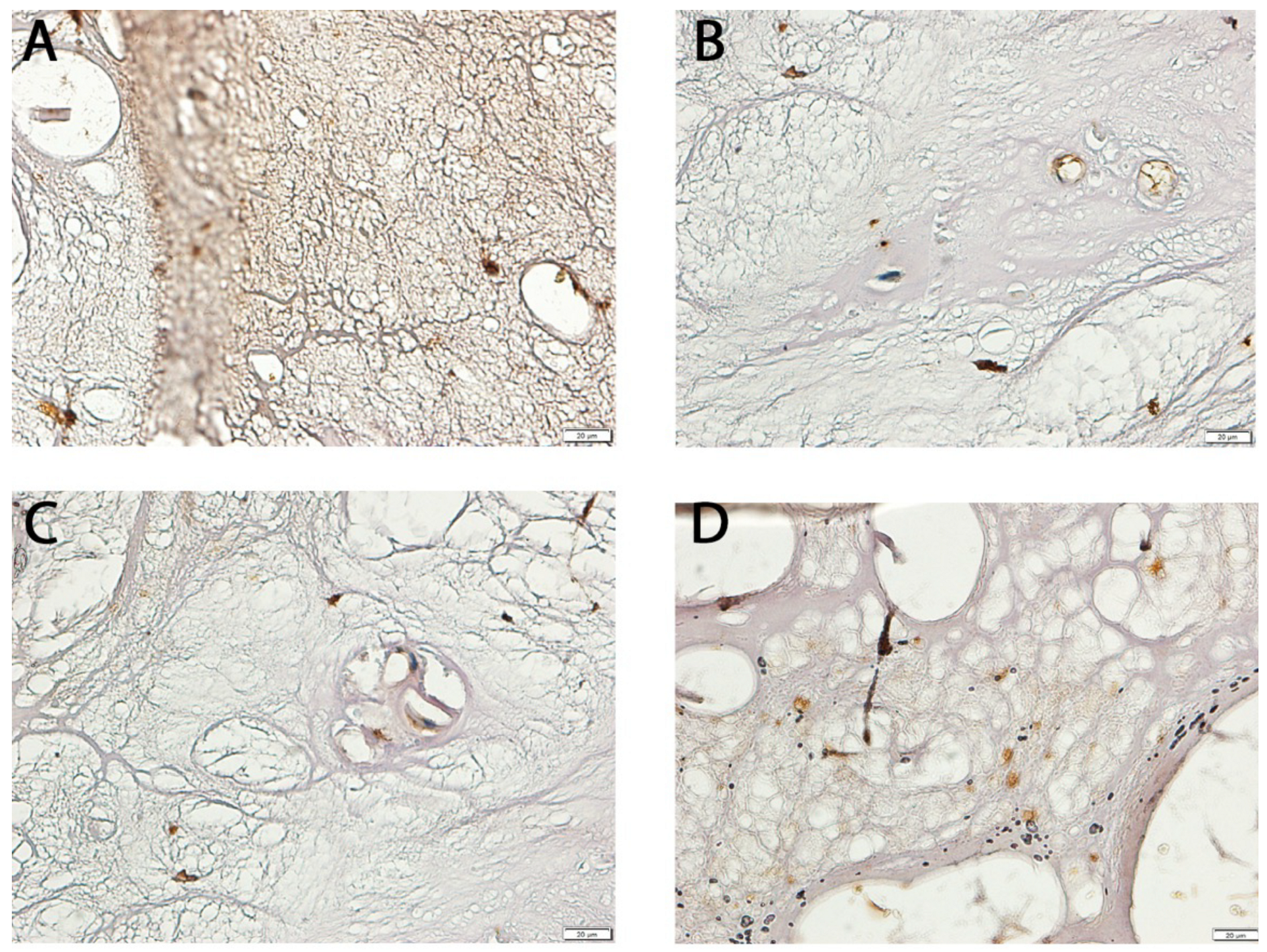
| Variable | Patients with DLSS (n = 96) | Controls (n = 85) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 68.3 ± 2.4 | 49.2 ± 2.6 | <0.001 |
| Sex (M/F) | 50/46 | 46/39 | 0.62 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 28.7 ± 3.9 | 24.5 ± 3.1 | <0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 22.9 | 8.2 | <0.01 |
| Smoking (%) | 37.5 | 28.2 | 0.15 |
| Alcohol use (%) | 52.1 | 45.9 | 0.38 |
| Mean VAS pain score | 6.1 ± 1.7 | — |
| mRNA | Oligonucleotide Sequence |
|---|---|
| NT-3 | Forward: 5′-CGTGGTGGCGAACAGAACAT-3′ Reverse 5′-GGCCGATGACTTGTCGGTC-3′ |
| NT-4 | Forward: 5′-CTGTGTGCGATGCAGTCAGT-3′ Reverse 5′-GCAGCGGGTTTCAAAGAAGT-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-GGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGA-3′ Reverse 5′-GAGGGATCTCGCTCCTGGAAGA-3′ |
| Neurotrophin | Pain Intensity on the VAS | Fold Change (mRNA) | Protein Concentration (pg/mL) | ANOVA (p) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT-3 | 2 | 1.65 ± 0.21 | 89.03 ± 2.65 | 0.032 a 0.041 b |
| 3 | 1.87 ± 0.18 | 95.16 ± 2.87 | ||
| 4 | 2.21 ± 0.43 | 133.18 ± 3.91 | ||
| 5 | 2.31 ± 0.12 | 143.02 ± 5.67 | ||
| 6 | 2.54 ± 0.23 | 159.19 ± 5.91 | ||
| 7 | 4.01 ± 0.18 | 172.12 ± 5.14 | ||
| 8 | 4.72 ± 0.54 | 196.52 ± 9.82 | ||
| 9 | 4.51 ± 0.41 | 197.83 ± 9.87 | ||
| 10 | 5.18 ± 0.76 | 201.63 ± 12.34 | ||
| NT-4 | 2 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 5.13 ± 0.65 | 0.87 a 0.022 b |
| 3 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 6.04 ± 0.49 | ||
| 4 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 7.15 ± 0.91 | ||
| 5 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 7.98 ± 0.55 | ||
| 6 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 17.06 ± 2.36 | ||
| 7 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 20.49 ± 2.91 | ||
| 8 | 0.11 ± 0.05 | 23.18 ± 2.45 | ||
| 9 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 24.15 ± 3.16 | ||
| 10 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 29.87 ± 3.81 |
| Protein | Comparison | mRNA | Student’s t-Test 1 or ANOVA 2 (Study Group) | Protein | Student’s t-Test 1 or ANOVA 2 (Control Group) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT-3 | Gender | Female (n = 46) | 3.39 ± 0.27 | 0.891 1 | 145.21 ± 12.19 | 0.701 1 |
| Male (n = 50) | 3.01 ± 0.54 | 163.18 ± 10.12 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m 2) | Normal (n = 40) | 1.00 | <0.0001 2 | 1.00 | <0.0001 2 | |
| Overweight (n = 32) | 2.02 ± 0.17 | 109.99 ± 8.12 | ||||
| Obesity (n = 24) | 4.37 ± 1.01 | 198.39 ± 12.34 | ||||
| Diabetes | No (n = 46) | 2.38 ± 0.52 | 0.001 1 | 101.67 ± 9.12 | <0.0001 1 | |
| Yes (n = 50) | 4.02 ± 0.43 | 206.71 ± 18.17 | ||||
| Smoking | No (n = 34) | 1.82 ± 0.51 | 0.008 1 | 129.93 ± 11.43 | 0.042 1 | |
| Yes (n = 62) | 4.57 ± 1.07 | 178.45 ± 8.17 | ||||
| Drinking alcohol | No (n = 11) | 2.97 ± 0.65 | 0.881 1 | 109.36 ± 9.91 | <0.0001 1 | |
| Yes (n = 85) | 3.43 ± 0.41 | 199.02 ± 16.91 | ||||
| NT-4 | Gender | Female (n = 46) | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.812 1 | 15.37 ± 1.09 | 0.753 1 |
| Male (n = 50) | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 15.97 ± 1.17 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m 2) | Normal (n = 40) | 1.00 | 0.002 2 | 1.00 | 0.023 2 | |
| Overweight (n = 32) | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 12.26 ± 0.98 | ||||
| Obesity (n = 24) | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 19.07 ± 1.34 | ||||
| Diabetes | No (n = 46) | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.0122 1 | 11.71 ± 1.65 | 0.0011 1 | |
| Yes (n = 50) | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 19.63 ± 1.97 | ||||
| Smoking | No (n = 34) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.001 1 | 12.70 ± 1.09 | 0.0032 1 | |
| Yes (n = 62) | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 18.64 ± 2.13 | ||||
| Drinking alcohol | No (n = 11) | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.765 1 | 13.21 ± 2.15 | 0.042 1 | |
| Yes (n = 85) | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 18.12 ± 2.78 | ||||
| Neurotrophin | Characteristic | Expression Level | Linear Regression | Multiple Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | R2 | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |||
| NT-3 | Sex | mRNA | 0.3 | 0.06 | 0.25 | ||
| Protein | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.27 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | mRNA | 0.78 | 0.6 | <0.0001 | 0.34 | <0.0001 | |
| Protein | 0.79 | 0.64 | <0.0001 | 0.405 | <0.0001 | ||
| Diabetes | mRNA | 0.7 | 0.75 | <0.0001 | 0.32 | 0.016 | |
| Protein | 0.75 | 0.73 | <0.0001 | 0.307 | 0.022 | ||
| Smoking | mRNA | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.002 | 0.47 | 0.023 | |
| Protein | 0.88 | 0.4 | 0.004 | 0.48 | 0.02 | ||
| Drinking alcohol | mRNA | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.025 | 0.23 | 0.027 | |
| Protein | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.022 | 0.26 | 0.028 | ||
| NT-4 | Sex | mRNA | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.43 | ||
| Protein | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.48 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | mRNA | 0.8 | 0.86 | <0.0001 | 0.405 | 0.019 | |
| Protein | 0.77 | 0.8 | <0.0001 | 0.415 | 0.022 | ||
| Diabetes | mRNA | 0.55 | 0.38 | <0.0001 | 0.316 | 0.018 | |
| Protein | 0.55 | 0.37 | <0.0001 | 0.319 | 0.022 | ||
| Smoking | mRNA | 0.79 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.305 | 0.023 | |
| Protein | 0.8 | 0.53 | 0.004 | 0.315 | 0.03 | ||
| Drinking alcohol | mRNA | 0.52 | 0.2 | 0.032 | 0.15 | 0.018 | |
| Protein | 0.4 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.165 | 0.021 | ||
| Neurotrophin | Characteristic | Expression Level | Control Group | Study Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |||
| NT-3 | Gender | mRNA | - | - | - | - |
| Protein | - | - | - | - | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | mRNA | 0.12 | 0.045 | 0.34 | <0.0001 | |
| Protein | 0.15 | 0.038 | 0.405 | <0.0001 | ||
| Diabetes | mRNA | 0.1 | 0.052 | 0.32 | 0.016 | |
| Protein | 0.14 | 0.048 | 0.307 | 0.022 | ||
| Smoking | mRNA | 0.18 | 0.041 | 0.47 | 0.023 | |
| Protein | 0.2 | 0.039 | 0.48 | 0.02 | ||
| Drinking Alcohol | mRNA | 0.09 | 0.060 | 0.23 | 0.027 | |
| Protein | 0.11 | 0.055 | 0.26 | 0.028 | ||
| NT-4 | Gender | mRNA | - | - | - | - |
| Protein | - | - | - | - | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | mRNA | 0.14 | 0.040 | 0.405 | 0.019 | |
| Protein | 0.16 | 0.035 | 0.415 | 0.022 | ||
| Diabetes | mRNA | 0.11 | 0.050 | 0.316 | 0.018 | |
| Protein | 0.13 | 0.045 | 0.319 | 0.022 | ||
| Smoking | mRNA | 0.17 | 0.039 | 0.305 | 0.023 | |
| Protein | 0.19 | 0.037 | 0.315 | 0.03 | ||
| Drinking Alcohol | mRNA | 0.08 | 0.058 | 0.15 | 0.018 | |
| Protein | 0.1 | 0.053 | 0.165 | 0.021 | ||
| Neurotrophin | Factor | Association with NT-3/-4 Protein (Univariate) | p-Value (Univariate) | Coefficient in Multivariate Model | p-Value (Multivariate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT-3 | VAS Pain Score | Positive | <0.0001 | 0.35 | <0.0001 |
| BMI | Positive | <0.0001 | 0.41 | <0.0001 | |
| Smoking | Positive | 0.004 | 0.28 | 0.015 | |
| Alcohol Consumption | Positive | 0.022 | 0.22 | 0.028 | |
| Diabetes | Positive | <0.0001 | 0.39 | <0.0001 | |
| NT-4 | VAS Pain Score | Positive | 0.022 | 0.25 | 0.019 |
| BMI | Positive | <0.0001 | 0.42 | <0.0001 | |
| Smoking | Positive | 0.01 | 0.3 | 0.02 | |
| Alcohol Consumption | Positive | 0.032 | 0.18 | 0.027 | |
| Diabetes | Positive | <0.0001 | 0.37 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobańska, M.; Sobański, D.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Gogol, P.; Grabarek, B.O. Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis Alters Neurotrophin-3 and -4 Expression: Impact of Metabolic and Behavioral Factors. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110962
Sobańska M, Sobański D, Staszkiewicz R, Gogol P, Grabarek BO. Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis Alters Neurotrophin-3 and -4 Expression: Impact of Metabolic and Behavioral Factors. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110962
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobańska, Małgorzata, Dawid Sobański, Rafał Staszkiewicz, Paweł Gogol, and Beniamin Oskar Grabarek. 2025. "Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis Alters Neurotrophin-3 and -4 Expression: Impact of Metabolic and Behavioral Factors" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110962
APA StyleSobańska, M., Sobański, D., Staszkiewicz, R., Gogol, P., & Grabarek, B. O. (2025). Degenerative Lumbosacral Spinal Stenosis Alters Neurotrophin-3 and -4 Expression: Impact of Metabolic and Behavioral Factors. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110962





