Ethyl Acetate Extract of Cynanchi Auriculati Radix Inhibits LPS-Induced M1 Polarization of RAW264.7 Macrophages and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Regulating NF-κB and PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. The Preparation for RCAEA
2.3. LC-MS/MS Instrumentation and Conditions
2.4. Network Aharmacology Analysis
2.5. Cell Culture and Viability Assays
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Assay of RAW264.7 Cells
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Cultivation and Synchronization of Caenorhabditis Elegans (C. elegans)
2.11. Bacterial Growth Rates
2.12. Locomotor Behavior Assays
2.13. Lifespan Assay
2.14. Reproduction Assay
2.15. Stress Assay
2.16. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.17. Lipofuscin Assays
2.18. qRT-PCR of C. Elegans
2.19. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Analysis of the Components in RCAEA by LC-MS/MS
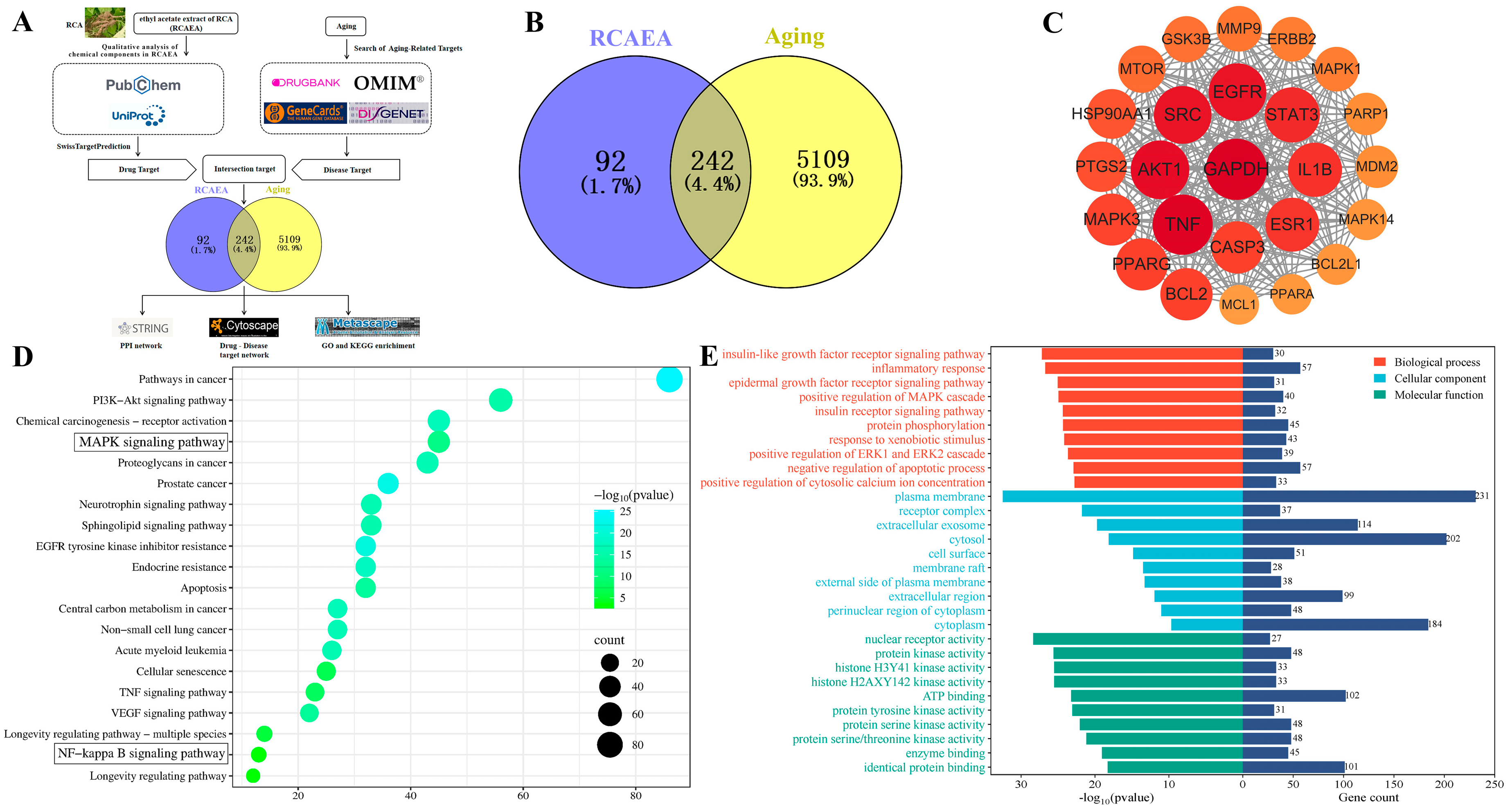
3.2. Predict the Anti-Aging Mechanism of RCAEA by Network Pharmacology Analysis
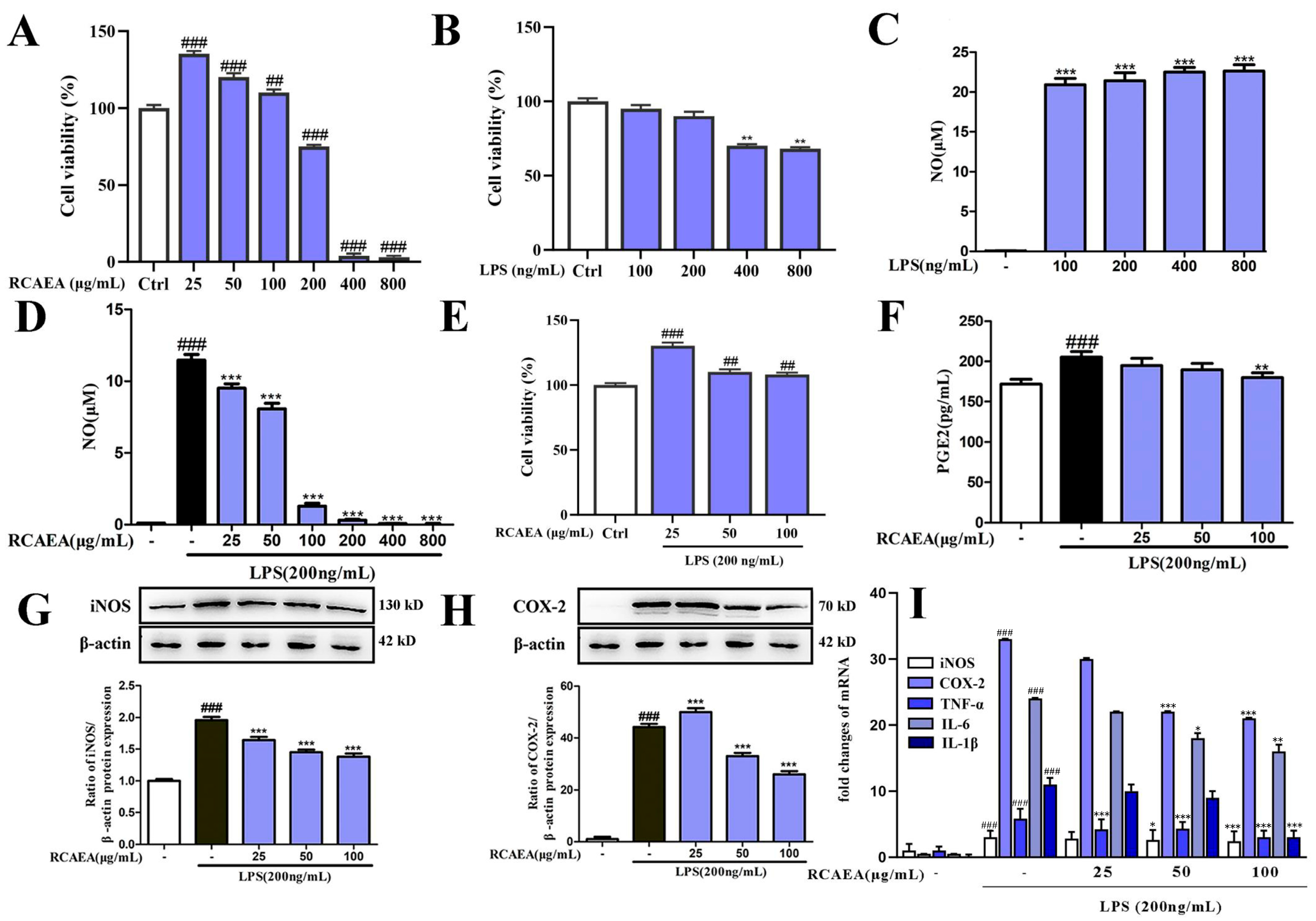
3.3. RCAEA Suppresses M1-Type Polarization in RAW264.7 Macrophages Under Inflammatory Environment
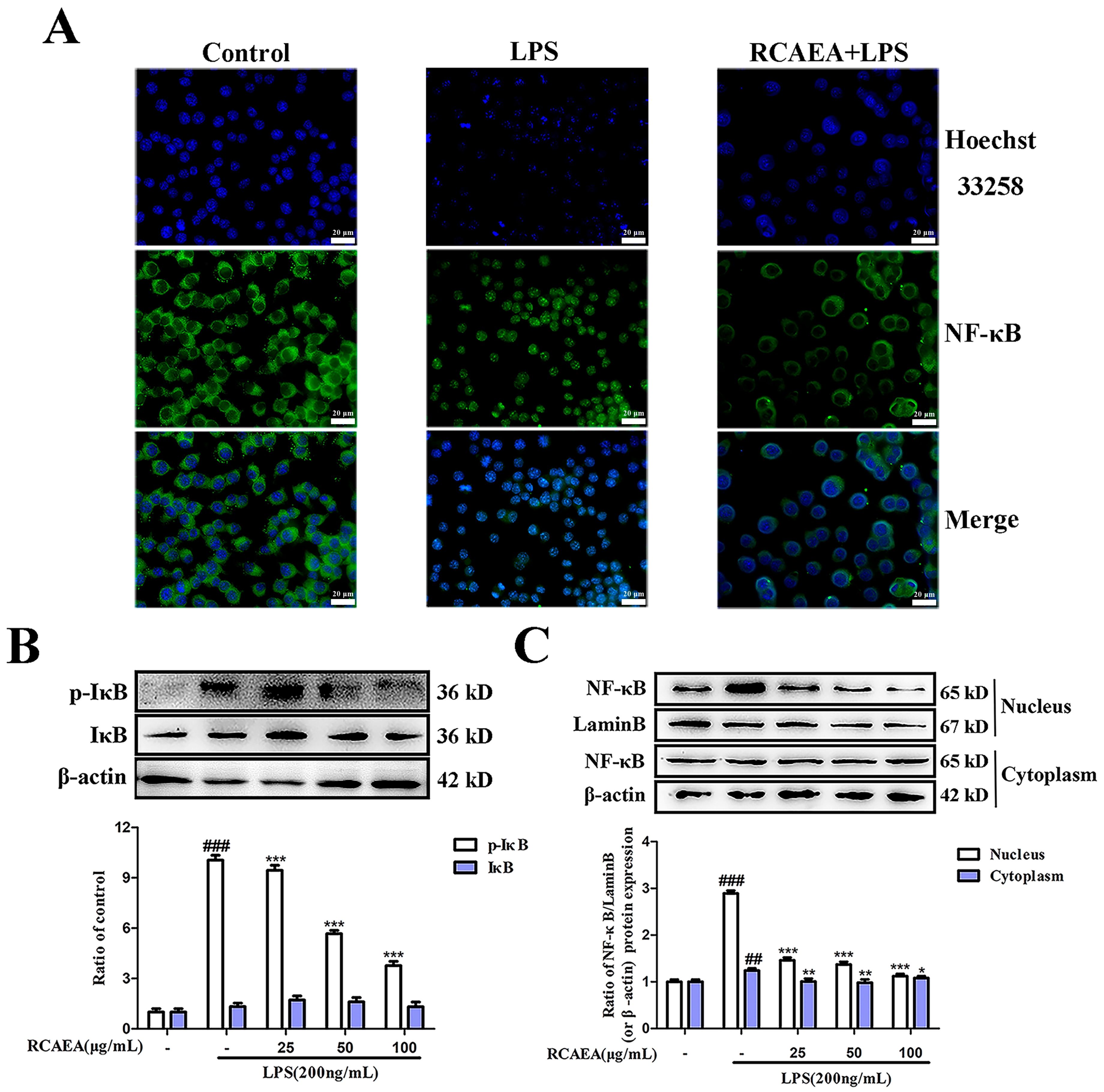
3.4. RCAEA Blocks NF-κB Pro-Inflammatory Signaling Pathway
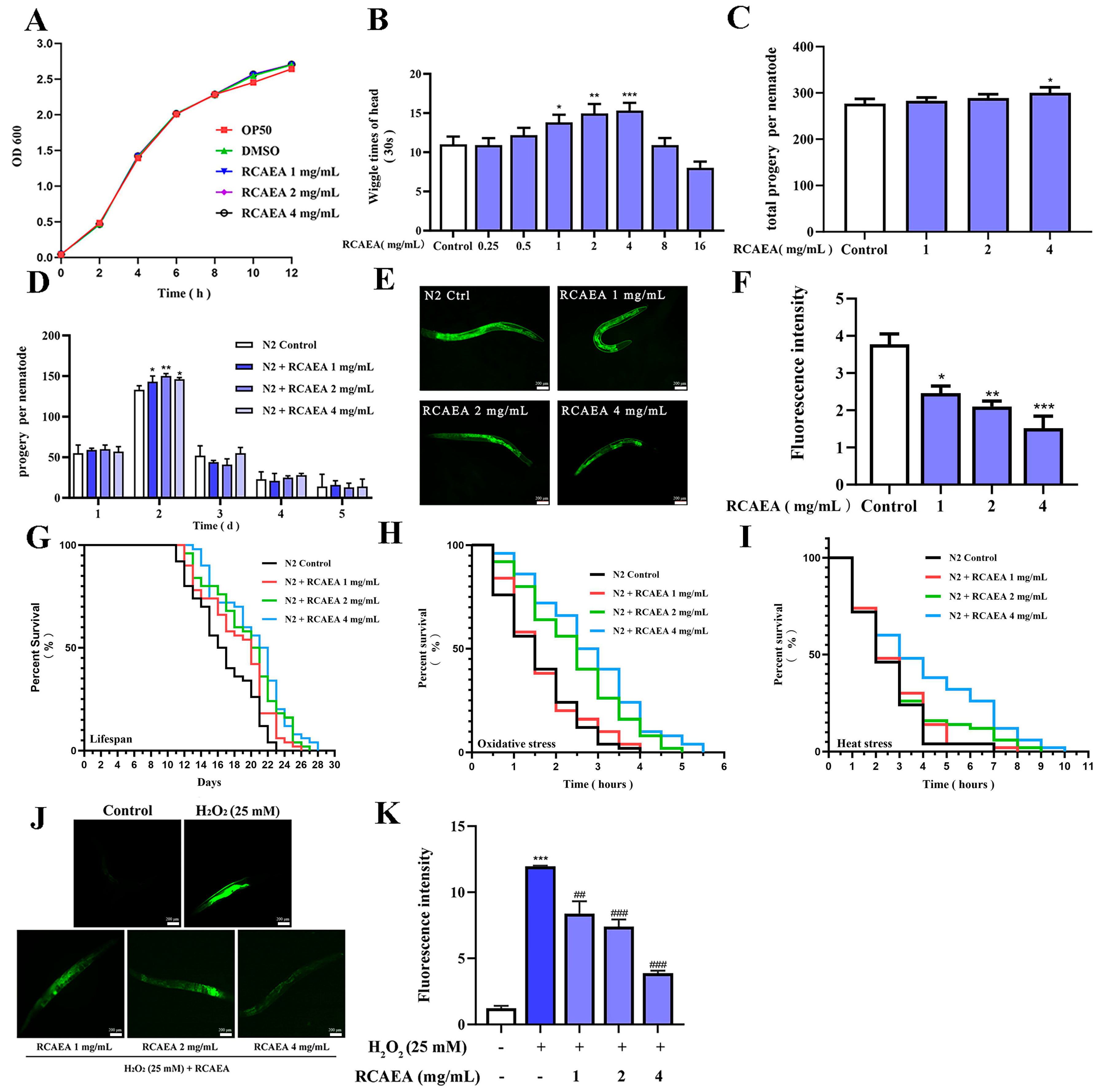
3.5. The Influence of RCAEA on the Biological Behaviors and Aging Process of C. elegans
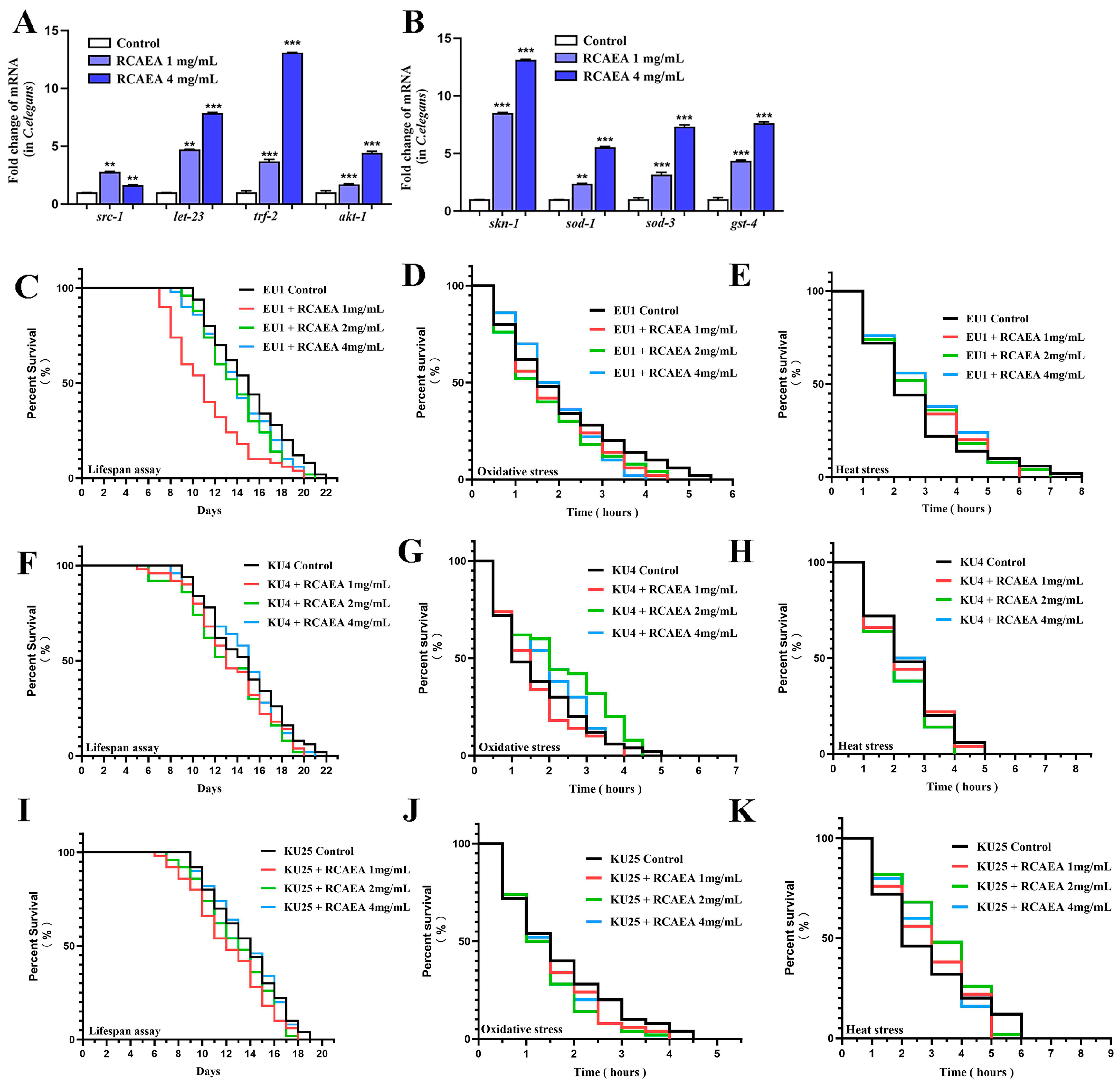
3.6. RCAEA Prolongs the Lifespan of C. elegans via the PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Meccariello, R.; D’angelo, S. Impact of Polyphenolic-Food on Longevity: An Elixir of Life. An Overview. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X. Tea Polyphenols as Prospective Natural Attenuators of Brain Aging. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonian, B.J.; Hippensteel, J.A.; Abuabara, K.; Boyle, E.M.; Colbert, J.F.; Devinney, M.J.; Faye, A.S.; Kochar, B.; Lee, J.; Litke, R.; et al. Inflammation and aging-related disease: A transdisciplinary inflammaging framework. GeroScience 2024, 47, 515–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Schurman, S.H.; Bektas, A.; Kaileh, M.; Roy, R.; Wilson, D.M.; Sen, R.; Ferrucci, L. Aging and Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2024, 14, a041197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Li, W.; Wu, H.; Xie, X.; Xie, M.; Nie, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cai, S. Aging-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 (SAMP8) Mice Experiment and Network Pharmacological Analysis of Aged Liupao Tea Aqueous Extract in Delaying the Decline Changes of the Body. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Tan, H.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, R.; Jin, Z.; Li, Y.; Ge, X.; et al. Lycopodium japonicum Thunb. inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis, senescence and inflammation in osteoarthritis through STING/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Namila; Hashentuya; Tana; Wuyunsiqin; Zhao, W.; Menggenduxi; Wang, M. Mongolian medicine Qiqirigan-8 inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway activation to ameliorate non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 265, 116975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.T.; Xi, Z.Q.; Wei, X.Q.; Wang, K. A network pharmacology approach to predict potential targets and mechanisms of “Ramulus cinnamomi (cassiae)—Paeonia lactiflora” herb pair in the treatment of chronic pain with comorbid anxiety and depression. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Bai, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, T.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Gao, F.; Yu, H.; Gu, X. Network pharmacology to dissect the mechanisms of Yinlai Decoction for pneumonia. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Li, X.; Zou, J.; Wu, L.; Cheng, B.; Wang, J. Discovery of potential quality markers of Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus in pneumonia by combining UPLC-QTOF-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular docking. Mol. Divers. 2023, 28, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, F.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J.; Kong, D.; Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; An, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight., Cynanchum bungei Decne. and Cynanchum wilfordii (Maxim.) Hemsl.: Current Research and Prospects. Molecules 2021, 26, 7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; Rao, Z.; Lei, Z.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Z.; Shen, C.; Zeng, N. The antitumour activity of C21 steroidal glycosides and their derivatives of Baishouwu: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Qian, S.; Wei, Y.; Shu, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Total C-21 steroidal glycosides, isolated from the root tuber of Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight, attenuate hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative injury and inflammation in L02 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 3157–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Peng, H.; You, R.; Bai, F.; Chen, D.; Abdin, M.; Peng, C.; Li, X.; Cai, H.; et al. Chemical Composition of Cynanchum auriculatum Royle Ex Wight and Its Potential Role in Ameliorating Colitis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, S.; Yin, X.; Wu, N.; Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Polysaccharides from Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight ameliorate symptoms of hyperglycemia by regulating gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 139878, Erratum in Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Su, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, J.; Yi, S.; Xing, Y.; Kun, H. Ethyl Acetate Extract of Radix Cynanchi Auriculati Exerts Antioxidant Effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 Cells by Regulating MAPKs/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, C.; Xia, Y.-F.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z.-F. 3, 3′-diindolylmethane enhances macrophage efferocytosis and subsequently relieves visceral pain via the AhR/Nrf2/Arg-1-mediated arginine metabolism pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Su, D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 387, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, A.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Shen, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhi, S. SZC-6 Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing in Mice by Modulating the M1/M2 Macrophage Ratio and Inhibiting the MyD88/NF-χB Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Miao, J.; Zhu, S.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Xing, Y.; Hu, K.; Ren, J.; Yang, H. Pongamol Prevents Neurotoxicity via the Activation of MAPKs/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in H2O2-Induced Neuronal PC12 Cells and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 8219–8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, D.; Xu, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Hu, K.; Ren, J.; Yang, H. Tricetin, a Dietary Flavonoid, Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Promotes Autophagy in Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 9677–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Song, B.; Jia, X.; Yin, H.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, S. Ceramides from Sea Red Rice Bran Improve Health Indicators and Increase Stress Resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans through Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling (IIS) Pathway and JNK-1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15080–15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ückert, A.K.; Rütschlin, S.; Gutbier, S.; Wörz, N.C.; Miah, M.R.; Martins, A.C.; Hauer, I.; Holzer, A.-K.; Meyburg, B.; Mix, A.K.; et al. Identification of the bacterial metabolite aerugine as potential trigger of human dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Environ. Int. 2023, 180, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xin, Q.; Wei, P.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; She, G.; Yuan, R. Antioxidant and anti-aging activities of Longan crude and purified polysaccharide (LP-A) in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, L.; Fang, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Fan, S. 27-Hydroxymangiferolic Acid Extends Lifespan and Improves Neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans by Activating Nuclear Receptors. Molecules 2025, 30, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, K.; Ni, H.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Niu, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. Environmentally relevant concentrations of perfluorobutane sulfonate impair locomotion behaviors and healthspan by downregulating mitophagy in C. elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.; Wang, T.; Guan, S. Berberine Extends Lifespan in C. elegans Through Multi-Target Synergistic Antioxidant Effects. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Miao, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Chen, G.; et al. Pongamol Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Promotes Autophagy in Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating the Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13634–13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, Q.; Wen, T.; Luo, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Shen, X. Arteannuin B, a sesquiterpene lactone from Artemisia annua, attenuates inflammatory response by inhibiting the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2D3-mediated NF-κB activation. Phytomedicine 2024, 124, 155263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raish, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Aljenoobi, F.I.; Jan, B.L.; Al-Mohizea, A.M.; Khan, A.; Ali, N. Momordica charantia polysaccharides ameliorate oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in ethanol-induced gastritis in mucosa through NF-kB signaling pathway inhibition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, L.; Cai, C.; Gong, X. Caffeine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Suppressing MAPK/NF-κB and A2aR Signaling in LPS-Induced THP-1 Macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; et al. Hawthorn fruit extract ameliorates H2O2-induced oxidative damage in neuronal PC12 cells and prolongs the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via the IIS signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10680–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Feng, X.; Hua, Y.; Wang, D. Paeoniflorin attenuates polystyrene nanoparticle-induced reduction in reproductive capacity and increase in germline apoptosis through suppressing DNA damage checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 871, 162189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillman, J.M.; Mendes Lopes, F.; Lin, J.P.; Hu, K.; Reich, D.S.; Schafer, D.P. Lipofuscin-like autofluorescence within microglia and its impact on studying microglial engulfment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.C.; Côrrea, R.C.D.; Orué, S.L.; Leite, D.F.; Da Rocha, P.D.S.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Mussury, R.M.; Vit, P.; De Picoli Souza, K.; Dos Santos, E.L.; et al. Chemical Components and Antioxidant Activity of Geotrigona sp. and Tetragonisca fiebrigi Stingless Bee Cerumen Reduce Juglone-Induced Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.K.B.; Minhas, M.H.; Tong, J.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Mishra, R.K.; Gupta, B.P. C. elegans electrotaxis behavior is modulated by heat shock response and unfolded protein response signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, N.; Pan, F.; Song, C.; Yu, C.; Yu, C.; Qin, Y.; Hui, J.; et al. Sanguinarine promotes healthspan and innate immunity through a conserved mechanism of ROS-mediated PMK-1/SKN-1 activation. iScience 2022, 25, 103874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambara, A.L.; Silveira, É.C.; Soares, A.T.G.; Salgueiro, W.G.; Rodrigues, C.D.F.; Boldori, J.R.; Ávila, D.S.; Denardin, C.C. Butiá fruit extract (Butia eriospatha) protects against oxidative damage and increases lifespan on Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, D.; Slade, L.; Paikopoulos, Y.; D’andrea, D.; Savic, N.; Stancic, A.; Miljkovic, J.L.; Vignane, T.; Drekolia, M.K.; Mladenovic, D.; et al. Ergothioneine improves healthspan of aged animals by enhancing cGPDH activity through CSE-dependent persulfidation. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, N.; Shan, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, W. Acanthopanax senticosus Polysaccharide Enhances the Pathogen Resistance of Radiation-Damaged Caenorhabditis elegans through Intestinal p38 MAPK-SKN-1/ATF-7 Pathway and Stress Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, O.; Ribeiro, A.R.S.; Verbeeren, J.; Cetinbas, M.; Sood, H.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Garcia, S.M.D.A. Loss of muscleblind splicing factor shortens Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan by reducing the activity of p38 MAPK/PMK-1 and transcription factors ATF-7 and Nrf/SKN-1. Genetics 2021, 219, iyab114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.H.; Li, D.Y.; Liang, S.; Yang, C.; Tang, J.X.; Liu, H.F. Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 946832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Qu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Dai, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, L. Macrophage PTEN controls STING-induced inflammation and necroptosis through NICD/NRF2 signaling in APAP-induced liver injury. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Xu, D.; Tian, Y.; Qu, X.; Sheng, M.; Lin, Y.; Ke, M.; Jiang, L.; Xia, Q.; Kaldas, F.M.; et al. Novel role of macrophage TXNIP-mediated CYLD–NRF2–OASL1 axis in stress-induced liver inflammation and cell death. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capece, D.; Verzella, D.; Flati, I.; Arboretto, P.; Cornice, J.; Franzoso, G. NF-κB: Blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, M.; Xing, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.; Mei, X.; Zhu, Z.-J. Citrulline regulates macrophage metabolism and inflammation to counter aging in mice. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Guan, G.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Duan, X.; Xu, X. p-Hydroxy benzaldehyde, a phenolic compound from Nostoc commune, ameliorates DSS-induced colitis against oxidative stress via the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1/NF-κB/AP-1 pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Z.R.; Li, J.M.; Deng, H.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Lau, C.C.; Yao, Y.J.; Pan, H.D.; et al. Syringic acid attenuates acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization in LPS-induced mice. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Duan, B.; Wu, J.; Huang, L.; Dai, S.; Ding, J.; Sun, M.; Lin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, T.; et al. Bilirubin ameliorates osteoarthritis via activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and suppressing NF-κB signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Chen, Z.; Weng, S.; Guo, R.; Shi, B.; Liu, D.; Huang, S. Study on the mechanism of action of Penehyclidine hydrochloride on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating autophagy through the mTOR/Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 263, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dai, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, H. Nanozymes Regulate Redox Homeostasis in ROS-Related Inflammation. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 740607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, D.; He, J.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Q. NAT10 regulates the LPS-induced inflammatory response via the NOX2-ROS-NF-κB pathway in macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2023, 1870, 119521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Rodrigues, C.; Ramos Boldori, J.; Valandro Soares, M.; Somacal, S.; Emanuelli, T.; Izaguirry, A.; Weber Santos Cibin, F.; Rossini Augusti, P.; Casagrande Denardin, C. Goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.) juice reduces lifespan and premature aging of Caenorhabditis elegans: Is it safe to consume it? Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, H.; Lin, D.; Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guan, S. Ginsenoside Prolongs the Lifespan of C. elegans via Lipid Metabolism and Activating the Stress Response Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Gao, S.; Qiu, J.; He, J.; Yang, T.; Tan, N.; Cheng, S.; Song, Z. Research on the anti-oxidant and anti-aging effects of Polygonatum kingianum saponins in Caenorhabditis elegans. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhong, X.; Sun, D.; Xu, L.; Shi, L.; Sui, J.; Liu, Y. Anti-aging effects of polysaccharides from ginseng extract residues in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.C.; Dillin, A. XBP-1 Is a Cell-Nonautonomous Regulator of Stress Resistance and Longevity. Cell 2013, 153, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.E.H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.J.V. Survival assays using Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Guo, F.; Tao, S.; Huang, R.; Ma, L.; Fu, P. Flavonoid fisetin alleviates kidney inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting Src-mediated NF-κB p65 and MAPK signaling pathways in septic AKI mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Rak, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 354, Erratum in Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, H.T.; Sternberg, P.W. A sequencing-based screening method identifies regulators of EGFR signaling from nonviable mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Signal. 2025, 18, eadp9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detienne, G.; De Haes, W.; Ernst, U.R.; Schoofs, L.; Temmerman, L. Royalactin extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans through epidermal growth factor signaling. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajant, H.; Grell, M.; Scheurich, P. TNF receptor associated factors in cytokine signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999, 10, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, S.; Lang, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Dong, D. The clinical antiprotozoal drug nitazoxanide and its metabolite tizoxanide extend Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan and healthspan. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 3266–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yi, Q.; Wang, J.; Miao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Y.; Tao, M. Paeonol promotes longevity and fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans through activating the DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/Nrf2 transcription factors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jattujan, P.; Srisirirung, S.; Watcharaporn, W.; Chumphoochai, K.; Kraokaew, P.; Sanguanphun, T.; Prasertsuksri, P.; Thongdechsri, S.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran and Palmitic Acid from Holothuria scabra Enhance C. elegans Lifespan and Healthspan via DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/NRF2 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; Grau, R. Biofilm proficient Bacillus subtilis prevents neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson’s disease models via PMK-1/p38 MAPK and SKN-1/Nrf2 signaling. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, L.; Su, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Ba, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, B.; et al. Arginine methylation of SKN-1 promotes oxidative stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcicchia, C.; Tozzi, F.; Arancio, O.; Watterson, D.M.; Origlia, N. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Synaptic Function and Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Ni, L.; Kong, X.; Ren, R.; Shi, X.; Xu, Y.; Qu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X. Unveiling the therapeutic potential of caudatin: Structural optimization, pharmacological mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1640365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ma, D. Caudatin blocks the proliferation, stemness and glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Hong, L. β-Sitosterol as a Promising Anticancer Agent for Chemoprevention and Chemotherapy: Mechanisms of Action and Future Prospects. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1085–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Nath, N.; Rauf, A.; Emran, T.B.; Mitra, S.; Islam, F.; Chandran, D.; Barua, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; Idris, A.M.; et al. Multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of β-sitosterol: Emerging evidence toward clinical applications. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 365, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yuan, F.; Liu, T.; Yin, R. Network pharmacology analysis, molecular docking integrated experimental verification reveal β-sitosterol as the active anti-NSCLC ingredient of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua by suppression of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 117900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Hong, L. β-Sitosterol targets ASS1 for Nrf2 ubiquitin-dependent degradation, inducing ROS-mediated apoptosis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovarian cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 214, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mao, J. Systematic pharmacology-based strategy to investigate the mechanism of beta-sitosterol for the treatment of rheumarthritis. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1507606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.; He, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H. 4-Hydroxyacetophenone is an Antipigmentation Reagent via Inhibiting Tryrosinase Activity. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 34811–34821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gou, J.; Qin, L.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Screening of anti-functional dyspepsia compounds in Cynanchum auriculatum: A spectrum-effect relationship analysis, and ATP-binding cassette transporters inhibitor evaluation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
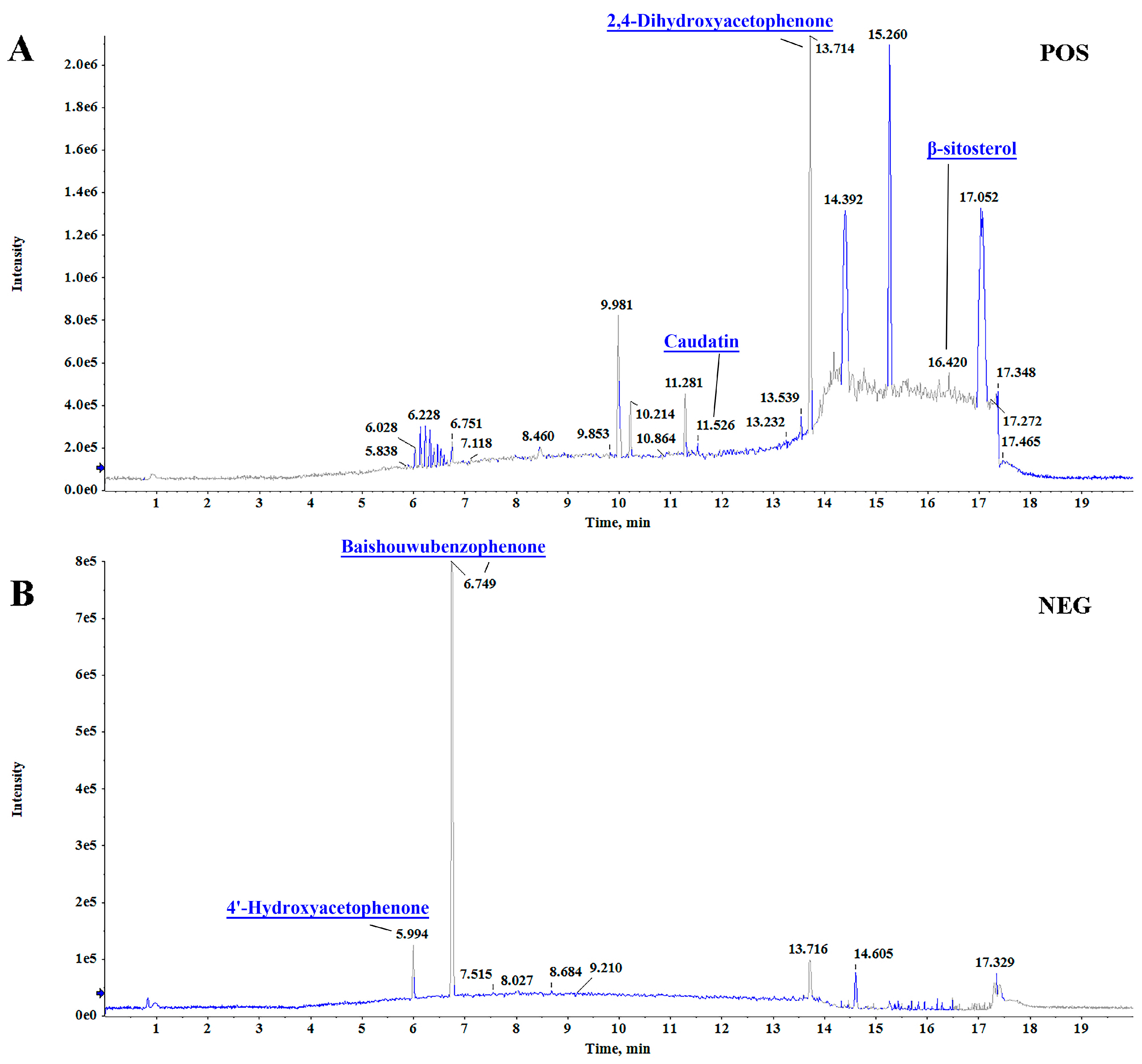
| tR | Compound Name | Formula | Precursor m/z | Reference m/z | Error (ppm) | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.669 | Caudatin | C28H42O7 | 491.29912 | 491.29999 | −1.77 | [M+H]+ |
| 16.415 | Beta-Sitosterol | C29H50O | 397.38257 | 397.38287 | −0.75 | [M+H]+ |
| 6.741 | Baishouwubenzophenone | C16H14O6 | 301.0731 | 301.0744 | 4.4 | [M-H]− |
| 5.994 | 4′-Hydroxyacetophenone | C8H8O2 | 135.0456 | 135.0460 | 3.3 | [M-H]− |
| 13.714 | 2,4-Dihydroxyacetophenone | C8H8O3 | 151.0400 | 151.0399 | −0.4 | [M+H]+ |
| Sample | Median Lifespan/d | Max Lifespan/d | Increase in Average Lifespan/% | p-Value vs. Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 16.33 ± 0.17 | 22.33 ± 0.67 | - | - |
| 1 mg/mL RCAEA | 20.22 ± 0.22 | 26.00 ± 0.00 | 16.42 | 0.0027 ** |
| 2 mg/mL RCAEA | 20.50 ± 0.29 | 26.33 ± 0.33 | 17.91 | 0.0029 ** |
| 4 mg/mL RCAEA | 21.33 ± 0.17 | 27.67 ± 0.33 | 23.88 | 0.0010 *** |
| Sample | Median Lifespan/d | Max Lifespan/d | Increase in Average Lifespan/% | p-Value vs. Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 14.67 ± 0.33 | 21.67 ± 0.33 | - | - |
| 1 mg/mL RCAEA | 11.67 ± 0.33 | 20.33 ± 0.33 | −6.15 | ns |
| 2 mg/mL RCAEA | 13.67 ± 0.33 | 20.67 ± 0.33 | −4.62 | ns |
| 4 mg/mL RCAEA | 14.00 ± 0.00 | 20.67 ± 0.33 | −4.62 | ns |
| Sample | Median Lifespan/d | Max Lifespan/d | Increase in Average Lifespan/% | p-Value vs. Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 14.67 ± 0.33 | 21.67 ± 0.33 | - | - |
| 1 mg/mL RCAEA | 12.67 ± 0.33 | 20.33 ± 0.33 | −6.15 | ns |
| 2 mg/mL RCAEA | 13.00 ± 0.00 | 21.00 ± 0.58 | −3.08 | ns |
| 4 mg/mL RCAEA | 14.33 ± 0.33 | 20.67 ± 0.33 | −4.62 | ns |
| Sample | Median Lifespan/d | Max Lifespan/d | Increase in Average Lifespan/% | p-Value vs. Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.67 ± 0.33 | 18.67 ± 0.33 | - | - |
| 1 mg/mL RCAEA | 11.33 ± 0.33 | 17.67 ± 0.33 | −5.36 | ns |
| 2 mg/mL RCAEA | 13.00 ± 0.58 | 17.00 ± 0.58 | −8.93 | ns |
| 4 mg/mL RCAEA | 12.67 ± 0.67 | 17.33 ± 0.33 | −7.14 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Su, Y.; Xing, Y.; Hu, K.; Ren, J.; Yang, J. Ethyl Acetate Extract of Cynanchi Auriculati Radix Inhibits LPS-Induced M1 Polarization of RAW264.7 Macrophages and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Regulating NF-κB and PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110934
Fan J, Su Y, Xing Y, Hu K, Ren J, Yang J. Ethyl Acetate Extract of Cynanchi Auriculati Radix Inhibits LPS-Induced M1 Polarization of RAW264.7 Macrophages and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Regulating NF-κB and PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110934
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiawei, Ya Su, Yi Xing, Kun Hu, Jie Ren, and Jia Yang. 2025. "Ethyl Acetate Extract of Cynanchi Auriculati Radix Inhibits LPS-Induced M1 Polarization of RAW264.7 Macrophages and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Regulating NF-κB and PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathways" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110934
APA StyleFan, J., Su, Y., Xing, Y., Hu, K., Ren, J., & Yang, J. (2025). Ethyl Acetate Extract of Cynanchi Auriculati Radix Inhibits LPS-Induced M1 Polarization of RAW264.7 Macrophages and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by Regulating NF-κB and PMK-1/SKN-1 Signaling Pathways. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110934







