Peucedanum japonicum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Alleviate Contact Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Preparation of PjELNs
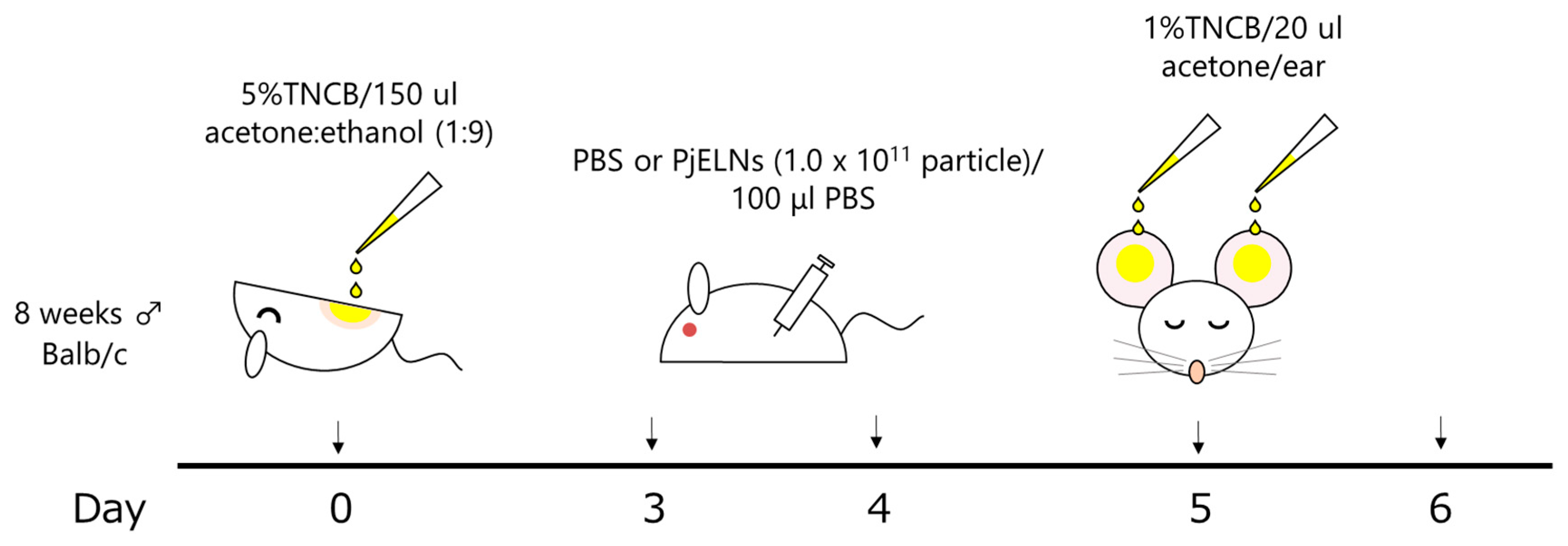
2.3. Allergic Contact Dermatitis Model
2.4. Histological Staining
2.5. FACS Analysis
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PjELNs Suppress TNCB-Induced Ear Swelling in Mice
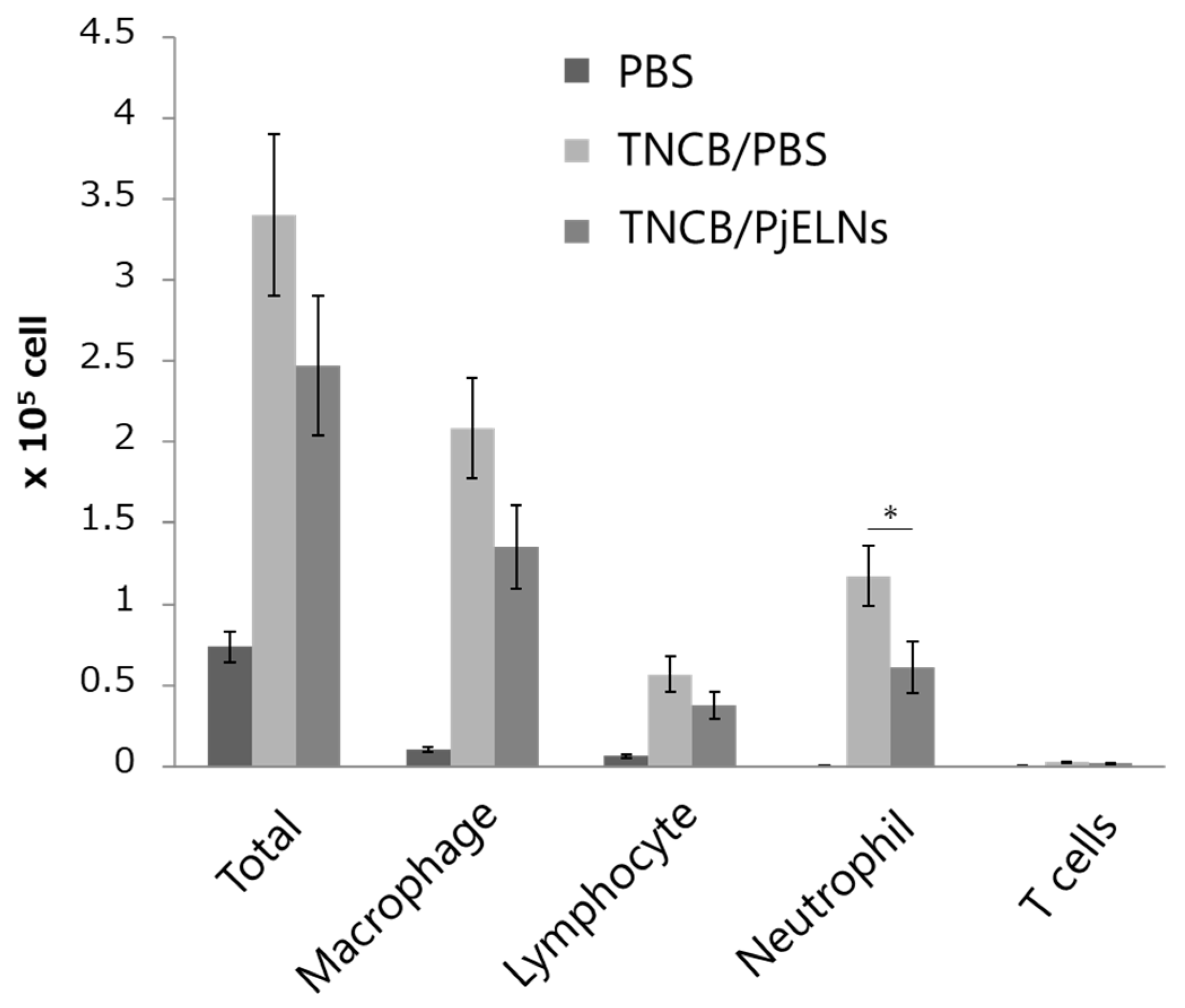
3.2. PjELNs Inhibit TNCB-Induced Inflammatory Cell Infiltration
3.3. PjELNs Suppress TNCB-Induced Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johansen, J.D.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Schwensen, J.F.B.; Thyssen, J.P.; Uter, W. Novel insights into contact dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, K.K. A review of contact dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemeyer, T. Immunological mechanisms in allergic contact dermatitis. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2022, 9, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.L.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Peeva, E. Role of innate immunity in allergic contact dermatitis: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.F.; Rühl-Muth, A.C.; Esser, P.R. Orchestration of inflammation in contact allergy by innate and cellular stress responses. Allergo J. Int. 2024, 33, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochez, P.; Choteau, M.; Limaye, N.; Baeck, M.; Dumoutier, L. Implication of T helper cytokines in contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2020, 7, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, M.; McGonagle, D.; Werfel, T. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in skin inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z. Extracellular vesicles in diagnosis and therapy of kidney diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 311, F844–F851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Vadgama, J.V. Tumor-derived exosomes in tumor-induced immune suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar]
- Gudbergsson, J.M.; Jønsson, K.; Simonsen, J.B.; Johnsen, K.B. Systematic review of targeted extracellular vesicles for drug delivery: Considerations on methodological and biological heterogeneity. J. Control. Release 2019, 306, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürtösi, B.; Kazsoki, A.; Zelkó, R. A systematic review on plant-derived extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Hayashi, T.; Kageyama, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Akiyama, T. Exosome-like nanovesicles of Peucedanum japonicum directly regulate inflammatory cytokines through small RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemelka-Wiacek, M.; Frossi, B.; Salvi, V.; Tamassia, N.; Gasperini, S.; Tecchio, C.; Cassatella, M.A. Contact Hypersensitivity as a Murine Model of Allergic Contact Dermatitis. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 191, e65254. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, L.; Fiocco, Z.; Satoh, T.K.; Peris, K.; French, L.E. Therapeutic potential of targeting interleukin-1 family cytokines in chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloteau, K.; Paris, I.; Pedretti, N.; Boniface, K.; Juchaux, F.; Huguier, V.; Guillet, G.; Bernard, F.X.; Lecron, J.C.; Morel, F. Skin Inflammation Induced by the Synergistic Action of IL-17A, IL-22, Oncostatin M, IL-1a, and TNF-a Recapitulates Some Features of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5263–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Moran, T.; Saunders, S.P.; Kaszlikowska, A.; Floudas, A.; Bom, J.; Nunez, G.; Iwakura, Y.; O’Neill, L.A.; Irvine, A.D.; et al. Spontaneous atopic dermatitis in mice with a defective skin barrier is independent of ILC2 and mediated by IL-1β. Allergy 2019, 74, 1920–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, T.; Clarke, M.; Steele, C.W.; Samuel, M.S.; Neumann, J.; Jung, A.; Huels, D.; Olson, M.F.; Das, S.; Nibbs, R.J.B.; et al. Inhibition of CXCR2 profoundly suppresses inflammation-driven and spontaneous tumorigenesis. J Clin Investig. 2012, 122, 3127–3144. [Google Scholar]
- Mattos, M.S.; Ferrero, M.R.; Kraemer, L.; Lopes, G.A.O.; Reis, D.C.; Cassali, G.D.; Oliveira, F.M.S.; Brandolini, L.; Allegretti, M.; Garcia, C.C.; et al. CXCR1 and CXCR2 Inhibition by Ladarixin Improves Neutrophil-Dependent Airway Inflammation in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 566953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girbl, T.; Lenn, T.; Perez, L.; Rolas, L.; Barkaway, A.; Thiriot, A.; Fresno, C.; Lynam, E.; Hub, E.; Thelen, M.; et al. Distinct Compartmentalization of the Chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2 and the Atypical Receptor ACKR1 Determine Discrete Stages of Neutrophil Diapedesis. Immunity 2018, 49, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutershan, J.; Ley, K. Bench-to-bedside review: Acute respiratory distress syndrome—How neutrophils migrate into the lung. Crit. Care 2004, 8, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hosoki, T.; Itazawa, T.; Boldogh, I.; Sur, S. Neutrophil recruitment by allergens contributes to allergic sensitization and allergic inflammation. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, A.V.; Ortega-Loayza, A.G.; Heath, M.; Morse, D.; Genovese, G.; Cugno, M. Mechanisms of inflammation in neutrophil-mediated skin diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.S.; Choi, H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, E.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, J.S.; Na, C.-S.; Kim, S. Peucedanum japonicum Thunberg and Its Active Components Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis after Urban Particulate Matter-Induced Ocular Surface Damage. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, T.Q.; Huong, N.T.; Son, N.T. The Medicinal Plant Peucedanum japonicum Thunberg: A Review of Traditional Use, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Fitoterapia 2024, 179, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Dendropanax Morbifera Extracts for Cosmetic Applications: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 13526–13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrich, P.; Rutter, B.D.; Karimi, H.Z.; Podicheti, R.; Meyers, B.C.; Innes, R.W. Plant Extracellular Vesicles Contain Diverse Small RNA Species and Are Enriched in 10- to 17-Nucleotide “Tiny” RNAs. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nueraihemaiti, N.; Dilimulati, D.; Baishan, A.; Hailati, S.; Maihemuti, N.; Aikebaier, A.; Paerhati, Y.; Zhou, W. Advances in Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Extraction Methods and Pharmacological Effects. Biology 2025, 14, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, D.; Harshnii, K.; Madhikiruba, K.G.; Nandhini, M.; Tamilselvi, K.S. Plant Derived Exosome- like Nanovesicles: An Updated Overview. Plant Nano Biol. 2023, 3, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamazumi, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kojima, T.; Oda, T.; Kageyama, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kamoshida, Y.; Akiyama, T. Peucedanum japonicum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Alleviate Contact Dermatitis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110909
Yamazumi Y, Hayashi T, Kojima T, Oda T, Kageyama Y, Nakamura T, Kamoshida Y, Akiyama T. Peucedanum japonicum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Alleviate Contact Dermatitis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110909
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamazumi, Yusuke, Tomoatsu Hayashi, Takuya Kojima, Takeaki Oda, Yasunari Kageyama, Tsutomu Nakamura, Yuki Kamoshida, and Tetsu Akiyama. 2025. "Peucedanum japonicum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Alleviate Contact Dermatitis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110909
APA StyleYamazumi, Y., Hayashi, T., Kojima, T., Oda, T., Kageyama, Y., Nakamura, T., Kamoshida, Y., & Akiyama, T. (2025). Peucedanum japonicum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Alleviate Contact Dermatitis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110909





