Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Critical Genes Involved in the Response of Stropharia rugosoannulata to High Temperature and Drought Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Stress Treatments
2.2. Total RNA Extraction, Construction of the cDNA Library, and RNA-seq
2.3. Discovery of New Genes and Functional Annotation
2.4. Differential Expression Gene Analysis
2.5. Enrichment Analysis of GO Function and KEGG Metabolic Pathway
2.6. Screening of Critical Differentially Expressed Genes and qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Summary of the Transcriptome Sequencing and Data Processing
3.2. Transcriptome Sequence Assembly and Gene Function Annotation
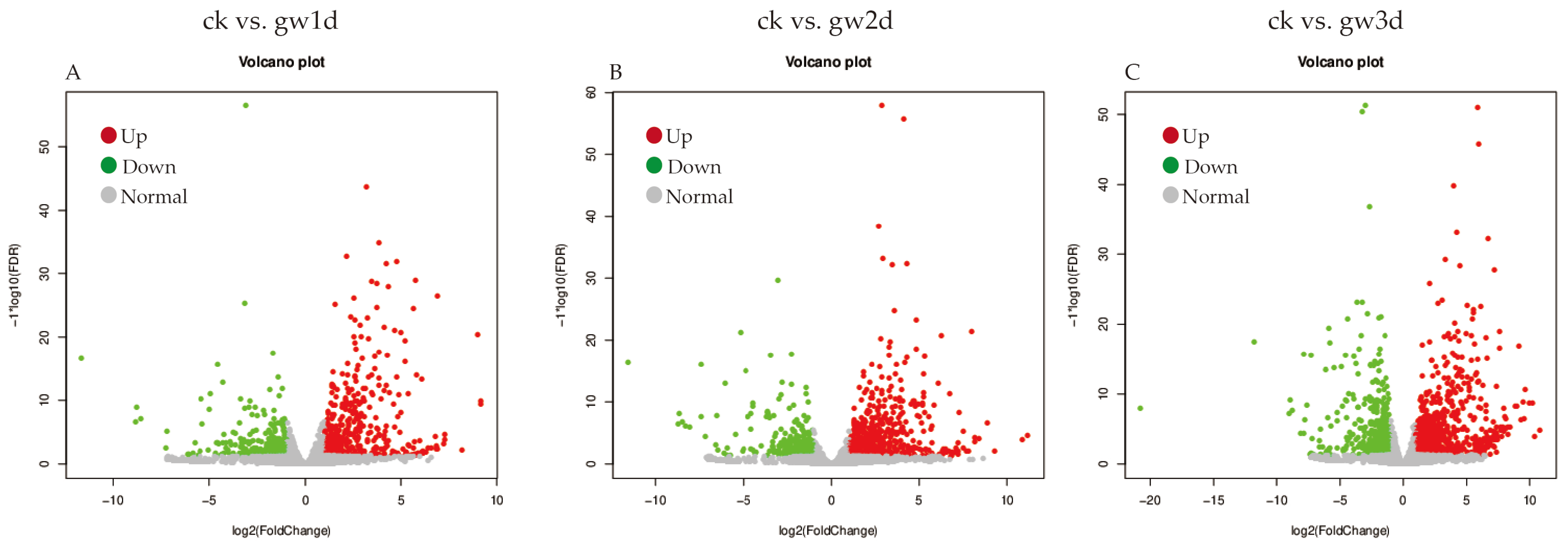
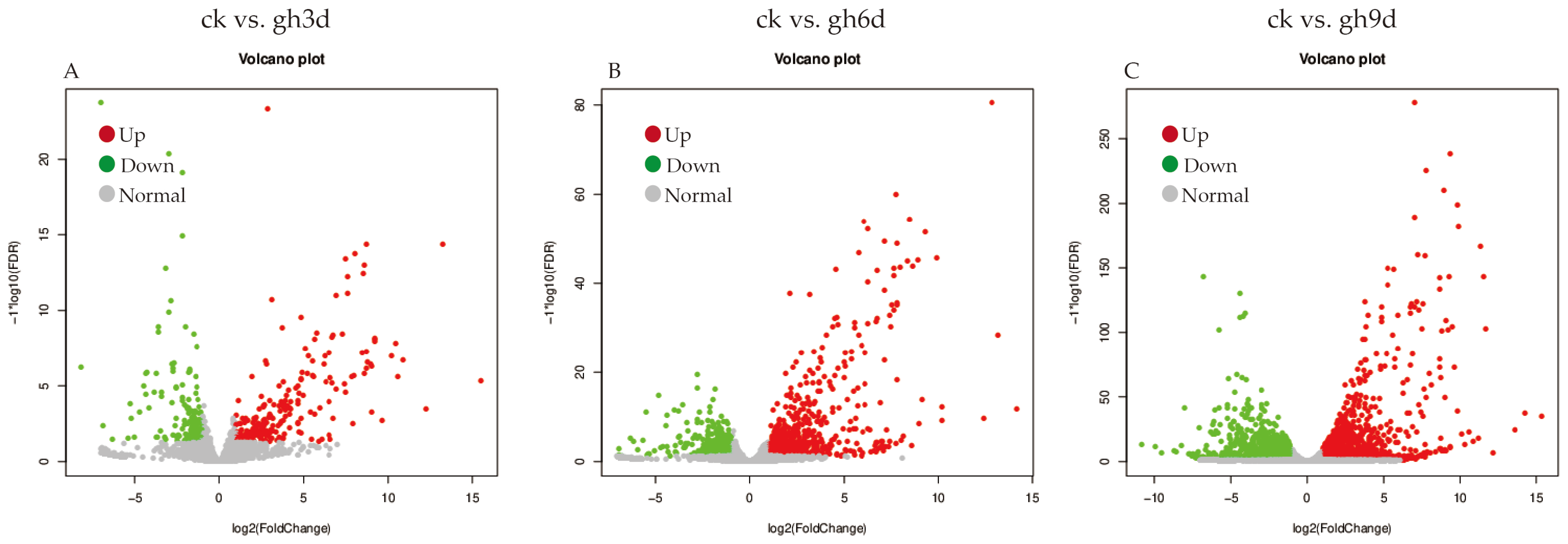
3.3. Sample Correlation Analysis and Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes
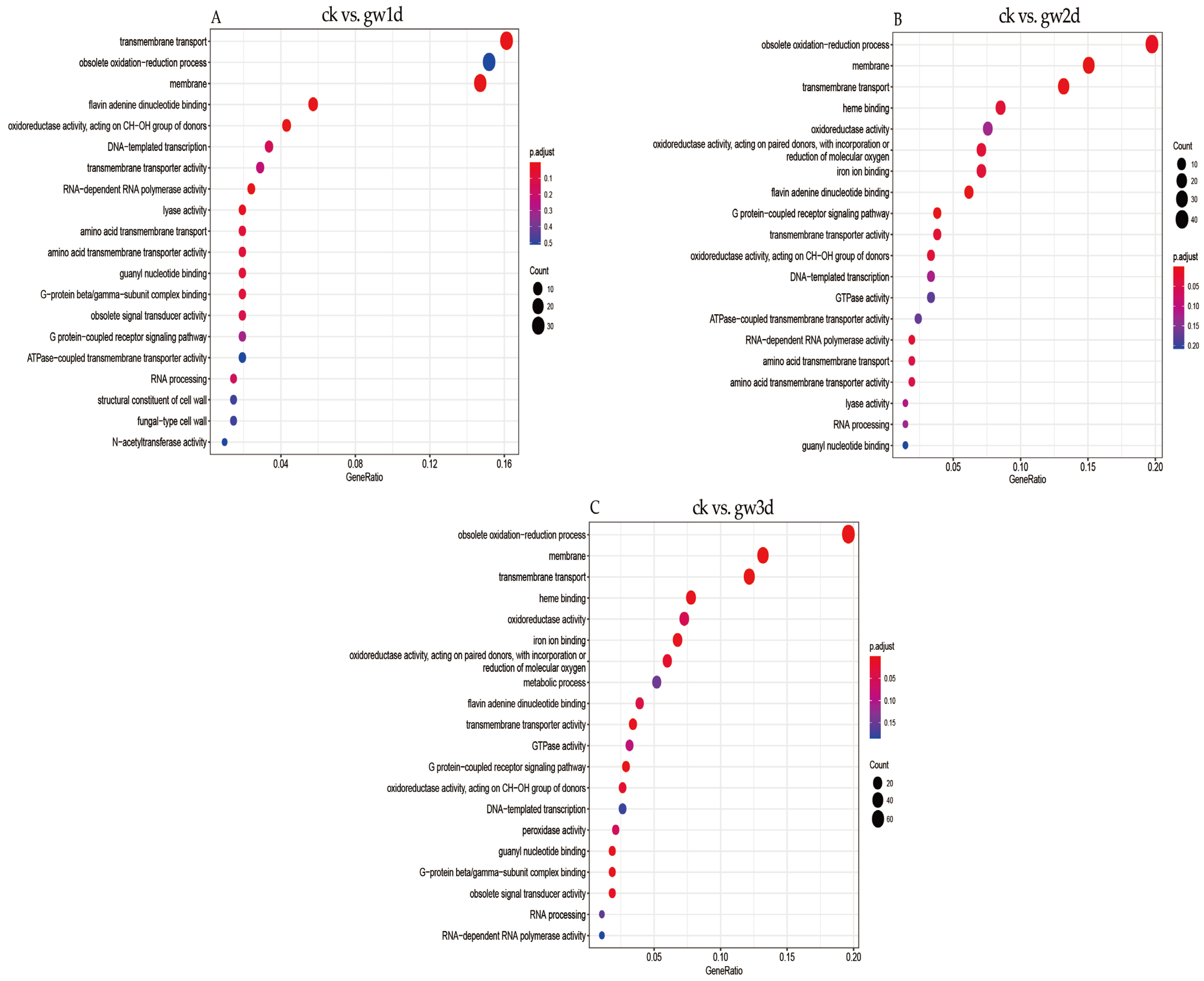
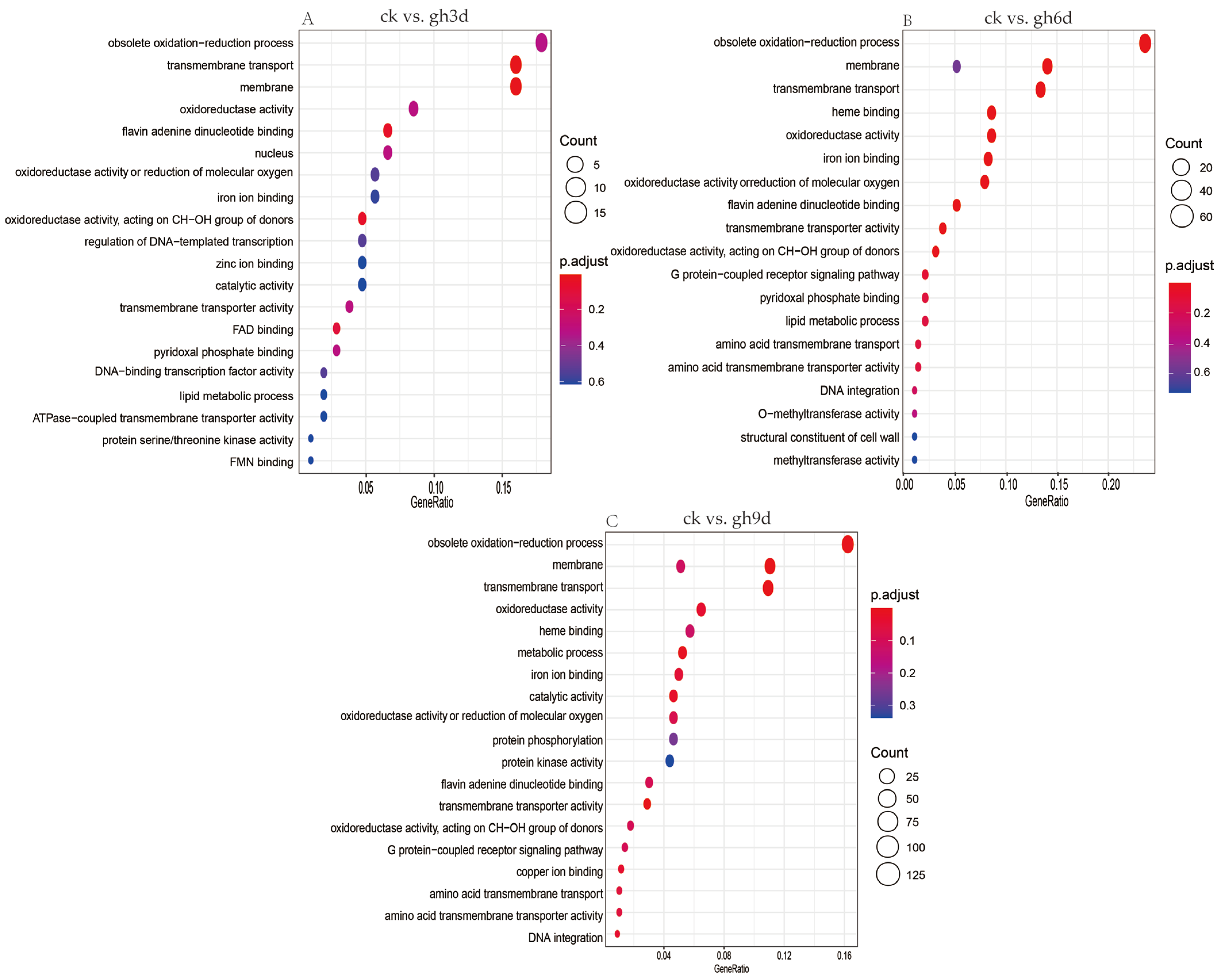
3.4. GO Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
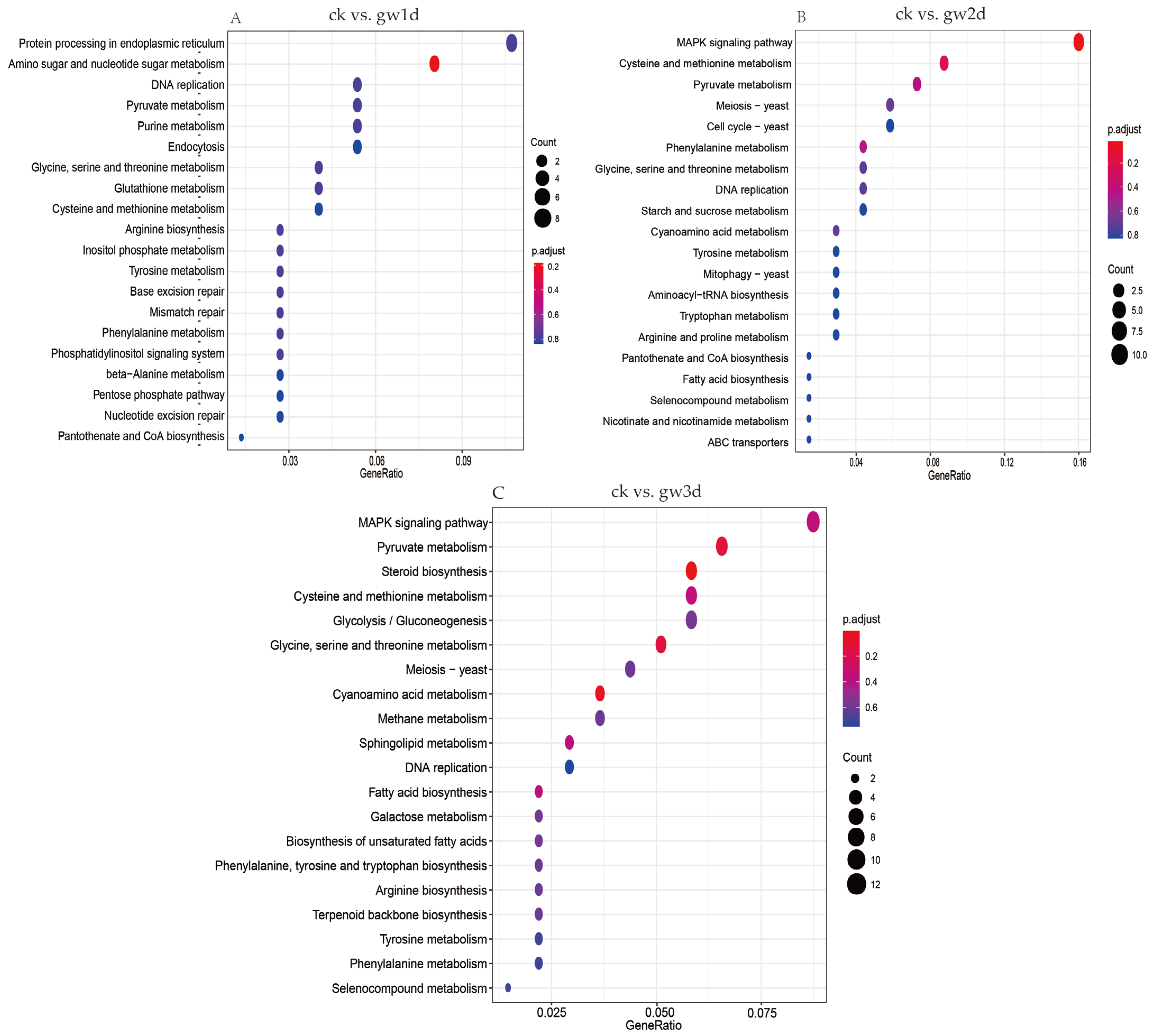
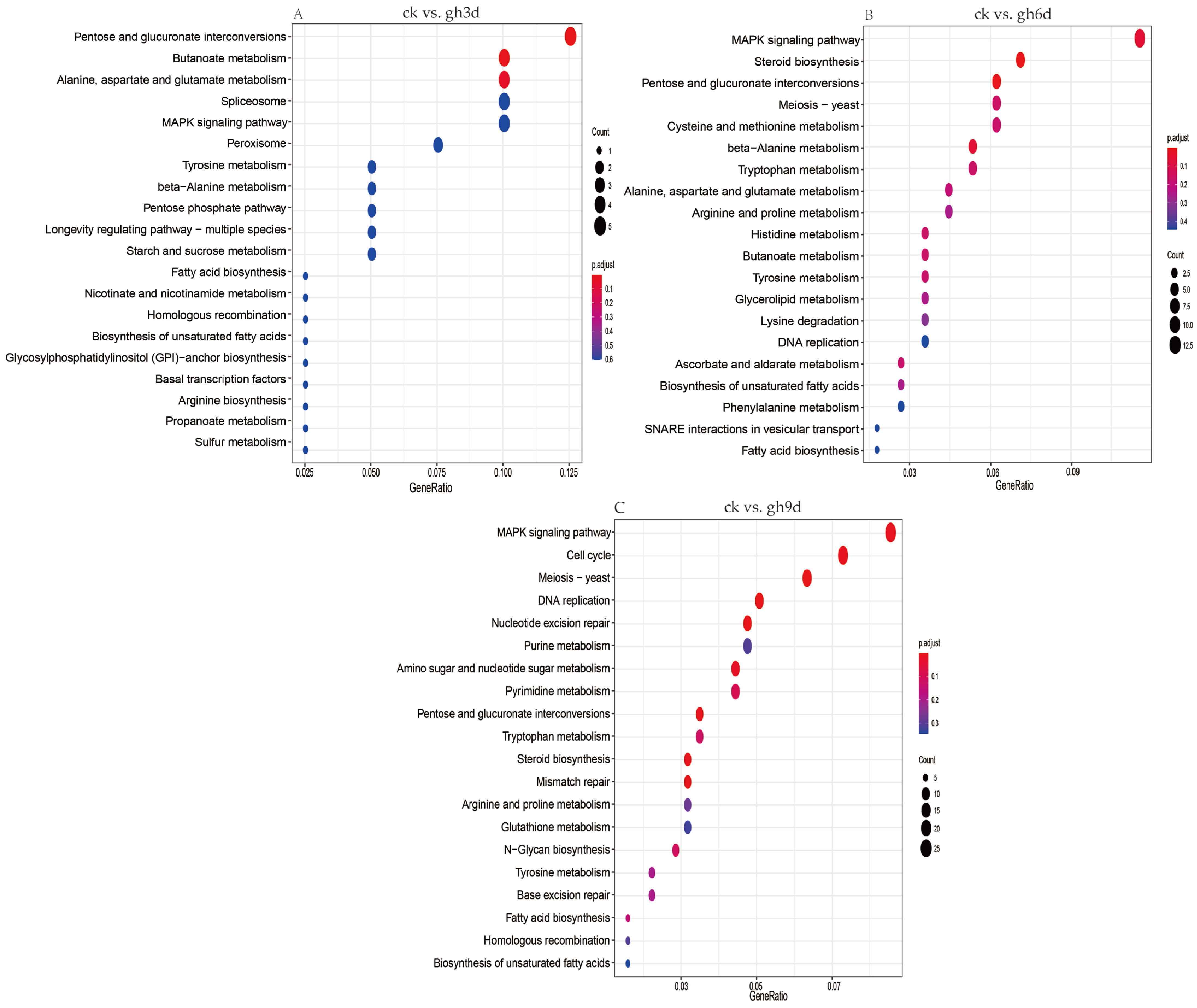
3.5. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
3.6. Screening of Critical Candidate Genes’ Response to High Temperature and Drought
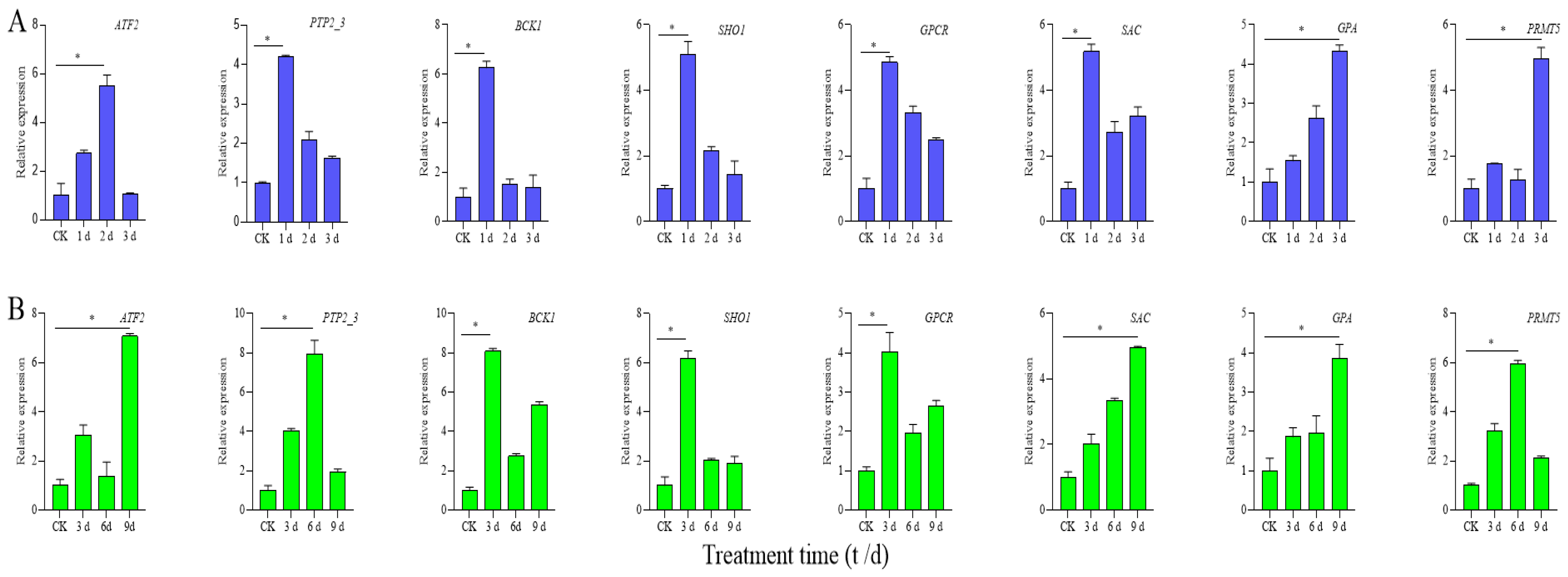
3.7. qRT-PCR Expression Analysis of Candidate Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Meng, G.L.; Ni, S.J.; Zhang, H.F.; Dong, C.H. Genomic analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata reveals its nutritional strategy and application potential in bioremediation. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.R.; Wang, L.; Ni, S.J.; Wang, H.H.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, C.X. The amino acids content of different part of Stropharia rugosoannulata and their nutrition evaluation. Food Res. Dev. 2017, 38, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, L.L.; Jiang, P. Analysis of amino acids content and food safety assessment of Stropharia rugosoannulata cultivated in the imitated wild environment under forest. Edible Fungi China 2021, 40, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.J.; Fan, T.T.; Jin, L.; Lei, P.; Shao, C.X.; Wu, S.L.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.L.; Ren, R.; Xu, J. Soil microbial diversity and functional capacity associated with the production of edible mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata in croplands. Peer J. 2022, 10, e14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, M.J. Research progresses on bioactive components in Stropharia rugosoannulata and their pharmacological effects. Acta Edulis Fungi 2018, 25, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhan, W.; Tao, M.X.; Ji, Z.S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, G.Y. Analysis of nutritional components and antioxidant active substances of Stropharia rugosoannulata. Edible Fungi 2007, 6, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Si, C.; He, C.M.; Liu, X.C.; Duan, J. The rise of Stropharia rugosoannulata industry in China: Current state and prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 109, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Si, C.; Shi, H.Y.; He, C.M.; Duan, J. Research on the stipe cracking of wine-cap mushroom (Stropharia rugosoannulata) in different humidity conditions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Du, Z.H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, Y.R.; Fu, S.B. Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome sheds light on flavonoid biosynthesis in the fruiting body of Stropharia rugosoannulata. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Zuo, J.; Jiang, S.X. Study of thermotolerant mechanism of Stropharia rugosoannulata under high temperature stress based on the transcriptome sequencing. Mycoscience 2021, 62, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y. Influences of environmental factors on fruiting body induction, development and maturation in mushroom-forming fungi. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2018, 32, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Shulaev, V.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen signaling and abiotic stress. Physiol. Plant 2008, 133, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyba, M.; Petijova, L.; Kosuth, J.; Koleva, D.; Ganeva, T.; Kapchinatoteva, V.; Cellarova, E. Oxidative stress and antioxidant response in Hypericum perforatum L. plants subjected to low temperature treatment. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellettini, M.B.; Fiorda, F.A.; Maieves, H.A.; Teixeira, G.L.; Ávila, S.; Hornung, P.S.; Júnior, A.M.; Ribani, R.H. Factors affecting mushroom Pleurotus spp. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Luo, K.M.; Wang, B.L.; Huang, B.Q.; Fei, P.; Zhang, G.G. Inhibition of polyphenol oxidase for preventing browning in edible mushrooms: A review. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6796–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, A.; Camardo Leggieri, M.; Toscano, P.; Battilani, P. Changing climate, shifting mycotoxins: A comprehensive review of climate change impact on mycotoxin contamination. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Isaac, E.L.; Paterson, R.R.M.; Maslin, M.A. A review of potential impacts of climate change on coffee cultivation and mycotoxigenic fungi. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.Y.; Zhao, M.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, J.X. Trehalose alleviates high-temperature stress in Pleurotus ostreatus by affecting central carbon metabolism. Microb. Cell Tact. 2021, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, Q.; Zou, Y.J.; Zhang, J.X. Nitric oxide alleviates heat stress-induced oxidative damage in Pleurotus eryngii var. tuoliensis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.B.; Huang, J.C.; Wang, Q.; Juan, J.X.; Xiao, T.T.; Song, X.X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.J. Effects of heat stress on differential expression of antioxidant enzymes and heat shock protein genes of Agaricus bisporus. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, T.; Yang, T.; Yang, Z.Y.; Ren, A.; Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.S.; Zhao, M.W. Nitric oxide regulates ganoderic acid biosynthesis by the S-nitrosylation of aconitase under heat stress in Ganoderma lucidum. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Complex plant responses to drought and heat stress under climate change. Plant J. 2024, 117, 1873–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.C.; Ma, X.J. Cultivation techniques of Morchella in greenhouse. Agricul. Technol. Equip. 2022, 4, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Boonyuen, N.; Ranaweera, C.B.; de Zoysa, H.K.S.; Padmathilake, R.E.; Nifla, F.; Dai, D.Q.; Liu, Y.; Suwannarach, N.; Kumla, J.; et al. OMICS and other advanced technologies in mycological applications. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Jang, M.J. Transcriptome analysis of the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes in response to blue light. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Li, Q.Z.; Shen, X.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; Lv, B.B.; Shang, X.D. Transcriptomic analysis of two Lentinula edodes genotypes with different cadmium accumulation ability. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 558104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.B.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, S.D.; Bai, J.; Zhuo, X.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Kuai, B.K.; Chen, H. Transcriptomic analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata reveals carbohydrate metabolism and cold resistance mechanisms under low-temperature stress. AMB Expr. 2022, 12, 56, Erratum in AMB Expr. 2022, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S. Blast2GO: A comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2008, 2008, 619832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, N.; Dawson, J.A.; Thomson, J.A.; Ruotti, V.; Rissman, A.I.; Smits, B.M.; Haag, J.D.; Gould, M.N.; Stewart, R.M.; Kendziorski, C. EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.B.; Hu, E.Q.; Cai, Y.T.; Xie, Z.J.; Luo, X.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.L.; Wang, Q.W.; Liu, B.D.; Wang, R.; et al. Using clusterProfiler to characterize multiomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3292–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, Z.T.; Xu, F.; Lu, G.L.; Su, Y.C.; Wu, Q.B.; Wang, T.; Que, Y.X.; Xu, L.P. Screening of candidate genes associated with brown stripe resistance in sugarcane via BSR-seq analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta CT) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, Y.Q.; Xiao, X.W.; Zhong, R.T.; Yang, C.F.; Liu, B.; Zhao, C. Nutrient properties and nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomic analysis of macrofungi. Foods 2019, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ramady, H.; Abdalla, N.; Badgar, K.; Llanaj, X.; Törős, G.; Hajdú, P.; Eid, Y.; Prokisch, J. Edible mushrooms for sustainable and healthy human food: Nutritional and medicinal attributes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.; Mylarapu, A.; Krishna, K.V.; Kumar, D.S. An insight into the nutritional and medicinal value of edible mushrooms: A natural treasury for human health. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 381, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.S.; Li, G.F.; Jiang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.T. Effects of nutrients and environmental factors on the mycelial growth of Stropharia rugosoannulata. Acta Edulis Fungi 2001, 1, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.W.; Kakumyan, P.; Bandara, A.R.; Mortimer, P.E. The nutrition, cultivation and biotechnology of Stropharia rugosoannulata. Fungal Biotec. 2021, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, J.N.; Abright, N.; Mihail, J.D. Forest farming of wine-cap Stropharia mushrooms. Agrofor. Syst. 2010, 79, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekşen, A.; Kibar, B. Determination of optimum culture conditions for mycelial growth of Macrolepiota procera mushroom. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2020, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Rivero, R.M.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J. 2017, 90, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Koussevitzky, S.; Mittler, R.; Miller, G. ROS and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Wu, S.J.; Pang, H.; Wang, C.Q.; Wu, X.J.; Wei, S.Y. High temperature resistance strains screening of Auricularia auricula-judae in Guangxi. Southwest China J. Agricul. Sci. 2018, 31, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.P.; Guo, G.L.; Xu, X.Q.; Luo, T.Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, X.M.; Heng, W.; Jia, B.; Liu, L. Transcriptome analysis reveals key genes involved in the response of Pyrus betuleafolia to drought and high-temperature stress. Plants 2024, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minina, E.A.; Moschou, P.N.; Vetukuri, R.R.; Sanchez-Vera, V.; Cardoso, C.; Liu, Q.; Elander, P.H.; Dalman, K.; Beganovic, M.; Lindberg Yilmaz, J.; et al. Transcriptional stimulation of rate-limiting components of the autophagic pathway improves plant fitness. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.M.; Xiang, Y.; Li, C.L.; Yu, G.H. Modulatory role of reactive oxygen species in root development in model plant of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 485932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, E.K.; Becker, K.; Krevet, S.; Teichert, I.; Kück, U. Transcription factor PRO1 targets genes encoding conserved components of fungal developmental signaling pathways. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 792–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.M.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Song, C.Y.; Chen, M.J. Expression and bioinformatics analysis of hydrophobin protein gene (hyd1) in Lentinula edodes under high temperature stress. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 2645–2652. [Google Scholar]
| Items | Raw Reads a (M) | Clean Reads b (G) | The Average Clean Data (G) c | Q30 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gh3d_1 | 45.06 | 6.74 | 6.78 | 97.99 |
| gh3d_2 | 46.19 | 6.91 | 98.00 | |
| gh3d_3 | 44.78 | 6.7 | 97.49 | |
| gh6d_1 | 44.54 | 6.67 | 6.58 | 97.96 |
| gh6d_2 | 45.42 | 6.8 | 98.02 | |
| gh6d_3 | 41.96 | 6.28 | 98.25 | |
| gh9d_1 | 46.12 | 6.9 | 7.12 | 97.90 |
| gh9d_2 | 48.04 | 7.19 | 97.8 | |
| gh9d_3 | 48.54 | 7.26 | 97.84 | |
| gw1d_1 | 45.24 | 6.77 | 6.83 | 98.05 |
| gw1d_2 | 47.52 | 7.11 | 98.02 | |
| gw1d_3 | 44.12 | 6.6 | 97.77 | |
| gw2d_1 | 43.54 | 6.52 | 6.36 | 97.88 |
| gw2d_2 | 40.78 | 6.09 | 98.02 | |
| gw2d_3 | 43.32 | 6.48 | 98.12 | |
| gw3d_1 | 43.35 | 6.49 | 6.83 | 98.07 |
| gw3d_2 | 49.15 | 7.36 | 97.80 | |
| gw3d_3 | 44.45 | 6.65 | 98.00 | |
| ck_1 | 45.29 | 6.77 | 6.97 | 97.74 |
| ck_2 | 47.95 | 7.18 | 97.77 | |
| ck_3 | 46.50 | 6.96 | 98.03 | |
| Total | 951.86 | 142.43 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Wang, S.; Zhan, M.; Huang, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, R.; Lu, H.; Luo, Q.; Ye, W. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Critical Genes Involved in the Response of Stropharia rugosoannulata to High Temperature and Drought Stress. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100835
Yan S, Wang S, Zhan M, Huang X, Xie T, Wang R, Lu H, Luo Q, Ye W. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Critical Genes Involved in the Response of Stropharia rugosoannulata to High Temperature and Drought Stress. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(10):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100835
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shengze, Shengyou Wang, Meirong Zhan, Xianxin Huang, Ting Xie, Ruijuan Wang, Huan Lu, Qingqing Luo, and Wei Ye. 2025. "Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Critical Genes Involved in the Response of Stropharia rugosoannulata to High Temperature and Drought Stress" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 10: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100835
APA StyleYan, S., Wang, S., Zhan, M., Huang, X., Xie, T., Wang, R., Lu, H., Luo, Q., & Ye, W. (2025). Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Critical Genes Involved in the Response of Stropharia rugosoannulata to High Temperature and Drought Stress. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(10), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100835






