Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Manifestation of SSc
1.2. Complications of SSc
1.3. Pathogenesis of SSc
1.3.1. Vascular Injury
1.3.2. Inflammation
1.3.3. Activation of Fibroblasts
1.3.4. Autoantibodies in SSc
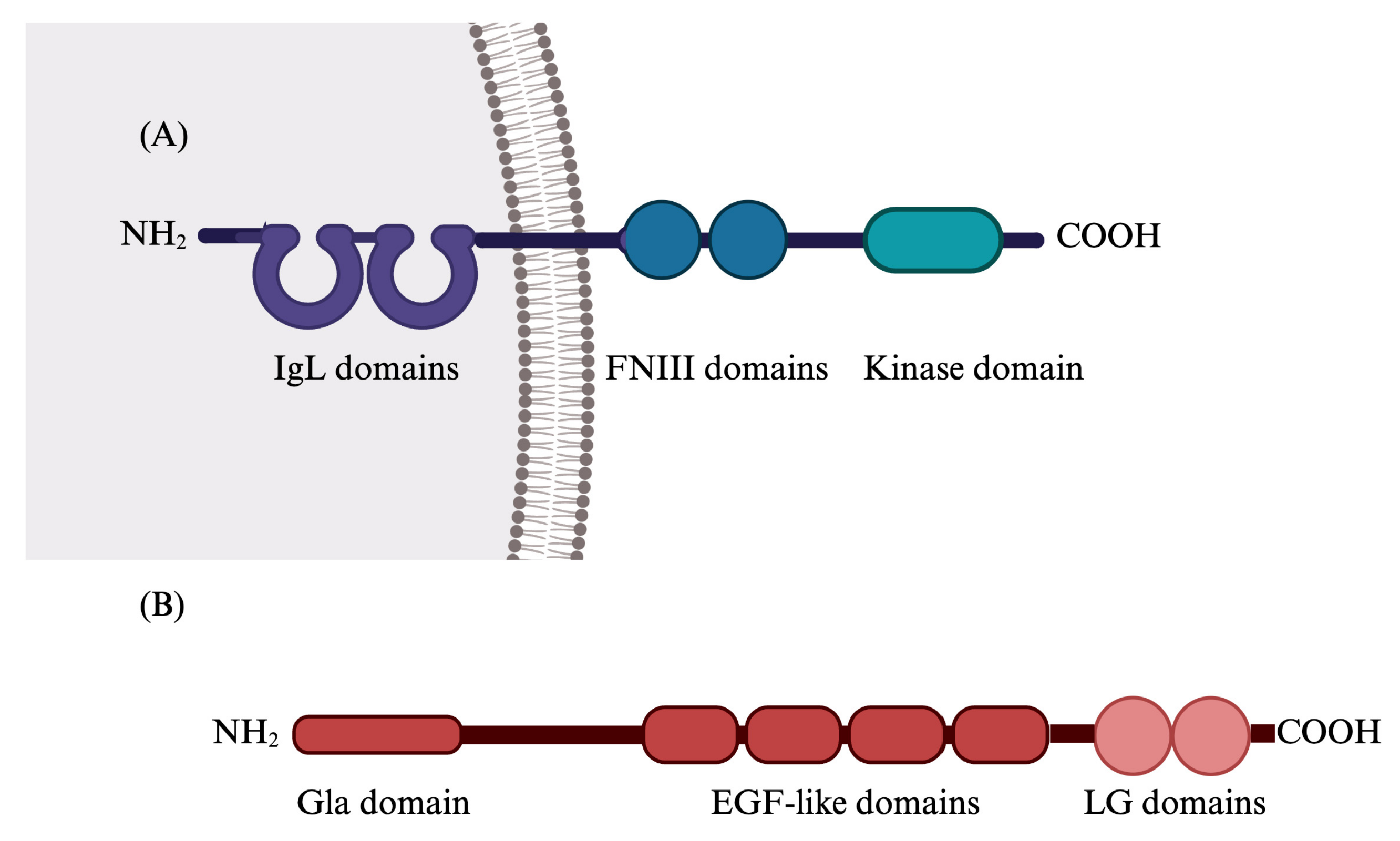
2. Gas6/TAM System
2.1. Gas6/TAM System’s Functions
2.2. Gas6/TAM System in Human Diseases
2.2.1. Gas6/TAM in Cancer
2.2.2. Gas6/TAM System in Liver Diseases
2.2.3. Gas6/TAM System in Lung Diseases
2.2.4. Gas6/TAM System in Infectious Diseases
2.2.5. Gas6/TAM System in Cardiovascular Diseases
2.2.6. Gas6/TAM System in Rheumatic Diseases
2.3. Gas6/TAM System in Systemic Sclerosis
3. Treatment of SSc
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbot, S.; Bossingham, D.; Proudman, S.; de Costa, C.; Ho-Huynh, A. Risk Factors for the Development of Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2018, 2, rky041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and Predicting Mortality from Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.; Scirè, C.A.; Talarico, R.; Airo, P.; Alexander, T.; Allanore, Y.; Bruni, C.; Codullo, V.; Dalm, V.; De Vries-Bouwstra, J.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis: State of the Art on Clinical Practice Guidelines. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Sepúlveda, A.; Esquinca-González, A.; Benavides-Suárez, S.A.; Sordo-Lima, D.E.; Caballero-Islas, A.E.; Cabral-Castañeda, A.R.; Rodríguez-Reyna, T.S. Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies, beyond the Fibroblast. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4569826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM Receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Ghosh, S.; Zuniga, E.I.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; Lemke, G. TAM Receptors Are Pleiotropic Inhibitors of the Innate Immune Response. Cell 2007, 131, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Lemke, G. Homeostatic Regulation of the Immune System by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases of the Tyro 3 Family. Science 2001, 293, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, D.; Gong, B.; Fan, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y. Molecular Insights of Gas6/TAM in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, S.K.; Ayoub, N.M.; Al Sharie, A.H.; Aldaod, J.M. Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinases as a Novel Strategy for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241234780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; Assassi, S.; Denton, C.P. Skin Involvement in Early Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: An Unmet Clinical Need. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderkötter, C.; Riemekasten, G. Pathophysiology and Clinical Consequences of Raynaud’s Phenomenon Related to Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herrick, A.L. The Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Raynaud Phenomenon. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yafawi, R.; Knauft, M.E.; Stokem, K.; Palminteri, J.M.; Wirth, J.A. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Encycl. Cardiovasc. Res. Med. 2018, 1–4, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherbeck, N.; Tamby, M.C.; Bussone, G.; Dib, H.; Perros, F.; Humbert, M.; Mouthon, L. The Role of Inflammation and Autoimmunity in the Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussone, G.; Mouthon, L. Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, P.; Maślińska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Łagun, Z.; Malewska, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Nitskovich, R.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. Systemic Sclerosis—Multidisciplinary Disease: Clinical Features and Treatment. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Steen, V.; Valentini, G. Pulmonary Complications: One of the Most Challenging Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-Art Evidence in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; O’reilly, S. The Immunopathogenesis of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 195, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doridot, L.; Jeljeli, M.; Chêne, C.; Batteux, F. Implication of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis via Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, R.; Birrer, P.; Schöni, M.H. Dose-Response Relationships and Time Course of the Response to Systemic Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists in Infants with Bronchopulmonary Disease. Thorax 1988, 43, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randone, S.B.; Guiducci, S.; Cerinic, M.M. Systemic Sclerosis and Infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Moreno, J.A.D.; Serrano, L.J.; Revuelta, L.; Sánchez, M.J.; Liras, A. The Vascular Endothelium and Coagulation: Homeostasis, Disease, and Treatment, with a Focus on the Von Willebrand Factor and Factors VIII and V. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Distler, O.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Neumann, E.; Gay, S. Mechanisms of Vascular Damage in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zou, P.; Xiao, R. Further Insight into Systemic Sclerosis from the Vasculopathy Perspective. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Noviani, M.; Chellamuthu, V.R.; Albani, S.; Low, A.H.L. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: The Origin of Fibrosis and Interlink with Vasculopathy and Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabquer, B.J.; Hou, Y.; Del Galdo, F.; Kenneth, H.G.; Gerber, M.L.; Jimenez, S.A.; Seibold, J.R.; Koch, A.E. The Proadhesive Phenotype of Systemic Sclerosis Skin Promotes Myeloid Cell Adhesion via ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauzy, S.; Olson, B.; May, C.K.; Parisi, D.; Massad, C.; Hansen, J.E.; Ryu, C.; Herzog, E.L.; Meffre, E. Defective Early B Cell Tolerance Checkpoints in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis Allow the Production of Self Antigen–Specific Clones. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worrell, J.C.; O’Reilly, S. Bi-Directional Communication: Conversations between Fibroblasts and Immune Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 113, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bon, L.; Popa, C.; Huijbens, R.; Vonk, M.; York, M.; Simms, R.; Hesselstrand, R.; Wuttge, D.M.; Lafyatis, R.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. Distinct Evolution of TLR-Mediated Dendritic Cell Cytokine Secretion in Patients with Limited and Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, Y. Cytokines Involved in the Pathogenesis of SSc and Problems in the Development of Anti-Cytokine Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Interplay between Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts: A Systematic Review Providing a New Angle for Understanding Skin Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, H. Scleroderma, Fibroblasts, Signaling, and Excessive Extracellular Matrix. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2005, 7, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbane, A.J.; Denton, C.P.; Holme, A.M. Scleroderma Pathogenesis: A Pivotal Role for Fibroblasts as Effector. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Abraham, D. Systemic Sclerosis: A Prototypic Multisystem Fibrotic Disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, S.; Jones, R.E.; Huang, G.-Q.; Gay, R.E. Immunohistologic Demonstration of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) and Sis-Oncogene Expression in Scleroderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of Fibrosis: Therapeutic Translation for Fibrotic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New Insights into Fibrosis from the ECM Degradation Perspective: The Macrophage-MMP-ECM Interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K. Anti-Nuclear Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: News and Perspectives. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Hudson, M.; Bentow, C.; Roup, F.; Beretta, L.; Pilar Simeón, C.; Guillén-Del-Castillo, A.; Casas, S.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies to Stratify Systemic Sclerosis Patients into Clinically Actionable Subsets. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, M.; Ariza-hutchinson, A.; Patel, R.A.; Sibbitt, W.L., Jr. Biomarkers in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 4633–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzana, I.; Vojinovic, T.; Airo, P.; Fredi, M.; Ceribelli, A.; Pedretti, E. Systemic Sclerosis—Specific Antibodies: Novel and Classical Biomarkers. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maggio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Trotta, L.; Ruggero, L.; Kodric, M.; Geri, P.; Hughes, M.; Bellan, M.; Gilio, M.; et al. Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: An Overview. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7775–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Oyama, N.; Hasegawa, M. Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Literature Review and Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, P.J.; Piera-velazquez, S.; Jimenez, S.A. Identification of Novel Systemic Sclerosis Biomarkers Employing Aptamer Proteomic Analysis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, S.; Walker, J.; Patterson, K.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoimmunity Reviews Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, E.C.; Morrow, W.J.W. Leaders Autoantibodies and Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Antonicelli, F. Autoantibodies Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases: What Meaning for Clinicians? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.A.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Biologic Functions, Signaling, and Potential Therapeutic Targeting in Human Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfioletti, G.; Brancolini, C.; Avanzi, G.; Schneider, C. The Protein Encoded by a Growth Arrest-Specific Gene (Gas6) Is a New Member of the Vitamin K-Dependent Proteins Related to Protein S, a Negative Coregulator in the Blood Coagulation Cascade. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 4976–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biology, R.T.; Davra, V.; Kimani, S.G.; Calianese, D.; Birge, R.B. Ligand Activation of TAM Family and Therapeutic Response. Cancers 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, M.R.; Chen, J.; Hammonds, R.G.; Sadick, M.; Godowsk, P.J. Characterization of Gas6, a Member of the Superfamily of G Domain-Containing Proteins, as a Ligand for Rse and Axl. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9785–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Ohashi, K.; Arita, H.; Zong, C.; Hanafusa, H.; Mizuno, K.; Hanafusa, H.; Mizuno, K. Cell Biology and Metabolism: Identification of the Product of Growth Arrest-specific Gene 6 as a Common Ligand for Axl, Sky, and Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30022–30027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Knyazev, P.G.; Clout, N.J.; Cheburkin, Y.; Ullrich, A.; Timpl, R.; Hohenester, E. Structural Basis for Gas6—Axl Signalling. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, I.N. Mechanisms of Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Monomers or Dimers. Cells 2014, 3, 304–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Review Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, E.; Vaisar, T.; Subramanian, M.; Mautner, L.; Blobel, C.; Tabas, I. Shedding of the Mer Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Is Mediated by ADAM17 Protein through a Pathway Involving Reactive Oxygen Species, Protein Kinase Cδ, and P38 Mitogen- Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33335–33344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, J.J.; Du, Y.; Vanarsa, K.; Mayeux, J.; Li, L.; Arriens, C.; Min, S.; Hutcheson, J.; Davis, L.S.; Chong, B.F.; et al. Heightened Cleavage of Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase by ADAM Metalloproteases May Contribute to Disease Pathogenesis in SLE. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 169, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, S.; Lemarié, C.A.; Blostein, M.D. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene6 (Gas6) and Vascular Hemostasis. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2012, 3, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutusaus, A.; Marí, M.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Morales, A.; García de Frutos, P. Role of Vitamin K-Dependent Factors Protein S and GAS6 and TAM Receptors in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19-Associated Immunothrombosis. Cells 2020, 9, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fernández, L.; Bellido-Martín, L.; De Frutos, P.G. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene 6 (GAS6): An Outline of Its Role in Haemostasis and Inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, L.A.; Graham, D.K.; Di Paola, J.; Branchford, B.R. GAS6/TAM Pathway Signaling in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelillo-scherrer, A.; Burnier, L.; Flores, N.; Savi, P.; Demol, M.; Schaeffer, P.; Herbert, J.; Lemke, G.; Goff, S.P.; Matsushima, G.K.; et al. Role of Gas6 Receptors in Platelet Signaling during Thrombus Stabilization and Implications for Antithrombotic Therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaragno, M.G.; Cavet, M.E.; Yan, C.; Tai, L.; Jin, Z.; Haendeler, J.; Berk, B.C. Gas6 Inhibits Apoptosis in Vascular Smooth Muscle: Role of Axl Kinase and Akt. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 37, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolo, D.; Ferreira, L.L.; Di Tizio, A.; Ruaro, B.; Patrucco, F.; Bellan, M. A Review: The Potential Involvement of Growth Arrest-Specific 6 and Its Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Lung Damage and in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Carrera-silva, E.A.; Bosurgi, L.; Ghosh, S. TAM Receptor Signaling in Immune Homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alciato, F.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Sola, D.; Castello, L.; Avanzi, G.C. TNF-Alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 Expression Is Inhibited by GAS6 in Monocytes/Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, M.; Penninger, J.M. The Role of TAM Family Receptors in Immune Cell Function: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2016, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Zhang, Y. Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of Gas 6 and ProS Expression Facilitates Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse Macrophages. Immunology 2011, 135, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstyn-, T.; Fresia, C.R. TAM Receptors in Phagocytosis: Beyond the Mere Internalization of Particles. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.A.; Maylock, C.A.; Williams, J.A.; Paweletz, C.P.; Shu, H.; Shacter, E. Serum-Derived Protein S Binds to Phosphatidylserine and Stimulates the Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, P.; Ravichandran, K.S. Drugging the Efferocytosis Process: Concepts and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Review Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebkar, A. The Role of Efferocytosis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R. The Clearance of Dead Cells by Efferocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzi, G.C.; Gallicchio, M.; Bottarel, F.; Gammaitoni, L.; Cavalloni, G.; Buonfiglio, D.; Bragardo, M.; Bellomo, G.; Albano, E.; Fantozzi, R.; et al. GAS6 Inhibits Granulocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells. Blood 1998, 91, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, G.; Wood, A.; Alexander, M.Y.; Varnum, B.C.; Boot-handford, R.P.; Ohanian, V.; Ohanian, J.; Fridell, Y.; Canfield, A.E. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl Modulates the Osteogenic Differentiation of Pericytes. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaragno, M.G.; Wuthrich, D.A.; Poppa, V.; Gill, D.; Lindner, V.; Berk, B.C.; Corson, M.A. Increased Expression of Axl Tyrosine Kinase after Vascular Injury and Regulation by G Protein-Coupled Receptor Agonists in Rats. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Xuan, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Jin, H.; Dong, H. How Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Switching Contributes to Vascular Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanbasic, I.; Cuerquis, J.; Varnum, B.; Blostein, M.D. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Involved in Gas6-Axl-Mediated Survival of Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2004, 4, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjwa, M.; Bellido-martin, L.; Lin, Y.; Lutgens, E.; Delesque-touchard, N.; Herve, C.; Moura, R.; Billiau, A.D.; Aparicio, C.; Levi, M.; et al. Gas6 Promotes Inflammation by Enhancing Interactions between Endothelial Cells, Platelets, and Leukocytes. Blood 2016, 111, 4096–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Woo, S.; Park, E.; Kang, J.L. RhoA/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/Mitogen- Activated Protein Kinase Signaling after Growth Arrest—Specific Protein 6/Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Engagement Promotes Epithelial Cell Growth and Wound Repair via Upregulation of Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.L. Gas6 Prevents Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Cells via Production of PGE2, PGD2 and Their Receptors. Cells 2019, 6, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Cittone, M.G.; Tonello, S.; Rigamonti, C.; Castello, L.M.; Gavelli, F.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Gas6/TAM System: A Key Modulator of the Interplay between Inflammation and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Chun, T. Anti-Inflammatory Role of Tam Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases via Modulating Macrophage Function. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, C.; Stefanovic, M.; Tutusaus, A.; Joannas, L.; Menéndez, A.; García-ruiz, C.; Sancho-bru, P.; Caballeria, J.; Rothlin, C.V.; Fernández-checa, J.C.; et al. Gas6/Axl Pathway Is Activated in Chronic Liver Disease and Its Targeting Reduces Fibrosis via Hepatic Stellate Cell Inactivation. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirne, C.; Rigamonti, C.; De Benedittis, C.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Bellan, M.; Burlone, M.E.; Castello, L.M.; Avanzi, G.C. Review Article Gas6/TAM Signaling Components as Novel Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 2304931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Birge, R.B.; Valenti, L.; Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Wang, X.; Shmarakov, I.O.; et al. Macrophage MerTK Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Article Macrophage MerTK Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2019, 31, 406–421.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Tang, X.X. Elevated Expression of Macrophage MERTK Exhibits Profibrotic Effects and Results in Defective Regulation of Efferocytosis Function in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Novel Therapeutic Targets in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Mol. B 2021, 8, 766855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellan, M.; Pogliani, G.; Marconi, C.; Minisini, R.; Franzosi, L.; Alciato, F.; Magri, A.; Avanzi, G.C.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Gas6 as a Putative Noninvasive Biomarker of Hepatic Fibrosis. Biomarks Med. 2016, 6, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, S.; Gilchrist, S.E.; Hafizi, S. Gas6 Induces Myelination through Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 and TGF-β Upregulation in White Matter and Glia. Cells 2020, 9, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Nikolic-paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The Master Regulator of Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, E.B.; Fuh, K.C.; Taylor, T.E.; Krieg, A.J.; Musser, M.; Yuan, J.; Wei, K.; Kuo, C.J.; Longacre, T.A.; Giaccia, A.J. AXL Is an Essential Factor and Therapeutic Target for Metastatic Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 6, 7570–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.A.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Middleton, D.H.G.; Lu, X.; Baro, A.E. Mer or Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Promotes Apoptosis, Blocks Growth and Enhances Chemosensitivity of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png, K.J.; Halberg, N.; Yoshida, M.; Tavazoie, S.F. A MicroRNA Regulon That Mediates Endothelial Recruitment and Metastasis by Cancer Cells. Nature 2012, 481, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosurgi, L.; Bernink, J.H.; Delgado, V.; Gagliani, N.; Joannas, L.; Schmid, E.T. Paradoxical Role of the Proto-Oncogene Axl and Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Colon Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13091–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, J.; Couderc, G.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Requirand, G.; Delteil, M. Identifying Intercellular Signaling Genes Expressed in Malignant Plasma Cells by Using Complementary DNA Arrays. Blood 2016, 98, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.K.; Salzberg, D.B.; Kurtzberg, J.; Sather, S.; Matsushima, G.K.; Keating, A.K.; Lovell, M.A.; Williams, S.A.; Dawson, T.L.; Schell, M.J.; et al. Human Cancer Biology Ectopic Expression of the Proto-Oncogene Mer in Pediatric T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.M.; Greenwade, M.M.; Palisoul, M.L.; Opara, G.; Massad, K.; Guo, L.; Zhao, P.; Beck-noia, H.; Hagemann, I.S.; Hagemann, R.; et al. Therapeutic Inhibition of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase AXL Improves Sensitivity to Platinum and Taxane in Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 18, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straten, P. TAM Receptor Inhibition-Implications for Cancer and the Immune System. Cancers 2021, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Maimon, A. TAM Receptors, Phosphatidylserine, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.K.; Deryckere, D.; Davies, K.D.; Earp, H.S. The TAM Family: Phosphatidylserine Sensing Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Gone Awry in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Tian, R.; Yong, B.; Luo, C.; Tan, P.; Shen, J.; Peng, T. Gas6/Axl Mediates Tumor Cell Apoptosis, Migration and Invasion and Predicts the Clinical Outcome of Osteosarcoma Patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, W.; Deng, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Chen, F. Targeting Gas6/TAM in Cancer Cells and Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.E.J.; Le, J.P.; Sather, S.; Pernu, B.M.; Graham, D.K.; Pierce, A.M.; Keating, A.K. Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Impedes Glioblastoma Multiforme Migration and Alters Cellular Morphology. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, K.; Shieh, Y.; Lee, C.; Shiah, S.; Wu, C. Axl Promotes Cell Invasion by Inducing MMP-9 Activity through Activation of NF- j B and Brg-1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Logsdon, C.D.; Rashid, A.; Fleming, J.B. Overexpression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl Promotes Tumor Cell Invasion and Survival in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. The Crosstalk Between Tumor- Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Valls, A.F.; Yerbes, R.; Von Richter, S.; Almodovar, D.; Ulrich, A.; Schmidt, T. TAM Receptors Tyro3 and Mer as Novel Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 1991, 7, 56355–56370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimani, S.G.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, N.; Singh, K.; Kholodovych, V.; Comollo, T.; Peng, Y.; Kotenko, S.V.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Bertino, J.R.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitors Block Gas6-Inducible TAM Activation and Tumorigenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, K.V.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting Tyro3, Axl and MerTK (TAM Receptors): Implications for Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.J.W.; Rahbech, A. FOCUSSED RESEARCH REVIEW TAM—Ing T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for TAM Receptor Targeting. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Zhang, W.; Menachof, K.K.; Hill, A.A.; Rinella, S.; Kirkpatrick, G.; Page, L.S.; Stashko, M.A.; Jordan, C.T.; Wei, Q.; et al. Efficacy of a Mer and Flt3 Tyrosine Kinase Small Molecule Inhibitor, UNC1666, in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6722–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minson, K.A.; Smith, C.C.; DeRyckere, D.; Libbrecht, C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Lasater, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, G.D.; Stashko, M.A.; Zhang, W.; et al. The MERTK/FLT3 Inhibitor MRX-2843 Overcomes Resistance-Conferring FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, C.G.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, H.R.; Cho, B.C.; Lim, S.M. The Development of AXL Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: Recent Progress and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 811247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zang, H.; Wen, Q.; Fan, S. AXL in Cancer: A Modulator of Drug Resistance and Therapeutic Target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.; Geng, A.; Flint, E.; Singanayagam, A.; Ercan, C.; Possamai, L.; Patel, V.C.; Kuenzler, P.; Meier, M.; Soysal, S.; et al. AXL Expression on Homeostatic Resident Liver Macrophages Is Reduced in Cirrhosis Following GAS6 Production by Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, V.; Breitenecker, K.; Djerlek, L.; Ortmayr, G.; Mikulits, W. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Control of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by TAM Receptors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metastasis, L.; Cedex, V.; Siba, S. Association of SIBA Treatment and a Met—Depleted Diet Inhibits in Vltro Growth and in Vivo Metastatic Spread of Experimenta l Tumor Cell Lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1988, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutusaus, A.; De Frutos, P.G.; Morales, A. Genetic and Clinical Data Reinforce the Role of GAS6 and TAM Receptors in Liver Fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 983–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolo, D.; Ferreira, L.L.; Vincenzi, F.; Vercellino, N.; Minisini, R.; Latini, F.; Ferrari, B.; Burlone, M.E.; Pirisi, M.; Bellan, M. From MASH to HCC: The Role of Gas6/TAM Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1332818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llacuna, L.; Bárcena, C.; Bellido-Martín, L.; Fernández, L.; Stefanovic, M.; Marí, M.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C.; García de Frutos, P.M.A. Growth Arrest-Specific Protein 6 Is Hepatoprotective against Murine Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Hepatology 2011, 52, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafdil, F.; Deveaux, V.; Zafrani, E.; Mavier, P.; Nakano, T.; Laperche, Y.; Brouillet, A. Growth Arrest-Specific Protein 6 Deficiency Impairs Liver Tissue Repair after Acute Toxic Hepatitis in Mice. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Cellular Mechanisms of Tissue Fibrosis. 5. Novel Insights into Liver Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 305, C789–C799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Raggi, C.; Navari, N.; Piombanti, B.; Di Maira, G.; Rovida, E.; Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; et al. Macrophage MerTK Promotes Profibrogenic Cross-Talk with Hepatic Stellate Cells via Soluble Mediators. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Zou, Q. Axl Expression Stratifies Patients with Poor Prognosis after Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, M.S.; Habiel, D.M.; Narayanan, R.; Jones, I.; Coelho, A.L.; Murray, L.A.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W.; Hogaboam, C.M. Targeting of TAM Receptors Ameliorates Fibrotic Mechanisms in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, N.; Kubo, H.; Maciewicz, R.A. Phenotypic Screening Identifies Axl Kinase as a Negative Regulator of an Alveolar Epithelial Cell Phenotype. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 97, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Wu, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, S.; Lee, C. Gas6/Axl Signaling Attenuates Alveolar Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion- Induced Acute Lung Injury by up-Regulating SOCS3-Mediated Pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.; Rello, S.R.; Cristóbal, H.; Fiz-López, A.; Arribas, E.; Marí, M.; Tutusaus, A.; de la Cal-Sabater, P.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; et al. Growth Arrest-Specific Factor 6 (Gas6) Is Increased in Covid-19 Patients and Predicts Clinical Outcome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonello, S.; Rizzi, M.; Matino, E.; Costanzo, M.; Casciaro, G.F.; Croce, A.; Rizzi, E.; Zecca, E.; Pedrinelli, A.; Vassia, V.; et al. Baseline Plasma Gas6 Protein Elevation Predicts Adverse Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1568352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolo, D.; Onghia, D.D.; Tonello, S.; Minisini, R.; Baricich, A.; Gramaglia, C.; Patrucco, F.; Zeppegno, P.; Acquaviva, A.; Balbo, P.E.; et al. Decreased Gas6 and SAxl Plasma Levels Are Associated with Hair Loss in COVID-19 Survivors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 2019, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, W.; Zheng, T.; Wu, P.; Xie, S. AXL Is a Candidate Receptor for SARS-CoV-2 That Promotes Infection of Pulmonary and Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, J.P.; Amaral, F.A.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Resolving Inflammation by TAM Receptor Activation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhaddou, M.; Memon, D.; Meyer, B.; White, K.M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Correa Marrero, M.; Polacco, B.J.; Melnyk, J.E.; Ulferts, S.; Kaake, R.M.; et al. The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell 2020, 182, 685–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórska, A.; Través, P.G.; Lew, E.D.; Dransfield, I.; Lemke, G. Diversification of TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Function. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meertens, L.; Carnec, X.; Lecoin, M.P.; Ramdasi, R.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Lew, E.; Lemke, G.; Schwartz, O.; Amara, A. The TIM and TAM Families of Phosphatidylserine Receptors Mediate Dengue Virus Entry. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morizono, K.; Chen, I.S.Y. Role of Phosphatidylserine Receptors in Enveloped Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meertens, L.; Labeau, A.; Dejarnac, O.; Cipriani, S.; Sinigaglia, L.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Le Charpentier, T.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Zamborlini, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; et al. Axl Mediates ZIKA Virus Entry in Human Glial Cells and Modulates Innate Immune Responses. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, M.; Recarte-Pelz, P.; Roig, E.; Castel, M.A.; Cardona, M.; Farrero, M.; Ortiz, J.T.; Campos, B.; Pulgarín, M.J.; Ramírez, J.; et al. AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is Increased in Patients with Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 173, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, R.; Xu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Dong, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; et al. Plasma GAS6 Predicts Mortality Risk in Acute Heart Failure Patients: Insights from the DRAGON-HF Trial. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Y. Downregulated Circulating Long Non-Coding RNA GAS6-AS1 Screens and Predicts Acute Myocardial Infarction. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2023, 27, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Thorp, E.B.; Doran, A.C.; Sansbury, B.E.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Dorweiler, B.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I. MerTK Receptor Cleavage Promotes Plaque Necrosis and Defective Resolution in Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShane, L.; Tabas, I.; Lemke, G.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Maffia, P. TAM Receptors in Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, F.; Zhu, H. Soluble TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Correlation with Disease Activity and Bone Destruction. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 192, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, I.H.; El-Wakd, M.M.; Azab, N.A.; Bassyouni, R.H. Diminished Soluble Levels of Growth Arrest Specific Protein 6 and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Axl in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humby, F.; Durez, P.; Buch, M.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Rizvi, H.; Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Giorli, G.; Mahto, A.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Rituximab versus Tocilizumab in Anti-TNF Inadequate Responder Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (R4RA): 16-Week Outcomes of a Stratified, Biopsy-Driven, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 4 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerviani, A.; Boutet, M.A.; Ghirardi, G.M.; Goldmann, K.; Sciacca, E.; Rivellese, F.; Pontarini, E.; Prediletto, E.; Abatecola, F.; Caliste, M.; et al. Axl and MerTK Regulate Synovial Inflammation and Are Modulated by IL-6 Inhibition in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, J.P.; Valdrighi, N.; Blaney-Davidson, E.N.; Hornikx, D.L.A.H.; Neefjes, M.; Barba-Sarasua, M.E.; Thielen, N.G.M.; van den Bosch, M.H.J.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Koenders, M.I.; et al. Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Brand, B.T.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Vermeij, E.A.; Bennink, M.B.; Arntz, O.J.; Rothlin, C.V.; Van Den Berg, W.B.; Van De Loo, F.A.J. Therapeutic Efficacy of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer Tyrosine Kinase Agonists in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wang, J.; Ma, N.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Liang, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, R. The Association of Tyro3/Axl/Mer Signaling with Inflammatory Response, Disease Activity in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Jt. Bone Spine 2015, 82, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturfelt, G.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Ekman, C.; Jo, A. Plasma Concentrations of Gas6 and SAxl Correlate with Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xing, L.; Ma, J.; Yu, C. Plasma SMer, SAxl and GAS6 Levels Correlate with Disease Activity and Severity in Lupus Nephritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellan, M.; Quaglia, M.; Nerviani, A.; Mauro, D.; Lewis, M.; Goegan, F.; Gibbin, A.; Pagani, S.; Salmi, L.; Molinari, L.; et al. Increased Plasma Levels of Gas6 and Its Soluble Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Mer and Axl Are Associated with Immunological Activity and Severity of Lupus Nephritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Dimagli, A.; Piccinino, C.; Giubertoni, A.; Ianniello, A.; Grimoldi, F.; Sguazzotti, M.; Nerviani, A.; Barini, M.; Carriero, A.; et al. Role of Gas6 and TAM Receptors in the Identification of Cardiopulmonary Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis and Scleroderma Spectrum Disorders. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 2696173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Lemke, G. TAM Receptor Signaling and Autoimmune Disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, A.; Bournazos, S.; Franz, S.; Perretti, M.; Morgan, B.P.; Haslett, C.; Dransfield, I. Glucocorticoids Induce Protein S-Dependent Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils by Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Kuwana, M. Nintedanib for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Autoantibodies | Phenotypes | Target | Clinical Associations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACA | lcSSc | ACA are mainly directed towards three centromere proteins, namely CENP-A, B, and C. | Cutaneous calcinosis, dermal thickness of hands and/or feet distally from elbow and knee, respectively, and PAH. |
| Anti-topo I | dcSSc | Anti-topo I are directed towards a nuclear protein of 70–100 kD, clustered with DNA molecules and involved in altering DNA chain conformation during cellular replication. | Ischemic digital ulcers, flexion contractures in metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, hand disability, and progressive pulmonary fibrosis. |
| Anti-RNA pol III | dcSSc | Anti-RNA pol III antibodies are reactive with RNA polymerase III. | Joint contractures, scleroderma renal crisis |
| Anti-Th/To | lcSSc | Anti-Th/To are directed towards protein components of the RNase MRP complex. | ILD and pericarditis. |
| Treatments | Effects | Involvement in Other Conditions | Possible Involvement of Gas6/TAM Axis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC and RTX, bDMARDs | TOC: Inhibition of the IL-6-mediated signaling pathways, leading to a reduction in inflammation and immune response modulation.RTX: Depletion of B cells. | Proven. | Increased expression of Axl and MerTK in the RA synovial tissue, suggesting that IL-6 inhibition may exert part of its anti-inflammatory effects through upregulation of TAM receptors. | [152] |
| Prednisolone, glucocorticoids | Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. | Proven. | Glucocorticoids can upregulate the expression of MerTK enhancing the clearance of apoptotic cells and promoting anti-inflammatory pathway. | [160,161] |
| Nintedanib, tyrosine kinase inhibitor | It targets multiple tyrosine kinases involved in the processes of fibrosis, inflammation, and vascular remodeling. | Proven. | Gas6/TAM receptor activity contributes to the activation of pulmonary fibroblasts in IPF and targeting of TAM receptors alleviates fibrotic mechanisms. | [131] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolo, D.; D’Onghia, D.; Nerviani, A.; Ghirardi, G.M.; Sola, D.; Perazzi, M.; Tonello, S.; Colangelo, D.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Bellan, M. Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
Apostolo D, D’Onghia D, Nerviani A, Ghirardi GM, Sola D, Perazzi M, Tonello S, Colangelo D, Sainaghi PP, Bellan M. Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(7):7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolo, Daria, Davide D’Onghia, Alessandra Nerviani, Giulia Maria Ghirardi, Daniele Sola, Mattia Perazzi, Stelvio Tonello, Donato Colangelo, Pier Paolo Sainaghi, and Mattia Bellan. 2024. "Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis?" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 7: 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
APA StyleApostolo, D., D’Onghia, D., Nerviani, A., Ghirardi, G. M., Sola, D., Perazzi, M., Tonello, S., Colangelo, D., Sainaghi, P. P., & Bellan, M. (2024). Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(7), 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444









