The Root Extract of Rosa multiflora Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Development via Blockade of De Novo Lipogenesis and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Rosa multiflora (YC-1102)
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Histology (Oil Red O, Sirius Red, and Immunohistochemistry)
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Plasma ALT, AST, and TG
2.6. Hepatic TG Measurement
2.7. Cell Isolation and Culture
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. YC-1102 Ameliorates Symptoms of FPC Diet-Induced NASH
3.2. De Novo Lipogenesis-Induced Hepatic Steatosis Is Inhibited by YC-1102 Treatment
3.3. YC-1102 Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation through Suppression of Macrophage Activation
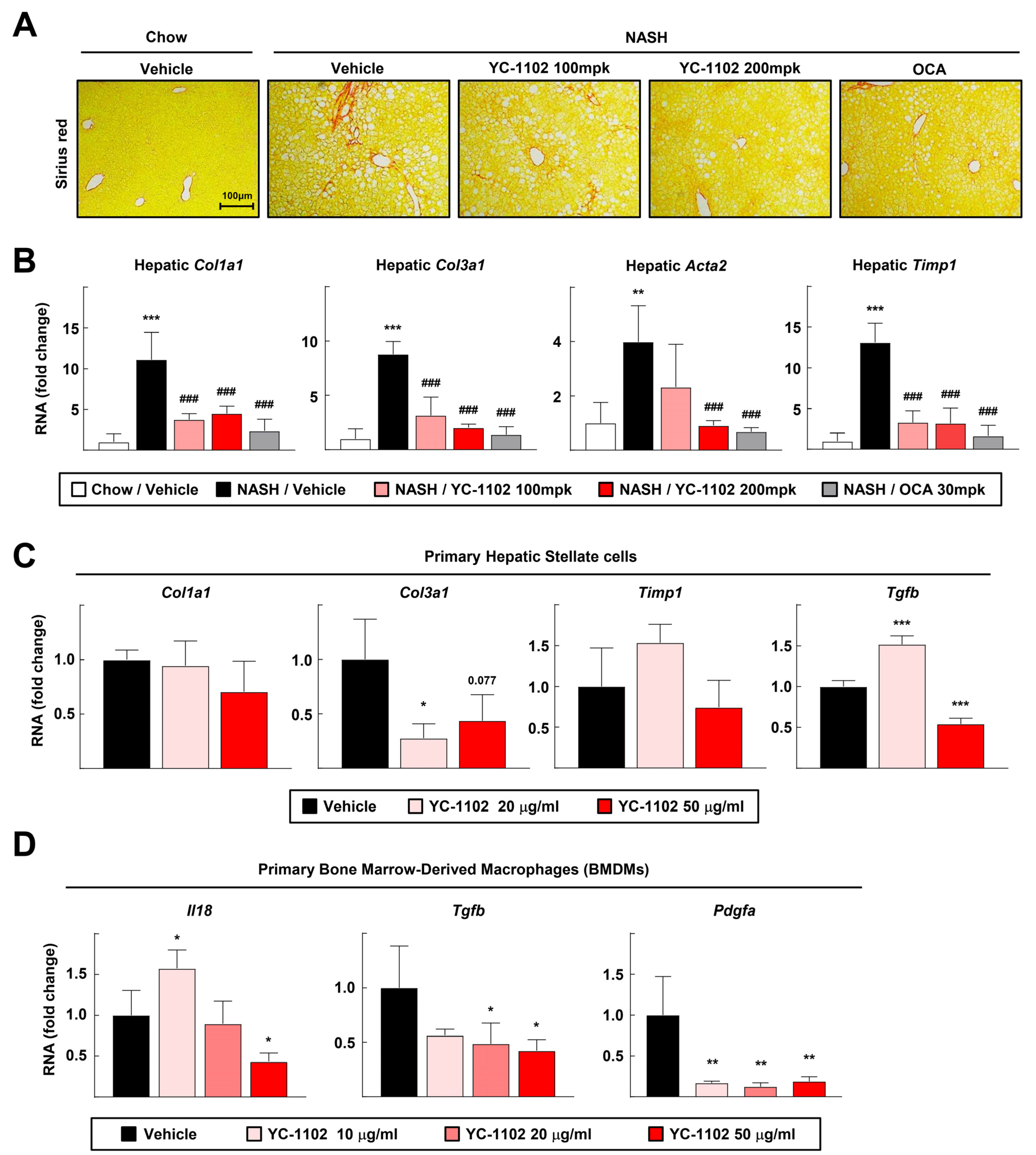
3.4. YC-1102 Suppresses Hepatic Fibrosis in FPC Diet-Induced NASH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knebel, B.; Fahlbusch, P.; Dille, M.; Wahlers, N.; Hartwig, S.; Jacob, S.; Kettel, U.; Schiller, M.; Herebian, D.; Koellmer, C.; et al. Fatty Liver Due to Increased de novo Lipogenesis: Alterations in the Hepatic Peroxisomal Proteome. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, J.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Harrison, S.; Loomba, R.; Paradis, V.; Tilg, H.; Wong, V.W.; Zelber-Sagi, S. Current therapies and new developments in NASH. Gut 2022, 71, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, F.W.; Griffin, J.L. De novo lipogenesis in the liver in health and disease: More than just a shunting yard for glucose. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2016, 91, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchuluun, B.; Pinkosky, S.L.; Steinberg, G.R. Lipogenesis inhibitors: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Xiaoli, A.M.; Yang, F. Regulation and Metabolic Significance of De Novo Lipogenesis in Adipose Tissues. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddin, M.; Muthiah, M.D.; Sanyal, A.J. Drug discovery and treatment paradigms in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 3, e00105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.G.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Murphy, A.J.; Febbraio, M.A. Diet-induced gut dysbiosis and inflammation: Key drivers of obesity-driven NASH. iScience 2023, 26, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Crosstalk Between Liver Macrophages and Surrounding Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, D.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, J.; Kaufmann, B.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Holtmann, T.M.; Geisler, L.; Hundertmark, J.; Kohlhepp, M.S.; Boosheri, L.M.; Chilin-Fuentes, D.R.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Interleukin-18 signaling promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells in mouse liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1968–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignat, S.R.; Dinescu, S.; Hermenean, A.; Costache, M. Cellular Interplay as a Consequence of Inflammatory Signals Leading to Liver Fibrosis Development. Cells 2020, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, S.E.; Kwon, J.H.; Oh, M.H.; Lee, M.W. Three new stereoisomers of condensed tannins from the roots of Rosa multiflora. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Park, K.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Park, K.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Seo, S.J.; Lee, M.W. Topical application of Rosa multiflora root extract improves atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by mite antigen in NC/Nga mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Baek, J.Y.; Choi, H.J. Effects of Rosa multiflora and Rosa multiflora Complex on Lipid Content in Rats Fed a High-Fat · High-Cholesterol Diet. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 44, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Kim, K.K.; Baek, S.H.; Park, C.I.; Jeon, H.J.; Song, A.R.; Park, H.-J.; Park, I.B.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; et al. Effect of YC-1102 on the Improvement of Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.S. Triterpenoids from Rubi fructus (bogbunja). Arch. Pharmacal Res. 1993, 16, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Caviglia, J.M.; Corey, K.E.; Herfel, T.M.; Cai, B.; Masia, R.; Chung, R.T.; Lefkowitch, J.H.; Schwabe, R.F. Hepatocyte TAZ/WWTR1 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, K.-S.; Hong, S.; Park, H.-G.; Lee, M.-O. RORα decreases oxidative stress through the induction of SOD2 and GPx1 expression and thereby protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Jeong, B.; Lee, G.-S.; Jeon, H.; Yang, Y.M.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.-H. Panaxydol extracted from Panax ginseng inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation to ameliorate NASH-induced liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Itoh, M.; Suganami, T.; Kanai, S.; Shirakawa, I.; Sakai, T.; Asakawa, M.; Yoneyama, T.; Kai, T.; Ogawa, Y. Obeticholic acid protects against hepatocyte death and liver fibrosis in a murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kořínková, L.; Pražienková, V.; Černá, L.; Karnošová, A.; Železná, B.; Kuneš, J.; Maletínská, L. Pathophysiology of NAFLD and NASH in Experimental Models: The Role of Food Intake Regulating Peptides. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 597583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huby, T.; Gautier, E.L. Immune cell-mediated features of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Miyata, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C.; Yang, J. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, Y.-J.; An, B.-J. Anti-Oxidant and Antiinflammatory Effects of Rosa multiflora Root. J. Life Sci. 2011, 21, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salvoza, N.; Giraudi, P.J.; Tiribelli, C.; Rosso, N. Natural Compounds for Counteracting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Advantages and Limitations of the Suggested Candidates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Han, J.H.; Hong, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Kwon, T.H. Antioxidant and lipid-reducing effects of Rosa rugosa root extract in 3T3-L1 cell. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlé, D.; Hegarty, B.; Bossard, P.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 2004, 86, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Park, J.E.; Lee, M.; Hardwick, J.P. Hepatic lipid homeostasis by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 2. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skat-Rørdam, J.; Højland Ipsen, D.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. A role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zou, X.B.; Chai, Y.F.; Yao, Y.M. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer | Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Fasn | Forward Reverse | CAACCGGCTCTCTTTCTTCT CTTGGTAGGCATTCTGTAGTG |
| Acaca | Forward Reverse | AGCCAGAAG GGACAGTAGAA CTCAGCCAAGCGGATGTAAA |
| Scd1 | Forward Reverse | GGCAGTTCTGAGGTGATTAGAG GTCTCTGGGAAG AGCAATGTAG |
| Acyl | Forward Reverse | CGGGAGGAAGCTGATGAATATG GTCAAGGTAGTGCCCAATGAA |
| Srebf1 | Forward Reverse | GGACTTCCC ATCTGTTGTAAGG CAAGGGTTATGAGCCATGAGAT |
| Pparg | Forward Reverse | GCCTAAGTTTGAGTTTGCTGTG GCGGTCTCCACTGAGAATAATG |
| Tnfa | Forward Reverse | AATGGCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTT CCACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGA |
| Il6 | Forward Reverse | GAACAACGATGA TGCACTTGC TCCAGGTAGCTATGGTACTCC |
| F4/80 | Forward Reverse | CGTCAGGTACGGGATGAATATAAG ATCTTGGAAGTGGATGGCATAG |
| Mcp1 | Forward Reverse | CACTCACCTGCTGCTACTCA GCTTGGTGACAAAAACTACAGC |
| Il12 | Forward Reverse | CTGGAACTACACAAGAACGAGAG GGCACA GGGTCATCATCAAA |
| Il1b | Forward Reverse | AGAGCCCATCCTCTGTGACTCA TGCTTGGGATCCACACTCTCCA |
| Col1a1 | Forward Reverse | GAAACCCGAGGTATGCTTGA GTTGGGACAGTCCAGTTCTT |
| Col3a1 | Forward Reverse | GGCTGCAAGATGGATGCTATAA GAATCTGTCCACCAGTGCTTAC |
| Acta2 | Forward Reverse | CCATCATGCGTCTGGACTT GGCAGTAGTCACGAAGGAATAG |
| Timp1 | Forward Reverse | GATTCAAGGCTGTGGGAAATG ACTCTTCACTGCGGTTCTG |
| Tgfb | Forward Reverse | CTTTAGGAAGGACCTGGGTTG GTGTGTCCAGGCTCCAAATA |
| Il18 | Forward Reverse | CAGCCTGTGTTCGAGGATATG TCACAGCCAGTCCTCTTACT |
| Pdgfa | Forward Reverse | TCCAGCGACTCTTGGAGATA TCTCGGGCACATGGTTAATG |
| 18S rRNA | Forward Reverse | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Song, A.R.; Park, H.-J.; Kang, J.S.; Cha, J.Y.; Han, Y.-H. The Root Extract of Rosa multiflora Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Development via Blockade of De Novo Lipogenesis and Inflammation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5881-5893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060351
Kim N-H, Lee S-J, Lee K-J, Song AR, Park H-J, Kang JS, Cha JY, Han Y-H. The Root Extract of Rosa multiflora Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Development via Blockade of De Novo Lipogenesis and Inflammation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(6):5881-5893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nam-Hee, Seung-Jin Lee, Kyeong-Jin Lee, Ae Ri Song, Hyun-Je Park, Jong Soo Kang, Joo Young Cha, and Yong-Hyun Han. 2024. "The Root Extract of Rosa multiflora Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Development via Blockade of De Novo Lipogenesis and Inflammation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 6: 5881-5893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060351
APA StyleKim, N.-H., Lee, S.-J., Lee, K.-J., Song, A. R., Park, H.-J., Kang, J. S., Cha, J. Y., & Han, Y.-H. (2024). The Root Extract of Rosa multiflora Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Development via Blockade of De Novo Lipogenesis and Inflammation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(6), 5881-5893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060351







