Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Visfatin Levels in Patients with Periodontitis and Obesity/Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Focused Question and Search Strategy
2.2.1. Primary PECO Question
- (Patient) Adult patients affected by periodontitis;
- (Exposure) Obesity;
- (Comparison) Normal weight as control;
- (Outcome) Biofluid RBP4/visfatin levels.
2.2.2. Secondary PECO Question
- (Patient) Adult patients;
- (Exposure) Obesity and periodontitis;
- (Comparison) Normal weight and periodontal healthy as control;
- (Outcome) Biofluid RBP4/visfatin levels.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
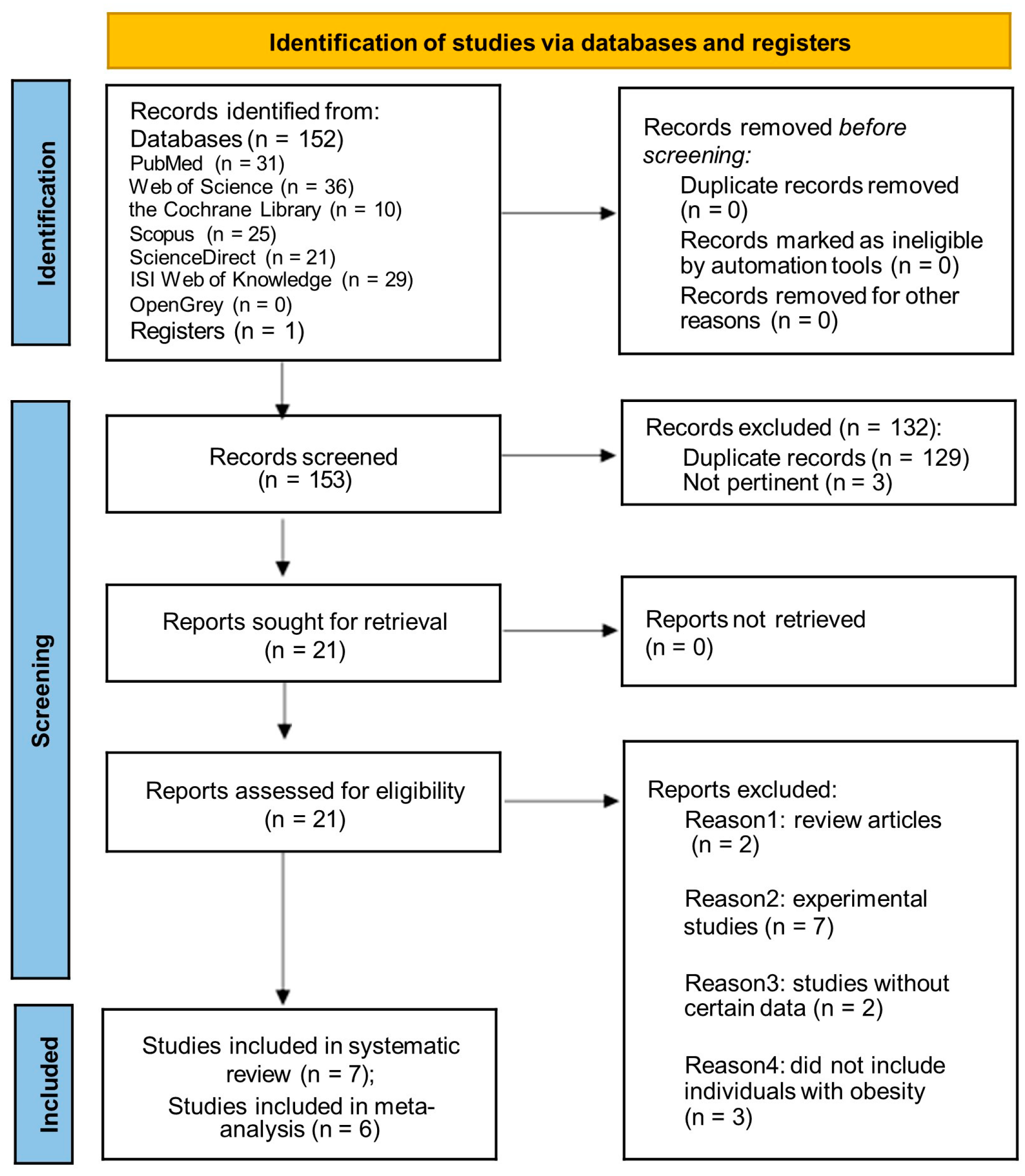
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Study
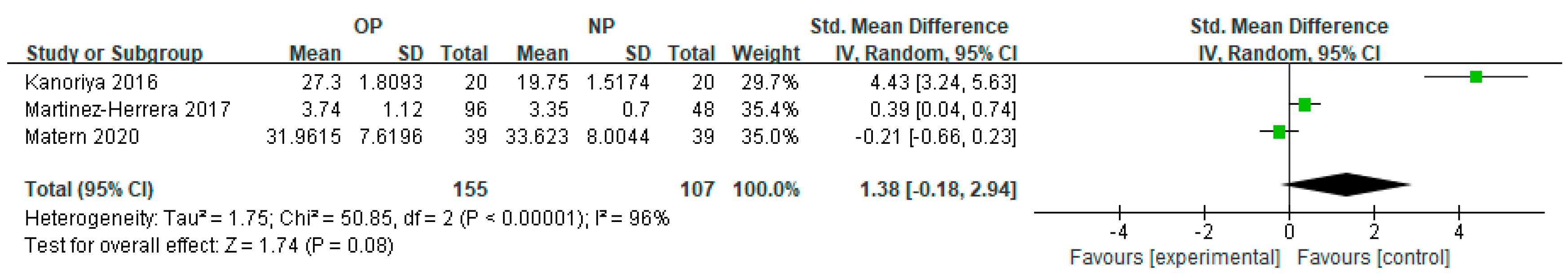
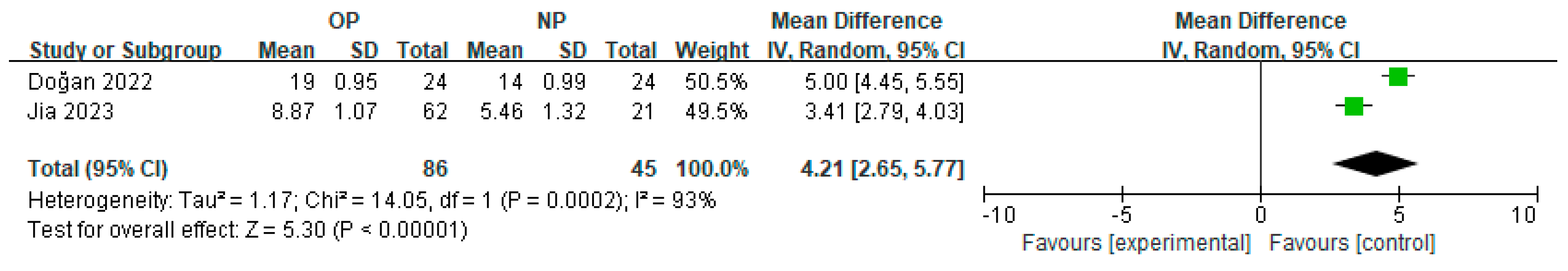
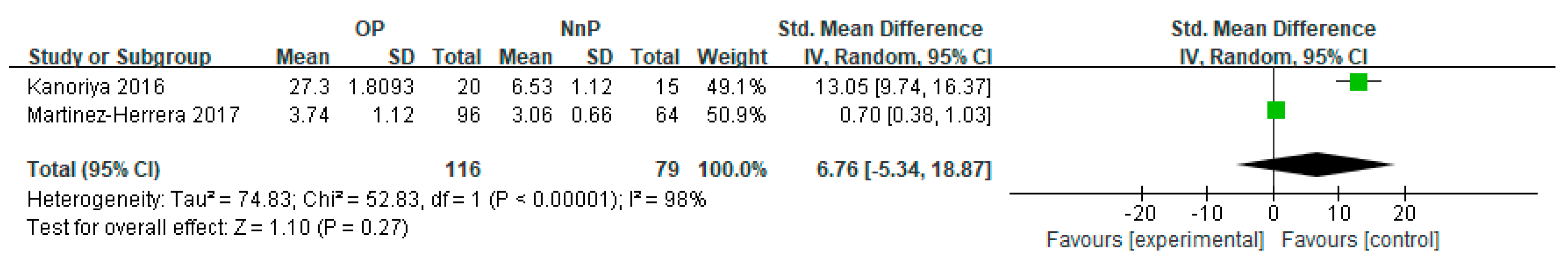
3.3. Subgroup Meta-Analysis
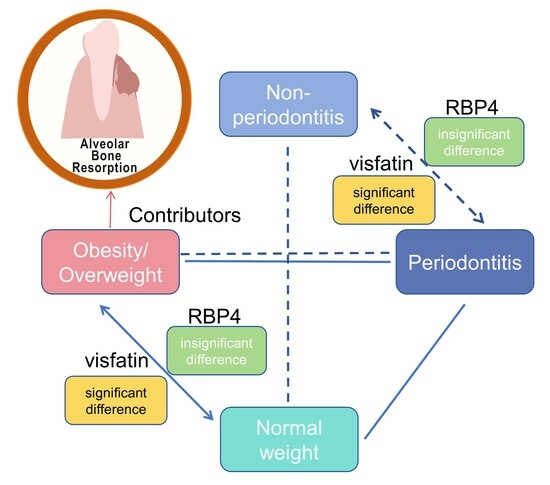
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niemiec, B.A. Periodontal disease. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2008, 23, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlstrom, B.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, N.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, G.C. Periodontal diagnoses and classification of periodontal diseases. Periodontology 2000 2004, 34, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Alasqah, M.; Alammar, L.M.; Alkhaibari, Y. Obesity and periodontal disease: A review. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamster, I.B.; Pagan, M. Periodontal disease and the metabolic syndrome. Int. Dent. J. 2017, 67, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Bissett, S.M. Periodontitis and diabetes. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 227, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zou, R.; Niu, L.; Dong, S. Reactive Oxygen Species Enlightened Therapeutic Strategy for Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases-Art of Destruction and Reconstruction. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, P.; Kamal, R.; Gupta, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Kaur, S. Reactive oxygen species in periodontitis. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesing, F.; Patiño, J.S.; da Silva, V.R.; Moreira, E.A. The interface between obesity and periodontitis with emphasis on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Obes. Rev. 2009, 10, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, A.; Leung, W.K. Obesity, Bone Loss, and Periodontitis: The Interlink. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Z. Visfatin regulates Pg LPS-induced proinflammatory/prodegradative effects in healthy and inflammatory periodontal cells partially via NF-κB pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919, quiz 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Mei, Y.; Zou, R.; Niu, L.; Dong, S. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on cytokines/adipocytokines levels among periodontitis patients with or without obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Herrera, M.; Abad-Jiménez, Z.; Silvestre, F.J.; López-Domènech, S.; Márquez-Arrico, C.F.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; Víctor, V.M.; Rocha, M. Effect of Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment on Oxidative Stress Markers in Leukocytes and Their Interaction with the Endothelium in Obese Subjects with Periodontitis: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matern, J.; Koch, R.; Petersmann, A.; Kocher, T.; Eickholz, P.; Lorenz, K.; Kim, T.S.; Meyle, J.; Kaner, D.; Schlagenhauf, U.; et al. Effect of periodontal therapy on adipokine biomarkers in overweight. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269, w264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. Jama 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudin, F.; Nie, J.Y.; Bartlett, J.C.; Grad, R.; Pluye, P.; Dawes, M. Combining classifiers for robust PICO element detection. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2010, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Herrera, M.; Silvestre, F.J.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; López-Domènech, S.; Bañuls, C.; Rocha, M. Levels of serum retinol-binding protein 4 before and after non-surgical periodontal treatment in lean and obese subjects: An interventional study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 45, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Rubio, M.A.; Barbany, M.; Moreno, B. SEEDO 2007 Consensus for the evaluation of overweight and obesity and the establishment of therapeutic intervention criteria. Med. Clin. 2007, 128, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, Y.S.; Bawadi, H.A.; Haroun, T.F.; Alomari, M.; Tayyem, R.F. The association between periodontal disease and obesity among adults in Jordan. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoriya, D.; Pradeep, A.R.; Mallika, A.; Singhal, S.; Garg, V. Correlation of crevicular fluid and serum levels of retinol-binding protein 4 and leptin in chronic periodontitis and obesity. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 21, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004, 363, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, H. Association between lipid metabolism and periodontitis in obese patients: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, 1–253.
- Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Qiu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Lai, R. Correlation of serum adipocytokine levels with glycolipid metabolism and inflammatory factors in obese patients with periodontal disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.P.; David Cheng, T.Y.; Tsai, S.P.; Chan, H.T.; Hsu, H.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Eriksen, M.P. Are Asians at greater mortality risks for being overweight than Caucasians? Redefining obesity for Asians. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, S. Visceral adiposity index is strongly associated with hyperuricemia independently of metabolic health and obesity phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemer Doğan, E.S.; Duran, N. Is periodontal inflamed surface area associated with serum and salivary levels of IL-1β, visfatin, and omentin-1 in overweight/obese patients? Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5351–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetiner, D.; Uraz, A.; Öztoprak, S.; Akça, G. The role of visfatin levels in gingival crevicular fluid as a potential biomarker in the relationship between obesity and periodontal disease. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2019, 27, e20180365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 60–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manresa, C.; Sanz-Miralles, E.C.; Twigg, J.; Bravo, M. Supportive periodontal therapy (SPT) for maintaining the dentition in adults treated for periodontitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, Cd009376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Cortez, Y.A.; Barragán-Bonilla, M.I.; Mendoza-Bello, J.M.; González-Calixto, C.; Flores-Alfaro, E.; Espinoza-Rojo, M. Interplay of retinol binding protein 4 with obesity and associated chronic alterations (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Bayani, M.; Tasorian, B.; Mahdian, S. The comparison of visfatin levels of gingival crevicular fluid in systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic periodontitis patients with healthy subjects. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3139–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, Z.A.; Keshani, F.; Sharbatdaran, M.; Banishahabadi, A.; Nejatifard, M.; Ghorbani, H. Visfatin expression in gingival tissues of chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis patients: An immunohistochemical analysis. Dent. Res. J. 2018, 15, 104–110. [Google Scholar]

| Study | Design; Setting | Criterion for Inclusion | Sample and Methods | Case Group | Control Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Average BMI (kg/m2) and Age (yrs) | Biomarkers | Sample Size | Average BMI (kg/m2) and Age (yrs) | Biomarkers | ||||
| Martinez-Herrera et al., 2017 [23] | Interventional study; Spain | Obesity: Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity [24]; Obesity: body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2; Lean/normal: BMI ≤ 25 kg/m2. Chronic periodontitis (CP): ≥4 teeth had ≥ 1 sites with probing depth (PD) ≥ 4 mm and clinical attachment loss (CAL) ≥ 3 mm [25] | Serum; nephelometry | Patients with obesity and periodontitis (OP) 96 male/female (m/f): 28/68 | OP Obesity BMI: (42.5 ± 2.1) Age: (42.7 ± 10.2) yrs. | Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4): (3.74 ± 1.12) mg/dL; tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α): (17.57 ± 9.91) pg/mL; interleukin (IL)-6: (3.72 ± 2.05) pg/mL | normal-weight patients and periodontal healthy (NnP) 64 m/f: 12/52; patients with obesity and periodontal healthy (OnP) 23 m/f: 3/20; normal-weight patients with periodontitis (NP) 48 m/f: 11/27 | NnP BMI: (21.8 ± 2.1) Age: (36.8 ± 11.7) yrs; OnP BMI: (39.6 ± 7.0) Age: (42.2 ± 11.1) yrs; NP BMI: (22.7 ± 1.9) Age: (39.4 ± 8.3) yrs; | NnP-RBP4: (3.06 ± 0.66) mg/dL; TNF-α: (7.72 ± 5.06) pg/mL; IL-6: (3.34 ± 2.78) pg/mL. OnP-RBP4: (3.21 ± 0.75) mg/dL; TNF-α: (12.41 ± 6.06) pg/mL; IL-6: (4.44 ± 2.71) pg/mL. NP-RBP4: (3.35 ± 0.70) mg/dL; TNF-α: (9.71 ± 4.36) pg/mL; IL-6: (4.06 ± 3.90) pg/mL. |
| Matern et al., 2020 [19] | Exploratory sub-analysis; prospective, randomized, double-blinded, parallel-group, multi-center ABPARO trial, Germany | Overweight: (Overweight: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2; Lean/normal: BMI ≤ 25 kg/m2). CP: ≥4 teeth had ≥ 1 sites with PD ≥ 4 mm and CAL ≥ 3 mm [25] | Plasma; ELISA | OP 40 m/f: 20/20 | OP Overweight BMI: 30.0 (28.9/32.3) Age: 54.0 (46.0/61.5) yrs. | RBP4: 31.5 (27.2/37.1) μg/mL; orosomucoid (ORM): 107.0 (89.0/123.0) mg/dL; high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP): 1.5 (0.9/3.5) mg/L; Chemerin: 113.6 (86.3/125.0) ng/mL | NP 40 m/f: 20/20 | NP BMI: 22.9 (21.8/23.3) Age: 51.0 (42.5/59.5) yrs | RBP4: 32.7 (28.8/39.2) μg/mL; ORM: 79.7 (71.9/92.6) mg/dL; hsCRP: 1.4 (0.7/2.4) mg/L; Chemerin: 87.9 (73.0/103.3) ng/mL |
| Kanoriya et al., 2016 [26] | Single-center, cross-sectional, case-controlled study; India | Obesity: World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [27] (Obesity: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, Lean/normal: BMI 18.5–22.9 kg/m2). CP: ≥4 teeth had ≥ 1 sites with PD ≥ 4 mm and CAL ≥ 3 mm, bone loss | GCF and serum; ELISA | OP 20 m/f: 9/11 | OP Obesity BMI: (29.09 ± 2.10) Age: (34.75 ± 6.01) yrs | Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) RBP4: 23.50 ± 1.63; serum RBP4: 27.30 ± 1.80 ng/mL; GCF leptin: 132.00 ± 10.01; serum leptin: 375.55 ± 11.86 pg/mL | NnP 15 m/f: 8/7; OnP 15 m/f: 8/7; NP 20 m/f: 10/10 | NnP BMI: (20.44 ± 1.29) Age: (33.1 ± 6.28) yrs; OnP BMI: (28.18 ± 1.70) Age: (33.1 ± 6.28) yrs; NP BMI: (20.45 ± 1.32) Age: (35.10 ± 6.24) yrs; | NnP-GCF RBP4: (3.53 ± 1.06); serum RBP4: (6.53 ± 1.12) ng/mL; IL-6: (3.34 ± 2.78) pg/mL; GCF leptin: (231.33 ± 9.02); serum leptin: (81.07 ± 11.02) pg/mL OnP-GCF RBP4: (9.00 ± 0.75); serum RBP4: (12.20 ± 1.37) ng/mL; IL-6: (3.34 ± 2.78) pg/mL; GCF leptin: (330.93 ± 8.31); serum leptin: (178.00 ± 12.64) pg/mL; NP-GCF RBP4: (16.75 ± 1.65); serum RBP4: (19.75 ± 1.51) ng/mL; GCF leptin: (33.00 ± 9.61); serum leptin: (272.70 ± 11.54) pg/mL |
| Jia et al., 2023 [28] | Cross-sectional study, case-controlled study; China | Obesity: WHO guidelines [29] (Obesity: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2; Overweight: 30 ≥ BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, Lean/normal: 25 > BMI > 18.5 kg/m2). CP: the newest 2017 international classification of periodontitis [3] | GCF and serum; ELISA | OP 62 m/f: 32/30 | OP Obesity BMI: (35.80 ± 3.90) Age: (42.50 ± 7.42) yrs; Overweight BMI: (28.53 ± 3.21) Age: (39.49 ± 5.39) yrs | Serum visfatin: 8.87 ± 1.07; serum resistin: 76.35 ± 10.56 ng/mL | NnP 15 m/f: 5/10; OnP 14 m/f: 7/7; NP 21 m/f: 13/8 | NnP BMI: (22.89 ± 0.55) Age: (40.40 ± 8.32) yrs; OnP BMI: (32.30 ± 1.39) Age: (40.5 ± 7.33) yrs; NP BMI: (20.35 ± 0.58) Age: (39.60 ± 7.64) yrs. | NnP-serum visfatin: 3.26 ± 1.28; serum resistin: 13.23 ± 7.62; OnP-serum visfatin: 5.86 ± 1.29; serum resistin: 37.42 ± 10.59; NP-serum visfatin: 5.46 ± 1.32 ng/mL; serum resistin: 24.75 ± 8.37 |
| Li et al., 2018 [30] | Cross-sectional, case-controlled study; China | Obesity: Western Pacific Regional Office of WHO (WPRO) for obesity in adult Asians [31,32] (Obesity: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2; Lean/normal: 25 > BMI > 18.5 kg/m2). CP: BOP, PD ≥ 3 mm, and CAL were presented in ≥ 1 site [4]. | Serum ELISA | OP 78 Classified as [1] Mild (33), [2] Moderate (42) and [3] severe (13). | OP Obesity BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | Visfatin: [1] 35.52 ± 4.19, [2] 40.84 ± 5.66, [3] 49.81 ± 5.57; leptin: [1] 12.89 ± 2.14, [2] 14.66 ± 2.37, [3] 17.39 ± 3.84; resistin: [1] 21.69 ± 3.43, [2] 29.64 ± 3.87, [3] 32.33 ± 4.06; adiponectin: [1] 7.64 ± 2.86, [2] 9.33 ± 3.24, [3] 9.89 ± 3.96 μg/L. | NnP 50; OnP 38 | NnP BMI (18.5, 25); OnP Obesity BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | NnP-visfatin: 18.78 ± 2.72; leptin: 6.90 ± 1.58, resistin: 11.42 ± 2.41, adiponectin: 23.67 ± 3.94; OnP-visfatin: 33.27 ± 4.21; leptin: 12.37 ± 2.06, resistin: 21.48 ± 3.70, adiponectin: 8.83 ± 3.25 μg/L. |
| Doğan et al., 2022 [33] | Cross-sectional, case-controlled studies; Turkey | Obesity: WHO guidelines [29] (Obesity/overweight: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, Lean/normal: BMI 18.5–25 kg/m2). CP: interdental CAL at ≥2 non-adjacent teeth or buccal or oral CAL ≥ 3 mm with PPD > 3 at ≥2 teeth [5] | Serum and saliva; ELISA | OP 24 | OP Obesity/overweight BMI: (29.87 ± 0.5) Age: (38.61 ± 1.24) yrs | Serum visfatin: 19 ± 0.95; Salivary visfatin: 23.5 ± 0.71 ng/mL | NnP 23; OnP 25; NP 24 | NP and NnP BMI: (22.09 ± 0.36) Age: (32.11 ± 1.11) yrs OnP Obesity/overweight BMI: (29.87 ± 0.5) Age: (38.61 ± 1.24) yrs | NnP-Serum visfatin: 11.5 ± 0.38; Salivary visfatin: 13.9 ± 0.67; OnP-Serum visfatin: 17.2 ± 0.88; Salivary visfatin: 19.8 ± 1.27; NP-Serum visfatin: 14 ± 0.99; Salivary visfatin: 19.7 ± 1.54 ng/mL. |
| ÇETİNER et al., 2018 [34] | Interventional study; Turkey | Obesity: WHO guidelines [29] (Obesity: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2; Lean/normal: BMI < 25kg/m2). CP: ≥30% of the sites with bone loss, and ≥2 nonadjacent teeth with ≥1 sites with PD ≥ 5 mm and CAL ≥ 5 mm in each quadrant, and positive bleeding on probing (BOP) | GCF; ELISA | OP 21 m/f: 0/21 | Obesity BMI: (34.76 ± 5.6) kg/m2 OP Age: (44.67 ± 10.87) yrs | Visfatin: 21.53 ± 39.55; TNF-α: 9.00 ± 6.10; IL-6: 3.61 ± 4.43 pg | NnP 10 m/f: 2/8; OnP 10 m/f: 1/9; NP 9 m/f: 7/2 | Lean/normal BMI: (23.53 ± 2.8) kg/m2; NnP-Age: (27.80 ± 3.12) yrs; OnP- Age: (46.50 ± 12.0) yrs; NP- Age: (44.22 ± 6.74) yrs | NnP-visfatin: 7.15 ± 3.12; TNF-α: 8.86 ± 0.87; IL-6: 0.00 ± 0; OnP -visfatin: 11.62 ± 10.71; TNF-α: 7.21 ± 9.77; IL-6: 1.32 ± 0.84; NP -visfatin: 10.65 ± 5.72; TNF-α: 10.54 ± 1.80; IL-6: 1.71 ± 2.01 pg. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, R.; Niu, L.; Dong, S. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Visfatin Levels in Patients with Periodontitis and Obesity/Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9838-9850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120614
Zhang Y, Jia R, Zhang Y, Zou R, Niu L, Dong S. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Visfatin Levels in Patients with Periodontitis and Obesity/Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(12):9838-9850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120614
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuwei, Ru Jia, Yifei Zhang, Rui Zou, Lin Niu, and Shaojie Dong. 2023. "Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Visfatin Levels in Patients with Periodontitis and Obesity/Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 12: 9838-9850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120614
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jia, R., Zhang, Y., Zou, R., Niu, L., & Dong, S. (2023). Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Visfatin Levels in Patients with Periodontitis and Obesity/Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(12), 9838-9850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120614