Functional Screenings Identify Regulatory Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DiR-seq Plasmid Library Construction for Breast Cancer Risk Variants
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Transfection
2.4. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
2.5. DiR-seq NGS Library Construction and Sequencing
2.6. DiR-seq Data Analyses
2.7. Quantitative PCR
2.8. Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements (FAIRE)
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.10. Genome Editing through CRISPR/Cas9
2.11. Genome Editing Efficiency Determination and Single-Cell Clone Screening
2.12. EGR1 Gene Knockdown and Overexpression
2.13. Cell Viability and Proliferation Assays
2.14. CRISPRi and CRISPRa Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
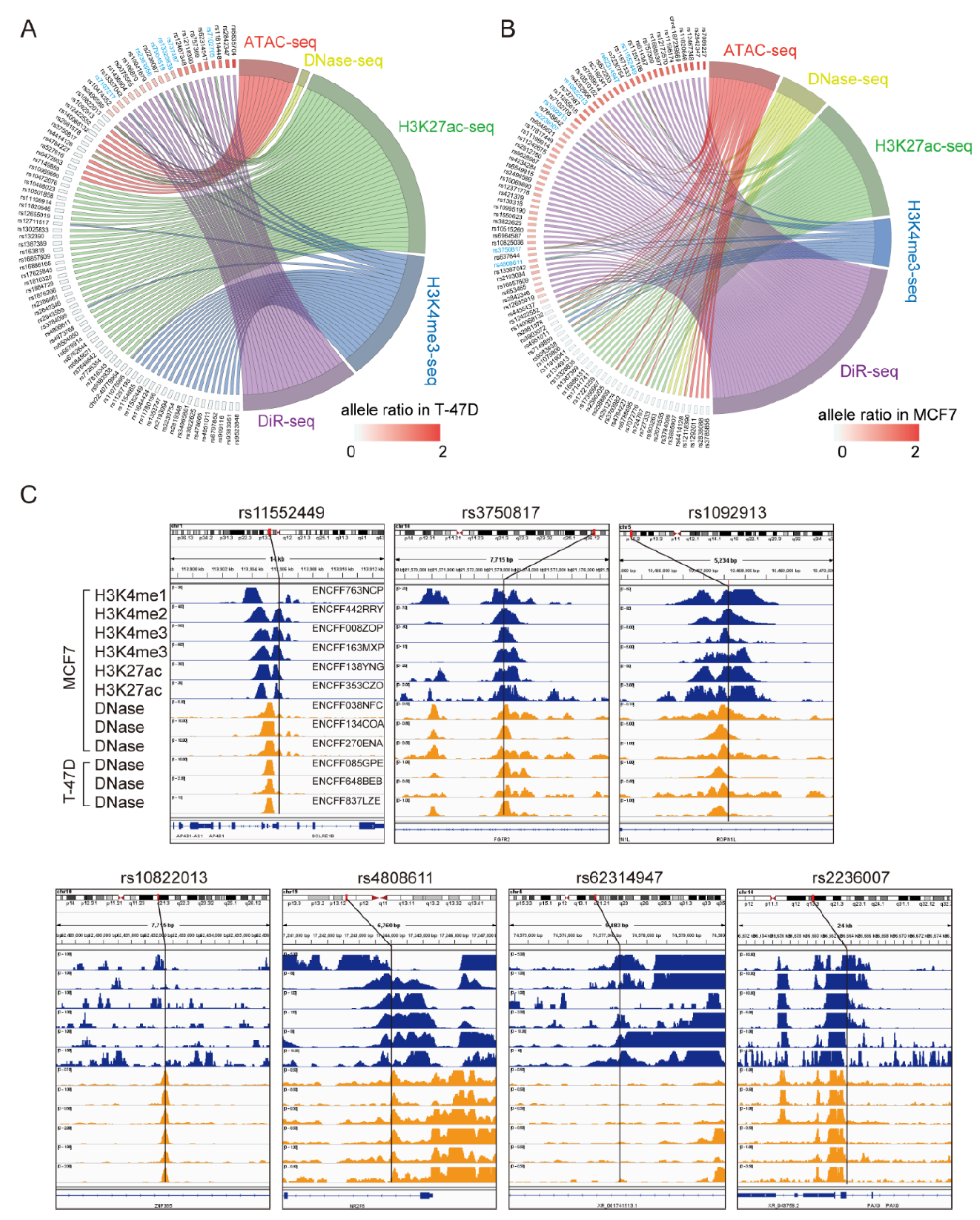
3.1. DiR-seq Identified Breast Cancer Risk-Associated Functional Variants
3.2. Multi-Omics Analysis Further Nominated Seven Most Plausible Variants
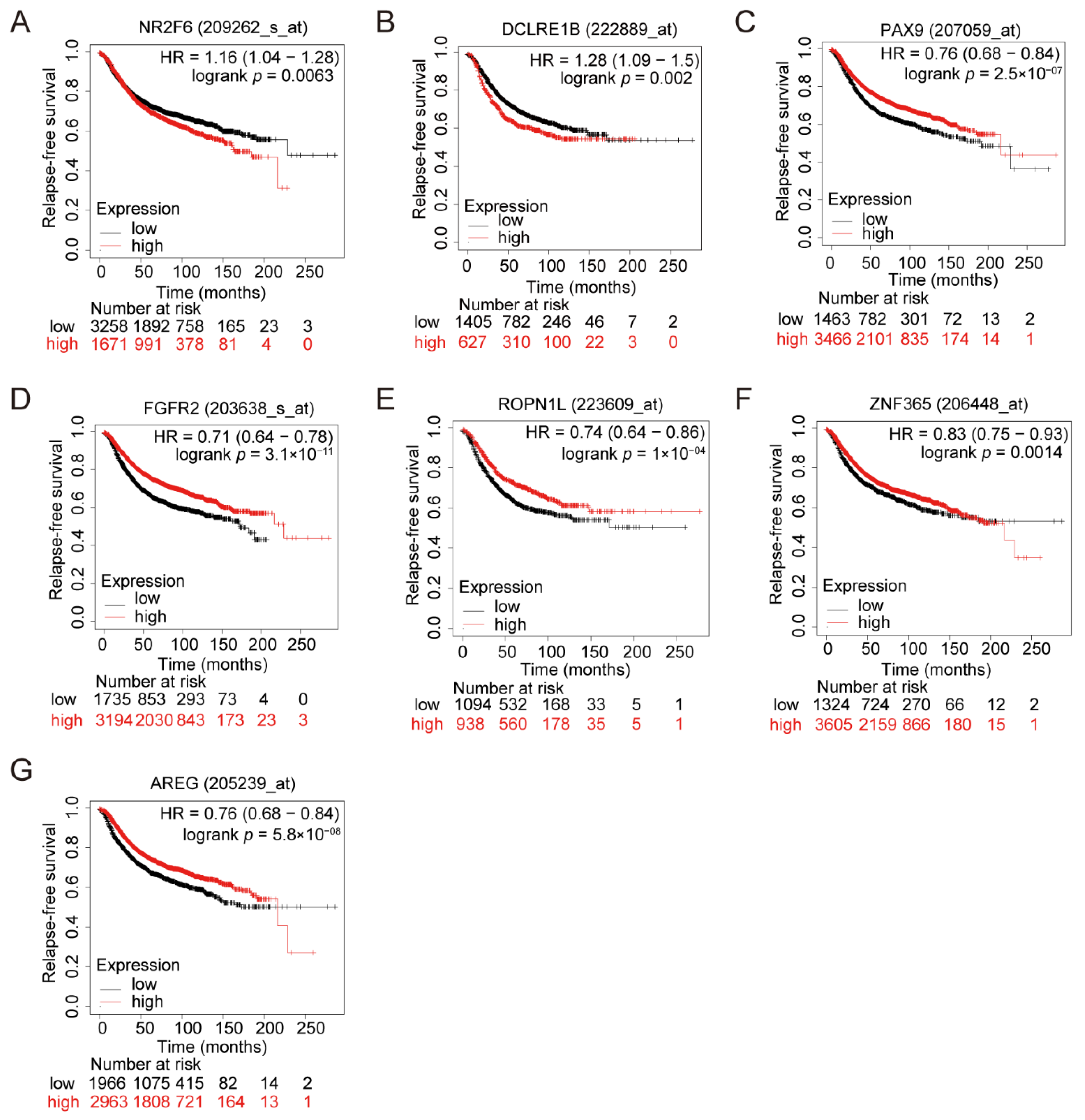
3.3. Clinical Impacts of the Related Genes of the Seven Variants
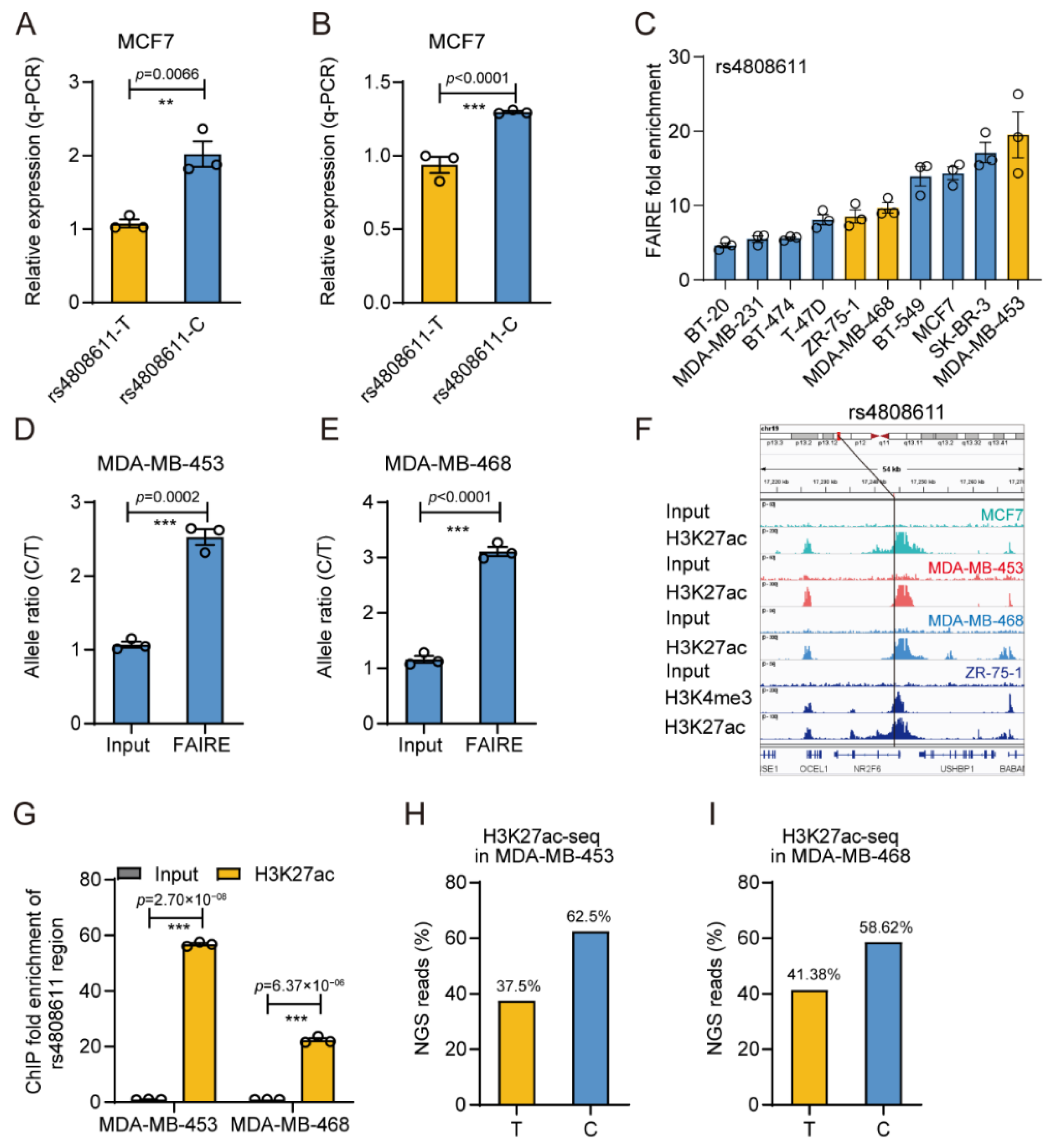
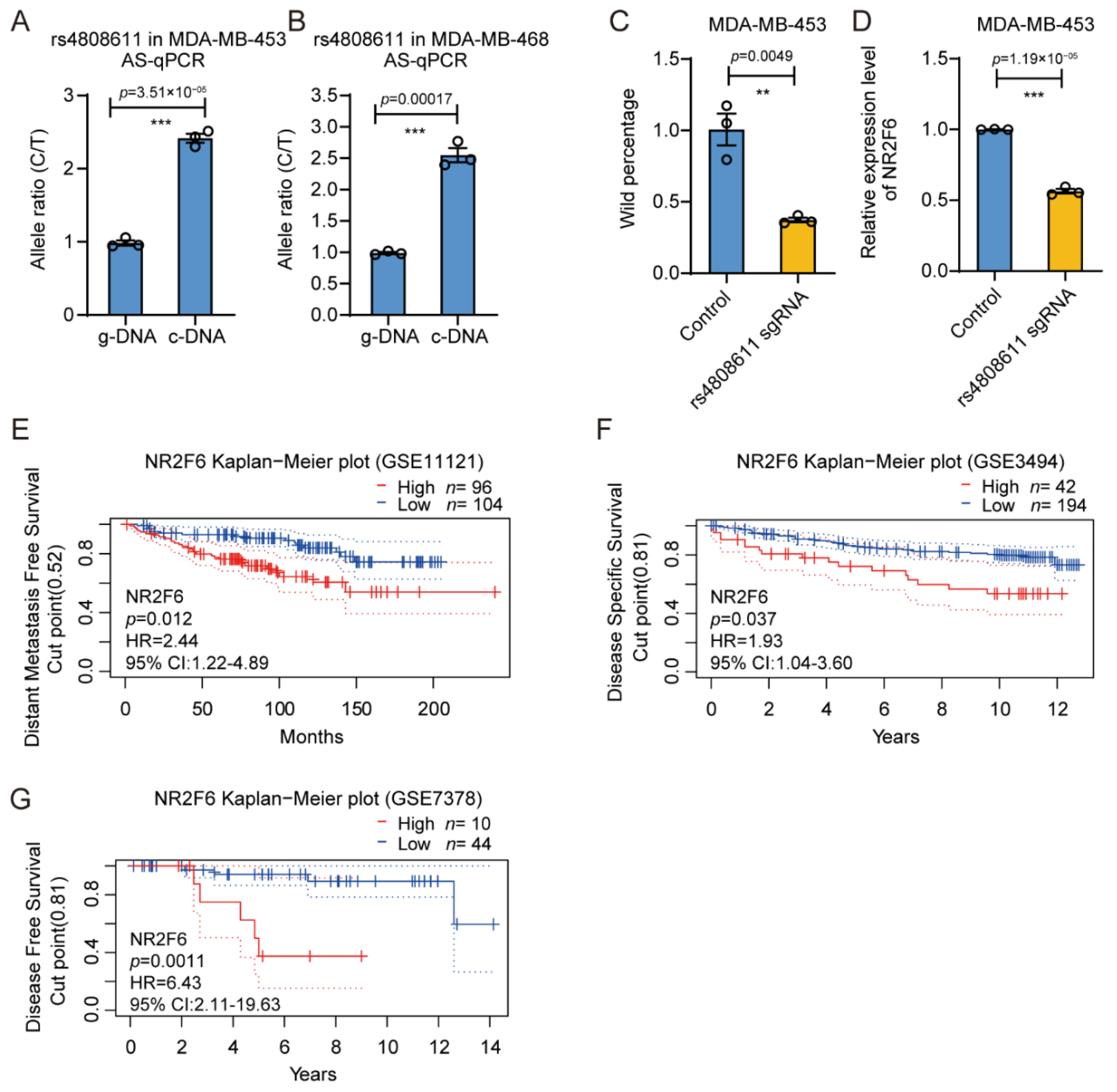
3.4. The Gene Regulatory Activity of rs4808611
3.5. rs4808611 Alters Gene Expression of NR2F6
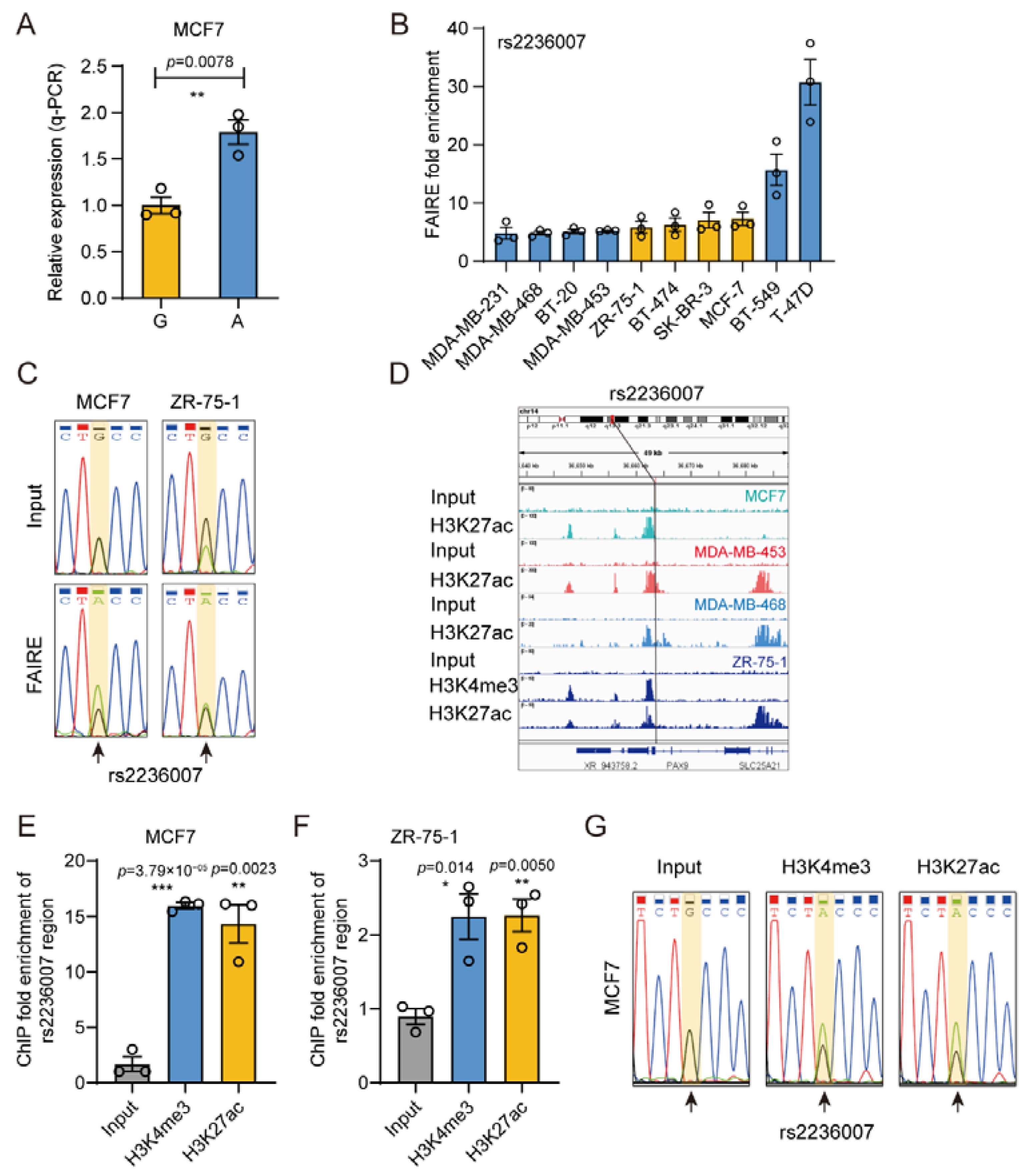
3.6. The Gene Regulatory Activity of rs2236007
3.7. rs2236007 Affects PAX9 Expression by Altering EGR1 Binding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ginsburg, O.; Bray, F.; Coleman, M.P.; Vanderpuye, V.; Eniu, A.; Kotha, S.R.; Sarker, M.; Huong, T.T.; Allemani, C.; Dvaladze, A.; et al. The global burden of women’s cancers: A grand challenge in global health. Lancet 2017, 389, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, A.; Kinnersley, B.; Houlston, R.S. Genome-wide association studies of cancer: Current insights and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.J.; Zeiss, C.; Chew, E.Y.; Tsai, J.Y.; Sackler, R.S.; Haynes, C.; Henning, A.K.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Mane, S.M.; Mayne, S.T.; et al. Complement factor H polymorphism in age-related macular degeneration. Science 2005, 308, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Ohnishi, Y.; Iida, A.; Sekine, A.; Yamada, R.; Tsunoda, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, H.; Hori, M.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.A.; Gamazon, E.R.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Aittomaki, K.; Andrulis, I.L.; Anton-Culver, H.; Arason, A.; Arndt, V.; Aronson, K.J.; Arun, B.K.; et al. Genome-wide association and transcriptome studies identify target genes and risk loci for breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Whitington, T.; Gao, P.; Lindberg, J.F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Vaisanen, M.R.; Szulkin, R.; Annala, M.; Yan, J.; et al. A prostate cancer susceptibility allele at 6q22 increases RFX6 expression by modulating HOXB13 chromatin binding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Zhang, T.; Vu, A.; Ablain, J.; Makowski, M.M.; Colli, L.M.; Xu, M.; Hennessey, R.C.; Yin, J.; Rothschild, H.; et al. Massively parallel reporter assays of melanoma risk variants identify MX2 as a gene promoting melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowper-Sal, R.; Zhang, X.; Wright, J.B.; Bailey, S.D.; Cole, M.D.; Eeckhoute, J.; Moore, J.H.; Lupien, M. Breast cancer risk-associated SNPs modulate the affinity of chromatin for FOXA1 and alter gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zheng, R.; Ma, G.; Chu, H.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Xin, J.; Tong, N.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; et al. Remote modulation of lncRNA GCLET by risk variant at 16p13 underlying genetic susceptibility to gastric cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Xia, J.H.; Sipeky, C.; Dong, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cruz, S.P.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, J.; et al. Biology and Clinical Implications of the 19q13 Aggressive Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Locus. Cell 2018, 174, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoussaini, M.; Edwards, S.L.; Michailidou, K.; Nord, S.; Cowper-Sal Lari, R.; Desai, K.; Kar, S.; Hillman, K.M.; Kaufmann, S.; Glubb, D.M.; et al. Evidence that breast cancer risk at the 2q35 locus is mediated through IGFBP5 regulation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 4, 4999, reprinted in Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.Q.; Ter Huurne, M.; Nguyen, L.N.; Peng, T.; Wang, S.Y.; Studd, J.B.; Joshi, O.; Ongen, H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Yan, J.; et al. The non-coding variant rs1800734 enhances DCLK3 expression through long-range interaction and promotes colorectal cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, M.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Rhie, S.K.; Farnham, P.J.; Shi, J.; et al. The prostate cancer risk variant rs55958994 regulates multiple gene expression through extreme long-range chromatin interaction to control tumor progression. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xia, J.H.; Zhu, J.; Gao, P.; Tian, Y.J.; Du, M.; Guo, Y.C.; Suleman, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kohli, M.; et al. High-throughput screening of prostate cancer risk loci by single nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Huang, Q.; Wei, G.H. The Role of HOX Transcription Factors in Cancer Predisposition and Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Ren, N.; Huang, Q. rs10514231 Leads to Breast Cancer Predisposition by Altering ATP6AP1L Gene Expression. Cancers 2021, 13, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Liu, Q.; Yan, L.; Huang, Q. Parallel Reporter Assays Identify Altered Regulatory Role of rs684232 in Leading to Prostate Cancer Predisposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Seo, J.H.; Stranger, B.; McKenna, A.; Pe’er, I.; Laframboise, T.; Brown, M.; Tyekucheva, S.; Freedman, M.L. Integrative eQTL-based analyses reveal the biology of breast cancer risk loci. Cell 2013, 152, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. Interpreting noncoding genetic variation in complex traits and human disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, E.; Fu, Y.; Chakravarty, D.; Demichelis, F.; Rubin, M.A.; Gerstein, M. Role of non-coding sequence variants in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farashi, S.; Kryza, T.; Clements, J.; Batra, J. Post-GWAS in prostate cancer: From genetic association to biological contribution. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, D.Y.; Spisak, S.; Seo, J.H.; Bell, C.; O’Connor, E.; Korthauer, K.; Ribli, D.; Csabai, I.; Solymosi, N.; Szallasi, Z.; et al. A Somatically Acquired Enhancer of the Androgen Receptor Is a Noncoding Driver in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.Y.; Han, J.X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.; Shen, C.; Guo, F.; Tang, J.; Yan, T.; Tian, X.; Zhu, X.; et al. A 16q22.1 variant confers susceptibility to colorectal cancer as a distal regulator of ZFP90. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldridge, D.A.; Wood, A.C.; Weichert-Leahey, N.; Crimmins, I.; Sussman, R.; Winter, C.; McDaniel, L.D.; Diamond, M.; Hart, L.S.; Zhu, S.; et al. Genetic predisposition to neuroblastoma mediated by a LMO1 super-enhancer polymorphism. Nature 2015, 528, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, N.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q. A dinucleotide tag-based parallel reporter gene assay method. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igolkina, A.A.; Zinkevich, A.; Karandasheva, K.O.; Popov, A.A.; Selifanova, M.V.; Nikolaeva, D.; Tkachev, V.; Penzar, D.; Nikitin, D.M.; Buzdin, A. H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 Histone Tags Suggest Distinct Regulatory Evolution of Open and Condensed Chromatin Landmarks. Cells 2019, 8, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitington, T.; Gao, P.; Song, W.; Ross-Adams, H.; Lamb, A.D.; Yang, Y.; Svezia, I.; Klevebring, D.; Mills, I.G.; Karlsson, R.; et al. Gene regulatory mechanisms underpinning prostate cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepsch, V.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; Do-Dinh, P.; Jakic, B.; Offermann, A.; Efremova, M.; Sopper, S.; Rieder, D.; Krogsdam, A.; Gamerith, G.; et al. Nuclear receptor NR2F6 inhibition potentiates responses to PD-L1/PD-1 cancer immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakic, B.; Olson, W.J.; Siegmund, K.; Klepsch, V.; Kimpel, J.; Labi, V.; Zehn, D.; Baier, G.; Hermann-Kleiter, N. Loss of the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 enhances CD8(+) T-cell memory via IFN-gamma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichim, C.V.; Atkins, H.L.; Iscove, N.N.; Wells, R.A. Identification of a role for the nuclear receptor EAR-2 in the maintenance of clonogenic status within the leukemia cell hierarchy. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Jiao, S.; Sun, H.; Xue, J.; Zhao, W.T.; Fan, L.; Wu, G.H.; Fang, J. The orphan nuclear receptor EAR2 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and it regulates survivability of colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 309, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, M.; Tang, X.; Xie, D.; Chen, J.; Ke, R. CENPL, ISG20L2, LSM4, MRPL3 are four novel hub genes and may serve as diagnostic and prognostic markers in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, K.L.; Tyrer, J.; Song, H.; Ramus, S.J.; Notaridou, M.; Jones, C.; Sher, T.; Gentry-Maharaj, A.; Wozniak, E.; Tsai, Y.Y.; et al. Common variants at 19p13 are associated with susceptibility to ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Adamson, E.; Mercola, D. Suppression of growth and transformation and induction of apoptosis by EGR-1. Cancer Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gashler, A.L.; Swaminathan, S.; Sukhatme, V.P. A Novel Repression Module, an Extensive Activation Domain, and a Bipartite Nuclear-Localization Signal Defined in the Immediate-Early Transcription Factor Egr-1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4556–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Shaw, A.L.; Madsen, B.; Jensen, K.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Freemont, P.S. Human PLU-1 has transcriptional repression properties and interacts with the developmental transcription factors BF-1 and PAX9. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20507–20513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, J.K.; Richter, T.; Kremmer, E.; Adamski, J.; Hofler, H.; Balling, R.; Peters, H. Progressive loss of PAX9 expression correlates with increasing malignancy of dysplastic and cancerous epithelium of the human oesophagus. J. Pathol. 2002, 197, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachal, L.; Dunning, A.M. From candidate gene studies to GWAS and post-GWAS analyses in breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 30, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masella, A.P.; Bartram, A.K.; Truszkowski, J.M.; Brown, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D. PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for illumina sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.; Anders, S.; Lawrence, M.; Aboyoun, P.; Pages, H.; Gentleman, R. ShortRead: A bioconductor package for input, quality assessment and exploration of high-throughput sequence data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2607–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.M.; Giresi, P.G.; Davis, I.J.; Lieb, J.D. Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ren, N.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q. A qPCR method for genome editing efficiency determination and single-cell clone screening in human cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, L.A.; Larson, M.H.; Morsut, L.; Liu, Z.R.; Brar, G.A.; Torres, S.E.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Brandman, O.; Whitehead, E.H.; Doudna, J.A.; et al. CRISPR-Mediated Modular RNA-Guided Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes. Cell 2013, 154, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.P.; Tong, F.; et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoon, M.J.; Imoto, S.; Nolan, J.; Miyano, S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1453–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, A.J. Java Treeview--extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3246–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, E.P.; Moore, J.E.; Purcaro, M.J.; Pratt, H.E.; Epstein, C.B.; Shoresh, N.; Adrian, J.; Kawli, T.; Davis, C.A.; Dobin, A.; et al. Expanded encyclopaedias of DNA elements in the human and mouse genomes. Nature 2020, 583, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Wenger, A.M.; Zehir, A.; Mesirov, J.P. Variant Review with the Integrative Genomics Viewer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e31–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lichtenberg, T.; Hoadley, K.A.; Poisson, L.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Cherniack, A.D.; Kovatich, A.J.; Benz, C.C.; Levine, D.A.; Lee, A.V.; et al. An Integrated TCGA Pan-Cancer Clinical Data Resource to Drive High-Quality Survival Outcome Analytics. Cell 2018, 173, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Munkacsy, G.; Gyorffy, B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Győrffy, B. Survival analysis across the entire transcriptome identifies biomarkers with the highest prognostic power in breast cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levo, M.; Segal, E. In pursuit of design principles of regulatory sequences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, Z.C. Distance and helical phase dependence of synergistic transcription activation in cis-regulatory module. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, K.; Beesley, J.; Lindstrom, S.; Canisius, S.; Dennis, J.; Lush, M.J.; Maranian, M.J.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Shah, M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of more than 120,000 individuals identifies 15 new susceptibility loci for breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, K.; Hall, P.; Gonzalez-Neira, A.; Ghoussaini, M.; Dennis, J.; Milne, R.L.; Schmidt, M.K.; Chang-Claude, J.; Bojesen, S.E.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Large-scale genotyping identifies 41 new loci associated with breast cancer risk. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, K.; Lindstrom, S.; Dennis, J.; Beesley, J.; Hui, S.; Kar, S.; Lemacon, A.; Soucy, P.; Glubb, D.; Rostamianfar, A.; et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature 2017, 551, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Y.; Lin, W.Q.; Bao, J.D.; Cai, Q.Y.; Pan, X.; Bai, M.Q.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, J.J.; Sun, Y.Q.; Han, M.R.; et al. A Comprehensive cis-eQTL Analysis Revealed Target Genes in Breast Cancer Susceptibility Loci Identified in Genome-wide Association Studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkin, S.R.; Graff, R.E.; Kachuri, L.; Thai, K.K.; Alexeeff, S.E.; Blatchins, M.A.; Cavazos, T.B.; Corley, D.A.; Emami, N.C.; Hoffman, J.D.; et al. Pan-cancer study detects genetic risk variants and shared genetic basis in two large cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, D.; Barrdahl, M.; Gaudet, M.M.; Black, A.; Chanock, S.J.; Diver, W.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Haiman, C.; Hankinson, S.; Hazra, A.; et al. Genetic risk variants associated with in situ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, D.; Kaaks, R.; Le Marchand, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Travis, R.C.; Berg, C.D.; Buring, J.E.; Chanock, S.J.; Diver, W.R.; Dostal, L.; et al. Interactions between genetic variants and breast cancer risk factors in the breast and prostate cancer cohort consortium. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Lu, M.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Genetic variants of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) are associated with breast cancer risk in Chinese women of the Han nationality. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Wu, D.; Wang, W.; He, X.; Wang, M. Variants of FGFR2 and their associations with breast cancer risk: A HUGE systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 155, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgazzar, S.; Zembutsu, H.; Takahashi, A.; Kubo, M.; Aki, F.; Hirata, K.; Takatsuka, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Ohsumi, S.; Yamakawa, T.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies a genetic variant in the SIAH2 locus associated with hormonal receptor-positive breast cancer in Japanese. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ballinger, D.G.; Dai, J.Y.; Peters, U.; Hinds, D.A.; Cox, D.R.; Beilharz, E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Rossouw, J.E.; McTiernan, A.; et al. Genetic variants in the MRPS30 region and postmenopausal breast cancer risk. Genome Med. 2011, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Hinds, D.A.; Peters, U.; Cox, D.R.; Beilharz, E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Rossouw, J.E.; Caan, B.; Ballinger, D.G. Variation in the FGFR2 gene and the effect of a low-fat dietary pattern on invasive breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Hinds, D.A.; Peters, U.; Pettinger, M.; Cox, D.R.; Beilharz, E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Rossouw, J.E.; Caan, B.; et al. Variation in the FGFR2 gene and the effects of postmenopausal hormone therapy on invasive breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 3079–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornes, O.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Khan, A.; van der Lee, R.; Zhang, X.; Richmond, P.A.; Modi, B.P.; Correard, S.; Gheorghe, M.; Baranasic, D.; et al. JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D87–D92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okegawa, T.; Ushio, K.; Imai, M.; Morimoto, M.; Hara, T. Orphan nuclear receptor HNF4G promotes bladder cancer growth and invasion through the regulation of the hyaluronan synthase 2 gene. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, J.; Jia, S.; Wu, M.Y.; An, J.H.; Zheng, Q.D.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D.D. miR675 upregulates long noncoding RNA H19 through activating EGR1 in human liver cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31958–31984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Yun, J.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, C.W.; Kwon, B.M.; Hong, S.H. EGR1-dependent PTEN upregulation by 2-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde attenuates cell invasion and EMT in colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yu, J.J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.Z.; Liu, L.Z.; Jiang, B.H. Downregulation of ATG14 by EGR1-MIR152 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting cyto-protective autophagy. Autophagy 2015, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Dass, C.R.; Sun, L.Q.; Khachigian, L.M. Inhibition of human breast carcinoma proliferation, migration, chemoinvasion and solid tumour growth by DNAzymes targeting the zinc finger transcription factor EGR-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 3065–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, N.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, P.; Ren, Y.; Huang, Q. Functional Screenings Identify Regulatory Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 1756-1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030124
Ren N, Li Y, Xiong Y, Li P, Ren Y, Huang Q. Functional Screenings Identify Regulatory Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2021; 43(3):1756-1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030124
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Naixia, Yingying Li, Yulong Xiong, Panfeng Li, Yutian Ren, and Qilai Huang. 2021. "Functional Screenings Identify Regulatory Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 43, no. 3: 1756-1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030124
APA StyleRen, N., Li, Y., Xiong, Y., Li, P., Ren, Y., & Huang, Q. (2021). Functional Screenings Identify Regulatory Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 43(3), 1756-1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030124





