Pain Management in Ambulatory Surgery—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Paracetamol
3. NSAIDS and Coxibs
4. Combination NSAID and Paracetamol
5. Local Anaesthesia
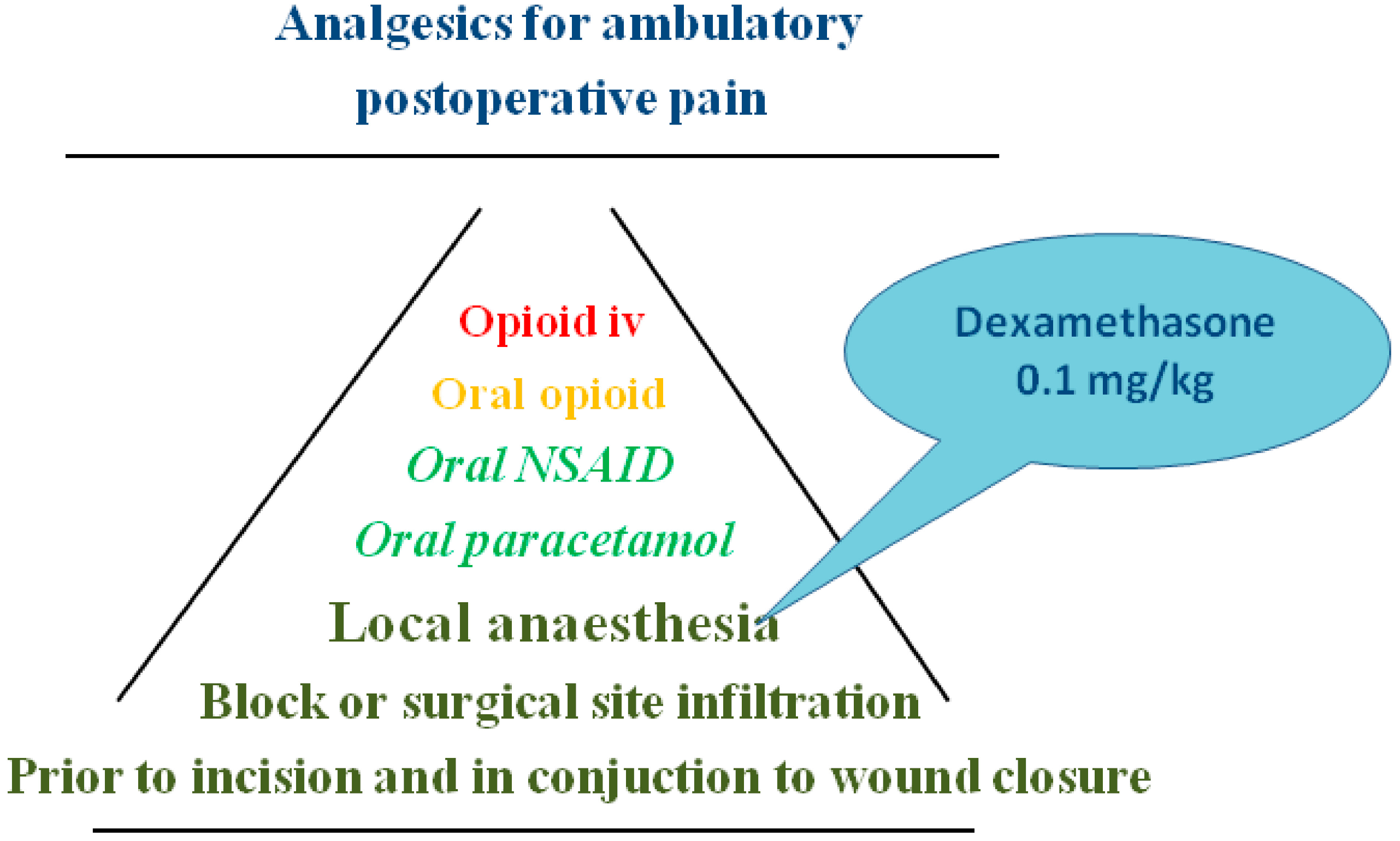
6. Adjuncts Facilitating the Analgesic Effects
6.1. Dexamethasone
6.2. Alfa-2-agonists
Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine
6.3. Ketamine
6.4. Gabapentin and Pregabalin
6.5. More Experimental
7. Discussion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kehlet, H.; Dahl, J.B. The value of “multimodal” or “balanced analgesia” in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 77, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, H.; Tenhunen, A.; Korttila, K. Balanced analgesia improves recovery and outcome after outpatient tubal ligation. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1996, 40, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaloliakou, C.; Chung, F.; Sharma, S. Preoperative multimodal analgesia facilitates recovery after ambulatory laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bandolier. Available online: http://www.medicine.ox.ac.uk/bandolier/booth/painpag/Acutrev/Analgesics/Leagtab.html (accessed on 9 July 2014).
- Graham, G.G.; Davies, M.J.; Day, R.O.; Mohamudally, A.; Scott, K.F. The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: Therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity and recent pharmacological findings. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blieden, M.; Paramore, L.C.; Shah, D.; Ben-Joseph, R. A perspective on the epidemiology of acetaminophen exposure and toxicity in the United States. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 7, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm381644.htm (accessed on 9 July 2014).
- Qi, D.S.; May, L.G.; Zimmerman, B.; Peng, P.; Atillasoy, E.; Brown, J.D.; Cooper, S.A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of acetaminophen 1000 mg versus acetaminophen 650 mg for the treatment of postsurgical dental pain. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Collaku, A.; Brown, J.; Buchanan, W.L.; Reed, K.; Cooper, S.A.; Otto, J. Efficacy and speed of onset of pain relief of fast-dissolving paracetamol on postsurgical dental pain: two randomized, single-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies. Clin Ther. 2013, 35, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmér Pettersson, P.; Owall, A.; Jakobsson, J. Early bioavailability of paracetamol after oral or intravenous administration. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2004, 48, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.N.; Barnett, S.G.; Pearson, J. Postoperative plasma paracetamol levels following oral or intravenous paracetamol administration: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2012, 40, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- McNicol, E.D.; Tzortzopoulou, A.; Cepeda, M.S.; Francia, M.B.; Farhat, T.; Schumann, R. Single-dose intravenous paracetamol or propacetamol for prevention or treatment of postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfel, C.C.; Souza, K.; Portillo, J.; Dalal, P.; Bergese, S.D. Patient Satisfaction with Intravenous Acetaminophen: A Pooled Analysis of Five Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Studies in the Acute Postoperative Setting. J. Healthc Qual. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, E.; Worthington, H.V.; van Wijk, A.; Yates, J.M.; Coulthard, P.; Afzal, Z. Ibuprofen and/or paracetamol (acetaminophen) for pain relief after surgical removal of lower wisdom teeth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Lamdin, R. Oral cyclo-oxygenase 2 inhibitors versus other oral analgesics for acute soft tissue injury: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2010, 30, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Takahashi, T.; Iwata, H.; Morikawa, A.; Imori, S.; Waki, S.; Tamura, T.; Yamazaki, F.; Eguchi, S.; Kumagai, N.; Yokoyama, M. Effects of ketoprofen for prevention of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats. J. Anesth. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.X.; Ma, L.; Zheng, L.W.; Kruse-Gujer, A.; Stübinger, S.; Lang, N.P.; Zwahlen, R.A. Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on osseointegration of dental implants in rabbit calvaria. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Derry, S.; Moore, R.A. Single dose oral etoricoxib for acute postoperative pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Haque, S.E.; Pillai, K.K. Assessment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickerts, L.; Warrén Stomberg, M.; Brattwall, M.; Jakobsson, J. Coxibs: Is there a benefit when compared to traditional non-selective NSAIDs in postoperative pain management? Minerva Anestesiol. 2011, 77, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Derry, C.J.; Derry, S.; Moore, R.A. Single dose oral ibuprofen plus paracetamol (acetaminophen) for acute postoperative pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, B.D.; Iohom, G. Regional anesthesia techniques for ambulatory orthopedic surgery. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 21, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.G.; Ross, S.M.; Williams, B.A. Regional anesthesia and ambulatory surgery. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 26, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.S.; Abrishami, A.; Lermitte, J.; Chung, F. Systematic review of spinal anaesthesia using bupivacaine for ambulatory knee arthroscopy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.J.; Alakkad, H.; Adhikary, S.D.; Singh, M. Infraclavicular brachial plexus block for regional anaesthesia of the lower arm. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Strodtbeck, W.M.; Richman, J.M.; Wu, C.L. A comparison of regional versus general anesthesia for ambulatory anesthesia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 101, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Tahiri, Y.; Tran de, Q.H.; Bouteaud, J.; Xu, L.; Lalonde, D.; Luc, M.; Nikolis, A. General anaesthesia versus thoracic paravertebral block for breast surgery: A meta-analysis. J. Plast Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2011, 64, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavaneswaran, P.; Rudkin, G.E.; Cooter, R.D.; Moyes, D.G.; Perera, C.L.; Maddern, G.J. Brief reports: Paravertebral block for anesthesia: A systematic review. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, A.; Reichl, S.U.; Kranke, P.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M.; Zahn, P.K. Efficacy and safety of paravertebral blocks in breast surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 105, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.S., Jr.; Castro-Alves, L.J.; Nader, A.; Kendall, M.C.; McCarthy, R.J. Transversus abdominis plane block to ameliorate postoperative pain outcomes after laparoscopic surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 118, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Rodseth, R.; McCartney, C.J. Effects of dexamethasone as a local anaesthetic adjuvant for brachial plexus block: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, F.W.; Brull, R. Facilitatory effects of perineural dexmedetomidine on neuraxial and peripheral nerve block: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, A.; Meyer-Frießem, C.H.; Zahn, P.K.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M. Ultrasound compared with nerve stimulation guidance for peripheral nerve catheter placement: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, G.C.; Megalla, S.A.; Habib, A.S. Impact of intravenous lidocaine infusion on postoperative analgesia and recovery from surgery: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Drugs 2010, 70, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, J. Preoperative single-dose intravenous dexamethasone during ambulatory surgery: Update around the benefit versus risk. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 23, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.S., Jr.; Almeida, M.D.; Benzon, H.T.; McCarthy, R.J. Perioperative single dose systemic dexamethasone for postoperative pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, N.H.; Jones, C.A.; Gan, T.J.; Allen, T.K.; Habib, A.S. Impact of perioperative dexamethasone on postoperative analgesia and side-effects: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Qian, X.; An, J.; Wen, H.; Cope, D.K.; Williams, J.P. Higher Dose Dexamethasone Increases Early Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, S.; Brasher, C.; Stany, I.; Golmard, J.; Skhiri, A.; Bruneau, B.; Nivoche, Y.; Constant, I.; Murat, I. Premedication with clonidine is superior to benzodiazepines. A meta analysis of published studies. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2010, 54, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- harti, N.; Dontukurthy, S.; Bala, I.; Singh, G. Postoperative analgesic effect of intravenous (i.v.) clonidine compared with clonidine administration in wound infiltration for open cholecystectomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Y.; Cao, J.P.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, H. Dexmedetomidine versus morphine or fentanyl in the management of children after tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2013, 122, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Na, H.S.; Song, I.A.; Park, H.S.; Hwang, J.W.; Do, S.H.; Kim, C.S. Dexmedetomidine is effective for monitored anesthesia care in outpatients undergoing cataract surgery. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2011, 61, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, Z.; Nguyen, H.; Young, N.; Shi, P.; Fleming, N.; Liu, H. Perioperative dexmedetomidine improves outcomes of cardiac surgery. Circulation 2013, 127, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, T.H.; Chae, M.S.; Cho, M.L.; Her, Y.M.; Lee, J. Effects of dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2013, 57, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaudszun, G.; Lysakowski, C.; Elia, N.; Tramèr, M.R. Effect of perioperative systemic α2 agonists on postoperative morphine consumption and pain intensity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfic, Q.A. A review of the use of ketamine in pain management. J. Opioid Manag. 2013, 9, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, N.; Tramèr, M.R. Ketamine and postoperative pain—A quantitative systematic review of randomised trials. Pain 2005, 113, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.W.; Li, C.; Farcas, E.; Haley, A.; Wong, W.; Bender, J.; Chung, F. Use of low-dose pregabalin in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 105, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, F.; Yağar, S.; Özgök, A.; Koç, M.; Güllapoğlu, H. A randomized, placebo-controlled study of pregabalin for postoperative pain intensity after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2012, 24, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekawi, M.S.; El Wakeel, L.M.; Al Taher, W.M.; Abdel Mageed, W.M. Clinical Study Evaluating Pregabalin Efficacy and Tolerability for Pain Management in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Clin. J. Pain. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakatsianou, C.; Theodorou, E.; Georgopoulou, S.; Stamatiou, G.; Tzovaras, G. Effect of pre-emptive pregabalin on pain intensity and postoperative morphine consumption after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ran, B.; Li, M.; Shi, Z. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine 2013, 38, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, Z.; Meltem Mortimer, N.; Sekerci, S. Single dose of preoperative analgesia with gabapentin (600 mg) is safe and effective in monitored anesthesia care for nasal surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 267, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, H.; Sizlan, A.; Yanarateş, O.; Senol, M.G.; Inangil, G.; Sücüllü, I.; Ozkan, S.; Dağli, G. The effects of gabapentin on acute and chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauri, M.; Faria, S.; Gatti, A.; Celidonio, L.; Carpenedo, R.; Sabato, A.F. Gabapentin and pregabalin for the acute post-operative pain management. A systematic-narrative review of the recent clinical evidences. Curr. Drug Targets 2009, 10, 716–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.S.; Bialek, J.; Fitzgerald, P.; Kim, J.Y.; McCarthy, R.J. Systemic magnesium to improve quality of post-surgical recovery in outpatient segmental mastectomy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Karanlik, H.; Akturk, R.; Camlica, H.; Asoglu, O. The effect of glyceryl trinitrate ointment on posthemorrhoidectomy pain and wound healing: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2009, 52, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Z.; Chung, F.; Hanna, D.B.; Raymundo, A.L.; Cheung, R.Y.; Chen, C. Dose-response relationship between opioid use and adverse effects after ambulatory surgery. J. Pain Symptom Manage 2004, 28, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, R.; Kroman, N.; Callesen, T.; Kehlet, H. Multimodal prevention of pain, nausea and vomiting after breast cancer surgery. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010, 76, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hanlon, D.M.; Thambipillai, T.; Colbert, S.T.; Keane, P.W.; Given, H.F. Timing of pre-emptive tenoxicam is important for postoperative analgesia. Can. J. Anaesth. 2001, 48, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.P. Postoperative pain management. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 1994, 32, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluri, S.; Wrench, I.J. Enhanced recovery from obstetric surgery: A UK survey of practice. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2014, 23, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Steinbrüchel, D.A.; Wanscher, M.J.; Andersen, L.W.; Navne, A.; Lilleoer, N.B.; Olsen, P.S. Multimodal analgesia versus traditional opiate based analgesia after cardiac surgery, a randomized controlled trial. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurusamy, K.S.; Vaughan, J.; Toon, C.D.; Davidson, B.R. Pharmacological interventions for prevention or treatment of postoperative pain in people undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homepage of Prospect. Available online: http://www.postoppain.org/frameset.htm (accessed on 9 July 2014).
- Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' (CNT) Collaboration; Bhala, N.; Emberson, J.; Merhi, A.; Abramson, S.; Arber, N.; Baron, J.A.; Bombardier, C.; Cannon, C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakobsson, J.G. Pain Management in Ambulatory Surgery—A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 850-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph7080850
Jakobsson JG. Pain Management in Ambulatory Surgery—A Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2014; 7(8):850-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph7080850
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakobsson, Jan G. 2014. "Pain Management in Ambulatory Surgery—A Review" Pharmaceuticals 7, no. 8: 850-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph7080850
APA StyleJakobsson, J. G. (2014). Pain Management in Ambulatory Surgery—A Review. Pharmaceuticals, 7(8), 850-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph7080850



