New Aspects of Gene-Silencing for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Mechanism of RNAi and Antisense
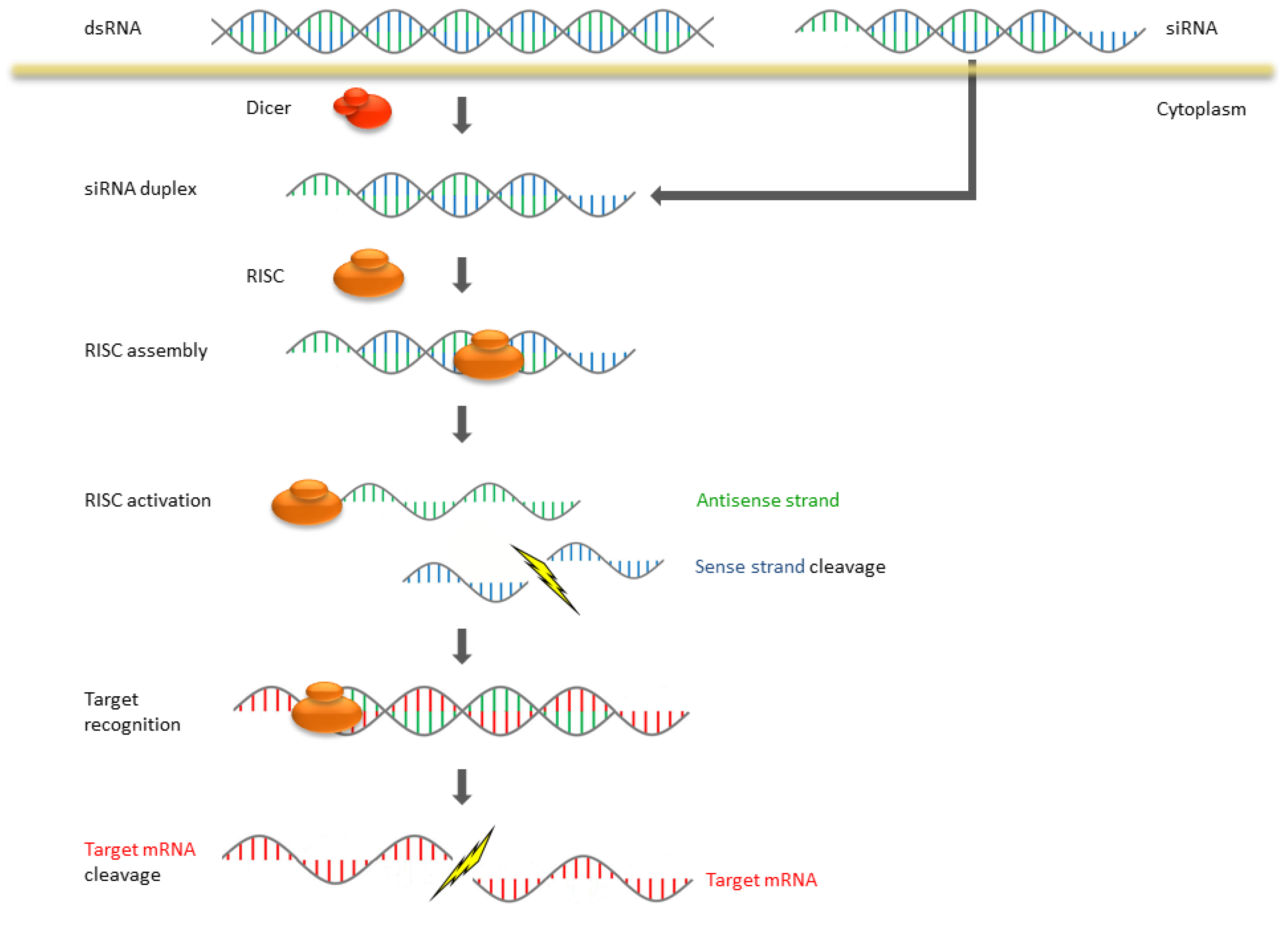
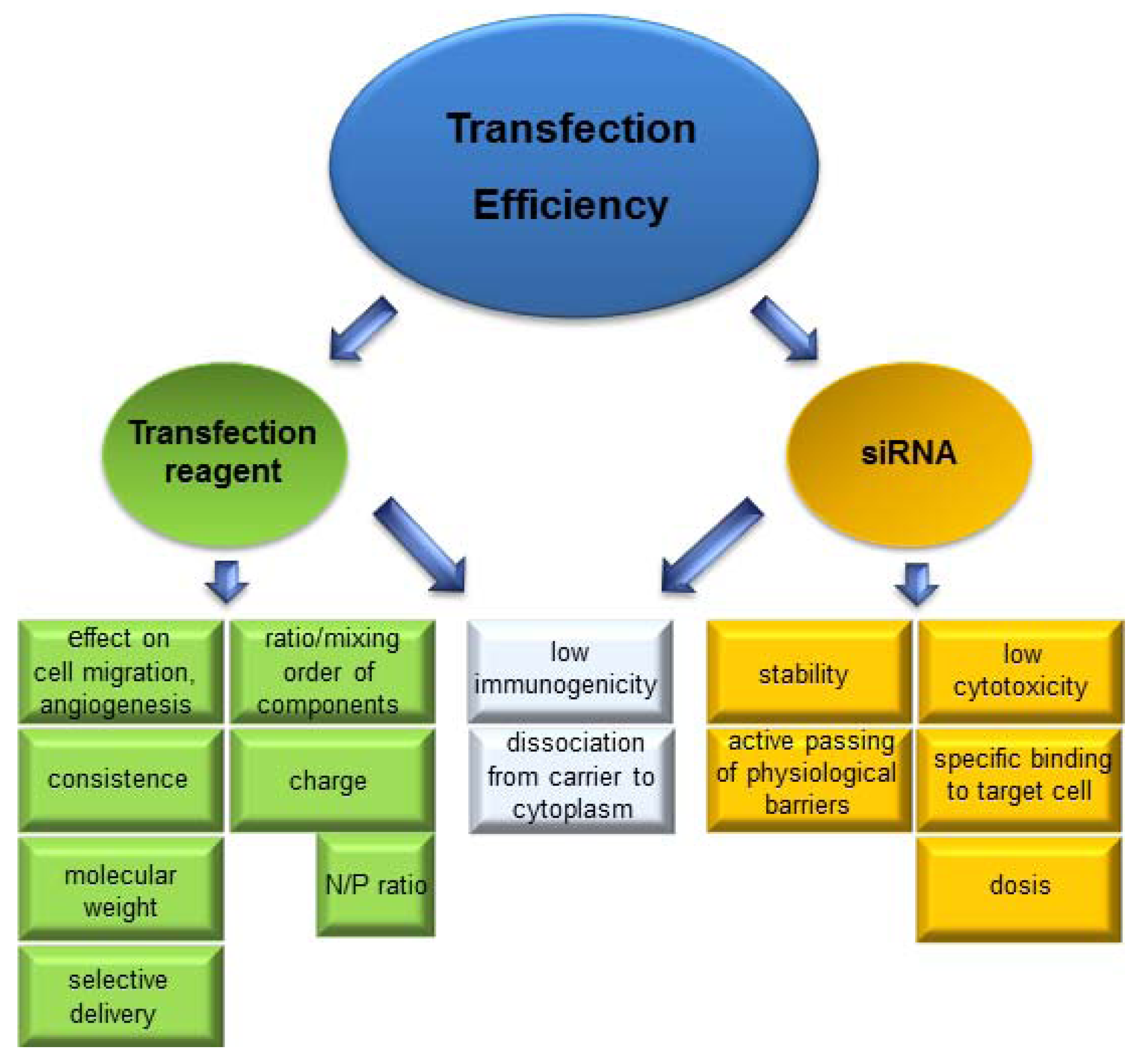
3. Stabilization of siRNA and Its Delivery Agents
3.1. Liposomes and Lipids
3.2. Polyethylenimine: A Cationic Synthetic Polymer
3.3. Atelocollagen: Collagen without Telopeptides
3.4. Chitosan: A Chitin Derivative
3.5. Hyaluronic Acid: Component of the ECM
4. Delivery Systems
5. Systemic Delivery Systems
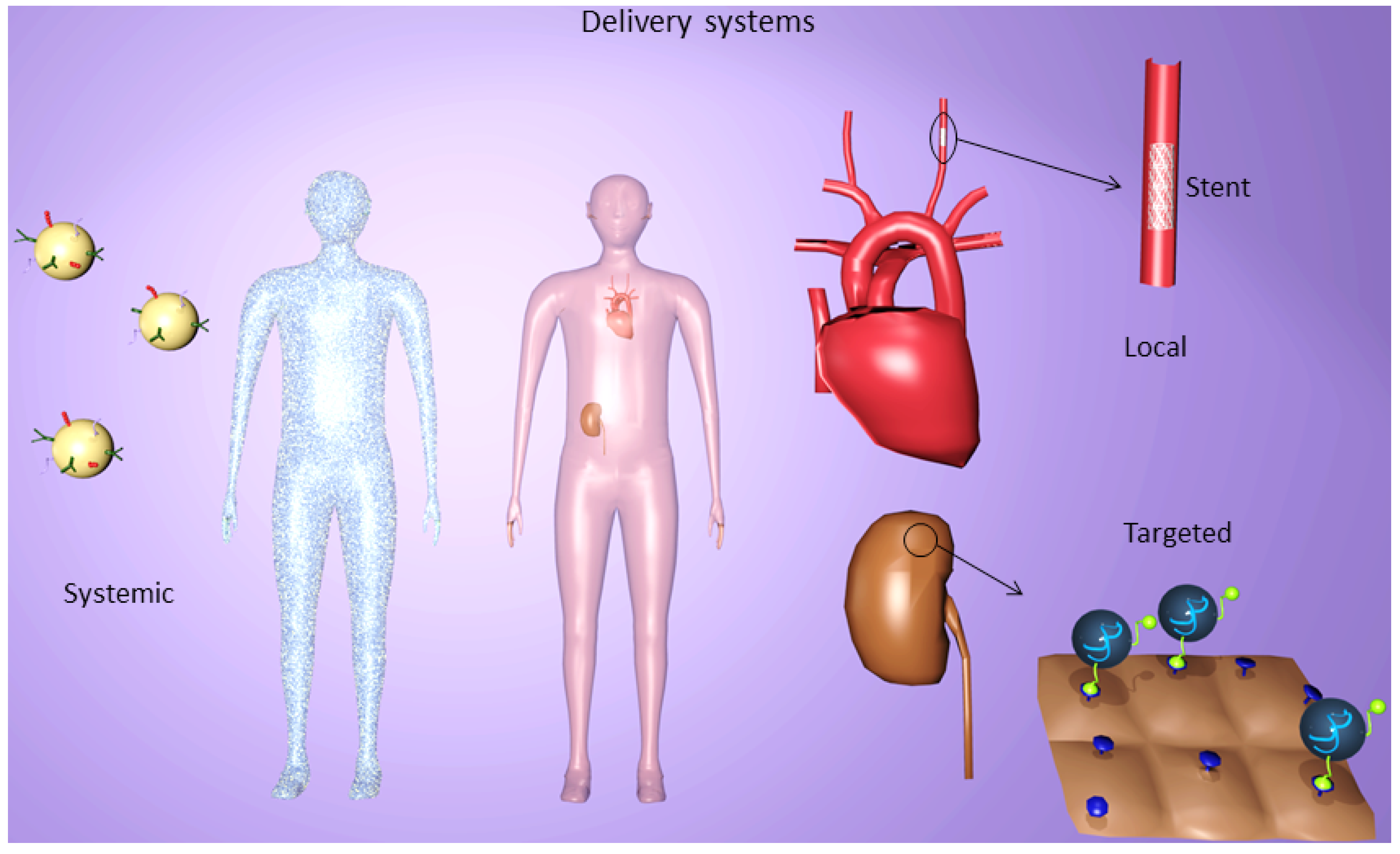
6. Targeted Delivery Systems
7. Local Delivery Systems
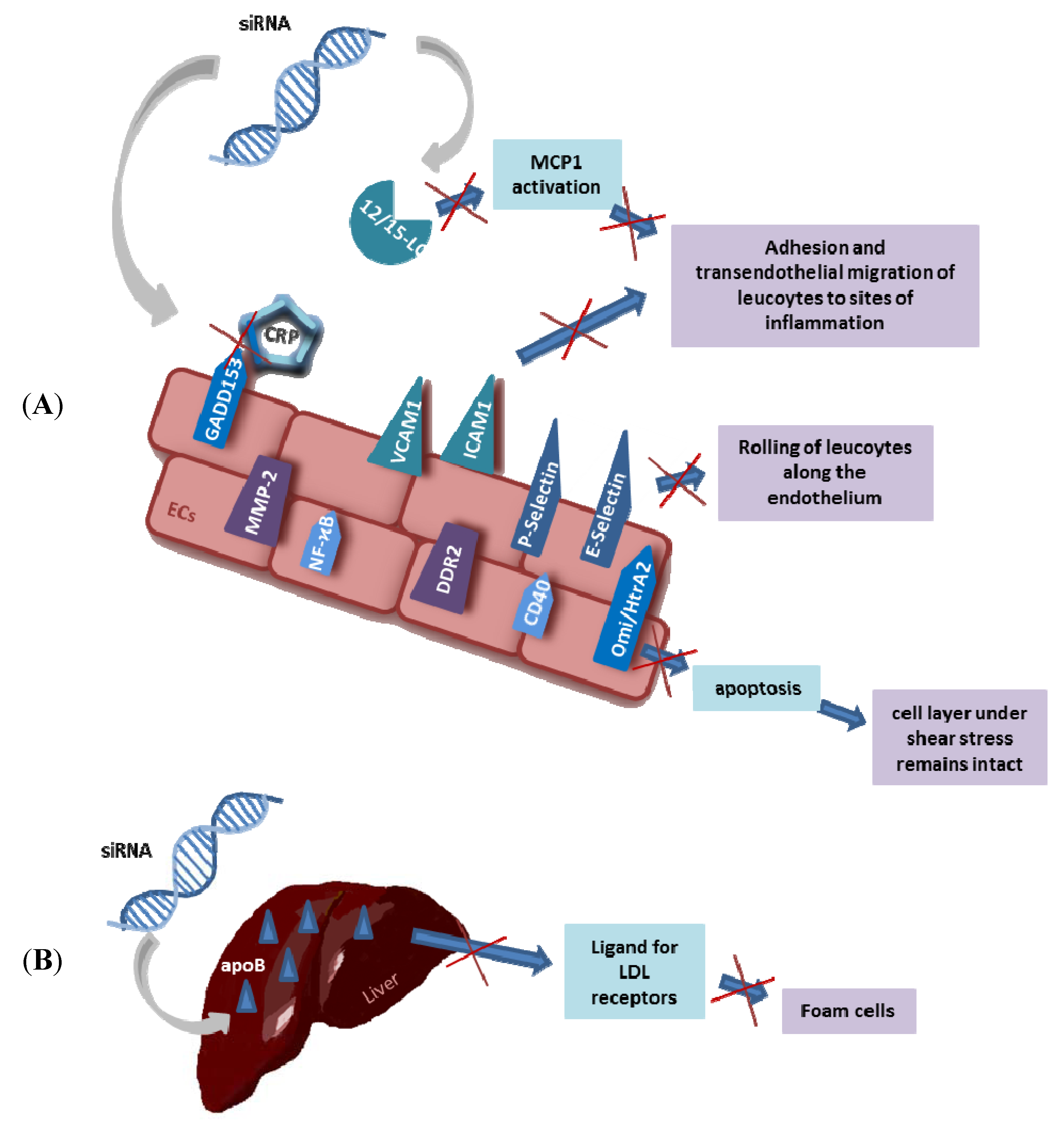
8. Chances for Atherosclerosis Therapies
9. Local Delivery of siRNA for Atherosclerosis and Restenosis Control
10. Treatment of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors by siRNA and ASOs
10.1. Hypertension
10.2. Hyperlipidemia
10.3. Diabetes
10.4. Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
11. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Espinola-Klein, C.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Bickel, C.; Lackner, K.; Schnabel, R.; Munzel, T.; Blankenberg, S. Inflammation, atherosclerotic burden and cardiovascular prognosis. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e126–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E.; Caudy, A.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Hannon, G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 2001, 409, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamore, P.D.; Tuschl, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: Double-Stranded RNA Directs the ATP-Dependent Cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 Nucleotide Intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykänen, A.; Haley, B.; Zamore, P.D. ATP Requirements and Small Interfering RNA Structure in the RNA Interference Pathway. Cell 2001, 107, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Boettcher, S.; Caudy, A.A.; Kobayashi, R.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2, a Link Between Genetic and Biochemical Analyses of RNAi. Science 2001, 293, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.; Stein, C.A. Antisense Oligonucleotides: Basic Concepts and Mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Crooke, S.T. Progress in antisense technology. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004, 55, 61–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowler, T.; Bergeron, D.; Tedeschi, A.-L.; Paquet, L.; Ferrari, N.; Damha, M.J. Improvements in siRNA properties mediated by 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-β-d-arabinonucleic acid (FANA). Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutschek, J.; Akinc, A.; Bramlage, B.; Charisse, K.; Constien, R.; Donoghue, M.; Elbashir, S.; Geick, A.; Hadwiger, P.; Harborth, J.; et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Meade, B.R.; Chang, Y.-C.; Fredrickson, C.T.; Willert, K.; Puri, N.; Dowdy, S.F. Efficient siRNA delivery into primary cells by a peptide transduction domain-dsRNA binding domain fusion protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landen, C.N.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Bucana, C.; Schmandt, R.; Deavers, M.T.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. Therapeutic EphA2 Gene Targeting In vivo Using Neutral Liposomal Small Interfering RNA Delivery. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6910–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Kamat, A.A.; Landen, C.N.; Han, L.Y.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Lin, Y.G.; Merritt, W.M.; Jennings, N.B.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Coleman, R.L.; et al. Focal Adhesion Kinase Targeting Using In vivo Short Interfering RNA Delivery in Neutral Liposomes for Ovarian Carcinoma Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4916–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villares, G.J.; Zigler, M.; Wang, H.; Melnikova, V.O.; Wu, H.; Friedman, R.; Leslie, M.C.; Vivas-Mejia, P.E.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; et al. Targeting Melanoma Growth and Metastasis with Systemic Delivery of Liposome-Incorporated Protease-Activated Receptor-1 Small Interfering RNA. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9078–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, A. Cellular delivery in vivo of siRNA-based therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3603–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.S.; Lee, A.C.H.; Akinc, A.; Bramlage, B.; Bumcrot, D.; Fedoruk, M.N.; Harborth, J.; Heyes, J.A.; Jeffs, L.B.; John, M.; et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2006, 441, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Andersen, J.B.; Song, H.-T.; Judge, A.D.; Seo, D.; Ishikawa, T.; Marquardt, J.U.; Kitade, M.; Durkin, M.E.; Raggi, C.; et al. Definition of Ubiquitination Modulator COP1 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8264–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Wilcox, D.; Zhao, X.; Song, J.; Lin, X.; Kohlbrenner, W.M.; Fesik, S.W.; Shen, Y. Tumor vasculature is a key determinant for the efficiency of nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, A.D.; Robbins, M.; Tavakoli, I.; Levi, J.; Hu, L.; Fronda, A.; Ambegia, E.; McClintock, K.; MacLachlan, I. Confirming the RNAi-mediated mechanism of action of siRNA-based cancer therapeutics in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, D.V.; Lockridge, J.A.; Shaw, L.; Blanchard, K.; Jensen, K.; Breen, W.; Hartsough, K.; Machemer, L.; Radka, S.; Jadhav, V.; et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussif, O.; Lezoualc'h, F.; Zanta, M.A.; Mergny, M.D.; Scherman, D.; Demeneix, B.; Behr, J.P. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7297–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.-P. The Proton Sponge: A Trick to Enter Cells the Viruses Did Not Exploit. Chimia (Aarau) 1997, 51, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zintchenko, A.; Philipp, A.; Dehshahri, A.; Wagner, E. Simple Modifications of Branched PEI Lead to Highly Efficient siRNA Carriers with Low Toxicity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards Grayson, A.C.; Doody, A.M.; Putnam, D. Biophysical and Structural Characterization of Polyethylenimine-Mediated siRNA Delivery in Vitro. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban-Klein, B.; Werth, S.; Abuharbeid, S.; Czubayko, F.; Aigner, A. RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo. Gene Ther. 2004, 12, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Gartel, A.L. The suppression of FOXM1 and its targets in breast cancer xenograft tumors by siRNA. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, K.C.; Little, S.R.; Langer, R.; Hammond, P.T. A Family of Hierarchically Self-Assembling Linear-Dendritic Hybrid Polymers for Highly Efficient Targeted Gene Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 6704–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Ramusovic, S.; Nguyen, T.; Lu, Z.-R. Novel Polymerizable Surfactants with pH-Sensitive Amphiphilicity and Cell Membrane Disruption for Efficient siRNA Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa Kim, S.; Hyeon Lee, S.; Tian, H.; Chen, X.; Gwan Park, T. Prostate cancer cell-specific VEGF siRNA delivery system using cell targeting peptide conjugated polyplexes. J. Drug Target 2009, 17, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Sawant, R.R.; Biswas, S.; Essex, S.; Tros de Ilarduya, C.; Torchilin, V.P. P-glycoprotein silencing with siRNA delivered by DOPE-modified PEI overcomes doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Nanomedicine (London) 2011, 7, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Höbel, S.; Appeldoorn, C.C.M.; Gaillard, P.J.; Aigner, A. Targeted CRM197-PEG-PEI/siRNA Complexes for Therapeutic RNAi in Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2011, 4, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R.; Engle, X.; Scarlett, U.K.; Martinez, D.; Barber, A.; Elgueta, R.; Wang, L.; Nesbeth, Y.; Durant, Y.; Gewirtz, A.T.; et al. Polyethylenimine-based siRNA nanocomplexes reprogram tumor-associated dendritic cells via TLR5 to elicit therapeutic antitumor immunity. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, T.G. Multimeric small interfering ribonucleic acid for highly efficient sequence-specific gene silencing. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, K.; Takada, Y.; Sato, S.; Miyata, T. Novel delivery system for proteins using collagen as a carrier material: the minipellet. J. Control Release 1995, 33, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, A.; Maeda, M.; Nagahara, S.; Ochiya, T.; Honma, K.; Itoh, H.; Miyata, T.; Fujioka, K. Atelocollagen for protein and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1651–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakuchi, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Kosaka, N.; Sasaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kouno, M.; Honma, K.; Nagahara, S.; Hanai, K.; Sano, A.; et al. Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, S.; Nagahara, S.; Makita, N.; Tarumi, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Matsuo, S.; Kadomatsu, K.; Takei, Y. Atelocollagen-mediated Systemic Delivery Prevents Immunostimulatory Adverse Effects of siRNA in Mammals. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, K.; Ochiya, T.; Nagahara, S.; Sano, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Hirai, K.; Aso, Y.; Terada, M. Atelocollagen-Based Gene Transfer in Cells Allows High-Throughput Screening of Gene Functions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Nagahara, S.; Makita, N.; Tarumi, Y.; Kadomatsu, K.; Takei, Y. Systemic delivery of siRNA specific to tumor mediated by atelocollagen: Combined therapy using siRNA targeting Bcl-xL and cisplatin against prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Kadomatsu, K.; Goto, T.; Muramatsu, T. Combinational antitumor effect of siRNA against midkine and paclitaxel on growth of human prostate cancer xenografts. Cancer 2006, 107, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Kadomatsu, K.; Yuzawa, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Muramatsu, T. A Small Interfering RNA Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor as Cancer Therapeutics. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, F.; Minakuchi, Y.; Nagahara, S.; Honma, K.; Sasaki, H.; Hirai, K.; Teratani, T.; Namatame, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hanai, K.; et al. Efficient delivery of small interfering RNA to bone-metastatic tumors by using atelocollagen in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12177–12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinouchi, N.; Ohsawa, Y.; Ishimaru, N.; Ohuchi, H.; Sunada, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tanimoto, Y.; Moriyama, K.; Noji, S. Atelocollagen-mediated local and systemic applications of myostatin-targeting siRNA increase skeletal muscle mass. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, E.; Kinouchi, N.; Adachi, T.; Ohsawa, Y.; Ishimaru, N.; Ohuchi, H.; Sunada, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Noji, S. Atelocollagen-mediated systemic administration of myostatin-targeting siRNA improves muscular atrophy in caveolin-3-deficient mice. Dev. Growth Differ. 2011, 53, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H. Insect chitin synthases: A review. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2006, 176, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and Chitosan: Functional Biopolymers from Marine Crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, P.L.; Milas, M.; Rinaudo, M.; Desbrières, J. Water soluble derivatives obtained by controlled chemical modifications of chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 24, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannan, T.; Kurita, K.; Iwakura, Y. Studies on chitin, 2. Effect of deacetylation on solubility. Die Makromolekulare Chemie 1976, 177, 3589–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katas, H.; Alpar, H.O. Development and characterisation of chitosan nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. J. Control Release 2006, 115, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Jiang, H.-L.; Jere, D.; Park, I.-K.; Cho, M.-H.; Nah, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-J.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.-S. Chemical modification of chitosan as a gene carrier in vitro and in vivo. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 726–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techaarpornkul, S.; Wongkupasert, S.; Opanasopit, P.; Apirakaramwong, A.; Nunthanid, J.; Ruktanonchai, U. Chitosan-Mediated siRNA Delivery In Vitro: Effect of Polymer Molecular Weight, Concentration and Salt Forms. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Dong, M.; Liu, X.; Howard, K.A.; Kjems, J.; Besenbacher, F. Direct Force Measurements between siRNA and Chitosan Molecules Using Force Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.P.; Danielsen, S.; Christensen, B.E.; Vårum, K.M. Influence of Chitosan Structure on the Formation and Stability of DNA−Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittnacht, U.; Hartmann, H.; Hein, S.; Oliveira, H.; Dong, M.; Pêgo, A.P.; Kjems, J.; Howard, K.A.; Schlosshauer, B. Chitosan/siRNA Nanoparticles Biofunctionalize Nerve Implants and Enable Neurite Outgrowth. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbacher, P.; Zou, S.; Bettinger, T.; Steffan, A.-M.; Remy, J.-S. Chitosan-Based Vector/DNA Complexes for Gene Delivery: Biophysical Characteristics and Transfection Ability. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorek, D.L.J.; Tsourkas, A. Size, charge and concentration dependent uptake of iron oxide particles by non-phagocytic cells. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.R.; Miranda, O.R.; Thompson, M.A.; Pabelick, C.M.; Bhattacharya, R.; Robertson, J.D.; Rotello, V.M.; Prakash, Y.S.; Mukherjee, P. Effect of nanoparticle surface charge at the plasma membrane and beyond. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Agoulnik, I.U.; Truong, A.; Li, Z.; Creighton, C.J.; Kaftanovskaya, E.M.; Pereira, R.; Han, H.D.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Klonisch, T.; et al. Suppression of relaxin receptor RXFP1 decreases prostate cancer growth and metastasis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, A.M.; Su, D.; Che, O.; Li, W.S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yang, B.; Xu, F. Functional gene silencing mediated by chitosan/siRNA nanocomplexes. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 405103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Han, H.D.; Mangala, L.S.; Ali-Fehmi, R.; Newton, C.S.; Ozbun, L.; Armaiz-Pena, G.N.; Hu, W.; Stone, R.L.; Munkarah, A.; et al. Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis by EZH2. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, S.; Dong, M.; Song, J.; Yang, C.; Howard, K.A.; Kjems, J.; Besenbacher, F. Chitosan/siRNA Nanoparticles Encapsulated in PLGA Nanofibers for siRNA Delivery. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4835–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.D.; Mora, E.M.; Roh, J.W.; Nishimura, M.; Lee, S.J.; Stone, R.L.; Bar-Eli, M.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. Chitosan hydrogel for localized gene silencing. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, T.C.; Laurent, U.B.G.; Fraser, J.R.E. The structure and function of hyaluronan: An overview. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, A1–A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, B.; Meyer, K. The Structure of Hyalobiuronic Acid and of Hyaluronic Acid from Umbilical Cord1,2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, P.H.; Frost, S.J.; McGary, C.T.; LeBoeuf, R.D. The role of hyaluronic acid in inflammation and wound healing. Int. J. Tissue React. 1988, 10, 355–365. [Google Scholar]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan: from extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, J.; Driver, V.R. Hyaluronic acid derivatives and their healing effect on burns, epithelial surgical wounds, and chronic wounds: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Wound Repair Regen 2012, 20, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronate derivatives in drug delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1998, 15, 513–555. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmrich, K.; von Heimburg, D.; Rendchen, R.; di Bartolo, C.; Milella, E.; Pallua, N. Implantation of preadipocyte-loaded hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds into nude mice to evaluate potential for soft tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7025–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, T.; Seino, S.; Sato, T.; Matsuoka, R.; Masuda, Y.; Fukui, N. Oral Administration of Polymer Hyaluronic Acid Alleviates Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study over a 12-Month Period. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 167928. [Google Scholar]
- Swann, D.A. Studies on hyaluronic acid: I. The preparation and properties of rooster comb hyaluronic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 156, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, G.; Šoltés, L.; Stern, R.; Gemeiner, P. Hyaluronic acid: a natural biopolymer with a broad range of biomedical and industrial applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bracke, J.W.; Thacker, K. Hyaluronic acid from bacterial culture. US4517295 A, 14 May 1985. [Google Scholar]
- O'Regan, M.; Martini, I.; Crescenzi, F.; de Luca, C.; Lansing, M. Molecular mechanisms and genetics of hyaluronan biosynthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1994, 16, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Stephanopoulos, G. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widner, B.; Behr, R.; von Dollen, S.; Tang, M.; Heu, T.; Sloma, A.; Sternberg, D.; DeAngelis, P.L.; Weigel, P.H.; Brown, S. Hyaluronic Acid Production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3747–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.-J.; Lee, C.-K. Hyaluronic acid production by recombinant Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, M.-Y.; Kim, K.S.; Hahn, S.K. Target specific tumor treatment by VEGF siRNA complexed with reducible polyethyleneimine–hyaluronic acid conjugate. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5258–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviña, M.; Cubillo, E.; Olmeda, D.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Fernandez-Megia, E.; Riguera, R.; Sánchez, A.; Cano, A.; Alonso, M. Hyaluronic Acid/Chitosan-g-Poly(ethylene glycol) Nanoparticles for Gene Therapy: An Application for pDNA and siRNA Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2544–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Shim, G.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Oh, Y.-K.; Shim, C.-K. Hyaluronic acid complexed to biodegradable poly L-arginine for targeted delivery of siRNAs. J. Gene Med. 2009, 11, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-E.; Kang, H.; Shim, G.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, H.-G.; Kim, J.; Hahn, S.K.; Oh, Y.-K. Cationic derivatives of biocompatible hyaluronic acids for delivery of siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides. J. Drug Target 2009, 17, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadi, S.; Alatorre-Meda, M.; Zaghloul, E.M.; Taboada, P.; Remunán-López, C. Chitosan–hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for gene silencing: The role of hyaluronic acid on the nanoparticles’ formation and activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Wang, J.C.; Zhao, E.Y.; Gao, L.Y.; Zhou, S.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Lu, W.L.; Zhang, Q. A comparative study of three ternary complexes prepared in different mixing orders of siRNA/redox-responsive hyperbranched poly (amido amine)/hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3837–3849. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, Y.; Tarin, D. Significance of CD44 gene products for cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. Lancet 1992, 340, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochon, V.; Mabilat, C.; Bertrand, P.; Legrand, Y.; Smadja-Joffe, F.; Soria, C.; Delpech, B.; Lu, H. Evidence of involvement of CD44 in endothelial cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savani, R.C.; Cao, G.; Pooler, P.M.; Zaman, A.; Zhou, Z.; DeLisser, H.M. Differential Involvement of the Hyaluronan (HA) Receptors CD44 and Receptor for HA-mediated Motility in Endothelial Cell Function and Angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36770–36778. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Li, L.; Kamiryo, M.; Asteriou, T.; Moustakas, A.; Yamashita, H.; Heldin, P. Hyaluronan Fragments Induce Endothelial Cell Differentiation in a CD44- and CXCL1/GRO1-dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24195–24204. [Google Scholar]
- Pilarski, L.M.; Masellis-Smith, A.; Belch, A.R.; Yang, B.; Savani, R.C.; Turley, E.A. RHAMM, a Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility, on Normal Human Lymphocytes, Thymocytes and Malignant B Cells: A Mediator in B cell Malignancy? Leuk. Lymphoma 1994, 14, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCourt, P.A.; Ek, B.; Forsberg, N.; Gustafson, S. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is a cell surface receptor for hyaluronan. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 30081–30084. [Google Scholar]
- Landesman-Milo, D.; Goldsmith, M.; Leviatan Ben-Arye, S.; Witenberg, B.; Brown, E.; Leibovitch, S.; Azriel, S.; Tabak, S.; Morad, V.; Peer, D. Hyaluronan grafted lipid-based nanoparticles as RNAi carriers for cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, S.C.; Akinc, A.; Chen, J.; Sandhu, A.P.; Mui, B.L.; Cho, C.K.; Sah, D.W.Y.; Stebbing, D.; Crosley, E.J.; Yaworski, E.; et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Dowdy, S.F. siRNA delivery using peptide transduction domains. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeim, M.T.; Hajjar, R.J. Gene therapy for heart failure. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 103, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Nunes, F.A.; Berencsi, K.; Furth, E.E.; Gönczöl, E.; Wilson, J.M. Cellular immunity to viral antigens limits E1-deleted adenoviruses for gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4407–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.D.; Stallwood, Y.; Green, N.K.; Ulbrich, K.; Mautner, V.; Seymour, L.W. Polymer-coated adenovirus permits efficient retargeting and evades neutralising antibodies. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, L.; Lehtonen, E.; Monahan, P.E. Evaluation of risks related to the use of adeno-associated virus-based vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2003, 3, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenjo, E.; Asai, T.; Yonenaga, N.; Ando, H.; Ishii, T.; Hatanaka, K.; Shimizu, K.; Urita, Y.; Dewa, T.; Nango, M.; et al. Systemic delivery of small interfering RNA by use of targeted polycation liposomes for cancer therapy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-M.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, I.-S.; Ahn, H.J. Systemic Delivery of siRNA by Chimeric Capsid Protein: Tumor Targeting and RNAi Activity in Vivo. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 10, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.-Q.; Xiong, M.-H.; Shu, X.-T.; Tang, R.-Z.; Wang, J. Therapeutic Delivery of siRNA Silencing HIF-1 Alpha with Micellar Nanoparticles Inhibits Hypoxic Tumor Growth. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Knocking down barriers: Advances in siRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, H.; Hatakeyama, H.; Khalil, I.A.; Yamada, Y.; Harashima, H. Delivery of Nucleic Acids and Gene Delivery. In Comprehensive Biomaterials; Ducheyne, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 411–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kriegel, C.; Attarwala, H.; Amiji, M. Multi-compartmental oral delivery systems for nucleic acid therapy in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, D.C.; Peppas, N.A. Oral delivery of small RNA and DNA. J. Control Release 2012, 162, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Keough, E.; Matter, A.; Leander, K.; Young, S.; Carlini, E.; Sachs, A.B.; Tao, W.; Abrams, M.; Howell, B.; et al. Biodistribution of Small Interfering RNA at the Organ and Cellular Levels after Lipid Nanoparticle-mediated Delivery. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Yamauchi, J.; Khalil, I.A.; Kajimoto, K.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. Cell penetrating peptide-mediated systemic siRNA delivery to the liver. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Novobrantseva, T.I.; Borodovsky, A.; Wong, J.; Klebanov, B.; Zafari, M.; Yucius, K.; Querbes, W.; Ge, P.; Ruda, V.M.; Milstein, S.; et al. Systemic RNAi-mediated Gene Silencing in Nonhuman Primate and Rodent Myeloid Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e4. [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner, F.; Dutta, P.; Gorbatov, R.; Novobrantseva, T.I.; Donahoe, J.S.; Courties, G.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.I.; Markmann, J.F.; Marinelli, B.; et al. Therapeutic siRNA silencing in inflammatory monocytes in mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santel, A.; Aleku, M.; Keil, O.; Endruschat, J.; Esche, V.; Fisch, G.; Dames, S.; Loffler, K.; Fechtner, M.; Arnold, W.; et al. A novel siRNA-lipoplex technology for RNA interference in the mouse vascular endothelium. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santel, A.; Aleku, M.; Keil, O.; Endruschat, J.; Esche, V.; Durieux, B.; Loffler, K.; Fechtner, M.; Rohl, T.; Fisch, G.; et al. RNA interference in the mouse vascular endothelium by systemic administration of siRNA-lipoplexes for cancer therapy. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, C.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Ternary Polymeric Nanoparticles for Oral siRNA Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.S.; Henne, W.A.; Doorneweerd, D.D. Discovery and Development of Folic-Acid-Based Receptor Targeting for Imaging and Therapy of Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 41, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Kularatne, S.A.; Qi, L.; Kleindl, P.; Leamon, C.P.; Hansen, M.J.; Low, P.S. Ligand-Targeted Delivery of Small Interfering RNAs to Malignant Cells and Tissues. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1175, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohmen, C.; Frohlich, T.; Lachelt, U.; Rohl, I.; Vornlocher, H.-P.; Hadwiger, P.; Wagner, E. Defined Folate-PEG-siRNA Conjugates for Receptor-specific Gene Silencing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e7. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Wang, T.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Long, H.; Gao, X.; Tang, S. Silencing of the MYCN gene by siRNA delivered by folate receptor-targeted liposomes in LA-N-5 cells. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2010, 26, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, J.; Wolf, A.; Steinbach, A.; Rössler, J.; Süss, R. Targeted Delivery to Neuroblastoma of Novel siRNA-anti-GD2-liposomes Prepared by Dual Asymmetric Centrifugation and Sterol-Based Post-Insertion Method. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, D.; Siu, K.; Wang, H.; Ichim, T.E.; Quan, D.; McAlister, V.; Chen, G.; et al. A novel in vivo siRNA delivery system specifically targeting liver cells for protection of ConA-induced fulminant hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.D.; Mangala, L.S.; Lee, J.W.; Shahzad, M.M.K.; Kim, H.S.; Shen, D.; Nam, E.J.; Mora, E.M.; Stone, R.L.; Lu, C.; et al. Targeted Gene Silencing Using RGD-Labeled Chitosan Nanoparticles. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3910–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-T.; Leng, Q.; Scaria, P.; Kahn, J.D.; Tricoli, L.J.; Woodle, M.; Mixson, A.J. Surface-Modified HK:siRNA Nanoplexes with Enhanced Pharmacokinetics and Tumor Growth Inhibition. Biomacromolecules 2013, 752–760. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.R.; Ming, X.; Fisher, M.; Lackey, J.G.; Rajeev, K.G.; Manoharan, M.; Juliano, R.L. Multivalent Cyclic RGD Conjugates for Targeted Delivery of Small Interfering RNA. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Taira, K. Ligand-Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic siRNA. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Zhu, P.; Lee, S.-K.; Chowdhury, D.; Kussman, S.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Feng, Y.; Palliser, D.; Weiner, D.B.; Shankar, P.; et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.D.; Sun, T.M.; Huang, S.Y.; Dou, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.N.; Ruan, J.B.; Mao, C.Q.; Yu, F.Y.; Zeng, M.S.; et al. Targeted delivery of PLK1-siRNA by ScFv suppresses Her2+ breast cancer growth and metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 130ra48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yun, K.-S.; Choi, C.S.; Shin, S.-H.; Ban, H.-S.; Rhim, T.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, K.Y. T Cell-Specific siRNA Delivery Using Antibody-Conjugated Chitosan Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Palliser, D.; Lieberman, J. The silent treatment: siRNAs as small molecule drugs. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, A.; Schneider, M.; Walker, T.; Wendel, H.P. Gene-Silencing for Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. In Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering—Cells and Biomaterials; Eberli, D., Ed.; InTech: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moschos, S.A.; Jones, S.W.; Perry, M.M.; Williams, A.E.; Erjefalt, J.S.; Turner, J.J.; Barnes, P.J.; Sproat, B.S.; Gait, M.J.; Lindsay, M.A. Lung Delivery Studies Using siRNA Conjugated to TAT(48−60) and Penetratin Reveal Peptide Induced Reduction in Gene Expression and Induction of Innate Immunity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanotto, D.; Rossi, J.J. The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature 2009, 457, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliser, D.; Chowdhury, D.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Lee, S.J.; Bronson, R.T.; Knipe, D.M.; Lieberman, J. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature 2006, 439, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B.; Teng, J.; Gao, C. RNAi functionalized collagen-chitosan/silicone membrane bilayer dermal equivalent for full-thickness skin regeneration with inhibited scarring. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yoo, H.S. Matrix metalloproteinase-inspired suicidal treatments of diabetic ulcers with siRNA-decorated nanofibrous meshes. Gene Ther. 2012, 20, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Park, M.-R.; Song, S.-C. Injectable Polyplex Hydrogel for Localized and Long-Term Delivery of siRNA. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5757–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legein, B.; Temmerman, L.; Biessen, E.L.; Lutgens, E. Inflammation and immune system interactions in atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/index.html (accessed on 11 July 2013).
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An Inflammatory Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control; Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Hwang, S.-J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Smith, L.C.; Davis, C.E.; Gotto, A.M.; Boerwinkle, E. Circulating Adhesion Molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in Carotid Atherosclerosis and Incident Coronary Heart Disease Cases: The Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 1997, 96, 4219–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerath, E.; Towne, B.; Blangero, J.; Siervogel, R.M. The relationship of soluble ICAM-1, VCAM-1, P-selectin and E-selectin to cardiovascular disease risk factors in healthy men and women. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2001, 28, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudijanto, A. The role of vascular smooth muscle cells on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Acta Med Indones 2007, 39, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.J.; Miyoshi, T.; Yuan, Z.; Hirohata, S.; Li, J.Z.; Shi, W.; Angle, J.F. siRNA silencing reveals role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Atherosclerosis 2008, 198, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Han, S.; Yu, C.; Li, J. VCAM-1 siRNA reduces neointimal formation after surgical mechanical injury of the rat carotid artery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluvinet, R.; Pétriz, J.; Torras, J.; Herrero-Fresneda, I.; Cruzado, J.M.; Grinyó, J.M.; Aran, J.M. RNAi-mediated silencing of CD40 prevents leukocyte adhesion on CD154-activated endothelial cells. Blood 2004, 104, 3642–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Yan, J. Regression of atherosclerosis plaques in apolipoprotein E−/− mice after lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of CD40. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 163, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Murphy, A.; Chen, Y.-C.; Woollard, K.J.; Bassler, N.; Qian, H.; von zur Muhlen, C.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Ahrens, I.; et al. Dissociation of Pentameric to Monomeric C-Reactive Protein on Activated Platelets Localizes Inflammation to Atherosclerotic Plaques. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, F.; Bruemmer, D.; Yin, F.; Takata, Y.; Wang, W.; Fishbein, M.C.; Okura, T.; Higaki, J.; Graf, K.; Fleck, E.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Induces Apoptosis in Human Coronary Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circulation 2004, 110, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Reidy, M.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Is Necessary for the Regulation of Smooth Muscle Cell Replication and Migration After Arterial Injury. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuya, M.; Nakamura, K.; Sasaki, T.; Wu Cheng, X.; Itohara, S.; Iguchi, A. Effect of MMP-2 Deficiency on Atherosclerotic Lesion Formation in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlawaty, H.; San Juan, A.; Jacob, M.-P.; Vranckx, R.; Letourneur, D.; Feldman, L.J. Inhibition of MMP-2 gene expression with small interfering RNA in rabbit vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H3593–H3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, K.-G.; Wang, B.-W.; Kuan, P.; Chang, H. RNA Interference for Discoidin Domain Receptor 2 Attenuates Neointimal Formation in Balloon Injured Rat Carotid Artery. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrus, T.; Witztum, J.L.; Rader, D.J.; Tangirala, R.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F.; Funk, C.D. Disruption of the 12/15-lipoxygenase gene diminishes atherosclerosis in apo E-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 1597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrus, T.; Praticò, D.; Zhao, L.; Witztum, J.L.; Rader, D.J.; Rokach, J.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Funk, C.D. Absence of 12/15-Lipoxygenase Expression Decreases Lipid Peroxidation and Atherogenesis in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Circulation 2001, 103, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hyman, M.C.; Shashkin, P.; Harry, B.L.; Burcin, T.; Forlow, S.B.; Stark, M.A.; Smith, D.F.; Clarke, S.; et al. Critical Role of Macrophage 12/15-Lipoxygenase for Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Circulation 2004, 110, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Gu, J.; Vandenhoff, G.E.; Liu, X.; Nadler, J.L. Role of 12/15-lipoxygenase in the expression of MCP-1 in mouse macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H1933–H1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakanath, R.S.; Sahar, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Castanotto, D.; Rossi, J.J.; Natarajan, R. Regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by the oxidized lipid, 13-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoic acid, in vascular smooth muscle cells via nuclear factor–kappa B (NF-кB). J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 36, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.; Iaccarino, I.; Tenev, T.; Gschmeissner, S.; Totty, N.F.; Lemoine, N.R.; Savopoulos, J.; Gray, C.W.; Creasy, C.L.; Dingwall, C.; et al. The Serine Protease Omi/HtrA2 Regulates Apoptosis by Binding XIAP through a Reaper-like Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.L.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X. Effects of fluid shear stress on the expression of Omi/HtrA2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 7, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh, J.; Hockenhull, J.; Rao, N.; Dundar, Y.; Dickson Rumona, C.; Bagust, A. Drug-eluting stents versus bare metal stents for angina or acute coronary syndromes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD004587. [Google Scholar]
- 159. Douglas, G.; van Kampen, E.; Hale, A.B.; McNeill, E.; Patel, J.; Crabtree, M.J.; Ali, Z.; Hoerr, R.A.; Alp, N.J.; Channon, K.M. Endothelial cell repopulation after stenting determines in-stent neointima formation: effects of bare-metal vs. drug-eluting stents and genetic endothelial cell modification. Eur. Heart J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, A.; Walker, T.; Schneider, M.; Kray, O.; Avci-Adali, M.; Ziemer, G.; Wendel, H.P. Small-interfering RNA-eluting surfaces as a novel concept for intravascular local gene silencing. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossfeld, S.; Nolte, A.; Hartmann, H.; Recke, M.; Schaller, M.; Walker, T.; Kjems, J.; Schlosshauer, B.; Stoll, D.; Wendel, H.P.; et al. Bioactive coronary stent coating based on layer-by-layer technology for siRNA release. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6741–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, A.; Bala, M.; Hlawaty, H.; Portes, P.; Vranckx, R.; Feldman, L.J.; Letourneur, D. Development of a functionalized polymer for stent coating in the arterial delivery of small interfering RNA. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Newburger, P.E.; Gounis, M.J.; Dargon, P.; Zhang, X.; Messina, L.M. Local arterial nanoparticle delivery of siRNA for NOX2 knockdown to prevent restenosis in an atherosclerotic rat model. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.-L.; Bae, I.-H.; Lim, K.S.; Song, I.T.; Lee, H.; Muthiah, M.; Namgung, R.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, D.-G.; Ahn, Y.; et al. Suppression of post-angioplasty restenosis with an Akt1 siRNA-embedded coronary stent in a rabbit model. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8548–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Kintsurashvili, E.; Ona, D.; Ignjacev-Lazich, I.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Inhibition of the alpha(1D)-adrenergic receptor gene by RNA interference (RNAi) in rat vascular smooth muscle cells and its effects on other adrenergic receptors. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2007, 46, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasingham, S.J.; Raizada, M.K. Brain renin-angiotensin system dysfunction in hypertension: recent advances and perspectives. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.M. Brain and Pituitary Angiotensin. Endocr. Rev. 1992, 13, 329–380. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, J.; de Adjounian, M.F.C.; Sumners, C.; González, A.; Diez-Freire, C.; Raizada, M.K. Selective Silencing of Angiotensin Receptor Subtype 1a (AT1aR) by RNA Interference. Hypertension 2005, 45, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Beltz, T.G.; Yu, Y.; Guo, F.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Hay, M.; Johnson, A.K. Central interactions of aldosterone and angiotensin II in aldosterone- and angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H555–H564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Beltz, T.G.; Johnson, R.F.; Guo, F.; Hay, M.; Johnson, A.K. PVN adenovirus-siRNA injections silencing either NOX2 or NOX4 attenuate aldosterone/NaCl-induced hypertension in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H733–H741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Scholze, A.; Zhu, Z.; Kreutz, R.; Wehland-von-Trebra, M.; Zidek, W.; Tepel, M. Increased Transient Receptor Potential Channel TRPC3 Expression in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, D.; He, H.; Chen, X.; Cao, T.; Feng, X.; Ma, L.; Luo, Z.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z.; et al. Increased Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Type 3 Channels in Vasculature From Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2009, 53, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, M.E.; Witztum, J.L.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Kastelein, J.J.P. Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of dyslipidaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Roubtsova, A.; Essalmani, R.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Chamberland, A.; Hamelin, J.; Tremblay, M.; Jacques, H.; Jin, W.; Davignon, J.; et al. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): Hepatocyte-specific low-density lipoprotein receptor degradation and critical role in mouse liver regeneration. Hepatology 2008, 48, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibolla, G.; Norata, G.D.; Artali, R.; Meneghetti, F.; Catapano, A.L. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): From structure–function relation to therapeutic inhibition. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Fisker, N.; Asselin, M.C.; Lindholm, M.; Rosenbohm, C.; Orum, H.; Elmen, J.; Seidah, N.G.; Straarup, E.M. A locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotide (LNA) silences PCSK9 and enhances LDLR expression in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Grefhorst, A.; Anderson, N.N.; Racie, T.S.; Bramlage, B.; Akinc, A.; Butler, D.; Charisse, K.; Dorkin, R.; Fan, Y.; et al. Therapeutic RNAi targeting PCSK9 acutely lowers plasma cholesterol in rodents and LDL cholesterol in nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11915–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merki, E.; Graham, M.; Taleb, A.; Leibundgut, G.; Yang, X.; Miller, E.R.; Fu, W.; Mullick, A.E.; Lee, R.; Willeit, P.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide Lowers Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein (a) and Lipoprotein (a) in Transgenic Mice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.J.; Lee, R.G.; Bell, T.A.; Fu, W.; Mullick, A.E.; Alexander, V.J.; Singleton, W.; Viney, N.; Geary, R.; Su, J.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide Inhibition of Apolipoprotein C-III Reduces Plasma Triglycerides in Rodents, Nonhuman Primates, and Humans. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, N.B.; Haudenschild, C. Diabetes as an atherogenic factor. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1984, 26, 273–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinov, A.Y.; Tcherepanov, A.; Green, E.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Chervonsky, A.V. Contribution of Fas to diabetes development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, W.J.; Park, T.G.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, S.W. Non-viral systemic delivery of Fas siRNA suppresses cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD mice. J. Control Release 2010, 143, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Iwasaki, N.; Doi, K.; Noiri, E.; Iwamoto, Y.; Uchigata, Y.; Fujita, T.; Tokunaga, K. Inhibition of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion by KCNJ15, a Newly Identified Susceptibility Gene for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.; Bjelica, D.; Schenk, S.; Imamura, T.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Li, P.; Jadhar, V.; Vargeese, C.; Wang, W.; Bowman, K.; et al. Novel liver-specific TORC2 siRNA corrects hyperglycemia in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E1137–E1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, G.; Johnson, G.V.W. Complete transglutaminase 2 ablation results in reduced stroke volumes and astrocytes that exhibit increased survival in response to ischemia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jamal, K.T.; Gherardini, L.; Bardi, G.; Nunes, A.; Guo, C.; Bussy, C.; Herrero, M.A.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M.; Kostarelos, K.; et al. Functional motor recovery from brain ischemic insult by carbon nanotube-mediated siRNA silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10952–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoiu, A.; Mahajan, S.D.; Ye, L.; Kumar, R.; Ding, H.; Yong, K.T.; Roy, I.; Aalinkeel, R.; Nair, B.; Reynolds, J.L.; et al. MMP-9 gene silencing by a quantum dot-siRNA nanoplex delivery to maintain the integrity of the blood brain barrier. Brain Res. 2009, 1282, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesz, A.; Zhou, W.; Mracsko, E.; Karcher, S.; Bauer, H.; Schwarting, S.; Sun, L.; Bruder, D.; Stegemann, S.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain 2011, 134, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majmudar, M.D.; Keliher, E.J.; Heidt, T.; Leuschner, F.; Truelove, J.; Sena, B.F.; Gorbatov, R.; Iwamoto, Y.; Dutta, P.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; et al. Monocyte-Directed RNAi Targeting CCR2 Improves Infarct Healing in Atherosclerosis-Prone Mice. Circulation 2013, 127, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, M.; Tsuchida, K.; Hata, T.; Makino, N. RNA interference targeting SHP-1 attenuates myocardial infarction in rats. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2054–2056. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Koenig, O.; Walker, T.; Perle, N.; Zech, A.; Neumann, B.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.-P.; Nolte, A. New Aspects of Gene-Silencing for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 881-914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070881
Koenig O, Walker T, Perle N, Zech A, Neumann B, Schlensak C, Wendel H-P, Nolte A. New Aspects of Gene-Silencing for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals. 2013; 6(7):881-914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070881
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoenig, Olivia, Tobias Walker, Nadja Perle, Almuth Zech, Bernd Neumann, Christian Schlensak, Hans-Peter Wendel, and Andrea Nolte. 2013. "New Aspects of Gene-Silencing for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases" Pharmaceuticals 6, no. 7: 881-914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070881
APA StyleKoenig, O., Walker, T., Perle, N., Zech, A., Neumann, B., Schlensak, C., Wendel, H.-P., & Nolte, A. (2013). New Aspects of Gene-Silencing for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals, 6(7), 881-914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6070881



