Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Progress in Small Molecule Drug Development
Abstract
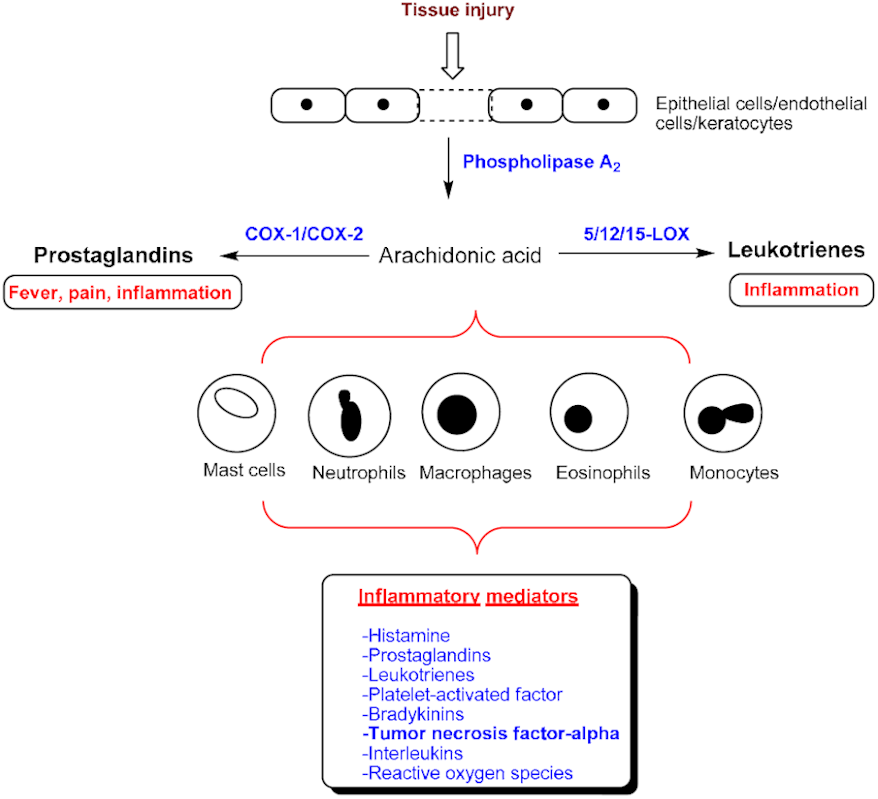
:1. Introduction
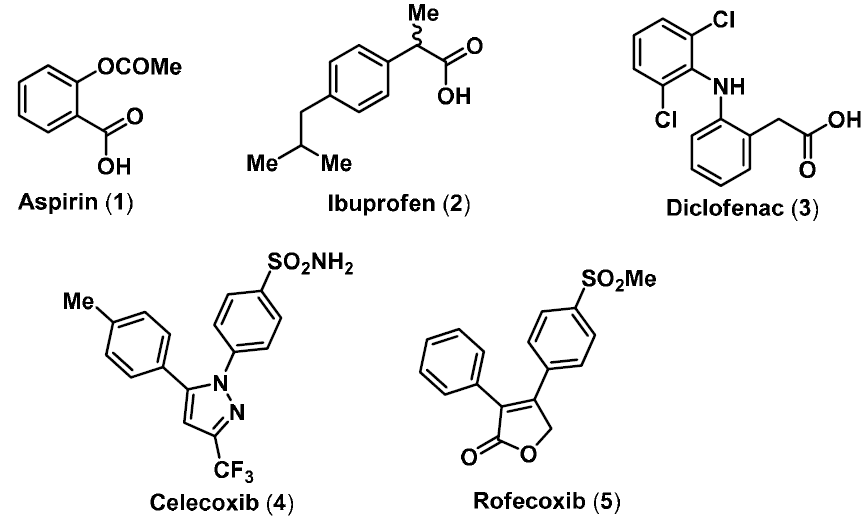
2. NO-NSAIDs

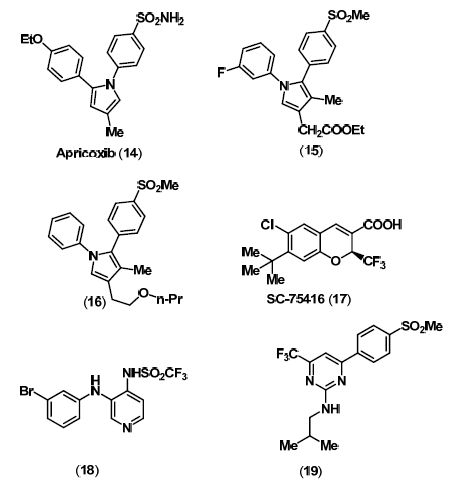
3. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors
4. Dual COX/LOX Inhibitors

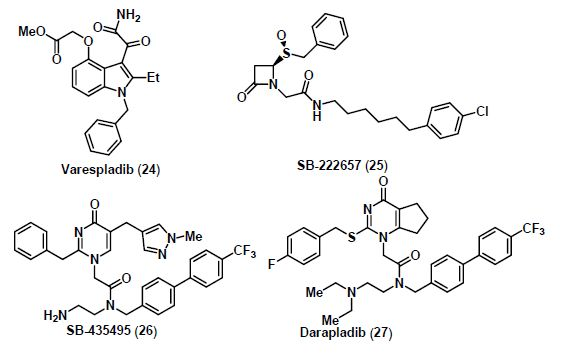
5. Lp-PLA2 Inhibitors
6. mPGES-1 Inhibitors
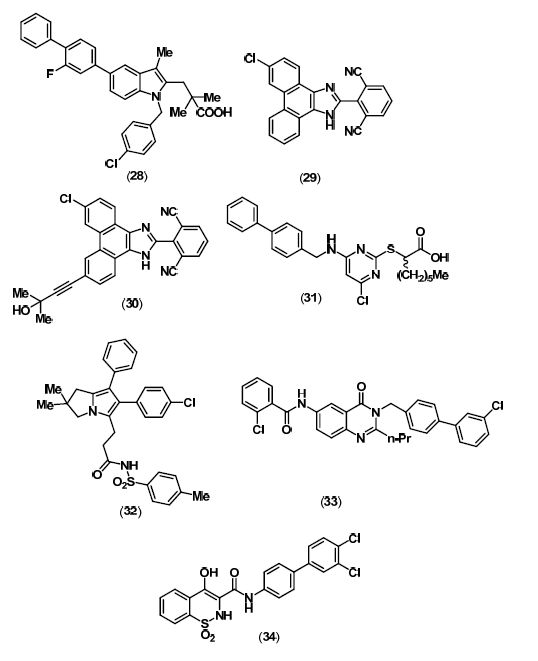
7. TNF-α Inhibitors
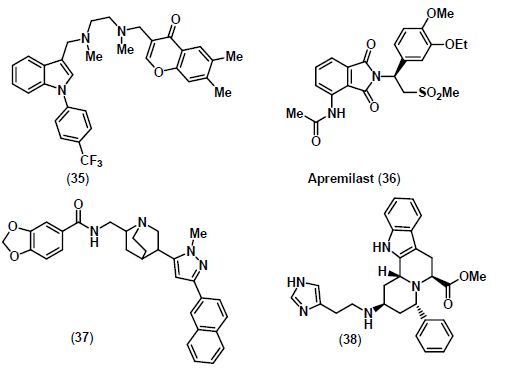
8. Conclusions
References
- Vane, J.R. The fight against rheumatism: From willow bark to COX-1 sparing drugs. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2000, 51, 573–586. [Google Scholar]
- Marnett, L.J. The COXIB experience: A look in the rearview mirror. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 265–290. [Google Scholar]
- Inotai, A.; Hanko, B.; Meszaro, A. Trends in the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug market in six central-eastern european countries based on retail information. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2010, 19, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Meade, E.A.; Smith, W.L.; DeWitt, D.L. Differential inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isozymes by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 6610–6614. [Google Scholar]
- Talley, J.J. Selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Prog. Med. Chem. Res. 1999, 36, 201–234. [Google Scholar]
- Black, W.C. Selective cycloxygenase-2 inhibitors. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Penning, T.D.; Talley, J.J.; Bertenshaw, S.R.; Carter, J.S.; Collins, P.W.; Docter, S.; Graneto, M.J.; Lee, L.F.; Malecha, J.W.; Miyashiro, J.M.; Rogers, R.S.; Rogier, D.J.; Yu, S.S.; Anderson, G.D.; Burton, E.G.; Cogburn, J.N.; Gregory, S.A.; Koboldt, C.M.; Perkins, W.E.; Seibert, K.; Veenhuizen, A.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Isakson, P.C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the 1,5-diarylpyrazole class of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: identification of 4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide (SC-58635, celecoxib). J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Prasit, P.; Wang, Z.; Brideau, C.; Chan, C.C.; Charleson, S.; Cromlish, W.; Ethier, D.; Evans, J.F.; Ford-Hutchinson, A.W.; Gauthier, J.Y.; Gordon, R.; Guay, J.; Gresser, M.; Kargman, S.; Kennedy, B.; Leblanc, Y.; Léger, S.; Mancini, J.; O'Neill, G.P.; Ouellet, M.; Percival, M.D.; Perrier, H.; Riendeau, D.; Rodger, I.; Zamboni, R. The discovery of rofecoxib, [MK 966, Vioxx, 4-(4'-methylsulfonylphenyl)-3-phenyl-2(5H)-furanone], an orally active cyclooxygenase-2-inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luong, C.; Miller, A.; Barnett, J.; Chow, J.; Ramesha, C.; Browner, M.F. Flexibility of the NSAID binding site in the structure of human cyclooxygenase-2. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 927–933. [Google Scholar]
- Kurumbail, R.G.; Stevens, A.M.; Gierse, J.K.; McDonald, J.J.; Stegeman, R.A.; Pak, J.Y.; Gildehaus, D.; Miyashiro, J.M.; Penning, T.D.; Seibert, K.; Isakson, P.C.; Stallings, W.C. Structural basis for selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by anti-inflammatory agents. Nature 1996, 384, 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Warner, T.D. COX isoforms in the cardiovascular system: Understanding the activities of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Ding, E.L.; Song, Y.Q. Adverse effects of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors on renal and arrhythmia events-meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA 2006, 296, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.J. Cyclooxygenases as the principle target for the action of NSAIDs. Rheum. Clinics N. Amer. 1998, 24, 501–523. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie, A.M. Modulation of inflammatory disease by inhibitors of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 10, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Charlier, C.; Michaux, C. Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) as a new strategy to provide safer nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 645–659. [Google Scholar]
- Poeckel, D.; Funk, C.D. The 5-lipoxygenase/leukotriene pathway in preclinical models of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. Prostaglandins and cancer. Gut 2006, 55, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, Y.I.; Dubois, R.N. NSAIDs and cancer prevention: targets downstream of COX-2. Annu. Rev. Med. 2007, 58, 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Palladino, M.A.; Bahjat, F.R.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Moldaver, L.L. Anti-TNF-α therapies: The next generation. Nat. Rev. Drug Disc. 2003, 2, 736–746. [Google Scholar]
- Seruga, B.; Zhang, H.; Bernstein, L.J.; Tannock, I.F. Cytokines and their relationship to the symptoms and outcome of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 887–899. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, J.M.; Watterson, D.M.; Van Eldik, L.J. Neuroinflammation: A potential therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 887–900. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, N. COX-2 inhibitors as antidepressants and antipsychotics: Clinical evidence. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2010, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rainsford, K.D. Anti-inflammatory drugs in the 21st century. Subcell. Biochem. 2007, 42, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.L.; Ignarro, L.J.; Fiorucci, S. Potential cardioprotective actions of NO-releasing aspirin. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, P. Chemistry and structure-activity relationships of leukotriene receptor antagonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, S220–S226. [Google Scholar]
- Ruschitzka, F.T.; Wenger, R.H.; Stallmach, T.; Quaschning, T.; de Wit, C.; Wagner, K.; Labugger, R.; Kelm, M.; Noll, G.; Rülicke, T.; Shaw, S.; Lindberg, R.L.; Rodenwaldt, B.; Lutz, H.; Bauer, C.; Lüscher, T.F.; Gassmann, M. Nitric oxide prevents cardiovascular disease and determines survival in polyglobulic mice overexpressing erythropoietin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11609–11613. [Google Scholar]
- Muscara, M.N.; McNight, W.; Del Soldato, P.; Wallace, J.L. Effects of a nitric oxide-releasing naproxen derivative on hypertension and gastric damage induced by chronic nitric oxide inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol. Lett. 1998, 62, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bandarage, U.K.; Chen, L.; Fang, X.; Garvey, D.S.; Glavin, A.; Janero, D.R.; Letts, L.G.; Mercer, G.J.; Saha, J.K.; Schroeder, J.D.; Shumway, M.J.; Tam, S.W. Nitrosothiol esters of diclofenac: Synthesis and pharmacological characterization as gastrointestinal-sparing prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4005–4016. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhugh, A.L.; Keefer, L.K. Diazeniumdiolates: pro- and antioxidant applications of the NONOates. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez, C.A.; Rao, P.N.P.; Knaus, E.E. Novel nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs possessing a nitric oxide donor diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate moiety: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and nitric oxide release studies. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, C.A.; Chen, Q.H.; Citro, M.L.; Keefer, L.K.; Knaus, E.E. Second-generation aspirin and indomethacin prodrugs possessing an O2-(acetoxymethyl)-1-(2-carboxypyrrolidin-1-yl)diazenium-1,2-diolate nitric oxide donor moiety: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and nitric oxide release studies. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chegaev, K.; Lazzarato, L.; Tosco, P.; Cena, C.; Marini, E.; Rolando, B.; Carrupt, P.A.; Fruttero, R.; Gasco, A. NO-donor COX-2 inhibitors: New nitrooxy-substituted 1,5-diarylimidazoles endowed with COX-2 inhibitory and vasodilator properties. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Wey, S.J.; Augustyniak, M.E.; Cochran, E.D.; Ellis, J.L.; Fang, X.; Garvey, D.S.; Janero, D.R.; Letts, L.G.; Martino, A.M.; Melim, T.L.; Murty, M.G.; Richardson, S.K.; Schroeder, J.D.; Selig, W.M.; Trocha, A.M.; Wexler, R.S.; Young, D.V.; Zemtseva, I.S.; Zifcak, B.M. Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of indomethacin derivatives as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibiting nitric oxide donors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6367–6382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazzarato, L.; Donnola, M.; Rolando, B.; Marini, E.; Cena, C.; Coruzzi, G.; Guaita, E.; Morini, G.; Fruttero, R.; Gasco, A.; Biondi, S. Searching for new NO-donor aspirin-like molecules: A new class of nitrooxy-acyl derivatives of salicylic acid. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, L.M.; Lally, M.N.; Carolan, C.G.; Jones, M.; Clancy, J.M.; Gilmer, J.F. Discovery of a true aspirin prodrug. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7991–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarato, L.; Donnola, M.; Rolando, B.; Chegaev, K.; Marini, E.; Cena, C.; Di Stilo, A.; Fruttero, R.; Biondi, S.; Ongini, E.; Gasco, A. (Nitrooxyacyloxy)methyl esters of aspirin as novel nitric oxide releasing aspirins. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5058–5068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.N.P.; Rajesh, K.G. Apricoxib, a COX-2 inhibitor for the potential treatment of pain and cancer. IDrugs 2009, 12, 711–722. [Google Scholar]
- Biava, M.; Porretta, G.C.; Poce, G.; Supino, S.; Forli, S.; Rovini, M.; Cappelli, A.; Manetti, F.; Botta, M.; Sautebin, L.; Rossi, A.; Pergola, C.; Ghelardini, C.; Vivoli, E.; Makovec, F.; Anzellotti, P.; Patrignani, P.; Anzini, M. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. 1,5-diarylpyrrol-3-acetic esters with enhanced inhibitory activity toward cyclooxygenase-2 and improved cyclooxygenase-2/cyclooxygenase-1 selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5403–5411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anzini, M.; Rovini, M.; Cappelli, A.; Vomero, S.; Manetti, F.; Botta, M.; Sautebin, L.; Rossi, A.; Pergola, C.; Ghelardini, C.; Norcini, M.; Giordani, A.; Makovec, F.; Anzellotti, P.; Patrignani, P.; Biava, M. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and enzyme docking simulations of 1,5-diarylpyrrole-3-alkoxyethyl ethers as selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors endowed with anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4476–4481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biava, M.; Porretta, G.C.; Poce, G.; Battilocchio, C.; Manetti, F.; Botta, M.; Forli, S.; Sautebin, L.; Rossi, A.; Pergola, C.; Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N.; Makovec, F.; Giordani, A.; Anzellotti, P.; Patrignani, P.; Anzini, M. Novel ester and acid derivatives of the 1,5-diarylpyrrole scaffold as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents: Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gierse, J.; Nickols, M.; Leahy, K.; Warner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cortes-Burgos, L.; Carter, J.; Seibert, K.; Masferrer, J. Evaluation of COX-1/COX-2 selectivity and potency of a new class of COX-2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 588, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, J.F.; Arslan, D.; Garbacki, N.; Pirotte, B.; de Leval, X. Pyridine analogues of nimesulide: design, synthesis, and in vitro and in vivo pharmacological evaluation as promising cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarbrick, M.E.; Beswick, P.J.; Gleave, R.J.; Green, R.H.; Bingham, S.; Bountra, C.; Carter, M.C.; Chambers, L.J.; Chessell, I.P.; Clayton, N.M.; Collins, S.D.; Corfield, J.A.; Hartley, C.D.; Kleanthous, S.; Lambeth, P.F.; Lucas, F.S.; Mathews, N.; Naylor, A.; Page, L.W.; Payne, J.J.; Pegg, N.A.; Price, H.S.; Skidmore, J.; Stevens, A.J.; Stocker, R.; Stratton, S.C.; Stuart, A.J.; Wiseman, J.O. Identification of [4-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyrimidinyl] amines and ethers as potent and selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4504–4508. [Google Scholar]
- Beswick, P.J.; Blackaby, A.P.; Bountra, C.; Brown, T.; Browning, K.; Campbell, I.B.; Corfield, J.; Gleave, R.J.; Guntrip, S.B.; Hall, R.M.; Hindley, S.; Lambeth, P.F.; Lucas, F.; Mathews, N.; Naylor, A.; Player, H.; Price, H.S.; Sidebottom, P.J.; Taylor, N.L.; Webb, G.; Wiseman, J. Identification and optimisation of a novel series of pyrimidine based cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Utilisation of a biotransformation approach. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4509–4514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, T.C.; Rocha, M.V.J.; Da Cunna, E.F.F.; Freitas, M.P. The search for new COX-2 inhibitors: A review of 2002-2008 patents. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2009, 19, 1193–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.V.R.; Billa, V.K.; Pallela, V.R.; Mallireddigari, M.R.; Boominathan, R.; Gabriel, J.L.; Reddy, E.P. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 1-(4-sulfamylphenyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-5-indolyl pyrazolines as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and lipoxygenase (LOX) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronikaki, A.A.; Lagunin, A.A.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.I.; Eleftheriou, P.T.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V.V.; Alam, I.; Saxena, A.K. Computer-aided discovery of anti-inflammatory thiazolidinones with dual cyclooxygenase/lipoxygenase inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Dailey, L.A.; Imming, P. 12-Lipoxygenase: Classification, possible therapeutic benefits from inhibition and inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999, 6, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Abdellatif, K.R.; Dong, Y.; Das, D.; Yu, G.; Velázquez, C.A.; Suresh, M.R.; Knaus, E.E. Synthesis and biological evaluation of salicylic acid and N-acetyl-2-carboxybenzenesulfonamide regioisomers possessing a N-difluoromethyl-1,2-dihydropyrid-2-one pharmacophore: dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase with anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 19, 6855–6861. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Abdellatif, K.R.; Dong, Y.; Das, D.; Suresh, M.R.; Knaus, E.E. Synthesis of celecoxib analogues possessing a N-difluoromethyl-1,2-dihydropyrid-2-one 5-lipoxygenase pharmacophore: Biological evaluation as dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Abdellatif, K.R.; Dong, Y.; Rao, P.N.P.; Das, D.; Velázquez, C.A.; Suresh, M.R.; Knaus, E.E. Phenylacetic acid regioisomers possessing a N-difluoromethyl-1,2-dihydropyrid-2-one pharmacophore: Evaluation as dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase with anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 20, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Tan, C.M.; Huang, C.H.; Chang, L.C.; Wang, J.P.; Cheng, F.C.; Chern, J.W. Discovery of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-6-nitrobenzo[1.3.2]dithiazolium ylide 1,1-dioxide as a novel dual cyclooxygenase/5-lipoxygenase inhibitor that also inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Insel, P.A.; Dennis, E.A. Regulation and inhibition of phospholipase A2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, M.L.; Lee, T.; Fitzgerald, V.; Snyder, F. A specific acetylhydrolase for 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (a hypotensive and platelet-activating lipid). J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berliner, J.A.; Subbanagounder, G.; Leitinger, N.; Watson, A.D.; Vora, D. Evidence for a role of phospholipid oxidation products in atherogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 11, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Eberhardt, C.; Unger, J.; Trong, H.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Stafforini, D.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Gray, P.W. Plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a secreted phospholipase A2 with a catalytic triad. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25481–25487. [Google Scholar]
- Macphee, C.H.; Nelson, J.; Zalewski, A. Role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Wilder, C.; Eberhardt, C.; Stafforini, D.M.; Dietsch, G.; Schimpf, B.; Hooper, S.; Le Trong, H.; Cousens, L.S.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Yamadat, Y.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescot, S.M.; Gray, P.W. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature 1995, 374, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Tellis, C.C.; Tselepsis, A.D. The role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis may depend on its lipoprotein carrier in plasma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caslake, M.J.; Packard, C.J. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as a biomarker for coronary disease and stroke. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2005, 2, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Wilensky, R.L.; Shi, Y.; Mohler, E.R.; Hamamdzic, D.; Burgert, M.E.; Li, J.; Postle, A.; Fenning, R.S.; Bollinger, J.G.; Hoffman, B.E.; Pelchovitz, D.J.; Yang, J.; Mirabile, R.C.; Webb, C.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Gelb, M.H.; Walker, M.C.; Zalewski, A.; Macphee, C.H. Inhibition of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 reduces complex coronary atherosclerotic plaque development. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zalewski, A.; Nelson, J.J.; Hegg, L.; Macphee, C. Role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis: Biology, epidemiology, and possible therapeutic target. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Osman, H.; Mohler, E.R.; Macpheec, C.; Zalewski, A.; Postle, A.; Wilensky, R.L. Role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in leukocyte activation and inflammatory responses. Atherosclerosis 2007, 191, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewski, A.; Nelson, J.J.; Heg, J.J.; Macphee, C. Lp-PLA2: A new kid on the block. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.L.; Foley, M.A.; Chen, L.; Behnke, M.L.; Lovering, F.E.; Kirincich, S.J.; Wang, W.; Shim, J.; Tam, S.; Shen, M.W.; Khor, S.; Xu, X.; Goodwin, D.G.; Ramarao, M.K.; Nickerson-Nutter, C.; Donahue, F.; Ku, M.S.; Clark, J.D.; McKew, J.C. Discovery of ecopladib, an indole inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2α. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1380–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, K.E. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors in the treatment of atherosclerosis: A new approach moves forward in the clinic. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2009, 18, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Hislop, C.; McConnell, D.; Elliott, M.; Stasiv, Y.; Wang, N.; Waters, D.D. Effects of 1-H-indole-3-glyoxamide (A-002) on concentration of secretory phospholipase A2 (PLASMA study): A phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corson, M.A. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors in atherosclerosis: The race is on. Lancet 2009, 373, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tew, D.G.; Boyd, H.F.; Ashman, S.; Theobald, C.; Leach, C.A. Mechanism of inhibition of LDL phospholipase A2 by monocyclic beta-lactams: Burst kinetics and the effect of stereochemistry. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 10087–10093. [Google Scholar]
- Blackie, J.A.; Bloomer, J.C.; Brown, M.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Hammond, B.; Hickey, D.M.; Ife, R.J.; Leach, C.A.; Lewis, V.A.; Macphee, C.H.; Milliner, K.J.; Moores, K.E.; Pinto, I.L.; Smith, S.A.; Stansfield, I.G.; Stanway, S.J.; Taylor, M.A.; Theobald, C.J. The identification of clinical candidate SB-480848: A potent inhibitor of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, C.A.; Smith, S.A. N-Substituted pyridinone and pyrimidinone derivatives for use as Lp-PLA2 inhibitors in the treatment atherosclerosis. World Patent WO 03/086400, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mohler, E.R.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Davidson, M.H.; Hanefeld, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Zalewski, A. The effect of darapladib on plasma lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity and cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with stable coronary heart disease or coronary heart disease risk equivalent: The results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S. Future role for selective phospholipase A2 inhibitors in the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2009, 23, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, P.A. Darapladib and atherosclerotic plaque: Should lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 be a therapeutic target? Curr. Atherosclerosis Rep. 2009, 11, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, P.J.; Morgenstern, R.; Mancini, J.; Ford-Hutchinson, A.; Persson, B. Common structural features of MAPEG—A widespread superfamily of membrane associated proteins with highly divergent functions in eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson, P.J.; Thore´n, S.; Morgenstern, R.; Samuelsson, B. Identification of human prostaglandin E synthase: A microsomal, glutathione-dependent, inducible enzyme, constituting a potential novel drug target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson, B.; Morgenstern, R.; Jakobsson, P.J. Membrane prostaglandin E synthase-1: A novel therapeutic target. Pharmacol. Rev. 2007, 59, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, R.W.; Mancini, J.A. Microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1): A novel anti-inflammatory therapeutic target. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar]
- Jegerschoeld, C.; Pawelzik, S.-C.; Purhonen, P.; Bhakat, P.; Gheorghe, K.R.; Gyobu, N.; Mitsuoka, K.; Morgenstern, R.; Jakobsson, P.J.; Hebert, H. Structural basis for induced formation of the inflammatory mediator prostaglandin E2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 105, 11110–11115. [Google Scholar]
- Riendeau, D.; Aspiotis, R.; Ethier, D.; Gareau, Y.; Grimm, E.L.; Guay, J.; Guiral, S.; Juteau, H.; Mancini, J.A.; Méthot, N.; Rubin, J.; Friesen, R.W. Inhibitors of the inducible microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase (mPGES-1) derived from MK-886. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3352–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, B.; Boulet, L.; Brideau, C.; Claveau, D.; Ethier, D.; Frenette, R.; Gagnon, M.; Giroux, A.; Guay, J.; Guiral, S.; Mancini, J.; Martins, E.; Massé, F.; Méthot, N.; Riendeau, D.; Rubin, J.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Ducharme, Y.; Friesen, R.W. Substituted phenanthrene imidazoles as potent, selective, and orally active mPGES-1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6816–6820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giroux, A.; Boulet, L.; Brideau, C.; Chau, A.; Claveau, D.; Côté, B.; Ethier, D.; Frenette, R.; Gagnon, M.; Guay, J.; Guiral, S.; Mancini, J.; Martins, E.; Massé, F.; Méthot, N.; Riendeau, D.; Rubin, J.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Ducharme, Y.; Friesen, R.W. Discovery of disubstituted phenanthrene imidazoles as potent, selective and orally active mPGES-1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5837–5841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koeberle, A.; Zettl, H.; Greiner, C.; Wurglics, M.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Werz, O. Pirinixic acid derivatives as novel dual inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 and 5-lipoxygenase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 8068–8076. [Google Scholar]
- Issemann, I.; Green, S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature 1990, 347, 645–650. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, H.; Devchand, P.R.; Perroud, M.; Wahli, W. PPAR alpha structure-function relationships derived from species-specific differences in responsiveness to hypolipidemic agents. Biol. Chem. 1997, 378, 651–655. [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke, A.J.; Keck, P.R.; Lehmann, F.; Koeberle, A.; Werz, O.; Laufer, S.A. Arylpyrrolizines as inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or as dual inhibitors of mPGES-1 and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX). J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4968–4972. [Google Scholar]
- Rörsch, F.; Wobst, I.; Zettl, H.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Grösch, S.; Geisslinger, G.; Schneider, G.; Proschak, E. Nonacidic inhibitors of human microsomal prostaglandin synthase 1 (mPGES 1) identified by a multistep virtual screening protocol. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 911–915. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Limburg, D.; Carter, J.; Mbalaviele, G.; Gierse, J.; Vazquez, M. Selective inducible microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 (mPGES-1) inhibitors derived from an oxicam template. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell, B.; Andreakos, E.; Brennan, F.; Feldmann, M.; Smith, C.; Conron, M. Prospects for the development of small molecular weight compounds to replace anti-tumour necrosis factor biological agents. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, ii90–ii93. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, J.A.; McClendon, C.L. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.C. The future of TNF-α antagonism. Future Rheumatol. 2007, 2, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.M.; Smith, A.S.; Oslob, J.D.; Flanagan, W.M.; Braisted, A.C.; Whitty, A.; Cancilla, M.T.; Wang, J.; Lugovskoy, A.A.; Yoburn, J.C.; Fung, A.D.; Farrington, G.; Eldredge, J.K.; Day, E.S.; Cruz, L.A.; Cachero, T.G.; Miller, S.K.; Friedman, J.E.; Choong, I.C.; Cunningham, B.C. Small-molecule inhibition of TNF-alpha. Science 2005, 310, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Man, H.W.; Schafer, P.; Wong, L.M.; Patterson, R.T.; Corral, L.G.; Raymon, H.; Blease, K.; Leisten, J.; Shirley, M.A.; Tang, Y.; Babusis, D.M.; Chen, R.; Stirling, D.; Muller, G.W. Discovery of (S)-N-[2-[1-(3-ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methanesulfonylethyl]-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-4-yl] acetamide (apremilast), a potent and orally active phosphodiesterase 4 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1522–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, D.S.; Lee, H.M.; Yang, F.; Che, C.M.; Wong, C.C.L.; Abagyan, R.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. Structure-based discovery of natural-product-like TNF-α inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2860–2864. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, P.P.N.; Kabir, S.N.; Mohamed, T. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Progress in Small Molecule Drug Development. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1530-1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051530
Rao PPN, Kabir SN, Mohamed T. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Progress in Small Molecule Drug Development. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(5):1530-1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051530
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Praveen P. N., Saad N. Kabir, and Tarek Mohamed. 2010. "Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Progress in Small Molecule Drug Development" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 5: 1530-1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051530
APA StyleRao, P. P. N., Kabir, S. N., & Mohamed, T. (2010). Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Progress in Small Molecule Drug Development. Pharmaceuticals, 3(5), 1530-1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3051530



